Elo rating system
Encyclopedia


Chess
Chess is a two-player board game played on a chessboard, a square-checkered board with 64 squares arranged in an eight-by-eight grid. It is one of the world's most popular games, played by millions of people worldwide at home, in clubs, online, by correspondence, and in tournaments.Each player...
. It is named after its creator Arpad Elo
Árpád Élo
Arpad Emrick Elo is the creator of the Elo rating system for two-player games such as chess. Born in Egyházaskesző, Austro-Hungarian Empire, he moved to the United States with his parents as a child in 1913.Elo was a professor of physics at Marquette University in Milwaukee, Wisconsin. He was...
, a Hungarian
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
-born American
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
professor.
The Elo system was invented as an improved chess rating system, but today it is also used in many other games. It is also used as a rating system for multiplayer competition in a number of computer games, and has been adapted to team sports including association football, American college football, basketball, and Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball is the highest level of professional baseball in the United States and Canada, consisting of teams that play in the National League and the American League...
.
History
Arpad Elo was a master-level chess player and an active participant in the United States Chess FederationUnited States Chess Federation
The United States Chess Federation is a non-profit organization, the governing chess organization within the United States, and one of the federations of the FIDE. The USCF was founded in 1939 from the merger of two regional chess organizations, and grew gradually until 1972, when membership...
(USCF) from its founding in 1939. The USCF used a numerical ratings system, devised by Kenneth Harkness
Kenneth Harkness
Kenneth Harkness was a chess organizer. He is the creator of the Harkness rating system.-Life and career:...
, to allow members to track their individual progress in terms other than tournament wins and losses. The Harkness system was reasonably fair, but in some circumstances gave rise to ratings which many observers considered inaccurate. On behalf of the USCF, Elo devised a new system with a more statistical
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
basis.
Elo's system replaced earlier systems of competitive rewards with a system based on statistical estimation. Rating systems for many sports award points in accordance with subjective evaluations of the 'greatness' of certain achievements. For example, winning an important golf
Golf
Golf is a precision club and ball sport, in which competing players use many types of clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a golf course using the fewest number of strokes....
tournament might be worth an arbitrarily chosen five times as many points as winning a lesser tournament.
A statistical endeavor, by contrast, uses a model that relates the game results to underlying variables representing the ability of each player.
Elo's central assumption was that the chess performance of each player in each game is a normally distributed random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
. Although a player might perform significantly better or worse from one game to the next, Elo assumed that the mean value of the performances of any given player changes only slowly over time. Elo thought of a player's true skill as the mean of that player's performance random variable.
A further assumption is necessary, because chess performance in the above sense is still not measurable. One cannot look at a sequence of moves and say, "That performance is 2039." Performance can only be inferred from wins, draws and losses. Therefore, if a player wins a game, he is assumed to have performed at a higher level than his opponent for that game. Conversely if he loses, he is assumed to have performed at a lower level. If the game is a draw, the two players are assumed to have performed at nearly the same level.
Elo did not specify exactly how close two performances ought to be to result in a draw as opposed to a win or loss. And while he thought it is likely that each player might have a different standard deviation
Standard deviation
Standard deviation is a widely used measure of variability or diversity used in statistics and probability theory. It shows how much variation or "dispersion" there is from the average...
to his performance, he made a simplifying assumption to the contrary.
To simplify computation even further, Elo proposed a straightforward method of estimating the variables in his model (i.e., the true skill of each player). One could calculate relatively easily, from tables, how many games a player is expected to win based on a comparison of his rating to the ratings of his opponents. If a player won more games than he was expected to win, his rating would be adjusted upward, while if he won fewer games than expected his rating would be adjusted downward. Moreover, that adjustment was to be in exact linear proportion to the number of wins by which the player had exceeded or fallen short of his expected number of wins.
From a modern perspective, Elo's simplifying assumptions are not necessary because computing power is inexpensive and widely available. Moreover, even within the simplified model, more efficient estimation techniques are well known. Several people, most notably Mark Glickman, have proposed using more sophisticated statistical machinery to estimate the same variables. On the other hand, the computational simplicity of the Elo system has proven to be one of its greatest assets. With the aid of a pocket calculator, an informed chess competitor can calculate to within one point what his next officially published rating will be, which helps promote a perception that the ratings are fair.
Implementing Elo's scheme
The USCF implemented Elo's suggestions in 1960, and the system quickly gained recognition as being both more fair and accurate than the Harkness rating system. Elo's system was adopted by the World Chess FederationFédération Internationale des Échecs
The Fédération Internationale des Échecs or World Chess Federation is an international organization that connects the various national chess federations around the world and acts as the governing body of international chess competition. It is usually referred to as FIDE , its French acronym.FIDE...
(FIDE) in 1970. Elo described his work in some detail in the book The Rating of Chessplayers, Past and Present, published in 1978.
Subsequent statistical tests have shown that chess performance is almost certainly not distributed as a Normal distribution, as weaker players have significantly (but not highly significantly) greater winning chances than Elo's model predicts. Therefore, the USCF and some chess sites use a formula based on the logistic distribution. Significant statistical anomalies have also been found when using the logistic distribution in chess. FIDE continues to use the normal distribution. The normal and logistic distribution points are, in a way, arbitrary points in a spectrum of distributions which would work well. In practice both of these distributions work very well for a number of different games.
Different ratings systems
The phrase "Elo rating" is often used to mean a player's chess rating as calculated by FIDE. However, this usage is confusing and often misleading, because Elo's general ideas have been adopted by many different organizations, including the USCF (before FIDE), the Internet Chess ClubInternet Chess Club
The Internet Chess Club is a commercial Internet chess server devoted to the play and discussion of chess and chess variants. ICC currently has over 30,000 subscribing members...
(ICC), Yahoo!
Yahoo!
Yahoo! Inc. is an American multinational internet corporation headquartered in Sunnyvale, California, United States. The company is perhaps best known for its web portal, search engine , Yahoo! Directory, Yahoo! Mail, Yahoo! News, Yahoo! Groups, Yahoo! Answers, advertising, online mapping ,...
