
Electricity market
Encyclopedia
In economic terms, electricity
(both power and energy) is a commodity
capable of being bought, sold and traded. An electricity market is a system for effecting purchases, through bids to buy; sales, through offers to sell; and short-term trades
, generally in the form of financial or obligation swaps. Bids and offers use supply and demand
principles to set the price. Long-term trades are contracts similar to power purchase agreement
s and generally considered private bi-lateral transactions between counterparties.
Wholesale transactions (bids and offers) in electricity are typically cleared and settled by the market operator or a special-purpose independent entity charged exclusively with that function. Market operators do not clear trades but often require knowledge of the trade in order to maintain generation and load balance.
The commodities within an electric market generally consist of two types: Power
and Energy. Power is the metered net electrical transfer rate at any given moment and is measured in Megawatts (MW). Energy is electricity that flows through a metered point for a given period and is measured in Megawatt Hours (MWh).
Markets for power related commodities are net generation output for a number of intervals usually in increments of 5, 15 and 60 minutes. Markets for energy related commodities required by, managed by (and paid for by) market operators to ensure reliability, are considered Ancillary Services
and include such names as spinning reserve, non-spinning reserve, operating reserve
s, responsive reserve, regulation up, regulation down, and installed capacity
.
In addition, for most major operators, there are markets for transmission congestion and electricity derivatives
, such as electricity futures
and options
, which are actively traded. These markets developed as a result of the restructuring of electric power systems around the world. This process has often gone on in parallel with the restructuring of natural gas
markets.
concepts and privatization
to electric power systems took place in Chile
in the early 1980s, in parallel with other market-oriented reforms associated with the Chicago Boys
. The Chilean model was generally perceived as successful in bringing rationality and transparency to power pricing, but it contemplated the continuing dominance of several large incumbents and suffered from the attendant structural problems. Argentina
improved on the Chilean model by imposing strict limits on market concentration and by improving the structure of payments to units held in reserve to assure system reliability. One of the principal purposes of the introduction of market concepts in Argentina
was to privatize existing generation assets (which had fallen into disrepair under the government-owned monopoly, resulting in frequent service interruptions) and to attract capital needed for rehabilitation of those assets and for system expansion. The World Bank
was active in introducing a variety of hybrid markets in other Latin American nations, including Peru, Brazil, and Colombia, during the 1990s, with limited success.
A key event for electricity markets occurred in 1990 when the UK
government under Margaret Thatcher
privatised the UK electricity supply industry. The process followed by the British was then used as a model or at least a catalyst for the deregulation
of several other Commonwealth
countries, notably Australia
and New Zealand
, and regional markets such as Alberta
. However, in many of these other instances the market deregulation occurred without the widespread privatisation that characterised the UK example.
In the USA
the traditional model of the vertically integrated electric utility
with a transmission system designed to serve its own customers worked extremely well for decades. As dependence on a reliable supply of electricity grew and electricity was transported over increasingly greater distances, power pools were formed and interconnections
developed. Transactions were relatively few and generally planned well in advance.
However, in the last decade of the 20th century, some US policy makers and academics projected that the electrical power industry would ultimately experience deregulation and Independent System Operators (ISOs) and Regional Transmission Organization
s (RTOs) were established. They were conceived as the way to handle the vastly increased number of transactions that take place in a competitive environment. About a dozen states decided to deregulate but some pulled back following the California electricity crisis
of 2000 and 2001.
In different deregulation processes the institutions and market designs were often very different but many of the underlying concepts were the same. These are: separate the potentially competitive functions of generation
and retail
from the natural monopoly
functions of transmission
and distribution
; and establish a wholesale electricity market and a retail electricity market. The role of the wholesale market is to allow trading between generators, retailers and other financial intermediaries both for short-term delivery of electricity (see spot price
) and for future delivery periods (see forward price
).
is by its nature difficult to store and has to be available on demand. Consequently, unlike other products, it is not possible, under normal operating conditions, to keep it in stock, ration it or have customers queue for it. Furthermore, demand and supply vary continuously.
There is therefore a physical requirement for a controlling agency, the transmission system operator
, to coordinate the dispatch of generating units to meet the expected demand of the system across the transmission grid
. If there is a mismatch between supply and demand the generators speed up or slow down causing the system frequency
(either 50 or 60 hertz
) to increase or decrease. If the frequency falls outside a predetermined range the system operator will act to add or remove either generation or load.
In addition, the laws of physics
determine how electricity flows through an electricity network
. Hence the extent of electricity lost in transmission and the level of congestion on any particular branch of the network will influence the economic dispatch
of the generation units.
The scope of each electricity market consists of the transmission grid or network that is available to the wholesalers, retailers and the ultimate consumers in any geographic area. Markets may extend beyond national boundaries.
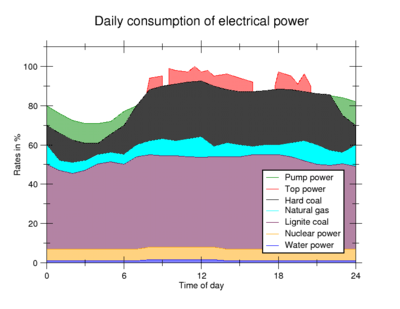 A wholesale electricity market exists when competing generators
A wholesale electricity market exists when competing generators
offer their electricity output to retailers
. The retailers then re-price the electricity and take it to market. While wholesale pricing used to be the exclusive domain of large retail suppliers, increasingly markets like New England are beginning to open up to end-users. Large end-users seeking to cut out unnecessary overhead in their energy costs are beginning to recognize the advantages inherent in such a purchasing move. Consumers buying electricity directly from generators is a relatively recent phenomenon.
Buying wholesale electricity is not without its drawbacks (market uncertainty, membership costs, set up fees, collateral investment), however, the larger the end user's electrical load, the greater the benefit and incentive to make the switch.
For an economically efficient electricity wholesale market to flourish it is essential that a number of criteria are met. Professor William Hogan of Harvard University
has identified these criteria. Central to his criteria is a coordinated spot market that has "bid-based, security-constrained, economic dispatch with nodal prices". Other academics such as Professors Shmuel Oren and Pablo Spiller of the University of California, Berkeley
have proposed other criteria. Variants of Professor Hogan's model have largely been adopted in the US, Australia and New Zealand.
