.gif)
Elf (Middle-earth)
Encyclopedia
In J. R. R. Tolkien
's legendarium
, Elves are one of the races that inhabit a fictional Earth, often called Middle-earth
, and set in the remote past. They appear in The Hobbit
and in The Lord of the Rings
, but their complex history is described more fully in The Silmarillion
. Tolkien had been writing about Elves long before he published The Hobbit.
derives from the Old English word ælf (which has cognates in all other Germanic languages
). Numerous types of elves appear in Germanic mythology
, the West Germanic concept appears to have come to differ from the Scandinavian notion in the early Middle Ages, and Anglo-Saxon concept diverged even further, possibly under Celtic
influence. Tolkien would make it clear in a letter that his Elves differ from those "of the better known lore", referring to Scandinavian mythology.
By 1915 when Tolkien was writing his first elven poems, the words elf, fairy and gnome had many divergent and contradictory associations. Tolkien had been gently warned against using the term 'fairy', which John Garth supposes may have been due to the word becoming increasingly used to indicate homosexuality
.
The fairy had been taken up by as a utopian theme by late 19th century writers and used to critique social and religious values, a tradition which Tolkien along with TH White are seen to continue. One of the last of the Victorian Fairy-paintings, The Pipe of Dreams by Estella Canziani
, sold 250,000 copies and was well known within the trenches of World War 1, where Tolkien saw active service. Illustrated posters of Robert Louis Stevenson
's poem Land of Nod had been sent out by a philanthropist to brighten servicemen's quarters and Faery was used in other contexts as an image of "Old England
" to inspire patriotism.
According to Marjorie Burns, Tolkien eventually chose the term elf over fairy, but still retained some doubts. In his 1939 essay On Fairy-Stories
, Tolkien wrote that
appear in much of Tolkien's early poetry, and have influence upon his later works in part due to the influence of a production of J.M. Barrie's Peter Pan
in Birmingham
in 1910 and his familiarity with the work of Catholic
mystic poet, Francis Thompson
which Tolkien had acquired in 1914.
As a philologist
, Tolkien's interest in languages led him to invent several languages of his own as a pastime. In considering the nature of who might speak these languages, and what stories they might tell, Tolkien again turned to the concept of elves.
, Tolkien develops a theme that the diminutive fairy-like race of Elves had once been a great and mighty people, and that as Men took over the world, these Elves had "diminished" themselves. This theme was influenced especially by the god-like and human-sized Ljósálfar
of Norse mythology
, and medieval works such as Sir Orfeo
, the Welsh Mabinogion
, Arthurian romances and the legends of the Tuatha Dé Danann
.
Some of the stories Tolkien wrote as elven history have been seen to be directly influenced by Celtic Mythology. For example, the "Flight of The Noldoli
" is based on the Tuatha Dé Danann
and Lebor Gabála Érenn
, and their migratory nature comes from early Irish/Celtic history. John Garth also sees that with the underground enslavement of the Noldoli to Melkor, Tolkien was essentially rewriting Irish myth regarding the Tuatha Dé Danann into a Christian eschatology.
The name Inwe
(in the first draft Ing
), given by Tolkien to the eldest of the elves and his clan is similar to the name found in Norse mythology as that of the god Ingwi-Freyr
(and Ingui-Frea in Anglo-Saxon paganism), a god who is gifted the elf world Álfheimr. Terry Gunnell also claims that the relationship between beautiful ships and the Elves is reminiscent of the god Njörðr and the god Freyr's ship Skíðblaðnir
. He also retains the usage of the French
derived term "fairy" for the same creatures.
The larger Elves are also inspired by Tolkien's personal Catholic
theology – as representing the state of Men in Eden who have not yet "fallen", similar to humans but fairer and wiser, with greater spiritual powers, keener senses, and a closer empathy with nature. Tolkien wrote of them:
In The Book of Lost Tales Tolkien includes both the more serious "medieval" type of elves such as Fëanor
and Turgon
alongside the frivolous, Jacobean
type of elves such as the Solosimpi and Tinúviel
.
Alongside the idea of the greater Elves, Tolkien also developed the idea of children visiting Valinor, the island-homeland of the Elves in their sleep. Elves would also visit children at night and comfort them if they had been chided or were upset. This theme, linking elves with children's dreams and nocturnal travelling was largely abandoned in Tolkien's later writing.
, Tolkien again includes both the more serious 'medieval' type of elves, such as Elrond
and the Wood-elf king, and frivolous elves, such as those at Rivendell
.
Dimitra Fimi proposes that these comments are a product of his Anglophilia rather than a commentary on the texts themselves or their actual influence on his writing, and cites evidence to this effect in her essay "Mad" Elves and "elusive beauty": some Celtic strands of Tolkien's mythology.
'lord' and 'lady') are also given to Celeborn and Galadriel in the Lord of The Rings.
According to Tom Shippey the theme, of diminishment from semi-divine Elf to dimunitive Fairy resurfaces in The Lord of the Rings
in the dialogue of Galadriel
.
Writing in 1954, part way through proofing The Lord of the Rings Tolkien claimed the Elvish language Sindarin
has a character very like British-Welsh
"because it seems to fit the rather 'Celtic' type of legends and stories told of its speakers". In the same letter, Tolkien goes on to say that the elves had very little in common with elves or fairies of Europe, and that they really represent men with greater artistic ability, beauty and a longer life span. Tolkien also notes an Elven bloodline was the only real claim to 'nobility' that the Men of Middle-earth can have. Tolkien also wrote that the elves are primarily to blame for many of the ills of Middle-earth in The Lord of the Rings, having independently created the Three Rings in order to stop their domains in mortal-lands from 'fading' and attempting to prevent inevitable change and new growth.
. Ingwë, Finwë and Elwë now became the first ambassadors and the Kings of the Elves. This text only saw print in The War of the Jewels
, part of the analytical The History of Middle-earth
series, in 1994, but a similar version was included in The Silmarillion in 1977.
According to the earliest account, the first Elves are awakened by Eru Ilúvatar
near the bay of Cuiviénen during the Years of the Trees in the First Age
. They awake under the starlit sky, as the Sun and Moon have yet to be created. The first Elves to awake are three pairs: Imin ("First") and his wife Iminyë, Tata ("Second") and Tatië, and Enel ("Third") and Enelyë.
Imin, Tata, and Enel and their wives join up and walk through the forests. They come across six, nine, and twelve pairs of Elves, and each "patriarch" claims the pairs as his folk in order. The now sixty Elves dwell by the rivers, and they invent poetry and music in Middle-earth
(the continent). Journeying further, they come across eighteen pairs of Elves watching the stars, whom Tata claims as his. These are tall and dark-haired, the fathers of most of the Noldor
. The ninety-six Elves now invented many new words. Continuing their journey, they find twenty-four pairs of Elves, singing without language, and Enel adds them to his people. These are the ancestors of most of the Lindar or "singers", later called Teleri
. They find no more Elves; Imin's people, the smallest group, are the ancestors of the Vanyar
. All in all the Elves number 144. Because all Elves had been found in groups of twelve, twelve becomes their base number and 144 their highest number (for a long time), and none of the later Elvish languages have a common name for a greater number.
They were discovered by the Vala
Oromë, who brought the tidings of their awakening to Valinor
.
The Silmarillion states that Melkor
, the Dark Lord, had already captured some wandering Elves, and twisted and mutilated them until they became the Orcs
. However, Tolkien ultimately became uncomfortable with this Elvish origin, and devised different theories about the origin of Orcs.
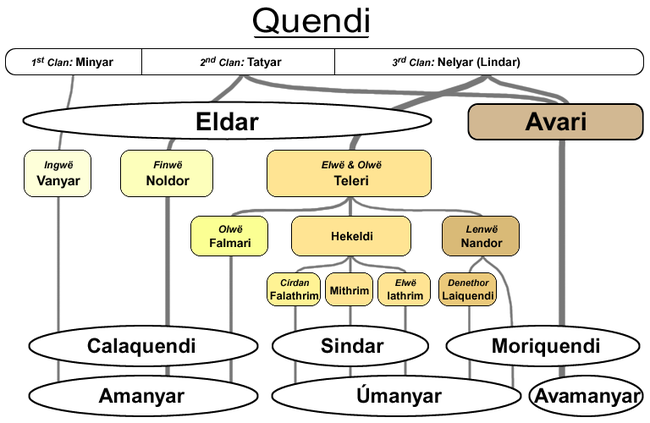 The Valar decided to summon the Elves to Valinor rather than leaving them dwelling in the place where they were first awakened, near the Cuiviénen lake in the eastern extremity of Middle-earth. They sent Oromë, who took Ingwë
The Valar decided to summon the Elves to Valinor rather than leaving them dwelling in the place where they were first awakened, near the Cuiviénen lake in the eastern extremity of Middle-earth. They sent Oromë, who took Ingwë
, Finwë
and Elwë as ambassadors to Valinor.
Returning to Middle-earth, Ingwë, Finwë and Elwë convinced a great host to take the journey to Valinor. Not all Elves accepted the summons though, and those who did not became known as the Avari
, The Unwilling.
The others were called Eldar, the People of the Stars by Oromë, and they took Ingwë, Finwë and Elwë as their leaders, and became respectively the Vanyar
, Noldor
and Teleri
. On their journey, some of the Teleri feared the Misty Mountains
and dared not cross them. They turned back and stayed in the vales of the Anduin
, and became the Nandor; these were led by Lenwë.
Oromë led the others over the Misty Mountains and Ered Lindon into Beleriand
. There Elwë became lost, and the Teleri stayed behind looking for him. The Vanyar and the Noldor moved onto a floating island that was moved by Ulmo
to Valinor.
After years, Ulmo returned to Beleriand to seek out the remaining Teleri. As Elwë had not yet been found, a great part of the Teleri took his brother Olwë as their leader and were ferried to Valinor. Some Teleri stayed behind though, still looking for Elwë, and others stayed on the shores, being called by Ossë
. They took Círdan
as their leader and became the Falathrim. All Teleri who stayed in Beleriand later became known as the Sindar
.
note: Ingwë, Finwë and Elwë are not the same elves as Imin, Tata and Enel
s in which he stored a part of the light of the Two Trees that were lighting Valinor. After three ages in the Halls of Mandos, Melkor was released. He spread his evil, and eventually killed Finwë and stole the Silmarils. Fëanor then named him Morgoth (S.
The Black Enemy). Fëanor and his seven sons
then swore to take the Silmarils back, and led a large army of the Noldor to Beleriand.
the Maia
. He became the overlord of Beleriand, naming himself Thingol (S
. Grey-cloak). After the First Battle of Beleriand
, during the first rising of the Moon, the Noldor arrived in Beleriand. They laid a siege
around Morgoth's fortress of Angband, but were eventually defeated.
Then Eärendil the Mariner, a half-elf
from the House of Finwë
, sailed to Valinor to ask the Valar for help. Then the Ban of the Noldor was lifted, and the Valar started the War of Wrath
, in which Morgoth was finally overcome.
they founded the Realms of Lindon
, Eregion
and Mirkwood
. Sauron
, Morgoth’s former servant, made war upon them, but with the aid of the Númenóreans they defeated him.
During the Second and Third Age
they held some protected realms with the aid of the Rings of Power
, but after the War of the Ring
they waned further, and most Elves left Middle-earth for Valinor. Tolkien's published writings give somewhat contradictory hints as to what happened to the Elves of Middle-earth after the One Ring
was destroyed at the end of the Third Age
.
After the destruction of the One Ring, the power of the Three Rings
of the Elves would also end and the Age of Men would begin. Elves that remained in Middle-earth were doomed to a slow decline until, in the words of Galadriel
, they faded and became a "rustic folk of dell and cave," and were greatly diminished from their ancient power and nobility. While the power of the remaining Noldor
would be immediately lessened, the "fading" of all Elvenkind was a phenomenon that would play out over hundreds and even thousands of years; until, in fact, our own times, when occasional glimpses of rustic Elves would fuel our folktales and fantasies.
