
Euler number (physics)
Encyclopedia
The Euler number is a dimensionless number used in fluid flow calculations. It expresses the relationship between a local pressure
drop e.g. over a restriction and the kinetic energy
per volume, and is used to characterize losses in the flow, where a perfect frictionless flow corresponds to an Euler number of 1.
It is defined as

where
The cavitation number has a similar structure, but a different meaning and use:
The Cavitation number is a dimensionless number used in flow calculations. It expresses the relationship between the difference of a local absolute pressure from the vapor pressure
and the kinetic energy
per volume, and is used to characterize the potential of the flow to cavitate
.
It is defined as
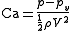
where
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
drop e.g. over a restriction and the kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
per volume, and is used to characterize losses in the flow, where a perfect frictionless flow corresponds to an Euler number of 1.
It is defined as

where
 is the density of the fluid.
is the density of the fluid.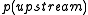 is the upstream pressure.
is the upstream pressure. is the downstream pressure.
is the downstream pressure. is a characteristic velocity of the flow.
is a characteristic velocity of the flow.
The cavitation number has a similar structure, but a different meaning and use:
The Cavitation number is a dimensionless number used in flow calculations. It expresses the relationship between the difference of a local absolute pressure from the vapor pressure
Pressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
and the kinetic energy
Kinetic energy
The kinetic energy of an object is the energy which it possesses due to its motion.It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its acceleration, the body maintains this kinetic energy unless its speed changes...
per volume, and is used to characterize the potential of the flow to cavitate
Cavitation
Cavitation is the formation and then immediate implosion of cavities in a liquidi.e. small liquid-free zones that are the consequence of forces acting upon the liquid...
.
It is defined as
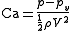
where
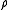 is the density of the fluid.
is the density of the fluid.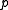 is the local pressure.
is the local pressure. is the vapor pressureVapor pressureVapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
is the vapor pressureVapor pressureVapor pressure or equilibrium vapor pressure is the pressure of a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases in a closed system. All liquids have a tendency to evaporate, and some solids can sublimate into a gaseous form...
of the fluid.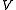 is a characteristic velocity of the flow.
is a characteristic velocity of the flow.