Games, and the now-defunct Professional Chess Association
Professional Chess Association
The Professional Chess Association , which existed between 1993 and 1996, was a rival organisation to FIDE, the international chess organization...
(PCA). Each organization has a unique implementation, and none of them precisely follows Elo's original suggestions. It would be more accurate to refer to all of the above ratings as Elo ratings, and none of them as the Elo rating.
Instead one may refer to the organization granting the rating, e.g. "As of August 2002, Gregory Kaidanov
Gregory Kaidanov
Gregory Kaidanov is a Grandmaster of chess.As of April 2007, his Elo rating was 2587, making him the #9 player in the US and the 179th-highest rated player in the world. His peak rating was 2646 in 2002....
had a FIDE rating of 2638 and a USCF rating of 2742." It should be noted that the Elo ratings of these various organizations are not always directly comparable. For example, someone with a FIDE rating of 2500 will generally have a USCF rating near 2600 and an ICC rating in the range of 2500 to 3100.
FIDE ratings
For top players, the most important rating is their FIDE rating. Since July 2009, FIDE issues a ratings list once every two months.The following analysis of the November FIDE rating list gives a rough impression of what a given FIDE rating means:
- 5839 players had an active rating between 2200 and 2299, and are usually associated with the Candidate Master title.
- 2998 players had an active rating between 2300 and 2399, and are usually associated with the FIDE Master title.
- 1382 players had an active rating between 2400 and 2499, most of whom had either the International Master or the International GrandmasterInternational GrandmasterThe title Grandmaster is awarded to strong chess players by the world chess organization FIDE. Apart from World Champion, Grandmaster is the highest title a chess player can attain....
title. - 587 players had an active rating between 2500 and 2599, most of whom had the International GrandmasterInternational GrandmasterThe title Grandmaster is awarded to strong chess players by the world chess organization FIDE. Apart from World Champion, Grandmaster is the highest title a chess player can attain....
title - 178 players had an active rating between 2600 and 2699, all but one of whom had the International GrandmasterInternational GrandmasterThe title Grandmaster is awarded to strong chess players by the world chess organization FIDE. Apart from World Champion, Grandmaster is the highest title a chess player can attain....
title - 42 players had an active rating between 2700 and 2799
- 4 active players had an rating over 2800: Magnus CarlsenMagnus CarlsenSven Magnus Øen Carlsen is a Norwegian chess Grandmaster and chess prodigy who is currently the number-one ranked player in the world. In January 2010 he became the seventh player ranked number one in the world on the official FIDE rating list...
, Viswanathan AnandViswanathan AnandV. Anand or Anand Viswanathan, usually referred as Viswanathan Anand, is an Indian chess Grandmaster, the current World Chess Champion, and currently second highest rated player in the world....
, Vladimir KramnikVladimir KramnikVladimir Borisovich Kramnik is a Russian chess grandmaster. He was the Classical World Chess Champion from 2000 to 2006, and the undisputed World Chess Champion from 2006 to 2007...
and Levon AronianLevon AronianLevon Grigor Aronian is an Armenian chess Grandmaster and the reigning World Blitz Chess Champion. On the September 2011 FIDE list, he has an Elo rating of 2807, making him number three in the world and Armenia's number one...
.
November 2011 marked the first time four players had a rating above 2800. The highest ever FIDE rating was 2851, which Garry Kasparov
Garry Kasparov
Garry Kimovich Kasparov is a Russian chess grandmaster, a former World Chess Champion, writer, political activist, and one of the greatest chess players of all time....
had on the July 1999 and January 2000 lists. A list of highest ever rated players is at Methods for comparing top chess players throughout history.
Performance rating
 |
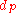 |
|---|---|
| 0.99 | +677 |
| 0.9 | +366 |
| 0.8 | +240 |
| 0.7 | +149 |
| 0.6 | +72 |
| 0.5 | 0 |
| 0.4 | -72 |
| 0.3 | -149 |
| 0.2 | -240 |
| 0.1 | -366 |
| 0.01 | -677 |
Performance Rating is a hypothetical rating that would result from the games of a single event only. Some chess organizations use the "algorithm of 400" to calculate performance rating. According to this algorithm, performance rating for an event is calculated by taking (1) the rating of each player beaten and adding 400, (2) the rating of each player lost to and subtracting 400, (3) the rating of each player drawn, and (4) summing these figures and dividing by the number of games played. This can be expressed by the following formula:
- Performance rating = [(Total of opponents' ratings + 400 * (Wins - Losses)) / Games].
This is a simplification because it doesn't take account of k-factors. But it offers an easy way to get an estimate of PR (Performance Rating).
FIDE, however, calculates performance rating by means of the formula: Opponents' Rating Average + Rating Difference. Rating Difference
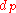 is based on a player's tournament percentage score
is based on a player's tournament percentage score 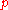 , which is then used as the key in a lookup table where
, which is then used as the key in a lookup table where 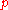 is simply the number of points scored divided by the number of games played. Note that, in case of a perfect or no score
is simply the number of points scored divided by the number of games played. Note that, in case of a perfect or no score 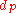 is indeterminate. The full table
is indeterminate. The full tablecan be found in the FIDE handbook online. A simplified version of this table is on the right.
FIDE tournament categories
| Category | Average rating | |
|---|---|---|
| Minimum | Maximum | |
| 16 | 2626 | 2650 |
| 17 | 2651 | 2675 |
| 18 | 2676 | 2700 |
| 19 | 2701 | 2725 |
| 20 | 2726 | 2750 |
| 21 | 2751 | 2775 |
| 22 | 2776 | 2800 |
FIDE classifies tournaments into categories according to the average rating of the players. Each category is 25 rating points wide. Category 1 is for an average rating of 2251 to 2275, category 2 is 2276 to 2300, etc. For women's tournaments, the categories are 200 rating points lower, so a Category 1 is an average rating of 2051 to 2075, etc. The highest rated tournaments have been category 22, with an average from 2776 to 2800. The top categories are in the table.