There are many references in The Lord of the Rings to the continued existence of Elves in Middle-earth during the early years of the Fourth Age
. Elladan and Elrohir, the sons of Elrond, do not accompany their father when the White Ship bearing the Ring-bearer and the chief Noldorin leaders sails from the Grey Havens to Valinor
; they are said to have remained in Lindon for a time. Celeborn is said (in Appendix A) to have added most of southern Mirkwood to the realm of Lórien at the end of the Third Age, but elsewhere Tolkien wrote that Celeborn dwelt for a while in Lindon before at last leaving Middle-earth for Valinor.
Tolkien also wrote that Elves moved to Ithilien
during King Elessar
's reign, and assisted in the rebuilding of Gondor
. They primarily resided in southern Ithilien, along the shores of the Anduin. It is also implied that Elves continued to dwell at the Grey Havens, at least for a certain period. Tolkien states that Sam Gamgee sailed from the Havens decades after Elrond's departure, implying that some Elves might have remained in Mithlond at that time. Legolas
also sailed to Valinor after Elessar's death, and the reference to this in The Lord of the Rings states that it was Legolas himself who built the ship.
In "The Tale of Aragorn and Arwen
" that is found in Appendix A, Tolkien depicts a Middle-earth where most Elves have already left. The majority of those who remained lived in Mirkwood, while a much smaller population was in Lindon. Aragorn speaks of the empty garden of Elrond in Rivendell. Most strikingly, after Elessar's voluntary death, Arwen
flees to a Lórien that is depicted as wholly abandoned, and gives up her own spirit in its sad and silent confines.
and in Tolkien's Letters
, Elves had a different life cycle from Men. Most of the following information strictly refers only to the Eldar, as found in his essay Laws and Customs among the Eldar, found in Morgoth's Ring
.
itself. Their minds develop more quickly than their bodies; by their first year, they can speak, walk and even dance, and their quicker onset of mental maturity makes young Elves seem, to Men, older than they really are. Physical puberty
comes in around their fiftieth to one hundredth year (by age fifty they reach their adult height), and by their first hundred years of life outside the womb all Elves are fully grown. Elven bodies eventually stop aging physically, while human bodies do not.
is practiced and adultery
is unthinkable; they marry only once (Finwë, first High King of the Noldor, was an exception, as he remarried after his first wife died).
Spouses can choose each other even long before they are married, thus becoming betrothed. The betrothal is subject to parental approval unless the parties are of age and intend to marry soon, at which point the betrothal is announced. They exchange rings and the betrothal lasts at least a year, and is revocable by the return of the rings; however, it is rarely broken. After their formal betrothal, the couple appoint a date, at least a year later, for the wedding.
Only the words exchanged by the bride and groom (including the speaking of the name of Eru Ilúvatar
) and the consummation are required for marriage. More formally, the couple's families celebrate the marriage with a feast. The parties give back their betrothal rings and receive others worn on their index fingers. The bride’s mother gives the groom a jewel to wear (Galadriel's gift of the Elfstone to Aragorn reflects this tradition; she is grandmother to his betrothed, Arwen, Arwen's mother Celebrían
having left Middle-earth for Valinor after grievous psychological injury after her capture by Orcs and liberation by her sons).
The Elves view the sexual act as extremely special and intimate, for it leads to the conception and birth of children. Extra-marital and premarital sex
are unthinkable, adultery is also unheard of and fidelity between spouses is absolute. Yet separation during pregnancy or during the early years of parenthood (caused by war, for example) is so grievous to the couple that they prefer to have children in peaceful times. Living Elves cannot be raped or forced to have sex; before that they will lose the will to endure and go to Mandos.
Elves have few children, as a rule (Fëanor and Nerdanel were an exception, conceiving seven sons), and there are relatively sizeable intervals between each child (but see below for notes on Elvish birth rates in Middle-earth versus in Aman
). They are soon preoccupied with other pleasures; their libido
wanes and they focus their interests elsewhere, like the arts. Nonetheless, they take great delight in the union of love, and they cherish the days of bearing and raising children as the happiest days of their lives.
There seems to only be one known example of extreme marital strife in Tolkien's mythology, that of Eöl
and Aredhel
, in which the latter actually left the former without his knowledge, resulting in Eöl ultimately killing her. However, this marriage was far from typical of the Elves.
.
the Shipwright dwells with his folk.
s) have no beards, Círdan in fact has a beard, which appears to be an anomaly and a simple oversight. However, Tolkien later devised at least three "cycles of life" for Elves around 1960; Círdan
had a beard because he was in his third cycle of life. (Mahtan, Nerdanel's father, had a beard in his second cycle of life, a rare phenomenon.) It is unclear what these cycles exactly are, since Tolkien left no notes further explaining this. Apparently, beards were the only sign of further natural physical ageing beyond maturity.
Nevertheless, Tolkien may have ultimately changed his mind about whether Elves had facial hair. As Christopher Tolkien states in Unfinished Tales
, his father wrote in December 1972 or later that the Elvish strain in Men, such as Aragorn
, was "observable in the beardlessness of those who were so descended", since "it was a characteristic of all Elves to be beardless". This would seemingly contradict the information above.
Elves sometimes appear to age under great stress. Círdan appeared to be aged himself, since he is described as looking old, save for the stars in his eyes; this may be due to all the sorrows he had seen and lived through since the First Age. Also, the people of Gwindor of Nargothrond
had trouble recognizing him after his time as a prisoner of Morgoth.
Spirits of dead Elves go to the Halls of Mandos in Valinor. After a certain period of time and rest that serves as "cleansing", their spirits are clothed in bodies identical to their old ones. However, they almost never go back to Middle-earth and remain in Valinor instead. An exception was Glorfindel
in The Lord of the Rings; as shown in later books, Tolkien decided he was a "reborn" hero from The Silmarillion rather than an individual with the same name. A rare and more unusual example of an Elf coming back from the Halls of Mandos is found in the tale of Beren and Lúthien, as Lúthien
was the other Elf to be sent back to Middle-earth – as a mortal, however. Tolkien's Elvish words for "spirit" and "body" were fëa
(plural fëar) and hröa
(plural hröar) respectively.
Eventually, their immortal spirits will overwhelm and consume their bodies, rendering them "bodiless", whether they opt to go to Valinor or remain in Middle-earth. At the end of the world, all Elves will have become invisible to mortal eyes, except to those to whom they wish to manifest themselves. Tolkien called the Elves of Middle-earth who had undergone this process "Lingerers".
The lives of Elves only endure as the world endures. It is said in the Second Prophecy of Mandos that at the end of time the Elves will join the other Children of Ilúvatar
in singing the Second Music of the Ainur. However it is disputable whether the Prophecy is canon, and the published Silmarillion states that only Men shall participate in the Second Music, and that the ultimate fate of the Elves is unknown. However, they do not believe that Eru will abandon them to oblivion.
and Frodo
's memoirs, collectively known as the "Red Book of Westmarch
". He says that those names and terms in the work (as well in the earlier The Hobbit) that appear in English
are meant to be his purported translations from the Common Speech.
Tolkien repeatedly expressed his misgivings concerning the name "elf
" and its "associations of a kind that I should particularly desire not to be present [...] e.g. those of Drayton
or of A Midsummer Night's Dream
", for the purpose of translations
stating his preference that "the oldest available form of the name to be used, and leave it to acquire its own associations for readers of my tale". He wanted to avoid the Victorian
notions of "fairies" or mischievous imps associated with the word and was aiming at the more elevated notions of beings "supposed to possess formidable magical powers in early Teutonic mythology" (OED viz. the Old English ælf, from Proto-Germanic *albo-z).
The Elves are also called the "Firstborn" (Q
. Minnónar) or the "Elder Kindred" (as opposed to Men
, the Secondborn) as they were "awakened" before Men by Eru Ilúvatar
(the creator
). The Elves named themselves Quendi ("the Speakers"), in honour of the fact that, when they were created, they were the only living beings able to speak. The Dúnedain
called them Nimîr ("the Beautiful"), while their usual name in Sindarin
was Eledhrim.
In other writings, part of The History of Middle-earth, Tolkien details Elvish naming conventions. The Quenya word for "name" was essë. An Elf of Valinor was typically given one name (ataressë) at birth by the father. It usually reflected either the name of the father or mother, indicating the person's descent, to which later some distinguishing prefix could be added. As the Elf grew older, they received a second name (amilessë), given by the mother. This name was extremely important and reflected personality, skills, or fate, sometimes being "prophetic".
The epessë or the "after-name" is the third type. It was given later in life, not necessarily by kin, as a title of admiration and honour. In some circumstances, yet another name was chosen by the Elf themselves, called kilmessë meaning "self-name".
The "true names" remained the first two, though an Elf could be referred to by any of these. Mother-names were usually not used by those who did not know the Elf well. In later history and song any of the four could become the one generally used and recognized.
After their Exile to Middle-earth and adoption of Sindarin
as the daily speech, most of the Noldor also chose for themselves a name that fitted the style of that language, translating or altering one of their Quenya
names.
A patronymic
surname is also used – the father's name with the suffix "-ion" (meaning "son") added. Thus, Gildor Inglorion
is "Gildor, son of Inglor".
Several examples include:
, and he said his stories grew out of his languages. Indeed, the languages were the first thing Tolkien ever created for his mythos, starting with what he originally called "Elfin" or "Qenya". This was later spelled Quenya
(High-elven) and, along with Sindarin
(Grey-elven), is one of the two most complete of Tolkien's constructed languages. In addition to these two Tolkien also created many other (related) Elvish languages.
Elves are also credited with creating the Tengwar
(by Fëanor
) and Cirth
(Daeron) runic scripts.
 The 1979 Rankin Bass animated version of The Hobbit, with character designs by Lester Abrams, features Wood Elves as green-skinned warriors with slightly Austrian
The 1979 Rankin Bass animated version of The Hobbit, with character designs by Lester Abrams, features Wood Elves as green-skinned warriors with slightly Austrian
-German
accents. High Elves are shown with pointed ears and beards.
In Middle-earth Role Playing
(Iron Crown Enterprises
, 1986), three tribes of elves are presented as player character
race options, the Silvan, Sindar and Noldor – each receiving statistic bonuses (ranging from 5 to 15) to all attributes apart from Strength, with the Noldo receiving the highest accumulative bonuses of any racial type in the game. All three tribes are statistically immune to disease (+100% chance of resistance), and must be given "Presence" as the highest randomly generated statistic. Elven characters also receive significant skill bonuses with missile weapons (such as a bow and arrow) and stealth skills (such as hiding).
All three elven tribes (Silvan, Noldor, Sindar) depicted in Lord of the Rings Roleplaying Game
(Decipher, Inc.
, 2001) have varying (one or two points) statistic bonuses to Bearing, Perception and Nimbleness, with the Noldor also receiving a bonus to Wits and the Sindar to Vitality, giving both of these the highest accumulative bonuses available to Player Characters. The system of skills, feats and flaws further outlines racial and cultural characteristics, bonuses being given to the Noldor in Lore and "Resisting the Shadow", to the Silvan elves for various wood-craft skills, and the Sindar to musical performance. All elves have the ability to enchant objects, and receive bonuses in any test regarding magic.
In The Lord of the Rings Strategy Battle Game
(Games Workshop
, 2001), Elves have similar statistics to similarly armed Men, except for much higher scores for their Fighting and Courage attributes. On average, Elven wargear (armour and weapons) give twice the advantage of weapons made by Men.
