
Emilio G. Segrè
Encyclopedia
Emilio Gino Segrè was an Italian
-born, naturalized American, physicist
and Nobel laureate in physics
, who with Owen Chamberlain
, discovered antiproton
s, a sub-atomic antiparticle
.
, near Rome
, and enrolled in the University of Rome La Sapienza
as an engineering
student. He switched to physics
in 1927 and earned his doctorate
in 1928, having studied under Enrico Fermi
.
After a stint in the Italian Army
from 1928 to 1929, he worked with Otto Stern
in Hamburg
and Pieter Zeeman
in Amsterdam
as a Rockefeller Foundation
fellow in 1930. Segrè was appointed assistant professor of physics at the University of Rome in 1932 and served until 1936. From 1936 to 1938 he was Director of the Physics Laboratory at the University of Palermo
. After a visit to Ernest O. Lawrence's Berkeley Radiation Laboratory, he was sent a molybdenum
strip from the laboratory's cyclotron
deflector in 1937 which was emitting anomalous forms of radioactivity. After careful chemical and theoretical analysis, Segrè was able to prove that some of the radiation was being produced by a previously unknown element, dubbed technetium
, and was the first artificially synthesized chemical element
which does not occur in nature.
He was a colleague and close friend of Ettore Majorana
, who disappeared mysteriously in 1938.
While Segrè was on a summer visit to California
in 1938, Benito Mussolini
's fascist government passed anti-Semitic laws barring Jews from university positions. As a Jew, Segrè was now rendered an indefinite émigré. At the Berkeley Radiation Lab, Lawrence offered him a job as a Research Assistant—a relatively lowly position for someone who had discovered an element—for US$300 a month. However, in Segrè's recollection, when Lawrence learned that Segrè was legally trapped in California
, he reduced his salary to US$116 a month which many, including Segrè, saw as exploiting the situation. Segrè also found work as a lecturer of the physics department at the University of California, Berkeley
.
While at Berkeley, he helped discover the element astatine
and the isotope plutonium
-239 (which was later used to make Fat Man
, the atom bomb dropped on Nagasaki). He found in April 1944 that Thin Man
, the proposed plutonium "gun-type" bomb, would not work (because of the presence of Pu-240 impurities), and priority was given to Fat Man, the plutonium "implosion" bomb.
 From 1943 to 1946 he worked at the Los Alamos National Laboratory
From 1943 to 1946 he worked at the Los Alamos National Laboratory
as a group leader for the Manhattan Project
. In 1944, he became a naturalized citizen of the United States. He taught at Columbia University
, University of Illinois and University of Rio de Janeiro. On his return to Berkeley
in 1946, he became a professor
of physics and of the history of science
, serving until 1972.
Professors Emilio Segrè and Owen Chamberlain
were co-heads of a research group at the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory. Their
group proposed the experiment to discover the anti-proton and this was the chief reason that the Bevatron
was built at LRL. The Bevatron was designed to reach proton energies of 6.2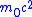 where mo is the rest mass of the proton
where mo is the rest mass of the proton
. With the new Bevatron, the Segrè/Chamberlain group produced the first anti-proton (as seen in bubble chamber
pictures) and the two shared the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physics
for their work.
In 1970, Segrè published a biography of Fermi (Enrico Fermi: Physicist, University of Chicago Press)
In 1974 he returned to the University of Rome as a professor of nuclear physics
.
Segrè was also active as a photographer
, and took many photos documenting events and people in the history of modern science. The American Institute of Physics
named its photographic archive of physics history in his honor.
Segrè died at the age of 84 of a heart attack
.
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
-born, naturalized American, physicist
Physicist
A physicist is a scientist who studies or practices physics. Physicists study a wide range of physical phenomena in many branches of physics spanning all length scales: from sub-atomic particles of which all ordinary matter is made to the behavior of the material Universe as a whole...
and Nobel laureate in physics
Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics is awarded once a year by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901; the others are the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and...
, who with Owen Chamberlain
Owen Chamberlain
Owen Chamberlain was an American physicist, and Nobel laureate in physics for his discovery, with collaborator Emilio Segrè, of antiprotons, a sub-atomic antiparticle.-Biography:...
