
Evapotranspiration
Encyclopedia
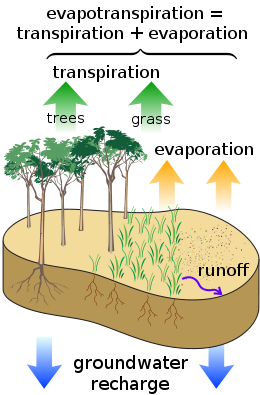
Evaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
and plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
transpiration
Transpiration
Transpiration is a process similar to evaporation. It is a part of the water cycle, and it is the loss of water vapor from parts of plants , especially in leaves but also in stems, flowers and roots. Leaf surfaces are dotted with openings which are collectively called stomata, and in most plants...
from the Earth's land surface to atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
. Evaporation accounts for the movement of water to the air from sources such as the soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
, canopy interception
Canopy interception
Canopy interception is the rainfall that is intercepted by the canopy of a tree and successively evaporate from the leaves. Precipitation that is not intercepted will fall as throughfall or stemflow on the forest floor....
, and waterbodies. Transpiration accounts for the movement of water within a plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
and the subsequent loss of water as vapor through stomata in its leaves
Leaf
A leaf is an organ of a vascular plant, as defined in botanical terms, and in particular in plant morphology. Foliage is a mass noun that refers to leaves as a feature of plants....
. Evapotranspiration is an important part of the water cycle
Water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or H2O cycle, describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. Water can change states among liquid, vapor, and solid at various places in the water cycle...
. An element (such as a tree) that contributes to evapotranspiration can be called an evapotranspirator.
Potential evapotranspiration (PET) is a representation of the environmental demand for evapotranspiration and represents the evapotranspiration rate of a short green crop, completely shading the ground, of uniform height and with adequate water status in the soil profile. It is a reflection of the energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
available to evaporate water, and of the wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
available to transport the water vapour from the ground up into the lower atmosphere
Earth's atmosphere
The atmosphere of Earth is a layer of gases surrounding the planet Earth that is retained by Earth's gravity. The atmosphere protects life on Earth by absorbing ultraviolet solar radiation, warming the surface through heat retention , and reducing temperature extremes between day and night...
. Evapotranspiration is said to equal potential evapotranspiration when there is ample water.
Evapotranspiration and the water cycle
Evapotranspiration is a significant water loss from drainage basinDrainage basin
A drainage basin is an extent or an area of land where surface water from rain and melting snow or ice converges to a single point, usually the exit of the basin, where the waters join another waterbody, such as a river, lake, reservoir, estuary, wetland, sea, or ocean...
s. Types of vegetation and land use significantly affect evapotranspiration, and therefore the amount of water leaving a drainage basin. Because water transpired through leaves comes from the roots, plants with deep reaching roots can more constantly transpire water. Herbaceous plant
Herbaceous plant
A herbaceous plant is a plant that has leaves and stems that die down at the end of the growing season to the soil level. They have no persistent woody stem above ground...
s generally transpire less than woody plant
Woody plant
A woody plant is a plant that uses wood as its structural tissue. These are typically perennial plants whose stems and larger roots are reinforced with wood produced adjacent to the vascular tissues. The main stem, larger branches, and roots of these plants are usually covered by a layer of...
s because they usually have less extensive foliage. Conifer forests tend to have higher rates of evapotranspiration than deciduous
Deciduous
Deciduous means "falling off at maturity" or "tending to fall off", and is typically used in reference to trees or shrubs that lose their leaves seasonally, and to the shedding of other plant structures such as petals after flowering or fruit when ripe...
forests, particularly in the dormant and early spring seasons. This is primarily due to the enhanced amount of precipitation intercepted and evaporated by conifer foliage during these periods. Factors that affect evapotranspiration include the plant's growth stage or level of maturity, percentage of soil cover, solar radiation, humidity
Humidity
Humidity is a term for the amount of water vapor in the air, and can refer to any one of several measurements of humidity. Formally, humid air is not "moist air" but a mixture of water vapor and other constituents of air, and humidity is defined in terms of the water content of this mixture,...