J. R. R. Tolkien
John Ronald Reuel Tolkien, CBE was an English writer, poet, philologist, and university professor, best known as the author of the classic high fantasy works The Hobbit, The Lord of the Rings, and The Silmarillion.Tolkien was Rawlinson and Bosworth Professor of Anglo-Saxon at Pembroke College,...
's legendarium
Legendarium
Legendary may refer to:*A hagiography, or study of the lives of saints and other religious figures**The South English Legendary, a Middle English legendary*A legend-Entertainment:*Legendary, an album by Kaysha*Legendary...
, Elves are one of the races that inhabit a fictional Earth, often called Middle-earth
Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of the majority of author J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy writings. The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings take place entirely in Middle-earth, as does much of The Silmarillion and Unfinished Tales....
, and set in the remote past. They appear in The Hobbit
The Hobbit
The Hobbit, or There and Back Again, better known by its abbreviated title The Hobbit, is a fantasy novel and children's book by J. R. R. Tolkien. It was published on 21 September 1937 to wide critical acclaim, being nominated for the Carnegie Medal and awarded a prize from the New York Herald...
and in The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings is a high fantasy epic written by English philologist and University of Oxford professor J. R. R. Tolkien. The story began as a sequel to Tolkien's earlier, less complex children's fantasy novel The Hobbit , but eventually developed into a much larger work. It was written in...
, but their complex history is described more fully in The Silmarillion
The Silmarillion
The Silmarillion is a collection of J. R. R. Tolkien's mythopoeic works, edited and published posthumously by his son Christopher Tolkien in 1977, with assistance from Guy Gavriel Kay, who later became a noted fantasy writer. The Silmarillion, along with J. R. R...
. Tolkien had been writing about Elves long before he published The Hobbit.
Background
The modern English word elfElf
An elf is a being of Germanic mythology. The elves were originally thought of as a race of divine beings endowed with magical powers, which they use both for the benefit and the injury of mankind...
derives from the Old English word ælf (which has cognates in all other Germanic languages
Germanic languages
The Germanic languages constitute a sub-branch of the Indo-European language family. The common ancestor of all of the languages in this branch is called Proto-Germanic , which was spoken in approximately the mid-1st millennium BC in Iron Age northern Europe...
). Numerous types of elves appear in Germanic mythology
Germanic mythology
Germanic mythology is a comprehensive term for myths associated with historical Germanic paganism, including Norse mythology, Anglo-Saxon mythology, Continental Germanic mythology, and other versions of the mythologies of the Germanic peoples...
, the West Germanic concept appears to have come to differ from the Scandinavian notion in the early Middle Ages, and Anglo-Saxon concept diverged even further, possibly under Celtic
Celtic mythology
Celtic mythology is the mythology of Celtic polytheism, apparently the religion of the Iron Age Celts. Like other Iron Age Europeans, the early Celts maintained a polytheistic mythology and religious structure...
influence. Tolkien would make it clear in a letter that his Elves differ from those "of the better known lore", referring to Scandinavian mythology.
By 1915 when Tolkien was writing his first elven poems, the words elf, fairy and gnome had many divergent and contradictory associations. Tolkien had been gently warned against using the term 'fairy', which John Garth supposes may have been due to the word becoming increasingly used to indicate homosexuality
Homosexuality
Homosexuality is romantic or sexual attraction or behavior between members of the same sex or gender. As a sexual orientation, homosexuality refers to "an enduring pattern of or disposition to experience sexual, affectional, or romantic attractions" primarily or exclusively to people of the same...
.
The fairy had been taken up by as a utopian theme by late 19th century writers and used to critique social and religious values, a tradition which Tolkien along with TH White are seen to continue. One of the last of the Victorian Fairy-paintings, The Pipe of Dreams by Estella Canziani
Estella Canziani
Estella Canziani was a British portrait and landscape painter, an interior decorator and a travel writer and folklorist.- Life and works :...
, sold 250,000 copies and was well known within the trenches of World War 1, where Tolkien saw active service. Illustrated posters of Robert Louis Stevenson
Robert Louis Stevenson
Robert Louis Balfour Stevenson was a Scottish novelist, poet, essayist and travel writer. His best-known books include Treasure Island, Kidnapped, and Strange Case of Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde....
's poem Land of Nod had been sent out by a philanthropist to brighten servicemen's quarters and Faery was used in other contexts as an image of "Old England
Merry England
"Merry England", or in more jocular, archaic spelling "Merrie England", refers to an English autostereotype, a utopian conception of English society and culture based on an idyllic pastoral way of life that was allegedly prevalent at some time between the Middle Ages and the onset of the Industrial...
" to inspire patriotism.
According to Marjorie Burns, Tolkien eventually chose the term elf over fairy, but still retained some doubts. In his 1939 essay On Fairy-Stories
On Fairy-Stories
"On Fairy-Stories" is an essay by J. R. R. Tolkien which discusses the fairy-story as a literary form. It was initially written for presentation by Tolkien as the Andrew Lang lecture at the University of St Andrews, Scotland, in 1939. It first appeared in print, with some enhancement, in 1947, in...
, Tolkien wrote that
Early writings
Traditional Victorian dancing fairies and elvesFairy painting
Fairy painting is a genre of painting and illustration featuring fairies and fairy tale settings, often with extreme attention to detail. The genre is most closely associated with the Victorian era in Great Britain, but has experienced a contemporary revival...
appear in much of Tolkien's early poetry, and have influence upon his later works in part due to the influence of a production of J.M. Barrie's Peter Pan
Peter Pan
Peter Pan is a character created by Scottish novelist and playwright J. M. Barrie . A mischievous boy who can fly and magically refuses to grow up, Peter Pan spends his never-ending childhood adventuring on the small island of Neverland as the leader of his gang the Lost Boys, interacting with...
in Birmingham
Birmingham
Birmingham is a city and metropolitan borough in the West Midlands of England. It is the most populous British city outside the capital London, with a population of 1,036,900 , and lies at the heart of the West Midlands conurbation, the second most populous urban area in the United Kingdom with a...
in 1910 and his familiarity with the work of Catholic
Catholic
The word catholic comes from the Greek phrase , meaning "on the whole," "according to the whole" or "in general", and is a combination of the Greek words meaning "about" and meaning "whole"...
mystic poet, Francis Thompson
Francis Thompson
Francis Thompson was an English poet and ascetic. After attending college, he moved to London to become a writer, but in menial work, became addicted to opium, and was a street vagrant for years. A married couple read his poetry and rescued him, publishing his first book, Poems in 1893...
which Tolkien had acquired in 1914.
As a philologist
Philology
Philology is the study of language in written historical sources; it is a combination of literary studies, history and linguistics.Classical philology is the philology of Greek and Classical Latin...
, Tolkien's interest in languages led him to invent several languages of his own as a pastime. In considering the nature of who might speak these languages, and what stories they might tell, Tolkien again turned to the concept of elves.
The Book of Lost Tales (c. 1917–1927)
In his The Book of Lost TalesThe Book of Lost Tales
The Book of Lost Tales is the title of a collection of early stories by J. R. R. Tolkien, and of the first two volumes of Christopher Tolkien's 12-volume series The History of Middle-earth, in which he presents and analyses the manuscripts of those stories, which were the earliest form of the...
, Tolkien develops a theme that the diminutive fairy-like race of Elves had once been a great and mighty people, and that as Men took over the world, these Elves had "diminished" themselves. This theme was influenced especially by the god-like and human-sized Ljósálfar
Dökkálfar and Ljósálfar
In Norse mythology, Dökkálfar and Ljósálfar are two contrasting types of elves; the prior dwell within the earth and are most swarthy, while the latter live in Álfheimr, located in heaven, and are "fairer than the sun to look at"...
of Norse mythology
Norse mythology
Norse mythology, a subset of Germanic mythology, is the overall term for the myths, legends and beliefs about supernatural beings of Norse pagans. It flourished prior to the Christianization of Scandinavia, during the Early Middle Ages, and passed into Nordic folklore, with some aspects surviving...
, and medieval works such as Sir Orfeo
Sir Orfeo
Sir Orfeo is an anonymous Middle English narrative poem, retelling the story of Orpheus as a king rescuing his wife from the fairy king.-History and Manuscripts:...
, the Welsh Mabinogion
Mabinogion
The Mabinogion is the title given to a collection of eleven prose stories collated from medieval Welsh manuscripts. The tales draw on pre-Christian Celtic mythology, international folktale motifs, and early medieval historical traditions...
, Arthurian romances and the legends of the Tuatha Dé Danann
Tuatha Dé Danann
The Tuatha Dé Danann are a race of people in Irish mythology. In the invasions tradition which begins with the Lebor Gabála Érenn, they are the fifth group to settle Ireland, conquering the island from the Fir Bolg....
.
Some of the stories Tolkien wrote as elven history have been seen to be directly influenced by Celtic Mythology. For example, the "Flight of The Noldoli
Noldor
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Noldor are Elves of the Second Clan who migrated to Valinor and lived in Eldamar. The Noldor are called Golodhrim or Gódhellim in Sindarin, and Goldoi by Teleri of Tol Eressëa. The singular form of the Quenya noun is Noldo and the adjective is Noldorin...
" is based on the Tuatha Dé Danann
Tuatha Dé Danann
The Tuatha Dé Danann are a race of people in Irish mythology. In the invasions tradition which begins with the Lebor Gabála Érenn, they are the fifth group to settle Ireland, conquering the island from the Fir Bolg....
and Lebor Gabála Érenn
Lebor Gabála Érenn
Lebor Gabála Érenn is the Middle Irish title of a loose collection of poems and prose narratives recounting the mythical origins and history of the Irish from the creation of the world down to the Middle Ages...
, and their migratory nature comes from early Irish/Celtic history. John Garth also sees that with the underground enslavement of the Noldoli to Melkor, Tolkien was essentially rewriting Irish myth regarding the Tuatha Dé Danann into a Christian eschatology.
The name Inwe
Ingwe
Ingwe may be:* Ingwë - a character in the fictional universe of J.R.R. Tolkien* Ingwe - a South African anti-tank guided missile* Ingwe Coal - a division of the BHP Billiton mining company* Ingwe - the Zulu word for leopard...
(in the first draft Ing
Yngvi
Yngvi, Yngvin, Ingwine, Inguin are names that relate to an older theonym Ing and which appears to have been the older name for the god Freyr ....
), given by Tolkien to the eldest of the elves and his clan is similar to the name found in Norse mythology as that of the god Ingwi-Freyr
Freyr
Freyr is one of the most important gods of Norse paganism. Freyr was highly associated with farming, weather and, as a phallic fertility god, Freyr "bestows peace and pleasure on mortals"...
(and Ingui-Frea in Anglo-Saxon paganism), a god who is gifted the elf world Álfheimr. Terry Gunnell also claims that the relationship between beautiful ships and the Elves is reminiscent of the god Njörðr and the god Freyr's ship Skíðblaðnir
Skíðblaðnir
In Norse mythology, Skíðblaðnir is the best of ships. Skíðblaðnir is attested in the Poetic Edda, compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and in the Prose Edda and Heimskringla, both written in the 13th century by Snorri Sturluson...
. He also retains the usage of the French
France
The French Republic , The French Republic , The French Republic , (commonly known as France , is a unitary semi-presidential republic in Western Europe with several overseas territories and islands located on other continents and in the Indian, Pacific, and Atlantic oceans. Metropolitan France...
derived term "fairy" for the same creatures.