Live ratings
FIDE updates its ratings list every two months. In contrast, the unofficial "Live ratings" calculate the change in players' ratings after every game. These Live ratings are based on the previously published FIDE ratings, so a player's Live rating is intended to correspond to what the FIDE rating would be if FIDE were to issue a new list that day.Although Live ratings are unofficial, interest arose in Live ratings in August/September 2008 when five different players took the "Live" #1 ranking.
The unofficial live ratings were published and maintained by Hans Arild Runde at the Live Rating website until August 2011. Another website 2700.com has been maintained since May 2011 by Artiom Tsepotan. Both websites cover players over 2700 only.
Currently, the #1 spot in both the official FIDE rating list and the live rating list is taken by Magnus Carlsen
Magnus Carlsen
Sven Magnus Øen Carlsen is a Norwegian chess Grandmaster and chess prodigy who is currently the number-one ranked player in the world. In January 2010 he became the seventh player ranked number one in the world on the official FIDE rating list...
.
United States Chess Federation ratings
The United States Chess FederationUnited States Chess Federation
The United States Chess Federation is a non-profit organization, the governing chess organization within the United States, and one of the federations of the FIDE. The USCF was founded in 1939 from the merger of two regional chess organizations, and grew gradually until 1972, when membership...
(USCF) uses its own classification of players:
- 2400 and above: Senior Master
- 2200–2399 plus 300 games above 2200: Original Life Master
- 2200–2399: National Master
- 2000–2199: Expert
- 1800–1999: Class A
- 1600–1799: Class B
- 1400–1599: Class C
- 1200–1399: Class D
- 1000–1199: Class E
- 800–999: Class F
- 600–799: Class G
- 400–599: Class H
- 200–399: Class I
- 100–199: Class J
In general, 1000 is considered a bright beginner. In 2007, the median rating of all USCF members was 657.
The K factor, in the USCF rating system, can be estimated by dividing 800 by the effective number of games a player's rating is based on (Ne) plus the number of games the player completed in a tournament (m).
Rating floors
The USCF maintains an absolute ratings floor of 100 for all ratings. Thus, no member can have a rating below 100, no matter their performance at USCF sanctioned events. However, players can have higher individual absolute ratings floors, calculated using the following formula: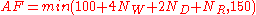
where
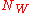 is the number of rated games won,
is the number of rated games won, 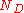 is the number of rated games drawn, and
is the number of rated games drawn, and 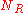 is the number of events in which the player completed three or more rated games.
is the number of events in which the player completed three or more rated games.Higher rating floors exist for experienced players who have achieved significant ratings. Such higher rating floors exist, starting at ratings of 1200 in 100 point increments up to 2100 (1200, 1300, 1400, ... , 2100). A player's rating floor is calculated by taking their peak rating, subtracting 200 points, and then rounding down to the nearest rating floor. For example, a player who has reached a peak rating of 1464 would have a rating floor of 1464 − 200 = 1264, which would be rounded down to 1200. Under this scheme, only Class C players and above are capable of having a higher rating floor than their absolute player rating. All other players would have a floor of at most 150.
There are two ways to achieve higher rating floors other than under the standard scheme presented above. If a player has achieved the rating of Original Life Master, his or her rating floor is set at 2200. The achievement of this title is unique in that no other recognized USCF title will result in a new floor. For players with ratings below 2000, winning a cash prize of $2,000 or more raises that player's rating floor to the closest 100-point level that would have disqualified the player for participation in the tournament. For example, if a player won $4,000 in a 1750 and under tournament, the player would now have a rating floor of 1800.
Ratings of computers
Since 2005–2006, human-computer chess matchesHuman-computer chess matches
This article documents the progress of significant human-computer chess matches.Chess computers were first able to beat strong chess players in the late 1980s...
have demonstrated that chess computers are capable of defeating even the strongest human players (Deep Blue versus Garry Kasparov
Deep Blue versus Garry Kasparov
Deep Blue versus Garry Kasparov was a pair of famous six-game human-computer chess matches played between the IBM supercomputer Deep Blue and the World Chess Champion Garry Kasparov. The first match was played in February 1996 in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Kasparov won the match 4–2, losing one...
). However ratings of computers are difficult to quantify. There have been too few games under tournament conditions to give computers or software engines an accurate rating. Also, for chess engines, the rating is dependent on the machine a program runs on.
For some ratings estimates, see Chess Engine.
Mathematical details
Performance can't be measured absolutely; it can only be inferred from wins, losses, and draws against other players. A player's rating depends on the ratings of his or her opponents, and the results scored against them. The relative difference in rating between two players determines an estimate for the expected score between them. Both the average and the spread of ratings can be arbitrarily chosen. Elo suggested scaling ratings so that a difference of 200 rating points in chess would mean that the stronger player has an expected score (which basically is an expected average score) of approximately 0.75, and the USCF initially aimed for an average club player to have a rating of 1500.A player's expected score is his probability of winning plus half his probability of drawing. Thus an expected score of 0.75 could represent a 75% chance of winning, 25% chance of losing, and 0% chance of drawing. On the other extreme it could represent a 50% chance of winning, 0% chance of losing, and 50% chance of drawing. The probability of drawing, as opposed to having a decisive result, is not specified in the Elo system. Instead a draw is considered half a win and half a loss.
If Player A has true strength
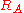 and Player B has true strength
and Player B has true strength 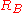 , the exact formula (using the logistic curve) for the expected score of Player A is
, the exact formula (using the logistic curve) for the expected score of Player A is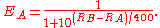
Similarly the expected score for Player B is

This could also be expressed by

and
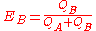
where
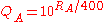 and
and 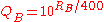 . Note that in the latter case, the same denominator applies to both expressions. This means that by studying only the numerators, we find out that the expected score for player A is
. Note that in the latter case, the same denominator applies to both expressions. This means that by studying only the numerators, we find out that the expected score for player A is 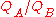 times greater than the expected score for player B. It then follows that for each 400 rating points of advantage over the opponent, the chance of winning is magnified ten times in comparison to the opponent's chance of winning.
times greater than the expected score for player B. It then follows that for each 400 rating points of advantage over the opponent, the chance of winning is magnified ten times in comparison to the opponent's chance of winning.Also note that
 . In practice, since the true strength of each player is unknown, the expected scores are calculated using the player's current ratings.