, usually on an hourly interval, and is calculated separately for subregions in which the system operator's load flow model indicates that constraints will bind transmission imports.
The theoretical prices of electricity at each node on the network is a calculated "shadow price
", in which it is assumed that one additional kilowatt-hour is demanded at the node in question, and the hypothetical incremental cost to the system that would result from the optimized redispatch of available units establishes the hypothetical production cost of the hypothetical kilowatt-hour. This is known as locational marginal pricing (LMP) or nodal pricing and is used in some deregulated markets, most notably in the PJM Interconnection
, ERCOT
, New York
, and New England
markets in the USA and in New Zealand
.
In practice, the LMP algorithm described above is run, incorporating a security-constrained, least-cost dispatch calculation (see below) with supply based on the generators that submitted offers in the day-ahead market, and demand based on bids from load-serving entities draining supplies at the nodes in question.
While in theory the LMP concepts are useful and not evidently subject to manipulation, in practice system operators have substantial discretion over LMP results through the ability to classify units as running in "out-of-merit dispatch", which are thereby excluded from the LMP calculation. In most systems, units that are dispatched to provide reactive power to support transmission grids are declared to be "out-of-merit" (even though these are typically the same units that are located in constrained areas and would otherwise result in scarcity signals). System operators also normally bring units online to hold as "spinning-reserve" to protect against sudden outages or unexpectedly rapid ramps in demand, and declare them "out-of-merit". The result is often a substantial reduction in clearing price at a time when increasing demand would otherwise result in escalating prices.
Researchers have noted that a variety of factors, including energy price caps set well below the putative scarcity value
of energy, the impact of "out-of-merit" dispatch, the use of techniques such as voltage reductions during scarcity periods with no corresponding scarcity price signal, etc., results in a "missing money" problem. The consequence is that prices paid to suppliers in the "market" are substantially below the levels required to stimulate new entry. The markets have therefore been useful in bringing efficiencies to short-term system operations and dispatch, but have been a failure in what was advertised as a principal benefit: stimulating suitable new investment where it is needed, when it is needed.
In LMP markets, where constraints exist on a transmission network, there is a need for more expensive generation to be dispatched on the downstream side of the constraint. Prices on either side of the constraint separate giving rise to congestion pricing
and constraint rentals.
A constraint can be caused when a particular branch of a network reaches its thermal limit or when a potential overload will occur due to a contingent event (e.g., failure of a generator or transformer or a line outage) on another part of the network. The latter is referred to as a security constraint. Transmission systems are operated to allow for continuity of supply even if a contingent event, like the loss of a line, were to occur. This is known as a security constrained system.
In most systems the algorithm used is a "DC" model rather than an "AC" model, so constraints and redispatch resulting from thermal limits are identified/predicted, but constraints and redispatch resulting from reactive power deficiencies are not. Some systems take marginal losses into account. The prices in the real-time market are determined by the LMP algorithm described above, balancing supply from available units. This process is carried out for each 5-minute, half-hour or hour (depending on the market) interval at each node on the transmission grid
. The hypothetical redispatch calculation that determines the LMP must respect security constraints and the redispatch calculation must leave sufficient margin to maintain system stability in the event of an unplanned outage anywhere on the system. This results in a spot market with "bid-based, security-constrained, economic dispatch with nodal prices".
Since the introduction of the market, New Zealand has experienced shortages in 2001 and 2003, high prices all through 2005 and even higher prices and the risk of a severe shortage in 2006 (as of April 2006). These problems arose because New Zealand is at risk from drought due to its high proportion of electricity generated from hydro.
Many established markets do not employ nodal pricing, examples being the UK, Powernext
, and Nord Pool Spot
(Nordic and Baltic countries).
A consequence of the complexity of a wholesale electricity market can be extremely high price volatility
at times of peak demand and supply shortages. The particular characteristics of this price risk are highly dependent on the physical fundamentals of the market such as the mix of types of generation plant and relationship between demand and weather patterns. Price risk can be manifest by price "spikes" which are hard to predict and price "steps" when the underlying fuel or plant position changes for long periods.
"Volume risk" is often used to denote the phenomenon whereby electricity market participants have uncertain volumes or quantities of consumption or production. For example, a retailer is unable to accurately predict consumer demand for any particular hour more than a few days into the future and a producer is unable to predict the precise time that they will have plant outage or shortages of fuel. A compounding factor is also the common correlation between extreme price and volume events. For example, price spikes frequently occur when some producers have plant outages or when some consumers are in a period of peak consumption. The introduction of substantial amounts of intermittent power sources such as wind energy
may have an impact on market prices.
Electricity retailers, who in aggregate buy from the wholesale market, and generators who in aggregate sell to the wholesale market, are exposed to these price and volume effects and to protect themselves from volatility, they will enter into "hedge
contracts" with each other. The structure of these contracts varies by regional market due to different conventions and market structures. However, the two simplest and most common forms are simple fixed price forward contract
s for physical delivery and contracts for differences
where the parties agree a strike price
for defined time periods. In the case of a contract for difference
, if a resulting wholesale price index (as referenced in the contract) in any time period is higher than the "strike" price, the generator will refund the difference between the "strike" price and the actual price for that period. Similarly a retailer will refund the difference to the generator when the actual price is less than the "strike price". The actual price index is sometimes referred to as the "spot" or "pool" price, depending on the market.
Many other hedging
arrangements, such as swing contracts, Virtual Bidding
, Financial Transmission Rights, call option
s and put option
s are traded in sophisticated electricity markets. In general they are designed to transfer financial risks between participants.
; one term used in the United States for this type of consumer choice is 'energy choice'. A separate issue for electricity markets is whether or not consumers face real-time pricing (prices based on the variable wholesale price) or a price that is set in some other way, such as average annual costs. In many markets, consumers do not pay based on the real-time price, and hence have no incentive to reduce demand at times of high (wholesale) prices or to shift their demand to other periods. Demand response
may use pricing mechanisms or technical solutions to reduce peak demand.