The larger Elves are also inspired by Tolkien's personal Catholic
Catholic
The word catholic comes from the Greek phrase , meaning "on the whole," "according to the whole" or "in general", and is a combination of the Greek words meaning "about" and meaning "whole"...
theology – as representing the state of Men in Eden who have not yet "fallen", similar to humans but fairer and wiser, with greater spiritual powers, keener senses, and a closer empathy with nature. Tolkien wrote of them:
In The Book of Lost Tales Tolkien includes both the more serious "medieval" type of elves such as Fëanor
Fëanor
Fëanor is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium who plays an important part in The Silmarillion. He was the eldest son of Finwë, the High King of the Noldor, and his first wife Míriel Serindë...
and Turgon
Turgon
In the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, Turgon "the Wise" is an Elven king of the Noldor, second son of Fingolfin, brother to Fingon, Aredhel and Argon, and ruler of the hidden city of Gondolin....
alongside the frivolous, Jacobean
Jacobean era
The Jacobean era refers to the period in English and Scottish history that coincides with the reign of King James VI of Scotland, who also inherited the crown of England in 1603 as James I...
type of elves such as the Solosimpi and Tinúviel
Lúthien
Lúthien Tinúviel is a fictional character in the fantasy-world Middle-earth of the English author J. R. R. Tolkien. She appears in The Silmarillion, the epic poem The Lay of Leithian, The Lord of the Rings and the Grey Annals, as well as in other material.-Character overview:Lúthien is a Telerin ...
.
Alongside the idea of the greater Elves, Tolkien also developed the idea of children visiting Valinor, the island-homeland of the Elves in their sleep. Elves would also visit children at night and comfort them if they had been chided or were upset. This theme, linking elves with children's dreams and nocturnal travelling was largely abandoned in Tolkien's later writing.
The Hobbit (c. 1930–1937)
Along with Book of Lost Tales, Douglas Anderson shows that in The HobbitThe Hobbit
The Hobbit, or There and Back Again, better known by its abbreviated title The Hobbit, is a fantasy novel and children's book by J. R. R. Tolkien. It was published on 21 September 1937 to wide critical acclaim, being nominated for the Carnegie Medal and awarded a prize from the New York Herald...
, Tolkien again includes both the more serious 'medieval' type of elves, such as Elrond
Elrond
Elrond Half-elven is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is introduced in The Hobbit, and plays a supporting role in The Lord of the Rings and The Silmarillion.-Character overview:...
and the Wood-elf king, and frivolous elves, such as those at Rivendell
Rivendell
Rivendell is an Elven outpost in Middle-earth, a fictional realm created by J. R. R. Tolkien. It was established and ruled by Elrond in the Second Age of Middle-earth...
.
The Quenta Silmarillion (c. 1937)
In 1937, having had his manuscript for The Silmarillion rejected by a publisher who disparaged all the "eye-splitting Celtic names" that Tolkien had given his Elves, Tolkien denied the names had a Celtic origin:Dimitra Fimi proposes that these comments are a product of his Anglophilia rather than a commentary on the texts themselves or their actual influence on his writing, and cites evidence to this effect in her essay "Mad" Elves and "elusive beauty": some Celtic strands of Tolkien's mythology.
The Lord of the Rings (c. 1937–1949)
Terry Gunner notes that the titles of the Germanic gods Freyr and Freyja (Old NorseOld Norse
Old Norse is a North Germanic language that was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and inhabitants of their overseas settlements during the Viking Age, until about 1300....
'lord' and 'lady') are also given to Celeborn and Galadriel in the Lord of The Rings.
According to Tom Shippey the theme, of diminishment from semi-divine Elf to dimunitive Fairy resurfaces in The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings is a high fantasy epic written by English philologist and University of Oxford professor J. R. R. Tolkien. The story began as a sequel to Tolkien's earlier, less complex children's fantasy novel The Hobbit , but eventually developed into a much larger work. It was written in...
in the dialogue of Galadriel
Galadriel
Galadriel is a character created by J.R.R. Tolkien, appearing in his Middle-earth legendarium. She appears in The Lord of the Rings, The Silmarillion, and Unfinished Tales....
.
Writing in 1954, part way through proofing The Lord of the Rings Tolkien claimed the Elvish language Sindarin
Sindarin
Sindarin is a fictional language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his secondary world, often called Middle-earth.Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the immortal Elves, called the Eledhrim or Edhellim in Sindarin....
has a character very like British-Welsh
Welsh language
Welsh is a member of the Brythonic branch of the Celtic languages spoken natively in Wales, by some along the Welsh border in England, and in Y Wladfa...
"because it seems to fit the rather 'Celtic' type of legends and stories told of its speakers". In the same letter, Tolkien goes on to say that the elves had very little in common with elves or fairies of Europe, and that they really represent men with greater artistic ability, beauty and a longer life span. Tolkien also notes an Elven bloodline was the only real claim to 'nobility' that the Men of Middle-earth can have. Tolkien also wrote that the elves are primarily to blame for many of the ills of Middle-earth in The Lord of the Rings, having independently created the Three Rings in order to stop their domains in mortal-lands from 'fading' and attempting to prevent inevitable change and new growth.
Origins
Originally, in the 1910s and 1920s, Ingwë, Finwë and Elwë (their final names) were the eldest of the Elves. By 1959 or 1960, Tolkien wrote a detailed account of the awakening of the Elves, called Cuivienyarna, part of Quendi and EldarThe War of the Jewels
The War of the Jewels is the 11th volume of Christopher Tolkien's series The History of Middle-earth, analysing the unpublished manuscripts of his father J. R. R...
. Ingwë, Finwë and Elwë now became the first ambassadors and the Kings of the Elves. This text only saw print in The War of the Jewels
The War of the Jewels
The War of the Jewels is the 11th volume of Christopher Tolkien's series The History of Middle-earth, analysing the unpublished manuscripts of his father J. R. R...
, part of the analytical The History of Middle-earth
The History of Middle-earth
The History of Middle-earth is a 12-volume series of books published from 1983 through to 1996 that collect and analyse material relating to the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, compiled and edited by his son, Christopher Tolkien. Some of the content consists of earlier versions of already published...
series, in 1994, but a similar version was included in The Silmarillion in 1977.
According to the earliest account, the first Elves are awakened by Eru Ilúvatar
Eru Ilúvatar
Eru Ilúvatar is a fictional deity in J.R.R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is introduced in The Silmarillion as the creator of all existence . In Tolkien's invented language of Elvish, Eru means "The One", or "He that is Alone" and Ilúvatar signifies "Father of All"...
near the bay of Cuiviénen during the Years of the Trees in the First Age
First Age
In the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, the First Age, or First Age of the Children of Ilúvatar is the heroic period in which most of Tolkien's early legends are set...
. They awake under the starlit sky, as the Sun and Moon have yet to be created. The first Elves to awake are three pairs: Imin ("First") and his wife Iminyë, Tata ("Second") and Tatië, and Enel ("Third") and Enelyë.
Imin, Tata, and Enel and their wives join up and walk through the forests. They come across six, nine, and twelve pairs of Elves, and each "patriarch" claims the pairs as his folk in order. The now sixty Elves dwell by the rivers, and they invent poetry and music in Middle-earth
Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of the majority of author J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy writings. The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings take place entirely in Middle-earth, as does much of The Silmarillion and Unfinished Tales....
(the continent). Journeying further, they come across eighteen pairs of Elves watching the stars, whom Tata claims as his. These are tall and dark-haired, the fathers of most of the Noldor
Noldor
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Noldor are Elves of the Second Clan who migrated to Valinor and lived in Eldamar. The Noldor are called Golodhrim or Gódhellim in Sindarin, and Goldoi by Teleri of Tol Eressëa. The singular form of the Quenya noun is Noldo and the adjective is Noldorin...
. The ninety-six Elves now invented many new words. Continuing their journey, they find twenty-four pairs of Elves, singing without language, and Enel adds them to his people. These are the ancestors of most of the Lindar or "singers", later called Teleri
Teleri
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Teleri, Those who come last in Quenya were the third of the Elf clans who came to Aman...
. They find no more Elves; Imin's people, the smallest group, are the ancestors of the Vanyar
Vanyar
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Vanyar are the fairest and most noble of the High Elves. They are the smallest of the three clans of the Eldar, and were the first to arrive in Aman. According to legend, the clan was founded by Imin, the first Elf to awake at Cuiviénen, his wife Iminyë, and...
. All in all the Elves number 144. Because all Elves had been found in groups of twelve, twelve becomes their base number and 144 their highest number (for a long time), and none of the later Elvish languages have a common name for a greater number.
They were discovered by the Vala
Vala (Middle-earth)
The Valar are fictional characters in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. They are first mentioned in The Lord of the Rings, but The Silmarillion develops them into the Powers of Arda or the Powers of the World...
Oromë, who brought the tidings of their awakening to Valinor
Valinor
Valinor is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the realm of the Valar in Aman. It was also known as the Undying Lands, along with Tol Eressëa and the outliers of Aman. This is something of a misnomer; only immortal beings were allowed to reside there, but the land itself,...
.
The Silmarillion states that Melkor
Morgoth
Morgoth Bauglir is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien’s Middle-earth legendarium. He is the main antagonist of The Silmarillion, figures in The Children of Húrin, and is mentioned briefly in The Lord of the Rings.Melkor was the most powerful of the Ainur, but turned to darkness and became...
, the Dark Lord, had already captured some wandering Elves, and twisted and mutilated them until they became the Orcs
Orc (Middle-earth)
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy writings, Orcs or Orks are a race of creatures who are used as soldiers and henchmen by both the greater and lesser villains of The Silmarillion and The Lord of the Rings — Morgoth, Sauron and Saruman...
. However, Tolkien ultimately became uncomfortable with this Elvish origin, and devised different theories about the origin of Orcs.
Sundering

Ingwe
Ingwe may be:* Ingwë - a character in the fictional universe of J.R.R. Tolkien* Ingwe - a South African anti-tank guided missile* Ingwe Coal - a division of the BHP Billiton mining company* Ingwe - the Zulu word for leopard...
, Finwë
Finwë
Finwë, sometimes surnamed Noldóran, is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. He was the first High King of the Elven Noldor to lead his people on the journey from Middle-earth to Valinor in the blessed realm of Aman. He was a great friend of Elu Thingol, the King of Doriath...
and Elwë as ambassadors to Valinor.
Returning to Middle-earth, Ingwë, Finwë and Elwë convinced a great host to take the journey to Valinor. Not all Elves accepted the summons though, and those who did not became known as the Avari
Avari (Middle-earth)
In the fictional works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Avari are an ethnic group of the Elves.- History of the Avari:Avari is a Quenya word meaning 'Refusers' or 'Recusants'. When the vala Oromë found the Elves who had awakened in Cuiviénen , he asked them to come with him to Valinor...
, The Unwilling.
The others were called Eldar, the People of the Stars by Oromë, and they took Ingwë, Finwë and Elwë as their leaders, and became respectively the Vanyar
Vanyar
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Vanyar are the fairest and most noble of the High Elves. They are the smallest of the three clans of the Eldar, and were the first to arrive in Aman. According to legend, the clan was founded by Imin, the first Elf to awake at Cuiviénen, his wife Iminyë, and...
, Noldor
Noldor
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Noldor are Elves of the Second Clan who migrated to Valinor and lived in Eldamar. The Noldor are called Golodhrim or Gódhellim in Sindarin, and Goldoi by Teleri of Tol Eressëa. The singular form of the Quenya noun is Noldo and the adjective is Noldorin...
and Teleri
Teleri
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Teleri, Those who come last in Quenya were the third of the Elf clans who came to Aman...
. On their journey, some of the Teleri feared the Misty Mountains
Misty Mountains
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy world of Middle-earth, the Misty Mountains is a mountain range, running for 795 miles from north to south, between Eriador and the valley of the Great River, Anduin, and...
and dared not cross them. They turned back and stayed in the vales of the Anduin
Anduin
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional Middle-earth, Anduin is the Sindarin name for the Great River of Wilderland, the longest river in the Third Age . The ancestors of the Rohirrim called it Langflood. It flowed from its source in the Grey and Misty Mountains to the Mouths of Anduin in the Great Sea...