, temperature
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, and wind
Wind
Wind is the flow of gases on a large scale. On Earth, wind consists of the bulk movement of air. In outer space, solar wind is the movement of gases or charged particles from the sun through space, while planetary wind is the outgassing of light chemical elements from a planet's atmosphere into space...
.
Through evapotranspiration, forests reduce water yield, except in unique ecosystems called cloud forests. Trees in cloud forests condense fog or low clouds into liquid water on their surface, which drips down to the ground. These trees still contribute to evapotranspiration, but often condense more water than they evaporate or transpire.
In areas that are not irrigated, actual evapotranspiration is usually no greater than precipitation
Precipitation (meteorology)
In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation In meteorology, precipitation (also known as one of the classes of hydrometeors, which are atmospheric water phenomena is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravity. The main forms of precipitation...
, with some buffer in time depending on the soil's ability to hold water. It will usually be less because some water will be lost due to percolation
Percolation
In physics, chemistry and materials science, percolation concerns the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials...
or surface runoff. An exception is areas with high water table
Water table
The water table is the level at which the submarine pressure is far from atmospheric pressure. It may be conveniently visualized as the 'surface' of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. However, saturated conditions may extend above the water table as...
s, where capillary action
Capillary action
Capillary action, or capilarity, is the ability of a liquid to flow against gravity where liquid spontanously rise in a narrow space such as between the hair of a paint-brush, in a thin tube, or in porous material such as paper or in some non-porous material such as liquified carbon fiber, or in a...
can cause water from the groundwater to rise through the soil matrix to the surface. If potential evapotranspiration is greater than actual precipitation, then soil will dry out, unless irrigation
Irrigation
Irrigation may be defined as the science of artificial application of water to the land or soil. It is used to assist in the growing of agricultural crops, maintenance of landscapes, and revegetation of disturbed soils in dry areas and during periods of inadequate rainfall...
is used.
Evapotranspiration can never be greater than PET, but can be lower if there is not enough water to be evaporated or plants are unable to transpire readily.
Estimating evapotranspiration
Evapotranspiration can be measured or estimated using several methods.Indirect methods
Pan evaporationPan evaporation
Pan evaporation is a measurement that combines or integrates the effects of several climate elements: temperature, humidity, rain fall, drought dispersion, solar radiation, and wind. Evaporation is greatest on hot, windy, dry days; and is greatly reduced when air is cool, calm, and humid...
data can be used to estimate lake evaporation, but transpiration and evaporation of intercepted rain on vegetation are unknown. There are three general approaches to estimate evapotranspiration indirectly.
Catchment water balance
Evapotranspiration may be estimated by creating an equation of the water balance of a drainage basin. The equation balances the change in water stored within the basin (S) with inputs and exports:
The input is precipitation (P), and the exports are evapotranspiration (which is to be estimated), streamflow (Q), and groundwater recharge (D). If the change in storage, precipitation, streamflow, and groundwater recharge are all estimated, the missing flux, ET, can be estimated by rearranging the above equation as follows:
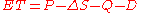
Hydrometeorological equations
The most general and widely used equation for calculating reference ET is the Penman equationPenman equation
The Penman equation describes evaporation from an open water surface, and was developed by Howard Penman in 1948. Penman's equation requires daily mean temperature, wind speed, relative humidity, and solar radiation to predict E...
. The Penman-Monteith
Penman-Monteith
Like the Penman equation, the Penman–Monteith equation predicts net evapotranspiration, requiring as input daily mean temperature, wind speed, relative humidity, and solar radiation...
variation is recommended by the Food and Agriculture Organization
Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations is a specialised agency of the United Nations that leads international efforts to defeat hunger. Serving both developed and developing countries, FAO acts as a neutral forum where all nations meet as equals to negotiate agreements and...