Generally, electricity retail reform follows from electricity wholesale reform. However, it is possible to have a single electricity generation company and still have retail competition. If a wholesale price can be established at a node on the transmission grid
and the electricity quantities at that node can be reconciled, competition for retail customers within the distribution
system beyond the node is possible. In the German market, for example, large, vertically integrated utilities compete with one another for customers on a more or less open grid.
Although market structures vary, there are some common functions that an electricity retailer has to be able to perform, or enter into a contract for, in order to compete effectively. Failure or incompetence in the execution of one or more of the following has led to some dramatic financial disasters:
The two main areas of weakness have been risk management
and billing
. In the USA in 2001, California
's flawed regulation
of retail competition led to the California electricity crisis
and left incumbent retailers subject to high spot prices but without the ability to hedge against these (see Manifesto on The Californian Electricity Crisis). In the UK
a retailer, Independent Energy, with a large customer base went bust when it could not collect the money due from customers.
New technology
is available and has been piloted by the US Department of Energy that may be better suited to real-time market pricing. A potential use of event-driven SOA
could be a virtual electricity market where home clothes dryers can bid on the price of the electricity they use in a real-time market pricing system. The real-time market price and control system could turn home electricity
customers into active participants in managing the power grid and their monthly utility bills. Customers can set limits on how much they would pay for electricity to run a clothes dryer, for example, and electricity providers willing to transmit power at that price would be alerted over the grid and could sell the electricity to the dryer.
On one side, consumer devices can bid for power based on how much the owner of the device were willing to pay, set ahead of time by the consumer. On the other side, suppliers can enter bids automatically from their electricity generators, based on how much it would cost to start up and run the generators. Further, the electricity suppliers could perform real-time market analysis
to determine return-on-investment
for optimizing profitability or reducing end-user cost of goods
.
Event-driven SOA
software could allow homeowners to customize many different types of electricity devices found within their home to a desired level of comfort or economy. The event-driven software could also automatically respond to changing electricity prices, in as little as five-minute intervals. For example, to reduce the home owner's electricity usage in peak periods (when electricity is most expensive), the software could automatically lower the target temperature of the thermostat on the central heating system (in winter) or raise the target temperature of the thermostat on the central cooling system (in summer).
and the Enron debacle
caused a slow down in the pace of change and in some regions an increase in market regulation and reduction in competition. However, this trend is widely regarded as a temporary one against the longer term trend towards more open and competitive markets.
Notwithstanding the favorable light in which market solutions are viewed conceptually, the "missing money" problem has to date proved intractable. If electricity prices were to move to the levels needed to incent new merchant (i.e., market-based) transmission and generation, the costs to consumers would be politically difficult.
The increase in annual costs to consumers in New England
alone were calculated at $3 billion during the recent FERC hearings on the NEPOOL market structure. Several mechanisms that are intended to incent new investment where it is most needed by offering enhanced capacity payments (but only in zones where generation is projected to be short) have been proposed for NEPOOL, PJM
and NYPOOL, and go under the generic heading of "locational capacity" or LICAP (the PJM version currently [May 2006] under FERC review is called the "Reliability Pricing Model", or "RPM"). There is substantial doubt as to whether any of these mechanisms will in fact incent new investment, given the regulatory risk and chronic instability of the market rules in US systems, and there are substantial concerns that the result will instead be to increase revenues to incumbent generators, and costs to consumers, in the constrained areas.
Reserve Capacity Mechanism Review Report
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
(both power and energy) is a commodity
Commodity
In economics, a commodity is the generic term for any marketable item produced to satisfy wants or needs. Economic commodities comprise goods and services....
capable of being bought, sold and traded. An electricity market is a system for effecting purchases, through bids to buy; sales, through offers to sell; and short-term trades
Short-term trading
Short-term trading refers to those trading strategies in stock market or futures market in which the time duration between entry and exit is within a range of few days to few weeks.There are two main school of thoughts: day trading and trend following....
, generally in the form of financial or obligation swaps. Bids and offers use supply and demand
Supply and demand
Supply and demand is an economic model of price determination in a market. It concludes that in a competitive market, the unit price for a particular good will vary until it settles at a point where the quantity demanded by consumers will equal the quantity supplied by producers , resulting in an...
principles to set the price. Long-term trades are contracts similar to power purchase agreement
Power Purchase Agreement
Power Purchase Agreements are contracts between two parties, one who generates electricity for the purpose of sale and one who is looking to purchase electricity . There are various forms of Power Purchase Agreements; these are differentiated by the source of energy harnessed...
s and generally considered private bi-lateral transactions between counterparties.
Wholesale transactions (bids and offers) in electricity are typically cleared and settled by the market operator or a special-purpose independent entity charged exclusively with that function. Market operators do not clear trades but often require knowledge of the trade in order to maintain generation and load balance.
The commodities within an electric market generally consist of two types: Power
Power (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
and Energy. Power is the metered net electrical transfer rate at any given moment and is measured in Megawatts (MW). Energy is electricity that flows through a metered point for a given period and is measured in Megawatt Hours (MWh).
Markets for power related commodities are net generation output for a number of intervals usually in increments of 5, 15 and 60 minutes. Markets for energy related commodities required by, managed by (and paid for by) market operators to ensure reliability, are considered Ancillary Services
Ancillary services (electric power)
The United States Federal Energy Regulatory Commission defines the ancillary services as:"those services necessary to support the transmission of electric power from seller to purchaser given the obligations of control areas and transmitting utilities within those control areas to maintain...
and include such names as spinning reserve, non-spinning reserve, operating reserve
Operating reserve
In electricity networks, the operating reserve is the generating capacity available to the system operator within a short interval of time to meet demand in case a generator goes down or there is another disruption to the supply...
s, responsive reserve, regulation up, regulation down, and installed capacity
Nameplate capacity
Nameplate capacity, also known as the rated capacity, nominal capacity, installed capacity or maximum effect, refers to the intended technical full–load sustained output of a facility such as a power plant, a chemical plant, fuel plant, metal refinery, mine, and many others.For dispatchable power,...
.