, and became the Nandor; these were led by Lenwë.
Oromë led the others over the Misty Mountains and Ered Lindon into Beleriand
Beleriand
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional legendarium, Beleriand was a region in northwestern Middle-earth during the First Age. Events in Beleriand are described chiefly in his work The Silmarillion, which tells the story of the early ages of Middle-earth in a style similar to the epic hero tales of Nordic...
. There Elwë became lost, and the Teleri stayed behind looking for him. The Vanyar and the Noldor moved onto a floating island that was moved by Ulmo
Ulmo
Ulmo is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He first appears in The Silmarillion as a god or Vala of the Elven pantheon. Ulmo is a title, which means He who pours. He is also known as King of the Sea and Lord of Waters...
to Valinor.
After years, Ulmo returned to Beleriand to seek out the remaining Teleri. As Elwë had not yet been found, a great part of the Teleri took his brother Olwë as their leader and were ferried to Valinor. Some Teleri stayed behind though, still looking for Elwë, and others stayed on the shores, being called by Ossë
Ossë
Ossë is a fictional character in the works of J. R. R. Tolkien. She is introduced in The Silmarillion as an angelic being known as a Maia, associated with Ulmo, one of the Valar ....
. They took Círdan
Círdan
Círdan the Shipwright is a fictional character created by J. R. R. Tolkien. He was a Telerin Elf, a great mariner and shipwright, and lord of the Falas during much of the First Age. He was the bearer of the Great Ring Narya, which he in turn gave to Gandalf.He had a beard, which was rare for...
as their leader and became the Falathrim. All Teleri who stayed in Beleriand later became known as the Sindar
Sindar
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the fictional Sindar are Elves of Telerin descent. They are also known as the Grey Elves. Their language is Sindarin...
.
note: Ingwë, Finwë and Elwë are not the same elves as Imin, Tata and Enel
Exile
In Valinor, Fëanor, son of Finwë, and the greatest of the Noldor, created the SilmarilSilmaril
The Silmarils are three brilliant jewels which contained the unmarred light of the Two Trees in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. The Silmarils were made out of the crystalline substance silima by Fëanor, a Noldorin Elf, in Valinor during the Years of the Trees...
s in which he stored a part of the light of the Two Trees that were lighting Valinor. After three ages in the Halls of Mandos, Melkor was released. He spread his evil, and eventually killed Finwë and stole the Silmarils. Fëanor then named him Morgoth (S.
Sindarin
Sindarin is a fictional language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his secondary world, often called Middle-earth.Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the immortal Elves, called the Eledhrim or Edhellim in Sindarin....
The Black Enemy). Fëanor and his seven sons
Sons of Fëanor
In J. R. R. Tolkien's world of Middle-earth, the seven sons of Fëanor, the eldest prince of the Noldor, led their people from Valinor to rule over kingdoms in the Northeast of Beleriand:...
then swore to take the Silmarils back, and led a large army of the Noldor to Beleriand.
Wars of Beleriand
In Beleriand, Elwë was eventually found, and married MelianMelian
Melian the Maia is a fictional character in the fantasy-world Middle-earth of the English author J. R. R. Tolkien. She appears in The Silmarillion, the epic poem The Lay of Leithian, The Children of Húrin, the Annals of Aman and the Grey Annals....
the Maia
Maia (Middle-earth)
The Maiar are beings from J. R. R. Tolkien's high fantasy legendarium. They are lesser Ainur who entered Eä in the beginning of time. Tolkien uses the term Valar to refer both to all the Ainur who entered Eä, and specifically to the greatest among them, the fourteen Lords and Queens of the Valar...
. He became the overlord of Beleriand, naming himself Thingol (S
Sindarin
Sindarin is a fictional language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his secondary world, often called Middle-earth.Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the immortal Elves, called the Eledhrim or Edhellim in Sindarin....
. Grey-cloak). After the First Battle of Beleriand
First Battle of Beleriand
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional Middle-earth, the First Battle of Beleriand is the first battle of the Wars of Beleriand, fought by the Sindarin Elves, led by Elu Thingol, King of Doriath and Lord of Beleriand, against the armies of Morgoth, the Great Enemy, the Dark Lord.-History:Morgoth,...
, during the first rising of the Moon, the Noldor arrived in Beleriand. They laid a siege
Siege of Angband
The Siege of Angband or "The Long Peace" in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fictional universe was the siege of the Noldor around the fortress of Morgoth in the early centuries of the Years of the Sun, which began following the Dagor Aglareb. For the most part, it was a time of plenitude, peace and...
around Morgoth's fortress of Angband, but were eventually defeated.
Then Eärendil the Mariner, a half-elf
Half-elven
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional universe of Middle-earth, the Half-elven are the children of the union of Elves and Men. The Half-elven are not a distinct race from Elves and Men, and must ultimately choose to which race they belong...
from the House of Finwë
House of Finwë
In J. R. R. Tolkien’s legendarium, the House of Finwë was the royal house of the Noldor. The house was founded by Finwë, the first High King of the Noldor, who led his people from Middle-earth to the realm of Valinor within the continent of Aman in . In Valinor, he ruled in the city of Tirion...
, sailed to Valinor to ask the Valar for help. Then the Ban of the Noldor was lifted, and the Valar started the War of Wrath
War of Wrath
The War of Wrath, or the Great Battle, is a key plot development in J.R.R. Tolkien's legendarium, portraying the final war against Morgoth at the end of the First Age....
, in which Morgoth was finally overcome.
Second and Third Age
After the War of Wrath, the Valar tried to summon the Elves back to Valinor. Many complied, but some stayed. During the Second AgeSecond Age
The Second Age is a time period from J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fantasy writings. Tolkien intended for the history of Middle-earth to be considered fictionally as a precursor to the history of the real Earth....
they founded the Realms of Lindon
Lindon (Middle-earth)
Lindon is the land beyond the Ered Luin, the Blue Mountains, in the northwest of Middle-earth in the fictional universe of J. R. R. Tolkien. It is the westernmost land of the continent. The Gulf of Lune divides it into Forlindon and Harlindon...
, Eregion
Eregion
In the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, Eregion or Hollin was a kingdom of the Noldorin Elves in Eriador during the Second Age, located near the West Gate of Moria under the shadow of the Hithaeglir . Its capital was Ost-in-Edhil...
and Mirkwood
Mirkwood
Mirkwood is a name used for two distinct fictional forests in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. In the First Age, the highlands of Dorthonion north of Beleriand were known as Mirkwood after falling under Morgoth's control. During the Third Age, the large forest in Rhovanion, east of the Anduin in ...
. Sauron
Sauron
Sauron is the primary antagonist and titular character of the epic fantasy novel The Lord of the Rings by J. R. R. Tolkien.In the same work, he is revealed to be the same character as "the Necromancer" from Tolkien's earlier novel The Hobbit...
, Morgoth’s former servant, made war upon them, but with the aid of the Númenóreans they defeated him.
During the Second and Third Age
Third Age
The Third Age is a time period from J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fantasy writings. The history of Middle-earth is to be taken fictionally as a history of the real Earth....
they held some protected realms with the aid of the Rings of Power
Rings of Power
The Rings of Power in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium are magical rings created by Sauron or by the Elves of Eregion under Sauron's tutelage...
, but after the War of the Ring
War of the Ring
In the fictional high fantasy-world of J. R. R. Tolkien, the War of the Ring was fought between Sauron and the free peoples of Middle-earth for control of the One Ring and dominion over the continent. The War of the Ring took place at the end of the Third Age. Together with the Quest of Mount Doom,...
they waned further, and most Elves left Middle-earth for Valinor. Tolkien's published writings give somewhat contradictory hints as to what happened to the Elves of Middle-earth after the One Ring
One Ring
The One Ring is a fictional artifact that appears as the central plot element in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fantasy novels. It is described in an earlier story, The Hobbit , as a magic ring of invisibility. The sequel The Lord of the Rings describes its powers as being more encompassing than...
was destroyed at the end of the Third Age
Third Age
The Third Age is a time period from J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fantasy writings. The history of Middle-earth is to be taken fictionally as a history of the real Earth....
.
After the destruction of the One Ring, the power of the Three Rings
Three Rings
In Tolkien's legendarium, the Three Rings are magical artifacts forged by the Elves of Eregion. After the One Ring, they are the most powerful of the twenty Rings of Power....
of the Elves would also end and the Age of Men would begin. Elves that remained in Middle-earth were doomed to a slow decline until, in the words of Galadriel
Galadriel
Galadriel is a character created by J.R.R. Tolkien, appearing in his Middle-earth legendarium. She appears in The Lord of the Rings, The Silmarillion, and Unfinished Tales....
, they faded and became a "rustic folk of dell and cave," and were greatly diminished from their ancient power and nobility. While the power of the remaining Noldor
Noldor
In the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Noldor are Elves of the Second Clan who migrated to Valinor and lived in Eldamar. The Noldor are called Golodhrim or Gódhellim in Sindarin, and Goldoi by Teleri of Tol Eressëa. The singular form of the Quenya noun is Noldo and the adjective is Noldorin...
would be immediately lessened, the "fading" of all Elvenkind was a phenomenon that would play out over hundreds and even thousands of years; until, in fact, our own times, when occasional glimpses of rustic Elves would fuel our folktales and fantasies.
There are many references in The Lord of the Rings to the continued existence of Elves in Middle-earth during the early years of the Fourth Age
Fourth Age
In the fictional world of middle earth "'the fourth age'" and the ages that preceded it, are time periods from J. R. R. Tolkien's universe of Middle-earth, described in his fantasy writings...
. Elladan and Elrohir, the sons of Elrond, do not accompany their father when the White Ship bearing the Ring-bearer and the chief Noldorin leaders sails from the Grey Havens to Valinor
Valinor
Valinor is a fictional location in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the realm of the Valar in Aman. It was also known as the Undying Lands, along with Tol Eressëa and the outliers of Aman. This is something of a misnomer; only immortal beings were allowed to reside there, but the land itself,...
; they are said to have remained in Lindon for a time. Celeborn is said (in Appendix A) to have added most of southern Mirkwood to the realm of Lórien at the end of the Third Age, but elsewhere Tolkien wrote that Celeborn dwelt for a while in Lindon before at last leaving Middle-earth for Valinor.
Tolkien also wrote that Elves moved to Ithilien
Ithilien
In J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional Middle-earth, Ithilien is a region and fiefdom of Gondor.Ithilien, or "Moon-land," is the easternmost province of Gondor, the only part of Gondor across the Great River Anduin lying between the river and the Mountains of Shadow , subdivided by the stream of...
during King Elessar
Aragorn
Aragorn II is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, one of the main protagonists of The Lord of the Rings. He is first introduced by the name Strider, which the hobbits continue to call him...
's reign, and assisted in the rebuilding of Gondor
Gondor
Gondor is a fictional kingdom in J. R. R. Tolkien's writings, described as the greatest realm of Men in the west of Middle-earth by the end of the Third Age. The third volume of The Lord of the Rings, The Return of the King, is concerned with the events in Gondor during the War of the Ring and with...
. They primarily resided in southern Ithilien, along the shores of the Anduin. It is also implied that Elves continued to dwell at the Grey Havens, at least for a certain period. Tolkien states that Sam Gamgee sailed from the Havens decades after Elrond's departure, implying that some Elves might have remained in Mithlond at that time. Legolas
Legolas
Legolas is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, featured in The Lord of the Rings. He is an Elf of the Woodland Realm and one of nine members of the Fellowship of the Ring.- Literature :...
also sailed to Valinor after Elessar's death, and the reference to this in The Lord of the Rings states that it was Legolas himself who built the ship.