. The simpler Blaney-Criddle equation
Blaney-Criddle equation
The Blaney–Criddle equation is a method for estimating reference crop evapotranspiration.- Usage :...
was popular in the Western United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
for many years but it is not as accurate in regions with higher humidities. Other solutions used includes Makkink, which is simple but must be calibrated to a specific location, and Hargreaves. To convert the reference evapotranspiration to actual crop evapotranspiration, a crop coefficient
Crop coefficient
Models of transpiration, or combined evapotranspiration , from plants often combine an idealized or well calibrated reference crop response model with coefficients that account for differences in response observed for the crop of interest...
and a stress coefficient must be used. Crop coefficient
Coefficient
In mathematics, a coefficient is a multiplicative factor in some term of an expression ; it is usually a number, but in any case does not involve any variables of the expression...
s referred to in many hydrological models are themselves the result of equations that describe predictable variation in coefficient values depending upon plant conditions that change during periods for which the model is used. This is because crops are seasonal, perennial plants mature over multiple seasons, and stress responses can significantly depend upon many aspects of plant condition.
Energy balance
A third methodology to estimate the actual evapotranspiration is the use of the energy balance.
where λE is the energy needed to change the phase of water from liquid to gas, Rn is the net radiation, G is the soil heat flux and H is the sensible heat flux. Using instruments like a scintillometer
Scintillometer
A scintillometer is a scientific device used to measure small fluctuations of the refractive index of air caused by variations in temperature, humidity, and pressure. It consists of an optical or radio wave transmitter and a receiver at both ends of an atmospheric propagation path...
, soil heat flux plates or radiation meters, the components of the energy balance can be calculated and the energy available for actual evapotranspiration can be solved.
The SEBAL
SEBAL
The Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land uses the energy balance to estimate aspects of the hydrological cycle. SEBAL maps evapotranspiration, biomass growth, water deficit and soil moisture. Its main creator is Prof. Dr. W.G.M...
algorithm solves the energy balance at the earth surface using satellite imagery. This allows for both actual and potential evapotranspiration to be calculated on a pixel-by-pixel basis. Evapotranspiration is a key indicator for water management and irrigation performance. SEBAL
SEBAL
The Surface Energy Balance Algorithm for Land uses the energy balance to estimate aspects of the hydrological cycle. SEBAL maps evapotranspiration, biomass growth, water deficit and soil moisture. Its main creator is Prof. Dr. W.G.M...
can map these key indicators in time and space, for days, weeks or years.
Experimental Method for measuring ET
One method for measuring ET is with a weighing lysimeterLysimeter
A lysimeter is a measuring device which can be used to measure the amount of actual evapotranspiration which is released by plants, usually crops or trees...
. The weight of a soil column is measured continuously and the change in storage of water in the soil is modeled by the change in weight. The change in weight is converted to units of length based on the surface area of the weighing lysimeter and the unit weight of water. ET is computed as the change in weight plus rainfall minus percolation.
Eddy covariance
The most direct method of measuring evapotranspiration is with the eddy covariance technique in which fast fluctuations of vertical wind speed are correlated with fast fluctuations in atmospheric water vapor density. This directly estimates the transfer of water vapor (evapotranspiration) from the land (or canopy) surface to the atmosphere.Potential evapotranspiration
Water
Water is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
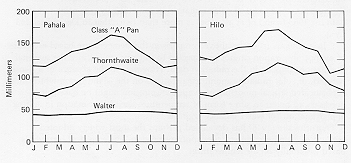
available. This demand incorporates the energy available for evaporation and the ability of the lower atmosphere to transport evaporated moisture away from the land surface. PET is higher in the summer, on less cloudy days, and closer to the equator, because of the higher levels of solar radiation that provides the energy for evaporation. PET is also higher on windy days because the evaporated moisture can be quickly moved from the ground or plant surface, allowing more evaporation to fill its place.