In addition, for most major operators, there are markets for transmission congestion and electricity derivatives
Derivative (finance)
A derivative instrument is a contract between two parties that specifies conditions—in particular, dates and the resulting values of the underlying variables—under which payments, or payoffs, are to be made between the parties.Under U.S...
, such as electricity futures
Futures contract
In finance, a futures contract is a standardized contract between two parties to exchange a specified asset of standardized quantity and quality for a price agreed today with delivery occurring at a specified future date, the delivery date. The contracts are traded on a futures exchange...
and options
Option (finance)
In finance, an option is a derivative financial instrument that specifies a contract between two parties for a future transaction on an asset at a reference price. The buyer of the option gains the right, but not the obligation, to engage in that transaction, while the seller incurs the...
, which are actively traded. These markets developed as a result of the restructuring of electric power systems around the world. This process has often gone on in parallel with the restructuring of natural gas
Natural gas
Natural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
markets.
History
The earliest introduction of energy marketEnergy market
Energy markets are those commodities markets that deal specifically with the trade and supply of energy. Energy market may refer to an electricity market, but can also refer to other sources of energy...
concepts and privatization
Privatization
Privatization is the incidence or process of transferring ownership of a business, enterprise, agency or public service from the public sector to the private sector or to private non-profit organizations...
to electric power systems took place in Chile
Electricity sector in Chile
The electricity sector in Chile relies predominantly on thermal and hydro power generation. Faced with natural gas shortages, Chile began in 2007 to build its first liquefied natural gas terminal and re-gasification plant at Quintero near the capital city of Santiago to secure supply for its...
in the early 1980s, in parallel with other market-oriented reforms associated with the Chicago Boys
Chicago Boys
The Chicago Boys were a group of young Chilean economists most of whom trained at the University of Chicago under Milton Friedman and Arnold Harberger, or at its affiliate in the economics department at the Catholic University of Chile...
. The Chilean model was generally perceived as successful in bringing rationality and transparency to power pricing, but it contemplated the continuing dominance of several large incumbents and suffered from the attendant structural problems. Argentina
Electricity sector in Argentina
The electricity sector in Argentina constitutes the third largest power market in Latin America. It relies mostly on thermal generation and hydropower generation , with new renewable energy technologies barely exploited. The country still has a large untapped hydroelectric potential...
improved on the Chilean model by imposing strict limits on market concentration and by improving the structure of payments to units held in reserve to assure system reliability. One of the principal purposes of the introduction of market concepts in Argentina
Electricity sector in Argentina
The electricity sector in Argentina constitutes the third largest power market in Latin America. It relies mostly on thermal generation and hydropower generation , with new renewable energy technologies barely exploited. The country still has a large untapped hydroelectric potential...
was to privatize existing generation assets (which had fallen into disrepair under the government-owned monopoly, resulting in frequent service interruptions) and to attract capital needed for rehabilitation of those assets and for system expansion. The World Bank
World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans to developing countries for capital programmes.The World Bank's official goal is the reduction of poverty...
was active in introducing a variety of hybrid markets in other Latin American nations, including Peru, Brazil, and Colombia, during the 1990s, with limited success.
A key event for electricity markets occurred in 1990 when the UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
government under Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Thatcher
Margaret Hilda Thatcher, Baroness Thatcher, was Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1979 to 1990...
privatised the UK electricity supply industry. The process followed by the British was then used as a model or at least a catalyst for the deregulation
Deregulation
Deregulation is the removal or simplification of government rules and regulations that constrain the operation of market forces.Deregulation is the removal or simplification of government rules and regulations that constrain the operation of market forces.Deregulation is the removal or...
of several other Commonwealth
Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, normally referred to as the Commonwealth and formerly known as the British Commonwealth, is an intergovernmental organisation of fifty-four independent member states...
countries, notably Australia
National Electricity Market
The National Electricity Market is the name of the Australian wholesale electricity market and the associated synchronous electricity transmission grid....
and New Zealand
New Zealand Electricity Market
New Zealand's electricity market is regulated by the Electricity Industry Participation Code administered by the Electricity Authority . The Authority was established in November 2010 to replace the Electricity Commission and its publication explains how the market works.- Overview :Until 1987,...
, and regional markets such as Alberta
Alberta
Alberta is a province of Canada. It had an estimated population of 3.7 million in 2010 making it the most populous of Canada's three prairie provinces...
. However, in many of these other instances the market deregulation occurred without the widespread privatisation that characterised the UK example.
In the USA
Electricity sector of the United States
The electricity sector of the United States includes a large array of stakeholders that provide services through electricity generation, transmission, distribution and marketing for industrial, commercial, public and residential customers...
the traditional model of the vertically integrated electric utility
Electric utility
An electric utility is a company that engages in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity for sale generally in a regulated market. The electrical utility industry is a major provider of energy in most countries. It is indispensable to factories, commercial establishments,...
with a transmission system designed to serve its own customers worked extremely well for decades. As dependence on a reliable supply of electricity grew and electricity was transported over increasingly greater distances, power pools were formed and interconnections
Wide area synchronous grid
A wide area synchronous grid, also called an "interconnection" in North America, is a power grid at a regional scale or greater that operates at a synchronized frequency and is electrically tied together during normal system conditions...
developed. Transactions were relatively few and generally planned well in advance.
However, in the last decade of the 20th century, some US policy makers and academics projected that the electrical power industry would ultimately experience deregulation and Independent System Operators (ISOs) and Regional Transmission Organization
Regional Transmission Organization
A regional transmission organization in the United States is an organization that is responsible for moving electricity over large interstate areas. Like a transmission system operator , an RTO coordinates, controls and monitors an electricity transmission grid that is larger with much higher...
s (RTOs) were established. They were conceived as the way to handle the vastly increased number of transactions that take place in a competitive environment. About a dozen states decided to deregulate but some pulled back following the California electricity crisis
California electricity crisis
The California electricity crisis, also known as the Western U.S. Energy Crisis of 2000 and 2001 was a situation in which California had a shortage of electricity caused by market manipulations and illegal shutdowns of pipelines by Texas energy consortiums...
of 2000 and 2001.