In "The Tale of Aragorn and Arwen
The Tale of Aragorn and Arwen
The Tale of Aragorn and Arwen is a story written by the English author J. R. R. Tolkien. It can be found in Appendix A of Tolkien's most famous book, The Lord of the Rings. It takes place in the Third Age of the author's fictional universe, Middle-earth...
" that is found in Appendix A, Tolkien depicts a Middle-earth where most Elves have already left. The majority of those who remained lived in Mirkwood, while a much smaller population was in Lindon. Aragorn speaks of the empty garden of Elrond in Rivendell. Most strikingly, after Elessar's voluntary death, Arwen
Arwen
Arwen Undómiel is a fictional character in J.R.R. Tolkien's legendarium. She appears in his novel, The Lord of the Rings, usually published in three volumes. Arwen is one of the Half-elven who lived during the Third Age.-Literature:...
flees to a Lórien that is depicted as wholly abandoned, and gives up her own spirit in its sad and silent confines.
Life cycle
As told in The History of Middle-earthThe History of Middle-earth
The History of Middle-earth is a 12-volume series of books published from 1983 through to 1996 that collect and analyse material relating to the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, compiled and edited by his son, Christopher Tolkien. Some of the content consists of earlier versions of already published...
and in Tolkien's Letters
The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien
The Letters of J. R. R. Tolkien is a selection of J. R. R. Tolkien's letters published in 1981, edited by Tolkien's biographer Humphrey Carpenter assisted by Christopher Tolkien...
, Elves had a different life cycle from Men. Most of the following information strictly refers only to the Eldar, as found in his essay Laws and Customs among the Eldar, found in Morgoth's Ring
Morgoth's Ring
Morgoth's Ring is the tenth volume of Christopher Tolkien's 12-volume series The History of Middle-earth in which he analyses the unpublished manuscripts of his father J. R. R. Tolkien. This volume, along with the subsequent The War of the Jewels, provides detailed writings and editorial commentary...
.
Early life
Elves are born about one year from their conception. The day of their conception is celebrated, not the actual birthdayBirthday
A birthday is a day or anniversary where a person celebrates his or her date of birth. Birthdays are celebrated in numerous cultures, often with a gift, party or rite of passage. Although the major religions celebrate the birth of their founders , Christmas – which is celebrated widely by...
itself. Their minds develop more quickly than their bodies; by their first year, they can speak, walk and even dance, and their quicker onset of mental maturity makes young Elves seem, to Men, older than they really are. Physical puberty
Puberty
Puberty is the process of physical changes by which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of reproduction, as initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads; the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy...
comes in around their fiftieth to one hundredth year (by age fifty they reach their adult height), and by their first hundred years of life outside the womb all Elves are fully grown. Elven bodies eventually stop aging physically, while human bodies do not.
Sexuality, marriage, and parenthood
Elves marry freely and for love early in life. MonogamyMonogamy
Monogamy /Gr. μονός+γάμος - one+marriage/ a form of marriage in which an individual has only one spouse at any one time. In current usage monogamy often refers to having one sexual partner irrespective of marriage or reproduction...
is practiced and adultery
Adultery
Adultery is sexual infidelity to one's spouse, and is a form of extramarital sex. It originally referred only to sex between a woman who was married and a person other than her spouse. Even in cases of separation from one's spouse, an extramarital affair is still considered adultery.Adultery is...
is unthinkable; they marry only once (Finwë, first High King of the Noldor, was an exception, as he remarried after his first wife died).
Spouses can choose each other even long before they are married, thus becoming betrothed. The betrothal is subject to parental approval unless the parties are of age and intend to marry soon, at which point the betrothal is announced. They exchange rings and the betrothal lasts at least a year, and is revocable by the return of the rings; however, it is rarely broken. After their formal betrothal, the couple appoint a date, at least a year later, for the wedding.
Only the words exchanged by the bride and groom (including the speaking of the name of Eru Ilúvatar
Eru Ilúvatar
Eru Ilúvatar is a fictional deity in J.R.R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is introduced in The Silmarillion as the creator of all existence . In Tolkien's invented language of Elvish, Eru means "The One", or "He that is Alone" and Ilúvatar signifies "Father of All"...
) and the consummation are required for marriage. More formally, the couple's families celebrate the marriage with a feast. The parties give back their betrothal rings and receive others worn on their index fingers. The bride’s mother gives the groom a jewel to wear (Galadriel's gift of the Elfstone to Aragorn reflects this tradition; she is grandmother to his betrothed, Arwen, Arwen's mother Celebrían
Celebrían
Celebrían is a fictional character created by J. R. R. Tolkien. She is an Elven noblewoman, the daughter of Celeborn and Galadriel, wife of Elrond, and mother of Elrohir, Elladan and Arwen. She was called the Lady of Rivendell. Her name means "silver queen" in Sindarin.- Biography :The place and...
having left Middle-earth for Valinor after grievous psychological injury after her capture by Orcs and liberation by her sons).
The Elves view the sexual act as extremely special and intimate, for it leads to the conception and birth of children. Extra-marital and premarital sex
Premarital sex
Premarital sex is sexual activity, including vaginal intercourse, oral sex, and anal sex, practiced by persons who are unmarried. Although it has always been practiced, in the West it has increased in prevalence since the mid-1950s...
are unthinkable, adultery is also unheard of and fidelity between spouses is absolute. Yet separation during pregnancy or during the early years of parenthood (caused by war, for example) is so grievous to the couple that they prefer to have children in peaceful times. Living Elves cannot be raped or forced to have sex; before that they will lose the will to endure and go to Mandos.
Elves have few children, as a rule (Fëanor and Nerdanel were an exception, conceiving seven sons), and there are relatively sizeable intervals between each child (but see below for notes on Elvish birth rates in Middle-earth versus in Aman
Aman
-External links:*...
). They are soon preoccupied with other pleasures; their libido
Libido
Libido refers to a person's sex drive or desire for sexual activity. The desire for sex is an aspect of a person's sexuality, but varies enormously from one person to another, and it also varies depending on circumstances at a particular time. A person who has extremely frequent or a suddenly...
wanes and they focus their interests elsewhere, like the arts. Nonetheless, they take great delight in the union of love, and they cherish the days of bearing and raising children as the happiest days of their lives.
There seems to only be one known example of extreme marital strife in Tolkien's mythology, that of Eöl
Eöl
Eöl, called the Dark Elf, is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is introduced in The Silmarillion as an Elf of Beleriand and is a character existing in some form from the earliest to the latest writings....
and Aredhel
Aredhel
Aredhel Ar-Feiniel is a fictional character created by J. R. R. Tolkien.She is called Ar-Feiniel, the White Lady of the Noldor. She is the daughter of Fingolfin and Anairë, sister of Fingon, Turgon and Argon, and mother of Maeglin...
, in which the latter actually left the former without his knowledge, resulting in Eöl ultimately killing her. However, this marriage was far from typical of the Elves.
Daily life
The Elves, particularly the Noldor, preoccupy themselves with various things such as smithwork, sculpture, music and other arts, and of course, what to eat. Males and females can do almost everything equally; however, the females often specialize in the arts of healing while the males go to war. This is because they believe that taking life interferes with the ability to preserve life. However, Elves are not stuck in rigid roles; females can defend themselves at need as well as males, and many males are skilled healers as well, such as ElrondElrond
Elrond Half-elven is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is introduced in The Hobbit, and plays a supporting role in The Lord of the Rings and The Silmarillion.-Character overview:...
.
Later life
Eventually, if they do not die in battle or from some other cause, the Elves of Middle-earth grow weary of it and desire to go to Valinor, where the Valar originally sheltered their kind. Those who wish to leave for the Undying Lands often go by boats provided at the Grey Havens, where CírdanCírdan
Círdan the Shipwright is a fictional character created by J. R. R. Tolkien. He was a Telerin Elf, a great mariner and shipwright, and lord of the Falas during much of the First Age. He was the bearer of the Great Ring Narya, which he in turn gave to Gandalf.He had a beard, which was rare for...
the Shipwright dwells with his folk.
"The third cycle of life", aging, and facial hair
Despite Tolkien's statements in The Hobbit that Elves (and HobbitHobbit
Hobbits are a fictional diminutive race who inhabit the lands of Middle-earth in J. R. R. Tolkien's fiction.Hobbits first appeared in the novel The Hobbit, in which the main protagonist, Bilbo Baggins, is the titular hobbit...
s) have no beards, Círdan in fact has a beard, which appears to be an anomaly and a simple oversight. However, Tolkien later devised at least three "cycles of life" for Elves around 1960; Círdan
Círdan
Círdan the Shipwright is a fictional character created by J. R. R. Tolkien. He was a Telerin Elf, a great mariner and shipwright, and lord of the Falas during much of the First Age. He was the bearer of the Great Ring Narya, which he in turn gave to Gandalf.He had a beard, which was rare for...
had a beard because he was in his third cycle of life. (Mahtan, Nerdanel's father, had a beard in his second cycle of life, a rare phenomenon.) It is unclear what these cycles exactly are, since Tolkien left no notes further explaining this. Apparently, beards were the only sign of further natural physical ageing beyond maturity.
Nevertheless, Tolkien may have ultimately changed his mind about whether Elves had facial hair. As Christopher Tolkien states in Unfinished Tales
Unfinished Tales
Unfinished Tales is a collection of stories and essays by J. R. R. Tolkien that were never completed during his lifetime, but were edited by his son Christopher Tolkien and published in 1980.Unlike The Silmarillion, for which the narrative fragments were modified to connect into a consistent and...
, his father wrote in December 1972 or later that the Elvish strain in Men, such as Aragorn
Aragorn
Aragorn II is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, one of the main protagonists of The Lord of the Rings. He is first introduced by the name Strider, which the hobbits continue to call him...
, was "observable in the beardlessness of those who were so descended", since "it was a characteristic of all Elves to be beardless". This would seemingly contradict the information above.
Elves sometimes appear to age under great stress. Círdan appeared to be aged himself, since he is described as looking old, save for the stars in his eyes; this may be due to all the sorrows he had seen and lived through since the First Age. Also, the people of Gwindor of Nargothrond
Nargothrond
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, Nargothrond , called Nulukkhizdīn by the Dwarves, was the stronghold built by Finrod Felagund...
had trouble recognizing him after his time as a prisoner of Morgoth.
Death
Elves are naturally immortal, and remain unwearied with age. In addition to their immortality, Elves can recover from wounds which would normally kill a mortal Man. However, Elves can be slain, or die of grief and weariness.Spirits of dead Elves go to the Halls of Mandos in Valinor. After a certain period of time and rest that serves as "cleansing", their spirits are clothed in bodies identical to their old ones. However, they almost never go back to Middle-earth and remain in Valinor instead. An exception was Glorfindel
Glorfindel
In the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, Glorfindel is a name used twice for an Elf appearing in the tales of Middle-earth. He is introduced in various material relating to the First Age of Middle-earth, including The Silmarillion. The second instance is for a character of The Lord of the Rings, which...
in The Lord of the Rings; as shown in later books, Tolkien decided he was a "reborn" hero from The Silmarillion rather than an individual with the same name. A rare and more unusual example of an Elf coming back from the Halls of Mandos is found in the tale of Beren and Lúthien, as Lúthien
Lúthien
Lúthien Tinúviel is a fictional character in the fantasy-world Middle-earth of the English author J. R. R. Tolkien. She appears in The Silmarillion, the epic poem The Lay of Leithian, The Lord of the Rings and the Grey Annals, as well as in other material.-Character overview:Lúthien is a Telerin ...
was the other Elf to be sent back to Middle-earth – as a mortal, however. Tolkien's Elvish words for "spirit" and "body" were fëa
Fëa and hröa
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, fëa and hröa are words for "soul" and "body". The plural form of fëa is fëar and the plural form of hröa is hröar...