. In practice, since the true strength of each player is unknown, the expected scores are calculated using the player's current ratings.When a player's actual tournament scores exceed his expected scores, the Elo system takes this as evidence that player's rating is too low, and needs to be adjusted upward. Similarly when a player's actual tournament scores fall short of his expected scores, that player's rating is adjusted downward. Elo's original suggestion, which is still widely used, was a simple linear adjustment proportional to the amount by which a player overperformed or underperformed his expected score. The maximum possible adjustment per game (sometimes called the K-value) was set at K = 16 for masters and K = 32 for weaker players.
Supposing Player A was expected to score
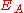 points but actually scored
points but actually scored 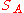 points. The formula for updating his rating is
points. The formula for updating his rating is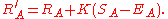
This update can be performed after each game or each tournament, or after any suitable rating period. An example may help clarify. Suppose Player A has a rating of 1613, and plays in a five-round tournament. He loses to a player rated 1609, draws with a player rated 1477, defeats a player rated 1388, defeats a player rated 1586, and loses to a player rated 1720. His actual score is (0 + 0.5 + 1 + 1 + 0) = 2.5. His expected score, calculated according to the formula above, was (0.506 + 0.686 + 0.785 + 0.539 + 0.351) = 2.867. Therefore his new rating is (1613 + 32· (2.5 − 2.867)) = 1601, assuming that a K factor of 32 is used.
Note that while two wins, two losses, and one draw may seem like a par score, it is worse than expected for Player A because his opponents were lower rated on average. Therefore he is slightly penalized. If he had scored two wins, one loss, and two draws, for a total score of three points, that would have been slightly better than expected, and his new rating would have been (1613 + 32· (3 − 2.867)) = 1617.
This updating procedure is at the core of the ratings used by FIDE, USCF, Yahoo! Games, the ICC, and FICS. However, each organization has taken a different route to deal with the uncertainty inherent in the ratings, particularly the ratings of newcomers, and to deal with the problem of ratings inflation/deflation. New players are assigned provisional ratings, which are adjusted more drastically than established ratings.
The principles used in these rating systems can be used for rating other competitions—for instance, international football matches.
Elo ratings have also been applied to games without the possibility of draw
Draw (chess)
In chess, a draw is when a game ends in a tie. It is one of the possible outcomes of a game, along with a win for White and a win for Black . Usually, in tournaments a draw is worth a half point to each player, while a win is worth one point to the victor and none to the loser.For the most part,...
s, and to games in which the result can also have a quantity (small/big margin) in addition to the quality (win/loss). See go rating with Elo for more.
Mathematical issues
There are three main mathematical concerns relating to the original work of Professor Elo, namely the correct curve, the correct K-factor, and the provisional period crude calculations.Most accurate distribution model
The first mathematical concern addressed by the USCF was the use of the normal distribution. They found that this did not accurately represent the actual results achieved by particularly the lower rated players. Instead they switched to a logistical distribution model, which the USCF found provided a better fit for the actual results achieved. FIDE still uses the normal distribution as the basis for rating calculations as suggested by Elo himself.Most accurate K-factor
The second major concern is the correct "K-factor" used. The chess statistician Jeff SonasJeff Sonas
Jeff Sonas is known as a statistical chess analyst who invented the Chessmetrics system for rating chess players, which is intended as an improvement on the Elo rating system. He is the founder and proprietor of the Chessmetrics.com website, which gives Sonas' calculations of the ratings of current...
reckons that the original K=10 value (for players rated above 2400) is inaccurate in Elo's work. If the K-factor coefficient is set too large, there will be too much sensitivity to just a few, recent events, in terms of a large number of points exchanged in each game. Too low a K-value, and the sensitivity will be minimal, and the system will not respond quickly enough to changes in a player's actual level of performance.
Elo's original K-factor estimation was made without the benefit of huge databases and statistical evidence. Sonas indicates that a K-factor of 24 (for players rated above 2400) may be more accurate both as a predictive tool of future performance, and also more sensitive to performance.
Certain Internet chess sites seem to avoid a three-level K-factor staggering based on rating range. For example the ICC seems to adopt a global K=32 except when playing against provisionally rated players. The USCF (which makes use of a logistic distribution as opposed to a normal distribution) has staggered the K-factor according to three main rating ranges of:
- Players below 2100 -> K factor of 32 used
- Players between 2100 and 2400 -> K factor of 24 used
- Players above 2400 -> K factor of 16 used
FIDE uses the following ranges:
- K = 30 (was 25) for a player new to the rating list until s/he has completed events with a total of at least 30 games.
- K = 15 as long as a player's rating remains under 2400.
- K = 10 once a player's published rating has reached 2400, and s/he has also completed events with a total of at least 30 games. Thereafter it remains permanently at 10.
In over-the-board chess, the staggering of the K-factor is important to ensure minimal inflation at the top end of the rating spectrum. This assumption might in theory apply equally to an online chess server, as well as a standard over-the-board chess organisation such as FIDE or USCF. In theory, it would make it harder for players to get much higher ratings if their K-factor was reduced when they got over 2400 rating. However, the ICC's help on K-factors indicates that it may simply be the choosing of opponents that enables 2800+ players to further increase their rating quite easily. This would seem to hold true, for example, if one analysed the games of a grandmaster on the ICC: one can find a string of games of opponents who are all over 3100. In over-the-board chess, it would only be in very high level all-play-all events that this player would be able to find a steady stream of 2700+ opponents – in at least a category 15+ FIDE event. A category 10 FIDE event would mean players are restricted in rating between 2476 to 2500. However, if the player entered normal Swiss-paired open over-the-board chess tournaments, he would likely meet many opponents less than 2500 FIDE on a regular basis. A single loss or draw against a player rated less than 2500 would knock the GM's FIDE rating down significantly.