In different deregulation processes the institutions and market designs were often very different but many of the underlying concepts were the same. These are: separate the potentially competitive functions of generation
Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
and retail
Electricity retailing
Electricity retailing is the final process in the delivery of electricity from generation to the consumer. The other main processes are transmission and distribution.- Beginnings :...
from the natural monopoly
Natural monopoly
A monopoly describes a situation where all sales in a market are undertaken by a single firm. A natural monopoly by contrast is a condition on the cost-technology of an industry whereby it is most efficient for production to be concentrated in a single form...
functions of transmission
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
and distribution
Electricity distribution
File:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg|thumb|380px|right|Simplified diagram of AC electricity distribution from generation stations to consumers...
; and establish a wholesale electricity market and a retail electricity market. The role of the wholesale market is to allow trading between generators, retailers and other financial intermediaries both for short-term delivery of electricity (see spot price
Spot price
The spot price or spot rate of a commodity, a security or a currency is the price that is quoted for immediate settlement . Spot settlement is normally one or two business days from trade date...
) and for future delivery periods (see forward price
Forward price
The forward price is the agreed upon price of an asset in a forward contract. Using the rational pricing assumption, for a forward contract on an underlying asset that is tradeable, we can express the forward price in terms of the spot price and any dividends etc...
).
Nature of the market
ElectricityElectricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
is by its nature difficult to store and has to be available on demand. Consequently, unlike other products, it is not possible, under normal operating conditions, to keep it in stock, ration it or have customers queue for it. Furthermore, demand and supply vary continuously.
There is therefore a physical requirement for a controlling agency, the transmission system operator
Transmission system operator
File:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg|thumb|380px|right|Simplified diagram of AC electricity distribution from generation stations to consumersrect 2 243 235 438 Power stationrect 276 317 412 556 Transformer...
, to coordinate the dispatch of generating units to meet the expected demand of the system across the transmission grid
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
. If there is a mismatch between supply and demand the generators speed up or slow down causing the system frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
(either 50 or 60 hertz
Hertz
The hertz is the SI unit of frequency defined as the number of cycles per second of a periodic phenomenon. One of its most common uses is the description of the sine wave, particularly those used in radio and audio applications....
) to increase or decrease. If the frequency falls outside a predetermined range the system operator will act to add or remove either generation or load.
In addition, the laws of physics
Physics
Physics is a natural science that involves the study of matter and its motion through spacetime, along with related concepts such as energy and force. More broadly, it is the general analysis of nature, conducted in order to understand how the universe behaves.Physics is one of the oldest academic...
determine how electricity flows through an electricity network
Electrical network
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical elements such as resistors, inductors, capacitors, transmission lines, voltage sources, current sources and switches. An electrical circuit is a special type of network, one that has a closed loop giving a return path for the current...
. Hence the extent of electricity lost in transmission and the level of congestion on any particular branch of the network will influence the economic dispatch
Economic dispatch
Economic dispatch is the short-term determination of the optimal output of a number of electricity generation facilities, to meet the system load, at the lowest possible cost, while serving power to the public in a robust and reliable manner...
of the generation units.
The scope of each electricity market consists of the transmission grid or network that is available to the wholesalers, retailers and the ultimate consumers in any geographic area. Markets may extend beyond national boundaries.
Wholesale electricity market

Electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
offer their electricity output to retailers
Electricity retailing
Electricity retailing is the final process in the delivery of electricity from generation to the consumer. The other main processes are transmission and distribution.- Beginnings :...
. The retailers then re-price the electricity and take it to market. While wholesale pricing used to be the exclusive domain of large retail suppliers, increasingly markets like New England are beginning to open up to end-users. Large end-users seeking to cut out unnecessary overhead in their energy costs are beginning to recognize the advantages inherent in such a purchasing move. Consumers buying electricity directly from generators is a relatively recent phenomenon.
Buying wholesale electricity is not without its drawbacks (market uncertainty, membership costs, set up fees, collateral investment), however, the larger the end user's electrical load, the greater the benefit and incentive to make the switch.
For an economically efficient electricity wholesale market to flourish it is essential that a number of criteria are met. Professor William Hogan of Harvard University
Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League university located in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States, established in 1636 by the Massachusetts legislature. Harvard is the oldest institution of higher learning in the United States and the first corporation chartered in the country...
has identified these criteria. Central to his criteria is a coordinated spot market that has "bid-based, security-constrained, economic dispatch with nodal prices". Other academics such as Professors Shmuel Oren and Pablo Spiller of the University of California, Berkeley
University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley , is a teaching and research university established in 1868 and located in Berkeley, California, USA...
have proposed other criteria. Variants of Professor Hogan's model have largely been adopted in the US, Australia and New Zealand.
Bid-based, security-constrained, economic dispatch with nodal prices
The system price in the day-ahead market is, in principle, determined by matching offers from generators to bids from consumers at each node to develop a classic supply and demand equilibrium priceEconomic equilibrium
In economics, economic equilibrium is a state of the world where economic forces are balanced and in the absence of external influences the values of economic variables will not change. It is the point at which quantity demanded and quantity supplied are equal...
, usually on an hourly interval, and is calculated separately for subregions in which the system operator's load flow model indicates that constraints will bind transmission imports.
The theoretical prices of electricity at each node on the network is a calculated "shadow price
Shadow price
In constrained optimization in economics, the shadow price is the instantaneous change per unit of the constraint in the objective value of the optimal solution of an optimization problem obtained by relaxing the constraint...
", in which it is assumed that one additional kilowatt-hour is demanded at the node in question, and the hypothetical incremental cost to the system that would result from the optimized redispatch of available units establishes the hypothetical production cost of the hypothetical kilowatt-hour. This is known as locational marginal pricing (LMP) or nodal pricing and is used in some deregulated markets, most notably in the PJM Interconnection
PJM Interconnection
PJM Interconnection LLC is a Regional Transmission Organization which is part of the Eastern Interconnection grid operating an electric transmission system serving all or parts of Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee,...
, ERCOT
ERCOT
The Electric Reliability Council of Texas formed in 1970, is one of eight Independent System Operators in North America, and is the successor to the Texas Interconnected System...
