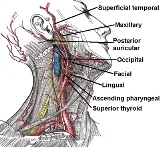
External carotid artery
Overview
Human anatomy
Human anatomy is primarily the scientific study of the morphology of the human body. Anatomy is subdivided into gross anatomy and microscopic anatomy. Gross anatomy is the study of anatomical structures that can be seen by the naked eye...
, the external carotid artery is a major artery
Artery
Arteries are blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart. This blood is normally oxygenated, exceptions made for the pulmonary and umbilical arteries....
of the head and neck. It arises from the common carotid artery
Common carotid artery
In human anatomy, the common carotid artery is an artery that supplies the head and neck with oxygenated blood; it divides in the neck to form the external and internal carotid arteries. - Structure :...
when it bifurcates into the external and internal carotid artery
Internal carotid artery
In human anatomy, the internal carotid arteries are two major arteries, one on each side of the head and neck. They arise from the common carotid arteries where these bifurcate into the internal and external carotid artery, and they supply the brain....
.
The external carotid artery begins at the level of the upper border of thyroid cartilage
Thyroid cartilage
The thyroid cartilage is the largest of the nine cartilages that make up the laryngeal skeleton, the cartilage structure in and around the trachea that contains the larynx....
, and, taking a slightly curved course, passes upward and forward, and then inclines backward to the space behind the neck of the mandible, where it divides into the superficial temporal and maxillary artery within the parotid gland
Parotid gland
The paired parotid glands are the largest of the salivary glands. They are each found wrapped around the mandibular ramus, and secrete saliva through Stensen's ducts into the oral cavity, to facilitate mastication and swallowing and to begin the digestion of starches.-Location:The parotid glands...
.
It rapidly diminishes in size in its course up the neck, owing to the number and large size of the branches given off from it.
In the child, it is somewhat smaller than the internal carotid; but in the adult, the two vessels are of nearly equal size.
Unanswered Questions