Even if the K-factor was 16, and the player defeated a 3100+ player several games in a row, his rating would still rise quite significantly in a short period of time, due to the speed of blitz games, and hence the ability to play many games within a few days. The K-factor would arguably only slow down the increases that the player achieves after each win. The evidence given in the ICC K-factor article relates to the auto-pairing system, where the maximum ratings achieved are seen to be only about 2500. So it seems that random-pairing as opposed to selective pairing is the key for combatting rating inflation at the top end of the rating spectrum, and possibly only to a much lesser extent, a slightly lower K-factor for a player >2400 rating.
Game activity versus protecting one's rating
In general the Elo system has increased the competitive climate for chess and inspired players for further study and improvement of their game. However, in some cases ratings can discourage game activity for players who wish to "protect their rating".Examples:
- They may choose their events or opponents more carefully where possible.
- If a player is in a Swiss tournament, and loses a couple of games in a row, they may feel the need to abandon the tournament in order to avoid any further rating "damage".
- Junior players, who may have high provisional ratings, might play less than they would, because of rating concerns.
In these examples, the rating "agenda" can sometimes conflict with the agenda of promoting chess activity and rated games.
Interesting from the perspective of preserving high Elo ratings versus promoting rated game activity is a recent proposal by British Grandmaster John Nunn
John Nunn
John Denis Martin Nunn is one of England's strongest chess players and once belonged to the world's top ten. He is also a three times world champion in chess problem solving, a chess writer and publisher, and a mathematician....
regarding qualifiers based on Elo rating for a World championship model.
Nunn highlights in the section on "Selection of players", that players not only be selected by high Elo ratings, but also their rated game activity. Nunn clearly separates the "activity bonus" from the Elo rating, and only implies using it as a tie-breaking mechanism.
Outside the chess world, concerns over players avoiding competitive play to protect their ratings, often referred to as "sitting on rating", are the main reason Wizards of the Coast
Wizards of the Coast
Wizards of the Coast is an American publisher of games, primarily based on fantasy and science fiction themes, and formerly an operator of retail stores for games...
has given for abandoning the Elo system for Magic: the Gathering
Magic: The Gathering
Magic: The Gathering , also known as Magic, is the first collectible trading card game created by mathematics professor Richard Garfield and introduced in 1993 by Wizards of the Coast. Magic continues to thrive, with approximately twelve million players as of 2011...
tournaments in favour of a system of their own devising called "Planeswalker Points".
Selective pairing
A more subtle issue is related to pairing. When players can choose their own opponents, they can choose opponents with minimal risk of losing, and maximum reward for winning. Such a luxury of being able to hand-pick your opponents is not present in Over-the-Board Elo type calculations, and therefore this may account strongly for the ratings on the ICC using Elo which are well over 2800.Particular examples of 2800+ rated players choosing opponents with minimal risk and maximum possibility of rating gain include: choosing computers that they know they can beat with a certain strategy; choosing opponents that they think are over-rated; or avoiding playing strong players who are rated several hundred points below them, but may hold chess titles such as IM or GM. In the category of choosing over-rated opponents, new-entrants to the rating system who have played less than 50 games are in theory a convenient target as they may be overrated in their provisional rating. The ICC compensates for this issue by assigning a lower K-factor to the established player if they do win against a new rating entrant. The K-factor is actually a function of the number of rated games played by the new entrant.
Therefore, Elo ratings online still provide a useful mechanism for providing a rating based on the opponent's rating. Its overall credibility, however, needs to be seen in the context of at least the above two major issues described — engine abuse, and selective pairing of opponents.
The ICC has also recently introduced "auto-pairing" ratings which are based on random pairings, but with each win in a row ensuring a statistically much harder opponent who has also won x games in a row. With potentially hundreds of players involved, this creates some of the challenges of a major large Swiss event which is being fiercely contested, with round winners meeting round winners. This approach to pairing certainly maximizes the rating risk of the higher-rated participants, who may face very stiff opposition from players below 3000 for example. This is a separate rating in itself, and is under "1-minute" and "5-minute" rating categories. Maximum ratings achieved over 2500 are exceptionally rare.
Ratings inflation and deflation
An increase or decrease in the average rating over all players in the rating system is often referred to as rating inflation or rating deflation respectively. For example, if there is inflation, a modern rating of 2500 means less than a historical rating of 2500, while the reverse is true if there is deflation. Using ratings to compare players between different eras is made more difficult when inflation and deflation is present. (See also Greatest chess player of all timeGreatest chess player of all time
This article examines a number of methodologies that have been suggested for the task of comparing top chess players throughout history, particularly the question of comparing the greatest players of different eras...
.)
It is commonly believed that, at least at the top level, modern ratings are inflated. For instance Nigel Short
Nigel Short
Nigel David Short MBE is an English chess grandmaster earning the title at the age of 19. Short is often regarded as the strongest English player of the 20th century as he was ranked third in the world, from January 1988 – July 1989 and in 1993, he challenged Garry Kasparov for the World Chess...
said in September 2009, "The recent ChessBase article on rating inflation by Jeff Sonas would suggest that my rating in the late 1980s would be approximately equivalent to 2750 in today's much debauched currency". (Short's highest rating in the 1980s was 2665 in July 1988, which was equal third in the world. When he made this comment, 2665 would have ranked him 65th, while 2750 would have ranked him equal 10th. In the May 2011 FIDE rating list, 2665 would have ranked him equal 77th, while 2750 would have ranked him 12th.)
It has been suggested that an overall increase in ratings reflects greater skill. The advent of strong chess computers allows a somewhat objective evaluation of the absolute playing skill of past chess masters, based on their recorded games, but this is also a measure of how computerlike the players' moves are, not merely a measure of how strongly they have played.
The number of people with ratings over 2700 has increased. Around 1979 there was only one active player (Anatoly Karpov
Anatoly Karpov
Anatoly Yevgenyevich Karpov is a Russian chess grandmaster and former World Champion. He was the official world champion from 1975 to 1985 when he was defeated by Garry Kasparov. He played three matches against Kasparov for the title from 1986 to 1990, before becoming FIDE World Champion once...
