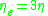Extensional viscosity
Encyclopedia
Extensional viscosity (also known as elongational viscosity) is a viscosity
coefficient when applied stress
is extensional stress.
Extensional viscosity can be measured using rheometers that apply extensional stress. Acoustic rheometer
is one example of such devices.

where
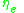 is the extensional viscosity or elongational viscosity
is the extensional viscosity or elongational viscosity is the normal stress:
is the normal stress: 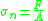
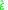 is the rate of strain:
is the rate of strain: 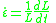
For a Newtonian Fluid
, the elongational viscosity is three times the shear viscosity which can be derived using the continuity equation
for incompressible fluids.
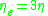
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
coefficient when applied stress
Stress (physics)
In continuum mechanics, stress is a measure of the internal forces acting within a deformable body. Quantitatively, it is a measure of the average force per unit area of a surface within the body on which internal forces act. These internal forces are a reaction to external forces applied on the body...
is extensional stress.
- This parameter is often used for characterizing polymer solutions.
Extensional viscosity can be measured using rheometers that apply extensional stress. Acoustic rheometer
Acoustic rheometer
An acoustic rheometer employs piezo-electric crystal that can easily launch a successive wave of extensions and contractions into the fluid. It applies an oscillating extensional stress to the system...
is one example of such devices.

where
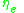 is the extensional viscosity or elongational viscosity
is the extensional viscosity or elongational viscosity is the normal stress:
is the normal stress: 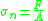
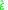 is the rate of strain:
is the rate of strain: 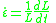
For a Newtonian Fluid
Newtonian fluid
A Newtonian fluid is a fluid whose stress versus strain rate curve is linear and passes through the origin. The constant of proportionality is known as the viscosity.-Definition:...
, the elongational viscosity is three times the shear viscosity which can be derived using the continuity equation
Continuity equation
A continuity equation in physics is a differential equation that describes the transport of a conserved quantity. Since mass, energy, momentum, electric charge and other natural quantities are conserved under their respective appropriate conditions, a variety of physical phenomena may be described...
for incompressible fluids.