, discovered antiproton
Antiproton
The antiproton is the antiparticle of the proton. Antiprotons are stable, but they are typically short-lived since any collision with a proton will cause both particles to be annihilated in a burst of energy....
s, a sub-atomic antiparticle
Antiparticle
Corresponding to most kinds of particles, there is an associated antiparticle with the same mass and opposite electric charge. For example, the antiparticle of the electron is the positively charged antielectron, or positron, which is produced naturally in certain types of radioactive decay.The...
.
Biography
Segrè was born into a Sephardic Jewish family in TivoliTivoli, Italy
Tivoli , the classical Tibur, is an ancient Italian town in Lazio, about 30 km east-north-east of Rome, at the falls of the Aniene river where it issues from the Sabine hills...
, near Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, and enrolled in the University of Rome La Sapienza
University of Rome La Sapienza
The Sapienza University of Rome, officially Sapienza – Università di Roma, formerly known as Università degli studi di Roma "La Sapienza", is a coeducational, autonomous state university in Rome, Italy...
as an engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
student. He switched to physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
in 1927 and earned his doctorate
Laurea
In Italy, the laurea is the main post-secondary academic degree.-Reforms due to the Bologna process:Spurred by the Bologna process, a major reform was instituted in 1999 to introduce easier university degrees comparable to the bachelors...
in 1928, having studied under Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi
Enrico Fermi was an Italian-born, naturalized American physicist particularly known for his work on the development of the first nuclear reactor, Chicago Pile-1, and for his contributions to the development of quantum theory, nuclear and particle physics, and statistical mechanics...
.
After a stint in the Italian Army
Italian Army
The Italian Army is the ground defence force of the Italian Armed Forces. It is all-volunteer force of active-duty personnel, numbering 108,355 in 2010. Its best-known combat vehicles are the Dardo infantry fighting vehicle, the Centauro tank destroyer and the Ariete tank, and among its aircraft...
from 1928 to 1929, he worked with Otto Stern
Otto Stern
Otto Stern was a German physicist and Nobel laureate in physics.-Biography:Stern was born in Sohrau, now Żory in the German Empire's Kingdom of Prussia and studied at Breslau, now Wrocław in Lower Silesia....
in Hamburg
Hamburg
-History:The first historic name for the city was, according to Claudius Ptolemy's reports, Treva.But the city takes its modern name, Hamburg, from the first permanent building on the site, a castle whose construction was ordered by the Emperor Charlemagne in AD 808...
and Pieter Zeeman
Pieter Zeeman
Pieter Zeeman was a Dutch physicist who shared the 1902 Nobel Prize in Physics with Hendrik Lorentz for his discovery of the Zeeman effect.-Childhood and youth:...
in Amsterdam
Amsterdam
Amsterdam is the largest city and the capital of the Netherlands. The current position of Amsterdam as capital city of the Kingdom of the Netherlands is governed by the constitution of August 24, 1815 and its successors. Amsterdam has a population of 783,364 within city limits, an urban population...
as a Rockefeller Foundation
Rockefeller Foundation
The Rockefeller Foundation is a prominent philanthropic organization and private foundation based at 420 Fifth Avenue, New York City. The preeminent institution established by the six-generation Rockefeller family, it was founded by John D. Rockefeller , along with his son John D. Rockefeller, Jr...
fellow in 1930. Segrè was appointed assistant professor of physics at the University of Rome in 1932 and served until 1936. From 1936 to 1938 he was Director of the Physics Laboratory at the University of Palermo
University of Palermo
The University of Palermo is a university located in Palermo, Italy, and founded in 1806. It is organized in 12 Faculties.-History:The University of Palermo was officially founded in 1806, although its earliest roots date back to 1498 when medicine and law were taught there...