) with a rating this high. This increased to 15 players in 1994, while 33 players have this rating in 2009, which has made this top echelon of chess mastery less exclusive. One possible cause for this inflation was the rating floor, which for a long time was at 2200, and if a player dropped below this they were stricken from the rating list. As a consequence, players at a skill level just below the floor would only be on the rating list if they were overrated, and this would cause them to feed points into the rating pool. In the November 2011 FIDE rating list, there were 47 players with ratings over 2700.
In 1995, the USCF experienced that several young scholastic players were improving faster than what the rating system was able to track. As a result, established players with stable ratings started to lose rating points to the young and underrated players. Several of the older established players were frustrated over what they considered an unfair rating decline, and some even quit chess over it.
Combating deflation
Because of the significant difference in timing of when inflation and deflation occur, and in order to combat deflation, most implementations of Elo ratings have a mechanism for injecting points into the system in order to maintain relative ratings over time. FIDE has two inflationary mechanisms. First, performances below a "ratings floor" are not tracked, so a player with true skill below the floor can only be unrated or overrated, never correctly rated. Second, established and higher-rated players have a lower K-factor. New players have a K=30, which drops to K=15 after 30 played games, and to K=10 when the player reaches 2400.The current system in the United States includes a bonus point scheme which feeds rating points into the system in order to track improving players, and different K-values for different players. Some methods, used in Norway for example, differentiate between juniors and seniors, and use a larger K factor for the young players, even boosting the rating progress by 100% for when they score well above their predicted performance.
Rating floors in the USA work by guaranteeing that a player will never drop below a certain limit. This also combats deflation, but the chairman of the USCF Ratings Committee has been critical of this method because it does not feed the extra points to the improving players. A possible motive for these rating floors is to combat sandbagging, i.e. deliberate lowering of ratings to be eligible for lower rating class sections and prizes.
Other chess rating systems
- Ingo system, designed by Anton Hoesslinger, used in Germany 1948-1992 .
- Harkness System, invented by Kenneth HarknessKenneth HarknessKenneth Harkness was a chess organizer. He is the creator of the Harkness rating system.-Life and career:...
, who published it in 1956 . - British Chess Federation Rating System, published in 1958, now termed the ECF grading systemECF grading systemThe ECF grading system is the name given to the rating system used by the English Chess Federation. A rating produced by the system is known as an ECF grade...
. - Correspondence Chess League of AmericaICCF U.S.A.ICCF U.S.A. is a member of the International Correspondence Chess Association for the territory of the United States.- History :The Correspondence Chess League of America was the first American chess club to become an ICCF affiliate. It was created in 1917 as a merger of four clubs, one of which...
Rating System (now uses Elo). - Glicko rating systemGlicko rating systemThe Glicko rating system and the Glicko-2 rating system are chess rating systems similar to the Elo rating system: a method for assessing a player's strength in games of skill such as chess. It was invented by Mark Glickman as an improvement of the Elo rating system...
- ChessmetricsChessmetricsChessmetrics is a system for rating chess players devised by Jeff Sonas. It is intended as an improvement over the Elo rating system.-Implementation:...
- In November 2005, the Xbox LiveXbox LiveXbox Live is an online multiplayer gaming and digital media delivery service created and operated by Microsoft Corporation. It is currently the only online gaming service on consoles that charges users a fee to play multiplayer gaming. It was first made available to the Xbox system in 2002...
online gaming service proposed the TrueSkillTrueSkillTrueSkill is a Bayesian ranking algorithm developed by Microsoft Research and used in the Xbox matchmaking system built to address some perceived flaws in the Elo rating system...
ranking system that is an extension of the Glicko rating systemGlicko rating systemThe Glicko rating system and the Glicko-2 rating system are chess rating systems similar to the Elo rating system: a method for assessing a player's strength in games of skill such as chess. It was invented by Mark Glickman as an improvement of the Elo rating system...
to multi-player and multi-team games.
Elo ratings in games other than chess
American Collegiate FootballCollege football
College football refers to American football played by teams of student athletes fielded by American universities, colleges, and military academies, or Canadian football played by teams of student athletes fielded by Canadian universities...
uses the Elo method as a portion of its Bowl Championship Series
Bowl Championship Series
The Bowl Championship Series is a selection system that creates five bowl match-ups involving ten of the top ranked teams in the NCAA Division I Football Bowl Subdivision , including an opportunity for the top two to compete in the BCS National Championship Game.The BCS relies on a combination of...
rating systems. Jeff Sagarin
Jeff Sagarin
Jeff Sagarin is an American sports statistician well-known for his development of a methodology for ranking and rating sports teams in a variety of sports...
of USA Today
USA Today
USA Today is a national American daily newspaper published by the Gannett Company. It was founded by Al Neuharth. The newspaper vies with The Wall Street Journal for the position of having the widest circulation of any newspaper in the United States, something it previously held since 2003...
publishes team rankings for most American sports, including Elo system ratings for College Football. The NCAA uses his Elo ratings as part of a formula to determine the annual participants in the College Football National Championship Game
NCAA Division I FBS National Football Championship
A college football national championship in the highest level of collegiate play in the United States, currently the National Collegiate Athletic Association Division I Football Bowl Subdivision , is a designation awarded annually by various third-party organizations to their selection of the best...
.
National Scrabble
Scrabble
Scrabble is a word game in which two to four players score points by forming words from individual lettered tiles on a game board marked with a 15-by-15 grid. The words are formed across and down in crossword fashion and must appear in a standard dictionary. Official reference works provide a list...
organizations compute normally-distributed Elo ratings except in the United Kingdom
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, where a different system is used. The North American Scrabble Players Association
North American SCRABBLE Players Association
The North American Scrabble Players Association is an organization founded in 2009 to coordinate competitive Scrabble tournaments and clubs in North America...
has the largest rated population of active members, numbering about 2,000 as of early 2011. Lexulous also uses the Elo system.