(plural fëar) and hröa
Fëa and hröa
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, fëa and hröa are words for "soul" and "body". The plural form of fëa is fëar and the plural form of hröa is hröar...
(plural hröar) respectively.
Eventually, their immortal spirits will overwhelm and consume their bodies, rendering them "bodiless", whether they opt to go to Valinor or remain in Middle-earth. At the end of the world, all Elves will have become invisible to mortal eyes, except to those to whom they wish to manifest themselves. Tolkien called the Elves of Middle-earth who had undergone this process "Lingerers".
The lives of Elves only endure as the world endures. It is said in the Second Prophecy of Mandos that at the end of time the Elves will join the other Children of Ilúvatar
Children of Ilúvatar
The Children of Ilúvatar is the name given to the two races of Elves and Men in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium because they were created by Ilúvatar, the One God, without the help of the Ainur....
in singing the Second Music of the Ainur. However it is disputable whether the Prophecy is canon, and the published Silmarillion states that only Men shall participate in the Second Music, and that the ultimate fate of the Elves is unknown. However, they do not believe that Eru will abandon them to oblivion.
Names and naming conventions
In The Lord of the Rings Tolkien pretends to be merely the translator of BilboBilbo Baggins
Bilbo Baggins is the protagonist and titular character of The Hobbit and a supporting character in The Lord of the Rings, two of the most well-known of J. R. R...
and Frodo
Frodo
Frodo may mean:*Frodo Baggins, a character in The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien*"Frodo", a song by New Zealand folk-duo Flight of the Conchords*Fróði, the name of a number of Danish kings, Latinized as Frodo*Frodo...
's memoirs, collectively known as the "Red Book of Westmarch
Red Book of Westmarch
The Red Book of Westmarch is a fictional manuscript written by hobbits, a conceit of author J. R. R...
". He says that those names and terms in the work (as well in the earlier The Hobbit) that appear in English
English language
English is a West Germanic language that arose in the Anglo-Saxon kingdoms of England and spread into what was to become south-east Scotland under the influence of the Anglian medieval kingdom of Northumbria...
are meant to be his purported translations from the Common Speech.
Tolkien repeatedly expressed his misgivings concerning the name "elf
Elf
An elf is a being of Germanic mythology. The elves were originally thought of as a race of divine beings endowed with magical powers, which they use both for the benefit and the injury of mankind...
" and its "associations of a kind that I should particularly desire not to be present [...] e.g. those of Drayton
Michael Drayton
Michael Drayton was an English poet who came to prominence in the Elizabethan era.-Early life:He was born at Hartshill, near Nuneaton, Warwickshire, England. Almost nothing is known about his early life, beyond the fact that in 1580 he was in the service of Thomas Goodere of Collingham,...
or of A Midsummer Night's Dream
A Midsummer Night's Dream
A Midsummer Night's Dream is a play that was written by William Shakespeare. It is believed to have been written between 1590 and 1596. It portrays the events surrounding the marriage of the Duke of Athens, Theseus, and the Queen of the Amazons, Hippolyta...
", for the purpose of translations
Translations of The Lord of the Rings
The Lord of the Rings by J. R. R. Tolkien appeared 1954–55 in the original English. It has since been translated, with various degrees of success, into dozens of other languages. Tolkien, an expert in Germanic philology, scrutinized those that were under preparation during his lifetime, and...
stating his preference that "the oldest available form of the name to be used, and leave it to acquire its own associations for readers of my tale". He wanted to avoid the Victorian
Victorian literature
Victorian literature is the literature produced during the reign of Queen Victoria . It forms a link and transition between the writers of the romantic period and the very different literature of the 20th century....
notions of "fairies" or mischievous imps associated with the word and was aiming at the more elevated notions of beings "supposed to possess formidable magical powers in early Teutonic mythology" (OED viz. the Old English ælf, from Proto-Germanic *albo-z).
The Elves are also called the "Firstborn" (Q
Quenya
Quenya is a fictional language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his Secondary world, often called Middle-earth.Quenya is one of the many Elvish languages spoken by the immortal Elves, called Quendi in Quenya. The tongue actually called Quenya was in origin the speech of two clans of Elves...
. Minnónar) or the "Elder Kindred" (as opposed to Men
Man (Middle-earth)
The race of Men in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth books, such as The Hobbit and The Lord of the Rings, refers to humanity and does not denote gender...
, the Secondborn) as they were "awakened" before Men by Eru Ilúvatar
Eru Ilúvatar
Eru Ilúvatar is a fictional deity in J.R.R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is introduced in The Silmarillion as the creator of all existence . In Tolkien's invented language of Elvish, Eru means "The One", or "He that is Alone" and Ilúvatar signifies "Father of All"...
(the creator
Creator deity
A creator deity is a deity responsible for the creation of the world . In monotheism, the single God is often also the creator deity, while polytheistic traditions may or may not have creator deities...
). The Elves named themselves Quendi ("the Speakers"), in honour of the fact that, when they were created, they were the only living beings able to speak. The Dúnedain
Dúnedain
In J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, the Dúnedain were a race of Men descended from the Númenóreans who survived the sinking of their island kingdom and came to Eriador in Middle-earth, led by Elendil and his sons, Isildur and Anárion...
called them Nimîr ("the Beautiful"), while their usual name in Sindarin
Sindarin
Sindarin is a fictional language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his secondary world, often called Middle-earth.Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the immortal Elves, called the Eledhrim or Edhellim in Sindarin....
was Eledhrim.
In other writings, part of The History of Middle-earth, Tolkien details Elvish naming conventions. The Quenya word for "name" was essë. An Elf of Valinor was typically given one name (ataressë) at birth by the father. It usually reflected either the name of the father or mother, indicating the person's descent, to which later some distinguishing prefix could be added. As the Elf grew older, they received a second name (amilessë), given by the mother. This name was extremely important and reflected personality, skills, or fate, sometimes being "prophetic".
The epessë or the "after-name" is the third type. It was given later in life, not necessarily by kin, as a title of admiration and honour. In some circumstances, yet another name was chosen by the Elf themselves, called kilmessë meaning "self-name".
The "true names" remained the first two, though an Elf could be referred to by any of these. Mother-names were usually not used by those who did not know the Elf well. In later history and song any of the four could become the one generally used and recognized.
After their Exile to Middle-earth and adoption of Sindarin
Sindarin
Sindarin is a fictional language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his secondary world, often called Middle-earth.Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the immortal Elves, called the Eledhrim or Edhellim in Sindarin....
as the daily speech, most of the Noldor also chose for themselves a name that fitted the style of that language, translating or altering one of their Quenya
Quenya
Quenya is a fictional language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his Secondary world, often called Middle-earth.Quenya is one of the many Elvish languages spoken by the immortal Elves, called Quendi in Quenya. The tongue actually called Quenya was in origin the speech of two clans of Elves...
names.
A patronymic
Patronymic
A patronym, or patronymic, is a component of a personal name based on the name of one's father, grandfather or an even earlier male ancestor. A component of a name based on the name of one's mother or a female ancestor is a matronymic. Each is a means of conveying lineage.In many areas patronyms...
surname is also used – the father's name with the suffix "-ion" (meaning "son") added. Thus, Gildor Inglorion
Gildor Inglorion
Gildor Inglorion is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He was a Noldorin Elf of the House of Finrod. In The Lord of the Rings he met Frodo Baggins and his friends in the Shire...
is "Gildor, son of Inglor".
Several examples include:
- GaladrielGaladrielGaladriel is a character created by J.R.R. Tolkien, appearing in his Middle-earth legendarium. She appears in The Lord of the Rings, The Silmarillion, and Unfinished Tales....
is the Sindarin translation of Alatáriel, the TelerinTelerinTelerin is a constructed language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien. It is one of the many fictional language set in his Secondary world, often called Middle-earth....
Quenya epessë originally given to her by CelebornCelebornCeleborn is a fictional character in J.R.R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He appears in The Lord of the Rings as the Elven husband of Galadriel, Lord of the Galadhrim; and co-ruler along with Galadriel of Lothlórien. He was the father of Celebrían — the wife of Elrond — and thus the...
, which means "Maiden Crowned by a Radiant Garland". Her father-name is Artanis (noble woman) and her mother-name is Nerwen (man-maiden).
- MaedhrosMaedhrosMaedhros is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium. First introduced in The Silmarillion and later mentioned in Unfinished Tales and The Children of Húrin, he is one of the most enduring characters in The Silmarillion, and has been the subject of paintings by artists such as Jenny...
, the oldest son of FëanorFëanorFëanor is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium who plays an important part in The Silmarillion. He was the eldest son of Finwë, the High King of the Noldor, and his first wife Míriel Serindë...
, was called Russandol (copper-top) by his brothers: He had earned this epessë because of his ruddy hair. His father-name had been Nelyafinwë (Finwë the third: Fëanor's own father-name had been (Curu) Finwë), and his mother-name Maitimo (well-shaped one). Maedhros is a rendering into Sindarin of parts of his mother-name and epessë.
- FinrodFinrod FelagundFinrod Felagund is a fictional character in the fantasy-world Middle-earth of the English author J. R. R. Tolkien. He appears in The Silmarillion, the epic poem The Lay of Leithian and the Grey Annals, as well as other material....
is usually referred to as Felagund (hewer of caves), a name the DwarvesDwarf (Middle-earth)In the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Dwarves are a race inhabiting the world of Arda, a fictional prehistoric Earth which includes the continent Middle-earth....
had given to him (originally Felakgundu) because of his dwellings at NargothrondNargothrondIn J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, Nargothrond , called Nulukkhizdīn by the Dwarves, was the stronghold built by Finrod Felagund...
. Finrod adopted the name, and made it a title of honour.
- CírdanCírdanCírdan the Shipwright is a fictional character created by J. R. R. Tolkien. He was a Telerin Elf, a great mariner and shipwright, and lord of the Falas during much of the First Age. He was the bearer of the Great Ring Narya, which he in turn gave to Gandalf.He had a beard, which was rare for...
(Shipwright) is the epessë of a TeleriTeleriIn the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, the Teleri, Those who come last in Quenya were the third of the Elf clans who came to Aman...
n Elf who remained in BeleriandBeleriandIn J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional legendarium, Beleriand was a region in northwestern Middle-earth during the First Age. Events in Beleriand are described chiefly in his work The Silmarillion, which tells the story of the early ages of Middle-earth in a style similar to the epic hero tales of Nordic...
, and later LindonLindon (Middle-earth)Lindon is the land beyond the Ered Luin, the Blue Mountains, in the northwest of Middle-earth in the fictional universe of J. R. R. Tolkien. It is the westernmost land of the continent. The Gulf of Lune divides it into Forlindon and Harlindon...
, until the end of the Third AgeThird AgeThe Third Age is a time period from J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth fantasy writings. The history of Middle-earth is to be taken fictionally as a history of the real Earth....
. His original name was only rarely remembered in traditions as Nōwē, and he was referred to always as Círdan, a title which had been given to him as Lord of the Falas.
Elvish languages
Tolkien created many languages for his Elves. His interest was primarily philologicalPhilology
Philology is the study of language in written historical sources; it is a combination of literary studies, history and linguistics.Classical philology is the philology of Greek and Classical Latin...
, and he said his stories grew out of his languages. Indeed, the languages were the first thing Tolkien ever created for his mythos, starting with what he originally called "Elfin" or "Qenya". This was later spelled Quenya
Quenya
Quenya is a fictional language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his Secondary world, often called Middle-earth.Quenya is one of the many Elvish languages spoken by the immortal Elves, called Quendi in Quenya. The tongue actually called Quenya was in origin the speech of two clans of Elves...