PET is expressed in terms of a depth of water, and can be graphed during the year (see figure).
Potential evapotranspiration is usually measured indirectly, from other climatic factors, but also depends on the surface type, such as free water (for lake
Lake
A lake is a body of relatively still fresh or salt water of considerable size, localized in a basin, that is surrounded by land. Lakes are inland and not part of the ocean and therefore are distinct from lagoons, and are larger and deeper than ponds. Lakes can be contrasted with rivers or streams,...
s and ocean
Ocean
An ocean is a major body of saline water, and a principal component of the hydrosphere. Approximately 71% of the Earth's surface is covered by ocean, a continuous body of water that is customarily divided into several principal oceans and smaller seas.More than half of this area is over 3,000...
s), the soil
Soil
Soil is a natural body consisting of layers of mineral constituents of variable thicknesses, which differ from the parent materials in their morphological, physical, chemical, and mineralogical characteristics...
type for bare soil, and the vegetation
Vegetation
Vegetation is a general term for the plant life of a region; it refers to the ground cover provided by plants. It is a general term, without specific reference to particular taxa, life forms, structure, spatial extent, or any other specific botanical or geographic characteristics. It is broader...
. Often a value for the potential evapotranspiration is calculated at a nearby climate station on a reference surface, conventionally short grass. This value is called the reference evapotranspiration, and can be converted to a potential evapotranspiration by multiplying with a surface coefficient. In agriculture, this is called a crop coefficient. The difference between potential evapotranspiration and precipitation is used in irrigation scheduling
Irrigation scheduling
Irrigation scheduling is the process used by irrigation system managers to determine the correct frequency and duration of watering.The following factors may be taken into consideration:...
.
Average annual PET is often compared to average annual precipitation, P. The ratio of the two, P/PET, is the aridity index
Aridity index
An aridity index is a numerical indicator of the degree of dryness of the climate at a given location. A number of aridity indices have been proposed ; these indicators serve to identify, locate or delimit regions that suffer from a deficit of available water, a condition that can severely affect...
.
See also
- Eddy covarianceEddy covarianceThe eddy covariance technique is a key atmospheric flux measurement technique to measure and calculate vertical turbulent fluxes within atmospheric boundary layers...
flux (aka eddy correlation, eddy flux) - Hydrology (agriculture)Hydrology (agriculture)Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
- Hydrologic Evaluation of Landfill Performance (HELP)
- Latent heat flux
- Water Evaluation And Planning system (WEAP)WEAPWEAP: the Water Evaluation And Planning system is a Windows-based decision support system for integrated water resources management and policy analysis...
- Soil plant atmosphere continuumSoil plant atmosphere continuumThe Soil-Plant-Atmosphere Continuum is the pathway for water moving from soil through plants to the atmosphere.The transport of water along this pathway occurs in components, variously defined among scientific disciplines:...
- Deficit irrigationDeficit irrigationDeficit irrigation is a watering strategy that can be applied by different types of irrigation application methods. The correct application of DI requires thorough understanding of the yield response to water and of the economic impact of reductions in harvest...
External links
- New Mexico Eddy Covariance Flux Network (Rio-ET)
- California's Irrigation Management Information System (CIMIS)
- Texas Evapotranspiration Network
- Use and Construction of a Lysimeter to Measure Evapotranspiration
- Evapotranspiration, from the U.S. Geological Survey's Water Cycle Web site
- Washoe County (NV) Et Project
- Irrigation Training and Research Center (ITRC) Cal Poly, San Luis Obispo
- Transpiration Benefits For Urban Catchment Management
- Non-Discharging evapotranspiration bed system for wastewater disposal at Lincoln
- Eto, an application written in python as a library providing the tools to calculate the reference evapotranspiration with a simple console based interface
- myCrop, an opensource crop management application written in java that can calculate among other things evapotranspiration