, New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, and New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
markets in the USA and in New Zealand
New Zealand Electricity Market
New Zealand's electricity market is regulated by the Electricity Industry Participation Code administered by the Electricity Authority . The Authority was established in November 2010 to replace the Electricity Commission and its publication explains how the market works.- Overview :Until 1987,...
.
In practice, the LMP algorithm described above is run, incorporating a security-constrained, least-cost dispatch calculation (see below) with supply based on the generators that submitted offers in the day-ahead market, and demand based on bids from load-serving entities draining supplies at the nodes in question.
While in theory the LMP concepts are useful and not evidently subject to manipulation, in practice system operators have substantial discretion over LMP results through the ability to classify units as running in "out-of-merit dispatch", which are thereby excluded from the LMP calculation. In most systems, units that are dispatched to provide reactive power to support transmission grids are declared to be "out-of-merit" (even though these are typically the same units that are located in constrained areas and would otherwise result in scarcity signals). System operators also normally bring units online to hold as "spinning-reserve" to protect against sudden outages or unexpectedly rapid ramps in demand, and declare them "out-of-merit". The result is often a substantial reduction in clearing price at a time when increasing demand would otherwise result in escalating prices.
Researchers have noted that a variety of factors, including energy price caps set well below the putative scarcity value
Scarcity value
Scarcity value is the economic factor that increases an item's relative price based more upon its relatively low supply. Whereas the prices of newly-produced manufactured products depends mostly on the cost of production , the prices of many goods—such as antiques, rare stamps, and those raw...
of energy, the impact of "out-of-merit" dispatch, the use of techniques such as voltage reductions during scarcity periods with no corresponding scarcity price signal, etc., results in a "missing money" problem. The consequence is that prices paid to suppliers in the "market" are substantially below the levels required to stimulate new entry. The markets have therefore been useful in bringing efficiencies to short-term system operations and dispatch, but have been a failure in what was advertised as a principal benefit: stimulating suitable new investment where it is needed, when it is needed.
In LMP markets, where constraints exist on a transmission network, there is a need for more expensive generation to be dispatched on the downstream side of the constraint. Prices on either side of the constraint separate giving rise to congestion pricing
Congestion pricing
Congestion pricing or congestion charges is a system of surcharging users of a transport network in periods of peak demand to reduce traffic congestion. Examples include some toll-like road pricing fees, and higher peak charges for utilities, public transport and slots in canals and airports...
and constraint rentals.
A constraint can be caused when a particular branch of a network reaches its thermal limit or when a potential overload will occur due to a contingent event (e.g., failure of a generator or transformer or a line outage) on another part of the network. The latter is referred to as a security constraint. Transmission systems are operated to allow for continuity of supply even if a contingent event, like the loss of a line, were to occur. This is known as a security constrained system.
In most systems the algorithm used is a "DC" model rather than an "AC" model, so constraints and redispatch resulting from thermal limits are identified/predicted, but constraints and redispatch resulting from reactive power deficiencies are not. Some systems take marginal losses into account. The prices in the real-time market are determined by the LMP algorithm described above, balancing supply from available units. This process is carried out for each 5-minute, half-hour or hour (depending on the market) interval at each node on the transmission grid
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
. The hypothetical redispatch calculation that determines the LMP must respect security constraints and the redispatch calculation must leave sufficient margin to maintain system stability in the event of an unplanned outage anywhere on the system. This results in a spot market with "bid-based, security-constrained, economic dispatch with nodal prices".
Since the introduction of the market, New Zealand has experienced shortages in 2001 and 2003, high prices all through 2005 and even higher prices and the risk of a severe shortage in 2006 (as of April 2006). These problems arose because New Zealand is at risk from drought due to its high proportion of electricity generated from hydro.
Many established markets do not employ nodal pricing, examples being the UK, Powernext
Powernext
Powernext is a regulated investment firm based in Paris and operating under the multilateral trading facility status. Powernext designs and operates electronic trading platforms for spot and derivatives markets in the European energy sector...
, and Nord Pool Spot
Nord Pool Spot
Nord Pool Spot runs the largest market for electrical energy in the world, measured in volume traded and in market share. It operates in Norway, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, and Estonia. More than 70% of the total consumption of electrical energy in the Nordic market is traded through Nord Pool...
(Nordic and Baltic countries).
Risk management
Financial risk management is often a high priority for participants in deregulated electricity markets due to the substantial price and volume risks that the markets can exhibit.A consequence of the complexity of a wholesale electricity market can be extremely high price volatility
Volatility (finance)
In finance, volatility is a measure for variation of price of a financial instrument over time. Historic volatility is derived from time series of past market prices...
at times of peak demand and supply shortages. The particular characteristics of this price risk are highly dependent on the physical fundamentals of the market such as the mix of types of generation plant and relationship between demand and weather patterns. Price risk can be manifest by price "spikes" which are hard to predict and price "steps" when the underlying fuel or plant position changes for long periods.
"Volume risk" is often used to denote the phenomenon whereby electricity market participants have uncertain volumes or quantities of consumption or production. For example, a retailer is unable to accurately predict consumer demand for any particular hour more than a few days into the future and a producer is unable to predict the precise time that they will have plant outage or shortages of fuel. A compounding factor is also the common correlation between extreme price and volume events. For example, price spikes frequently occur when some producers have plant outages or when some consumers are in a period of peak consumption. The introduction of substantial amounts of intermittent power sources such as wind energy
Wind energy
Wind energy is the kinetic energy of air in motion; see also wind power.Total wind energy flowing through an imaginary area A during the time t is:E = ½ m v2 = ½ v 2...
may have an impact on market prices.