The popular First Internet Backgammon Server
First Internet Backgammon Server
First Internet Backgammon Server is the earliest backgammon server on the Internet, operating since July 19, 1992.FIBS allows Internet users to play backgammon in real-time against other people and tracks player performance using a modified version of the Elo rating system. It was created by...
calculates ratings based on a modified Elo system. New players are assigned a rating of 1500, with the best humans and bots rating over 2000. The same formula has been adopted by several other backgammon sites, such as Play65
Play65
Play65 is an online backgammon operator established in 2004 by an Israeli-based company, SkillEmpire, that hosts real-time backgammon games and tournaments. With its client software available in 21 languages, including English, Arabic, Chinese, Danish, Dutch, etc. Play65 has more than 5,000,000...
, DailyGammon, GoldToken and VogClub. VogClub sets a new player's rating at 1600.
The European Go Federation
European Go Federation
The European Go Federation is a non-profit organization with the purpose of encouraging, regulating, co-ordinating, and disseminating the playing of the board game Go in Europe. The EGF was founded in 1957, the same year that the inaugural European Go Congress took place - in Cuxhaven, Germany...
adopted an Elo based rating system initially pioneered by the Czech Go Federation.
The Groshin's Score an Elo based game.
In other sports, individuals maintain rankings based on the Elo algorithm. These are usually unofficial, not endorsed by the sport's governing body. The World Football Elo Ratings
World Football Elo Ratings
The World Football Elo Ratings is a ranking system for men's national teams in association football. The method used to rank teams is based upon the Elo rating system method but modified to take various football-specific variables into account...
rank national teams in men's football. In 2006, Elo ratings were adapted for Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball
Major League Baseball is the highest level of professional baseball in the United States and Canada, consisting of teams that play in the National League and the American League...
teams by Nate Silver
Nate Silver
Nathaniel Read "Nate" Silver is an American statistician, psephologist, and writer. Silver first gained public recognition for developing PECOTA, a system for forecasting the performance and career development of Major League Baseball players, which he sold to and then managed for Baseball...
of Baseball Prospectus
Baseball Prospectus
Baseball Prospectus is an organization that publishes a website, BaseballProspectus.com, devoted to the sabermetric analysis of baseball. BP has a staff of regular columnists and provides advanced statistics as well player and team performance projections on the site...
. Based on this adaptation, Baseball Prospectus also makes Elo-based Monte Carlo
Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo methods are a class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to compute their results. Monte Carlo methods are often used in computer simulations of physical and mathematical systems...
simulations of the odds of whether teams will make the playoffs. One of the few Elo-based rankings endorsed by a sport's governing body is the FIFA Women's World Rankings
FIFA Women's World Rankings
The FIFA Women's World Rankings for football were introduced in 2003, with the first rankings published in March of that year, as a follow-on to the existing FIFA World Rankings for men...
, based on a simplified version of the Elo algorithm, which FIFA
FIFA
The Fédération Internationale de Football Association , commonly known by the acronym FIFA , is the international governing body of :association football, futsal and beach football. Its headquarters are located in Zurich, Switzerland, and its president is Sepp Blatter, who is in his fourth...
uses as its official ranking system for national teams in women's football.
Sports-reference.com uses the Elo rating system to rate the best professional players in basketball, football, baseball (batters and pitchers rated separately), and hockey (goalies and skaters rated separately. The list changes constantly, but as of August 30, 2011 at 12:50 pm EDT, the number 1's are Michael Jordan
Michael Jordan
Michael Jeffrey Jordan is a former American professional basketball player, active entrepreneur, and majority owner of the Charlotte Bobcats...
, Barry Sanders
Barry Sanders
Barry Sanders is a former American football running back who spent all of his professional career with the Detroit Lions in the NFL. Sanders left the game just short of the all-time rushing record...
(with Reggie White
Reggie White
Reginald Howard "Reggie" White was a professional American football player. He played 15 seasons as a defensive end in the National Football League for the Philadelphia Eagles, Green Bay Packers and Carolina Panthers, becoming one of the most decorated players in NFL history...
very close), Babe Ruth
Babe Ruth
George Herman Ruth, Jr. , best known as "Babe" Ruth and nicknamed "the Bambino" and "the Sultan of Swat", was an American Major League baseball player from 1914–1935...
, Walter Johnson
Walter Johnson
Walter Perry Johnson , nicknamed "Barney" and "The Big Train", was a Major League Baseball right-handed pitcher. He played his entire 21-year baseball career for the Washington Senators...
, Bobby Orr
Bobby Orr
Robert Gordon "Bobby" Orr, OC is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player. Orr played in the National Hockey League for his entire career, the first ten seasons with the Boston Bruins, joining the Chicago Black Hawks for two more. Orr is widely acknowledged to be one of the greatest...
(with Wayne Gretzky
Wayne Gretzky
Wayne Douglas Gretzky, CC is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player and former head coach. Nicknamed "The Great One", he is generally regarded as the best player in the history of the National Hockey League , and has been called "the greatest hockey player ever" by many sportswriters,...
very close), and Dominik Hasek
Dominik Hašek
Dominik Hašek is a Czech ice hockey goaltender who is currently with HC Spartak Moscow of the KHL.In his 16-season National Hockey League career, he played for the Chicago Blackhawks, Buffalo Sabres, Detroit Red Wings, and the Ottawa Senators. During his years in Buffalo, he became one of the...
.
The English Korfball
Korfball
Korfball is a mixed gender team sport, with similarities to netball and basketball. A team consists of eight players; four female and four male. A team also includes a coach. It was founded in the Netherlands in 1902 by Nico Broekhuysen. In the Netherlands there are around 580 clubs, and over a...
Association rated teams based on Elo ratings, to determine handicaps for their cup competition for the 2011/12 season.
Various online role-playing games use Elo ratings for player-versus-player rankings. In Guild Wars
Guild Wars
Guild Wars is an episodic series of online 3D fantasy role-playing games developed by ArenaNet and published by NCsoft. Although often defined as an MMORPG the developers define it as a CORPG due to significant differences from the MMORPG genre. It provides two main modes of gameplay—a cooperative...