. After a visit to Ernest O. Lawrence's Berkeley Radiation Laboratory, he was sent a molybdenum
Molybdenum
Molybdenum , is a Group 6 chemical element with the symbol Mo and atomic number 42. The name is from Neo-Latin Molybdaenum, from Ancient Greek , meaning lead, itself proposed as a loanword from Anatolian Luvian and Lydian languages, since its ores were confused with lead ores...
strip from the laboratory's cyclotron
Cyclotron
In technology, a cyclotron is a type of particle accelerator. In physics, the cyclotron frequency or gyrofrequency is the frequency of a charged particle moving perpendicularly to the direction of a uniform magnetic field, i.e. a magnetic field of constant magnitude and direction...
deflector in 1937 which was emitting anomalous forms of radioactivity. After careful chemical and theoretical analysis, Segrè was able to prove that some of the radiation was being produced by a previously unknown element, dubbed technetium
Technetium
Technetium is the chemical element with atomic number 43 and symbol Tc. It is the lowest atomic number element without any stable isotopes; every form of it is radioactive. Nearly all technetium is produced synthetically and only minute amounts are found in nature...
, and was the first artificially synthesized chemical element
Chemical element
A chemical element is a pure chemical substance consisting of one type of atom distinguished by its atomic number, which is the number of protons in its nucleus. Familiar examples of elements include carbon, oxygen, aluminum, iron, copper, gold, mercury, and lead.As of November 2011, 118 elements...
which does not occur in nature.
He was a colleague and close friend of Ettore Majorana
Ettore Majorana
Ettore Majorana was an Italian theoretical physicist who began work on neutrino masses. He disappeared suddenly in mysterious circumstances. He is noted for the eponymous Majorana equation and for Majorana fermions.-Gifted in mathematics:Majorana was born in Catania, Sicily...
, who disappeared mysteriously in 1938.
While Segrè was on a summer visit to California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
in 1938, Benito Mussolini
Benito Mussolini
Benito Amilcare Andrea Mussolini was an Italian politician who led the National Fascist Party and is credited with being one of the key figures in the creation of Fascism....
's fascist government passed anti-Semitic laws barring Jews from university positions. As a Jew, Segrè was now rendered an indefinite émigré. At the Berkeley Radiation Lab, Lawrence offered him a job as a Research Assistant—a relatively lowly position for someone who had discovered an element—for US$300 a month. However, in Segrè's recollection, when Lawrence learned that Segrè was legally trapped in California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
, he reduced his salary to US$116 a month which many, including Segrè, saw as exploiting the situation. Segrè also found work as a lecturer of the physics department at the University of California, Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley , is a teaching and research university established in 1868 and located in Berkeley, California, USA...
.
While at Berkeley, he helped discover the element astatine
Astatine
Astatine is a radioactive chemical element with the symbol At and atomic number 85. It occurs on the Earth only as the result of decay of heavier elements, and decays away rapidly, so much less is known about this element than its upper neighbors in the periodic table...
and the isotope plutonium
Plutonium
Plutonium is a transuranic radioactive chemical element with the chemical symbol Pu and atomic number 94. It is an actinide metal of silvery-gray appearance that tarnishes when exposed to air, forming a dull coating when oxidized. The element normally exhibits six allotropes and four oxidation...
-239 (which was later used to make Fat Man
Fat Man
"Fat Man" is the codename for the atomic bomb that was detonated over Nagasaki, Japan, by the United States on August 9, 1945. It was the second of the only two nuclear weapons to be used in warfare to date , and its detonation caused the third man-made nuclear explosion. The name also refers more...
, the atom bomb dropped on Nagasaki). He found in April 1944 that Thin Man
Thin Man nuclear bomb
The "Thin Man" nuclear bomb was a proposed plutonium gun-type nuclear bomb which the United States was developing during the Manhattan Project...
, the proposed plutonium "gun-type" bomb, would not work (because of the presence of Pu-240 impurities), and priority was given to Fat Man, the plutonium "implosion" bomb.

Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory, managed and operated by Los Alamos National Security , located in Los Alamos, New Mexico...
as a group leader for the Manhattan Project
Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a research and development program, led by the United States with participation from the United Kingdom and Canada, that produced the first atomic bomb during World War II. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the US Army...
. In 1944, he became a naturalized citizen of the United States. He taught at Columbia University
Columbia University
Columbia University in the City of New York is a private, Ivy League university in Manhattan, New York City. Columbia is the oldest institution of higher learning in the state of New York, the fifth oldest in the United States, and one of the country's nine Colonial Colleges founded before the...