Electricity retailers, who in aggregate buy from the wholesale market, and generators who in aggregate sell to the wholesale market, are exposed to these price and volume effects and to protect themselves from volatility, they will enter into "hedge
Hedge (finance)
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses that may be incurred by a companion investment.A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, many types of...
contracts" with each other. The structure of these contracts varies by regional market due to different conventions and market structures. However, the two simplest and most common forms are simple fixed price forward contract
Forward contract
In finance, a forward contract or simply a forward is a non-standardized contract between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a specified future time at a price agreed today. This is in contrast to a spot contract, which is an agreement to buy or sell an asset today. It costs nothing to enter a...
s for physical delivery and contracts for differences
Hedge (finance)
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses that may be incurred by a companion investment.A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, many types of...
where the parties agree a strike price
Strike price
In options, the strike price is a key variable in a derivatives contract between two parties. Where the contract requires delivery of the underlying instrument, the trade will be at the strike price, regardless of the spot price of the underlying instrument at that time.Formally, the strike...
for defined time periods. In the case of a contract for difference
Contract for difference
In finance, a contract for difference is a contract between two parties, typically described as "buyer" and "seller", stipulating that the buyer will pay to the seller the difference between the current value of an asset and its value at contract time...
, if a resulting wholesale price index (as referenced in the contract) in any time period is higher than the "strike" price, the generator will refund the difference between the "strike" price and the actual price for that period. Similarly a retailer will refund the difference to the generator when the actual price is less than the "strike price". The actual price index is sometimes referred to as the "spot" or "pool" price, depending on the market.
Many other hedging
Hedge (finance)
A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses that may be incurred by a companion investment.A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, many types of...
arrangements, such as swing contracts, Virtual Bidding
Virtual Bidding
Virtual bidding is a strategy implemented in various Independent System Operator electricity markets of trading Day-Ahead prices against Real-Time prices. The term "bid" can be used loosely in electricity markets to refer to an offer to buy or to sell...
, Financial Transmission Rights, call option
Call option
A call option, often simply labeled a "call", is a financial contract between two parties, the buyer and the seller of this type of option. The buyer of the call option has the right, but not the obligation to buy an agreed quantity of a particular commodity or financial instrument from the seller...
s and put option
Put option
A put or put option is a contract between two parties to exchange an asset, the underlying, at a specified price, the strike, by a predetermined date, the expiry or maturity...
s are traded in sophisticated electricity markets. In general they are designed to transfer financial risks between participants.
Wholesale electricity markets
- Czech RepublicCzech RepublicThe Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
/ EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
- OTE - Czech electricity and gas market operator and PXE - Power Exchange Central Europe - power futures for Czech Republic, Slovakia and Hungary - Western AustraliaWestern AustraliaWestern Australia is a state of Australia, occupying the entire western third of the Australian continent. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Great Australian Bight and Indian Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east and South Australia to the south-east...
- IMO the Independent Market Operator - AustraliaAustraliaAustralia , officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a country in the Southern Hemisphere comprising the mainland of the Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous smaller islands in the Indian and Pacific Oceans. It is the world's sixth-largest country by total area...
- AEMO the Australian Market Administrator - AustriaAustriaAustria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
- see EXAA Energy Exchange - BrazilElectricity sector in BrazilBrazil has the largest electricity market in South America, with a power consumption that is more than double the combined consumption of Argentina, Bolivia, Chile and Uruguay. Its installed capacity is comparable to that of Italy and the United Kingdom, although with a much larger transmission...
- Eletric Energy Commercialization Chamber - Canada - Independent Electricity System Operator (IESO) Ontario Market and Alberta Electric System Operator (AESO)
- ChileElectricity sector in ChileThe electricity sector in Chile relies predominantly on thermal and hydro power generation. Faced with natural gas shortages, Chile began in 2007 to build its first liquefied natural gas terminal and re-gasification plant at Quintero near the capital city of Santiago to secure supply for its...
- ScandinaviaScandinaviaScandinavia is a cultural, historical and ethno-linguistic region in northern Europe that includes the three kingdoms of Denmark, Norway and Sweden, characterized by their common ethno-cultural heritage and language. Modern Norway and Sweden proper are situated on the Scandinavian Peninsula,...
- Nord Pool SpotNord Pool SpotNord Pool Spot runs the largest market for electrical energy in the world, measured in volume traded and in market share. It operates in Norway, Denmark, Sweden, Finland, and Estonia. More than 70% of the total consumption of electrical energy in the Nordic market is traded through Nord Pool...
http://www.nordpoolspot.com/ - FranceElectricity sector in FranceThe electricity sector in France is the main article of electricity in France. Energy in France focus energy and electricity production, consumption and import in France. Energy policy of France will describe the politics of France related to energy more in detail.In the year 2009 electricity was...
, - PowernextPowernextPowernext is a regulated investment firm based in Paris and operating under the multilateral trading facility status. Powernext designs and operates electronic trading platforms for spot and derivatives markets in the European energy sector...
http://www.powernext.fr - GermanyElectricity sector in GermanyThe electricity sector in Germany included in the year 2009 fossil fuelled power 61 %, nuclear power 23 % and renewable energy 18 %. Germany has defined a phase-out policy of nuclear power by 2022...
- European Energy ExchangeEuropean Energy eXchangeEuropean Energy Exchange AG, Germany's energy exchange, is the leading energy exchange in Central Europe.-Overview:The European Energy Exchange is located in Leipzig. Preceding companies were LPX Leipzig Power Exchange, located in Leipzig and European Energy Exchange, located in Frankfurt...
EEX - Great BritainGreat BritainGreat Britain or Britain is an island situated to the northwest of Continental Europe. It is the ninth largest island in the world, and the largest European island, as well as the largest of the British Isles...
- Elexon - HungaryHungaryHungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
- http://www.hupx.hu/ Hungarian Power Exchange HUPX and PXE - Power Exchange Central Europe - power futures for Czech Republic, Slovakia and Hungary - IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
- Power Exchange India Limited, PXIL - IndiaIndiaIndia , officially the Republic of India , is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by geographical area, the second-most populous country with over 1.2 billion people, and the most populous democracy in the world...
- Indian Energy ExchangeIndian Energy ExchangeThe IEX was granted approval to operate as an automated electronic trading exchange by the regulator, the Central Electricity Regulatory Committee , on June 9, 2008. One year later IEX had recorded 37.4 million transactions, the same month that electricity prices on the exchange hit a record low 13... - IrelandIrelandIreland is an island to the northwest of continental Europe. It is the third-largest island in Europe and the twentieth-largest island on Earth...