, Elo ratings are used to record guild rating gained and lost through Guild versus Guild battles, which are two-team fights. The initial K-value was 30, but was changed to 5 in January 2007, then changed to 15 in July 2009. Vendetta Online
Vendetta Online
Vendetta Online is a twitch-based, science fiction massively multiplayer online role-playing game developed by Guild Software for the operating systems Android, Linux, Mac OS X, and Microsoft Windows...
uses Elo ratings to rank the flight combat skill of players when they have agreed to a one-on-one duel. World of Warcraft
World of Warcraft
World of Warcraft is a massively multiplayer online role-playing game by Blizzard Entertainment. It is the fourth released game set in the fantasy Warcraft universe, which was first introduced by Warcraft: Orcs & Humans in 1994...
formerly used the Elo Rating system when teaming up and comparing Arena players, but now uses a system similar to Microsoft's TrueSkill
TrueSkill
TrueSkill is a Bayesian ranking algorithm developed by Microsoft Research and used in the Xbox matchmaking system built to address some perceived flaws in the Elo rating system...
. Starcraft II: Wings of Liberty also uses a modified Elo rating system, having added a hidden rating mechanic. The game Puzzle Pirates uses the Elo rating system as well to determine the standings in the various puzzles. Also Roblox
Roblox
Roblox is a massively multiplayer online game virtual playground and workshop designed for children aged 7 and over. Players can build games with blocks of various shapes, sizes, and materials. Roblox users can code the places they design with a restricted and sandboxed version of Lua 5.1...
introduced the Elo rating in 2010. League of Legends
League of Legends
The BetFred League of Legends was a darts tournament featuring some of the legends of the game of darts which commenced in May 2008. The tournament is broadcast on Setanta Sports in the United Kingdom....
, Heroes of Newerth
Heroes of Newerth
Heroes of Newerth is a free-to-play science fantasy, action real-time strategy game developed by S2 Games for Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X and Linux. The game was heavily inspired by the Warcraft III: The Frozen Throne custom map, Defense of the Ancients and is S2 Games' first game title in the...
and Bloodline Champions
Bloodline Champions
Bloodline Champions is an arena-based free to play PvP game developed by the Swedish company Stunlock Studios and distributed by Funcom using Microsoft XNA. Bloodline Champions won both "Game of the Year" and "Winner XNA" in the Swedish Game Awards 2009...
use modified Elo rating systems to rank individuals in a team-based environment as will the upcoming Counter Strike: Global Offensive. UniWar
UniWar
UniWar is a video game for the iPhone and Android mobile platform first released in April 2009. The game has done so well on the iPhone and Android platforms that the developers have since released the application on other mobile devices. A post from Dec 16th 2009 on the UniWar website states that...
also uses the Elo system to give players scores based on their competitive results. For the third expansion Retribution of Dawn of War 2
THQ switched from Microsofts TrueSkill to the Elo-System. The upcoming title Counter Strike: Global Offensive has also been confirmed to use the Elo rating.
Despite questions of the appropriateness of using the Elo system to rate games in which luck is a factor, trading-card game manufacturers often use Elo ratings for their organized play efforts. The DCI
Duelists' Convocation International
The DCI is the official sanctioning body for competitive play in Magic: The Gathering and various other games produced by Wizards of the Coast and its subsidiaries, such as Avalon Hill. The DCI provides game rules, tournament operating procedures, and other materials to private tournament...
(formerly Duelists' Convocation International) uses Elo ratings for tournaments of Magic: The Gathering
Magic: The Gathering
Magic: The Gathering , also known as Magic, is the first collectible trading card game created by mathematics professor Richard Garfield and introduced in 1993 by Wizards of the Coast. Magic continues to thrive, with approximately twelve million players as of 2011...
and other Wizards of the Coast
Wizards of the Coast
Wizards of the Coast is an American publisher of games, primarily based on fantasy and science fiction themes, and formerly an operator of retail stores for games...
games. However, the DCI will be abandoning this system in 2012 in favour of a new cumulative system of "Planeswalker Points", chiefly because of the above-noted concern that Elo encourages highly rated players to avoid playing to "protect their rating". Pokémon USA uses the Elo system to rank its TCG organized play competitors. Prizes for the top players in various regions include holidays and world championships invites. Similarly, Decipher, Inc.
Decipher, Inc.
Decipher, Inc. is an American gaming company based in Norfolk, Virginia, USA. They began with three puzzles called "Decipher" then moved on to party games and Pente sets, but since 1994 produced collectible card and role-playing games. Their longest-running offering is the How to Host a Murder...
used the Elo system for its ranked games such as Star Trek Customizable Card Game
Star Trek Customizable Card Game
The Star Trek Customizable Card Game is a collectible card game based on the Star Trek universe. The name is commonly abbreviated as STCCG or ST:CCG. It was first introduced in 1994 by Decipher, Inc., under the name Star Trek: The Next Generation Customizable Card Game...
and Star Wars Customizable Card Game
Star Wars Customizable Card Game
Star Wars: Customizable Card Game is a customizable card game based on the Star Wars fictional universe. It was created by Decipher, Inc., which also produced the Star Trek Customizable Card Game and The Lord of the Rings Trading Card Game. The game was produced from December 1995 until December...
.
Moreover, online judge
Online judge
An online judge is an online system to test programs in programming contests. They are also used to practice for such contests. Many of these systems organize their own contests....
sites are also using Elo rating system or its derivatives. For example, TopCoder
TopCoder
TopCoder is a company which administers contests in computer programming. TopCoder hosts fortnightly online algorithm competitions — known as SRMs or "single round matches" — as well as weekly competitions in design and development. The work in design and development produces useful software...
is using a modified version based on normal distribution, while Codeforces is using another version based on logistic distribution.
External links
- Official FIDE Rating List
- All Time Rankings - lists the top 10 from 1970 to 1997
- Unofficial Live Top List
- GoBase.org: Introduction to the Elo Rating System
- Citations for Elo, A.E. 1978. The Ratings of Chess Players: Past and Present.
- Mark Glickman's research page, with a number of links to technical papers on chess rating systems
- PDF from Glickman's site explaining USCF ratings system
- http://chess.about.com/library/weekly/aa03a25.htm
- Elo query with world ranking list and historical development since 1990
- Multiplayer Elo Calculator
- GotGame.me uses the ELO rankings math to power its chess site