, University of Illinois and University of Rio de Janeiro. On his return to Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley , is a teaching and research university established in 1868 and located in Berkeley, California, USA...
in 1946, he became a professor
Professor
A professor is a scholarly teacher; the precise meaning of the term varies by country. Literally, professor derives from Latin as a "person who professes" being usually an expert in arts or sciences; a teacher of high rank...
of physics and of the history of science
History of science
The history of science is the study of the historical development of human understandings of the natural world and the domains of the social sciences....
, serving until 1972.
Professors Emilio Segrè and Owen Chamberlain
Owen Chamberlain
Owen Chamberlain was an American physicist, and Nobel laureate in physics for his discovery, with collaborator Emilio Segrè, of antiprotons, a sub-atomic antiparticle.-Biography:...
were co-heads of a research group at the Lawrence Radiation Laboratory. Their
group proposed the experiment to discover the anti-proton and this was the chief reason that the Bevatron
Bevatron
The Bevatron was a historic particle accelerator — specifically, a weak-focusing proton synchrotron — at Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, U.S.A., which began operating in 1954. The antiproton was discovered there in 1955, resulting in the 1959 Nobel Prize in physics for Emilio...
was built at LRL. The Bevatron was designed to reach proton energies of 6.2
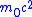 where mo is the rest mass of the proton
where mo is the rest mass of the protonProton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
. With the new Bevatron, the Segrè/Chamberlain group produced the first anti-proton (as seen in bubble chamber
Bubble chamber
A bubble chamber is a vessel filled with a superheated transparent liquid used to detect electrically charged particles moving through it. It was invented in 1952 by Donald A. Glaser, for which he was awarded the 1960 Nobel Prize in Physics...
pictures) and the two shared the 1959 Nobel Prize in Physics
Nobel Prize in Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics is awarded once a year by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901; the others are the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and...
for their work.
In 1970, Segrè published a biography of Fermi (Enrico Fermi: Physicist, University of Chicago Press)
In 1974 he returned to the University of Rome as a professor of nuclear physics
Nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies the building blocks and interactions of atomic nuclei. The most commonly known applications of nuclear physics are nuclear power generation and nuclear weapons technology, but the research has provided application in many fields, including those...
.
Segrè was also active as a photographer
Photography
Photography is the art, science and practice of creating durable images by recording light or other electromagnetic radiation, either electronically by means of an image sensor or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film...
, and took many photos documenting events and people in the history of modern science. The American Institute of Physics
American Institute of Physics
The American Institute of Physics promotes science, the profession of physics, publishes physics journals, and produces publications for scientific and engineering societies. The AIP is made up of various member societies...
named its photographic archive of physics history in his honor.
Segrè died at the age of 84 of a heart attack
Myocardial infarction
Myocardial infarction or acute myocardial infarction , commonly known as a heart attack, results from the interruption of blood supply to a part of the heart, causing heart cells to die...
.
See also
- List of Jewish Nobel laureates
- I ragazzi di via PanispernaI ragazzi di via Panispernais an Italian movie by director Gianni Amelio, telling the enthusiasms, fears, joys and disappointments of the life of a well-known group of boys fond of physics and mathematics, who just made history as the Via Panisperna boys.-Plot:The story is inspired by a real life fact and set in the...
(movie)
Further reading
- E. Segrè (1953) Experimental Nuclear Physics.
- E. Segrè (1964) Nuclei and Particles
- E. Segrè (1970) Enrico Fermi, Physicist, University Of Chicago Press.
- E. Segrè (1980) From X-rays to Quarks: Modern Physicists and Their Discoveries (Dover Classics of Science & Mathematics), Dover Publications.
- E. Segrè (1984) From Falling Bodies to Radio Waves: Classical Physicists and Their Discoveries.
External links
- National Academy of Sciences biography
- 1959 Nobel Prize in Physics
- Emilio G. Segrè
- Annotated bibliography for Emilio Segre from the Alsos Digital Library for Nuclear Issues
- Oral History interview transcript with Emilio G. Segre 13 February 1967, American Institute of Physics, Niels Bohr Library and Archives