(High-elven) and, along with Sindarin
Sindarin
Sindarin is a fictional language devised by J. R. R. Tolkien, and used in his secondary world, often called Middle-earth.Sindarin is one of the many languages spoken by the immortal Elves, called the Eledhrim or Edhellim in Sindarin....
(Grey-elven), is one of the two most complete of Tolkien's constructed languages. In addition to these two Tolkien also created many other (related) Elvish languages.
Elves are also credited with creating the Tengwar
Tengwar
The Tengwar are an artificial script created by J. R. R. Tolkien. In his fictional universe of Middle-earth, the tengwar were invented by the Elf Fëanor, and used first to write the Elven tongues: Quenya, Telerin, and also Valarin. Later a great number of languages of Middle-earth were written...
(by Fëanor
Fëanor
Fëanor is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium who plays an important part in The Silmarillion. He was the eldest son of Finwë, the High King of the Noldor, and his first wife Míriel Serindë...
) and Cirth
Cirth
The Cirth are the letters of an semi-artificial script which was invented by J. R. R. Tolkien for the constructed languages he devised and used in his works. The initial C in Cirth is pronounced as a K, never as an S....
(Daeron) runic scripts.
Adaptations

Austrians
Austrians are a nation and ethnic group, consisting of the population of the Republic of Austria and its historical predecessor states who share a common Austrian culture and Austrian descent....
-German
German language
German is a West Germanic language, related to and classified alongside English and Dutch. With an estimated 90 – 98 million native speakers, German is one of the world's major languages and is the most widely-spoken first language in the European Union....
accents. High Elves are shown with pointed ears and beards.
In Middle-earth Role Playing
Middle-earth Role Playing
Middle-earth Role Playing is a 1984 role-playing game based on the writings of J.R.R. Tolkien under license from Tolkien Enterprises. Iron Crown Enterprises published the game until they lost the license on 22 Sep 1999.-Setting:The setting for MERP is an expanded version of J. R. R...
(Iron Crown Enterprises
Iron Crown Enterprises
Iron Crown Enterprises was a publisher of role playing, board, miniature battle, and collectible card games.ICE was incorporated in 1980 shortly after the principal founders graduated from the University of Virginia...
, 1986), three tribes of elves are presented as player character
Player character
A player character or playable character is a character in a video game or role playing game who is controlled or controllable by a player, and is typically a protagonist of the story told in the course of the game. A player character is a persona of the player who controls it. Player characters...
race options, the Silvan, Sindar and Noldor – each receiving statistic bonuses (ranging from 5 to 15) to all attributes apart from Strength, with the Noldo receiving the highest accumulative bonuses of any racial type in the game. All three tribes are statistically immune to disease (+100% chance of resistance), and must be given "Presence" as the highest randomly generated statistic. Elven characters also receive significant skill bonuses with missile weapons (such as a bow and arrow) and stealth skills (such as hiding).
All three elven tribes (Silvan, Noldor, Sindar) depicted in Lord of the Rings Roleplaying Game
Lord of the Rings Roleplaying Game
The Lord of the Rings Roleplaying Game, released by Decipher Inc. in 2002, is a role-playing game set in the Middle-earth of J. R. R. Tolkien's fiction. The game is set in the years between The Hobbit and The Fellowship of the Ring, but may be run at any time from the First to Fourth Age and...
(Decipher, Inc.
Decipher, Inc.
Decipher, Inc. is an American gaming company based in Norfolk, Virginia, USA. They began with three puzzles called "Decipher" then moved on to party games and Pente sets, but since 1994 produced collectible card and role-playing games. Their longest-running offering is the How to Host a Murder...
, 2001) have varying (one or two points) statistic bonuses to Bearing, Perception and Nimbleness, with the Noldor also receiving a bonus to Wits and the Sindar to Vitality, giving both of these the highest accumulative bonuses available to Player Characters. The system of skills, feats and flaws further outlines racial and cultural characteristics, bonuses being given to the Noldor in Lore and "Resisting the Shadow", to the Silvan elves for various wood-craft skills, and the Sindar to musical performance. All elves have the ability to enchant objects, and receive bonuses in any test regarding magic.
In The Lord of the Rings Strategy Battle Game
The Lord of the Rings Strategy Battle Game
The Lord of the Rings Strategy Battle Game , and often referred to by players as Lord of the Rings, is a tabletop miniature wargame produced by Games Workshop . It is based on The Lord of the Rings film trilogy directed by Peter Jackson, and the book that inspired it, written by J. R. R...
(Games Workshop
Games Workshop
Games Workshop Group plc is a British game production and retailing company. Games Workshop has published the tabletop wargames Warhammer Fantasy Battle and Warhammer 40,000...
, 2001), Elves have similar statistics to similarly armed Men, except for much higher scores for their Fighting and Courage attributes. On average, Elven wargear (armour and weapons) give twice the advantage of weapons made by Men.
See also
- List of Middle-earth Elves
- Elvish languages (Middle-earth)
- FalmariFalmariThe Falmari , also known as the Sea-elves, were those of the Teleri who departed from Middle-earth and went into the West. They became known as the Sea-elves in the land of Aman, for they became enamoured with the sea and made music beside the breaking waves...
- IlkorinIlkorinIlkorin is a Quenya word, literally meaning "not of Kôr". The Ilkorindi were a group of Elves from J. R. R. Tolkien's fictional universe. They first appear in The Book of Lost Tales. It was then a name with a broad meaning for all the Elves who "never saw the light of Kôr" and also for their many...
- MoriquendiMoriquendiIn the fictional universe of J. R. R. Tolkien, Moriquendi is a Quenya word meaning "Dark-folk", but often translated "Elves of Darkness" or "Dark-elves"...
Notable Elves
Some notable Elves include:- Arwen Undómiel great, great granddaughter of Lúthien.
- BelegBelegIn the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, Beleg is a major character who appears in numerous books, tales and poems about the First Age of Middle-earth such as The Silmarillion, The Lays of Beleriand and the Children of Húrin.-Name:...
most skilled of all Elves in hunting and tracking. - CelebornCelebornCeleborn is a fictional character in J.R.R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He appears in The Lord of the Rings as the Elven husband of Galadriel, Lord of the Galadhrim; and co-ruler along with Galadriel of Lothlórien. He was the father of Celebrían — the wife of Elrond — and thus the...
husband of Galadriel. - CelebríanCelebríanCelebrían is a fictional character created by J. R. R. Tolkien. She is an Elven noblewoman, the daughter of Celeborn and Galadriel, wife of Elrond, and mother of Elrohir, Elladan and Arwen. She was called the Lady of Rivendell. Her name means "silver queen" in Sindarin.- Biography :The place and...
daughter of Galadriel, wife of Elrond, mother of Elladan, Elrohir and Arwen. - CelebrimborCelebrimborCelebrimbor is a fictional character In J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth. His name means "silver fist" or "Hand of silver" in Sindarin ....
maker of the Rings of Power. - CírdanCírdanCírdan the Shipwright is a fictional character created by J. R. R. Tolkien. He was a Telerin Elf, a great mariner and shipwright, and lord of the Falas during much of the First Age. He was the bearer of the Great Ring Narya, which he in turn gave to Gandalf.He had a beard, which was rare for...
Lord of the Grey Havens and one of the oldest Elves in Middle-earth at the end of the Third Age. - ElrondElrondElrond Half-elven is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is introduced in The Hobbit, and plays a supporting role in The Lord of the Rings and The Silmarillion.-Character overview:...
great grandson of Lúthien, Lord of Imladris through the Third Age. - ElwingElwingElwing is a character of Middle-earth, created by J. R. R. Tolkien. She is Half-elven but counted among the Elves, notable for saving a Silmaril from the destruction of the Havens of Sirion and, with her husband Eärendil, going to the Valar to ask their help for the people of Middle-earth...
wife of EärendilEärendilEärendil the Mariner is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is depicted in The Silmarillion as a great seafarer who, on his brow, carried the morning star across the sky.-Etymology:...
. - FëanorFëanorFëanor is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium who plays an important part in The Silmarillion. He was the eldest son of Finwë, the High King of the Noldor, and his first wife Míriel Serindë...
often referred to as the mightiest of the Eldar. - FingolfinFingolfinFingolfin is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, appearing in The Silmarillion.-Internal history:He was a High King of the Noldor in Beleriand, second eldest son of Finwë, full brother of Finarfin, and half-brother of Fëanor, who was the eldest of Finwë's sons. His mother was...
greatest warrior of all the Children of Ilúvatar. - Finrod FelagundFinrod FelagundFinrod Felagund is a fictional character in the fantasy-world Middle-earth of the English author J. R. R. Tolkien. He appears in The Silmarillion, the epic poem The Lay of Leithian and the Grey Annals, as well as other material....
King of Nargothrond. - GaladrielGaladrielGaladriel is a character created by J.R.R. Tolkien, appearing in his Middle-earth legendarium. She appears in The Lord of the Rings, The Silmarillion, and Unfinished Tales....
greatest of the Noldor save Fëanor. - Gil-galadGil-galadEreinion Gil-galad is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is mentioned in The Lord of the Rings, and featured in The Silmarillion.- Character overview :...
High-king of the Noldorin Elves in Exile. - GlorfindelGlorfindelIn the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, Glorfindel is a name used twice for an Elf appearing in the tales of Middle-earth. He is introduced in various material relating to the First Age of Middle-earth, including The Silmarillion. The second instance is for a character of The Lord of the Rings, which...
true savior of Frodo after his close call with morgul blade at WeathertopWeathertopIn the works of J. R. R. Tolkien, Weathertop is a hill in the Eriador region of Middle-earth, the southernmost and highest summit of the Weather Hills... - IdrilIdrilIdril Celebrindal is a fictional character in the fantasy-world Middle-earth of English author J. R. R. Tolkien. She appears in one of his chief works of literature, The Silmarillion, published posthumously by Christopher Tolkien.-Character Overview:...
wife of TuorTuorTuor is a fictional character from J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is the grandfather of Elrond Half-elven and one of the most renowned ancestors of the Men of Númenor and of the King of the Reunited Kingdom Aragorn Elessar...
and mother of EärendilEärendilEärendil the Mariner is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is depicted in The Silmarillion as a great seafarer who, on his brow, carried the morning star across the sky.-Etymology:... - LegolasLegolasLegolas is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's legendarium, featured in The Lord of the Rings. He is an Elf of the Woodland Realm and one of nine members of the Fellowship of the Ring.- Literature :...
one of Fellowship of the Ring, later Lord of the Elves of Ithilien - LúthienLúthienLúthien Tinúviel is a fictional character in the fantasy-world Middle-earth of the English author J. R. R. Tolkien. She appears in The Silmarillion, the epic poem The Lay of Leithian, The Lord of the Rings and the Grey Annals, as well as in other material.-Character overview:Lúthien is a Telerin ...
enchantress, fairest of all the Children of Ilúvatar. - ThingolThingolElu Thingol is a fictional character in J.R.R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He appears in The Silmarillion, The Lays of Beleriand and Children of Húrin as well as in numerous stories in the many volumes of The History of Middle-earth...
King of Beleriand, tallest of all the Eldar, father of Lúthien. - ThranduilThranduilThranduil is a fictional character in J. R. R. Tolkien's Middle-earth legendarium. He is a supporting character in The Hobbit, and is referenced briefly in The Lord of the Rings, The Silmarillion and Unfinished Tales.-In literature:...
king of the woodland Elves of Mirkwood, father of Legolas. - TurgonTurgonIn the fiction of J. R. R. Tolkien, Turgon "the Wise" is an Elven king of the Noldor, second son of Fingolfin, brother to Fingon, Aredhel and Argon, and ruler of the hidden city of Gondolin....
king of Gondolin.