- SEMO - ItalyItalyItaly , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
- GME - JapanElectricity sector in JapanThe electric power industry in Japan covers the generation, transmission, distribution, and sale of electric energy in Japan.- Consumption :In 2008, Japan consumed an average of 8507 kWh/person of electricity...
- see Japan Electric Power Exchange (JEPX) - NetherlandsNetherlandsThe Netherlands is a constituent country of the Kingdom of the Netherlands, located mainly in North-West Europe and with several islands in the Caribbean. Mainland Netherlands borders the North Sea to the north and west, Belgium to the south, and Germany to the east, and shares maritime borders...
, UKUnited KingdomThe United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
, BelgiumBelgiumBelgium , officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a federal state in Western Europe. It is a founding member of the European Union and hosts the EU's headquarters, and those of several other major international organisations such as NATO.Belgium is also a member of, or affiliated to, many...
- APX-ENDEXAPX-ENDEXAPX-ENDEX is an Anglo-Dutch energy exchange operating the spot and derivatives markets for electricity and natural gas in the Netherlands, the United Kingdom, and Belgium. Established in 1999, APX-ENDEX provides exchange trading, central clearing and settlement, and data distribution services as...
http://www.apxendex.com - New ZealandElectricity sector in New ZealandThe electricity sector in New Zealand uses mainly renewable energy sources such as hydropower, geothermal power and increasingly wind energy. The 70% share of renewable energy sources makes New Zealand one of the lowest carbon dioxide emitting countries in terms of electricity generation....
- see New Zealand Electricity MarketNew Zealand Electricity MarketNew Zealand's electricity market is regulated by the Electricity Industry Participation Code administered by the Electricity Authority . The Authority was established in November 2010 to replace the Electricity Commission and its publication explains how the market works.- Overview :Until 1987,... - PhilippinesPhilippinesThe Philippines , officially known as the Republic of the Philippines , is a country in Southeast Asia in the western Pacific Ocean. To its north across the Luzon Strait lies Taiwan. West across the South China Sea sits Vietnam...
- see Philippine Wholesale Electricity Spot Market - PortugalPortugalPortugal , officially the Portuguese Republic is a country situated in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula. Portugal is the westernmost country of Europe, and is bordered by the Atlantic Ocean to the West and South and by Spain to the North and East. The Atlantic archipelagos of the...
- see OMIP - Russian Federation - see Trade System Administrator (ATS)
- SingaporeSingaporeSingapore , officially the Republic of Singapore, is a Southeast Asian city-state off the southern tip of the Malay Peninsula, north of the equator. An island country made up of 63 islands, it is separated from Malaysia by the Straits of Johor to its north and from Indonesia's Riau Islands by the...
- see Energy Market Authority, Singapore and Energy Market Company (EMC) - SpainSpainSpain , officially the Kingdom of Spain languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Spain's official name is as follows:;;;;;;), is a country and member state of the European Union located in southwestern Europe on the Iberian Peninsula...
- see OMEL Electricity Market - USAUnited StatesThe United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
(summarized here)- PJMPJM InterconnectionPJM Interconnection LLC is a Regional Transmission Organization which is part of the Eastern Interconnection grid operating an electric transmission system serving all or parts of Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee,...
http://www.pjm.com/ - ERCOT Market,
- New York Market,
- Midwest Market,
- California ISO,
- New England Market
- PJM
Retail electricity market
A retail electricity market exists when end-use customers can choose their supplier from competing electricity retailersElectricity retailing
Electricity retailing is the final process in the delivery of electricity from generation to the consumer. The other main processes are transmission and distribution.- Beginnings :...
; one term used in the United States for this type of consumer choice is 'energy choice'. A separate issue for electricity markets is whether or not consumers face real-time pricing (prices based on the variable wholesale price) or a price that is set in some other way, such as average annual costs. In many markets, consumers do not pay based on the real-time price, and hence have no incentive to reduce demand at times of high (wholesale) prices or to shift their demand to other periods. Demand response
Demand response
In electricity grids, demand response is similar to dynamic demand mechanisms to manage customer consumption of electricity in response to supply conditions, for example, having electricity customers reduce their consumption at critical times or in response to market prices...
may use pricing mechanisms or technical solutions to reduce peak demand.
Generally, electricity retail reform follows from electricity wholesale reform. However, it is possible to have a single electricity generation company and still have retail competition. If a wholesale price can be established at a node on the transmission grid
Electric power transmission
Electric-power transmission is the bulk transfer of electrical energy, from generating power plants to Electrical substations located near demand centers...
and the electricity quantities at that node can be reconciled, competition for retail customers within the distribution
Electricity distribution
File:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg|thumb|380px|right|Simplified diagram of AC electricity distribution from generation stations to consumers...
system beyond the node is possible. In the German market, for example, large, vertically integrated utilities compete with one another for customers on a more or less open grid.
Although market structures vary, there are some common functions that an electricity retailer has to be able to perform, or enter into a contract for, in order to compete effectively. Failure or incompetence in the execution of one or more of the following has led to some dramatic financial disasters:
- BillingInvoiceAn invoice or bill is a commercial document issued by a seller to the buyer, indicating the products, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services the seller has provided the buyer. An invoice indicates the buyer must pay the seller, according to the payment terms...
- Credit control
- Customer management via an efficient call centreCall centreA call centre or call center is a centralised office used for the purpose of receiving and transmitting a large volume of requests by telephone. A call centre is operated by a company to administer incoming product support or information inquiries from consumers. Outgoing calls for telemarketing,...
- DistributionElectricity distributionFile:Electricity grid simple- North America.svg|thumb|380px|right|Simplified diagram of AC electricity distribution from generation stations to consumers...
use-of-system contract - Reconciliation agreement
- "Pool" or "spot market" purchase agreement
- HedgeHedge (finance)A hedge is an investment position intended to offset potential losses that may be incurred by a companion investment.A hedge can be constructed from many types of financial instruments, including stocks, exchange-traded funds, insurance, forward contracts, swaps, options, many types of...
contracts - contracts for differences to manage "spot price" risk
The two main areas of weakness have been risk management
Risk management
Risk management is the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks followed by coordinated and economical application of resources to minimize, monitor, and control the probability and/or impact of unfortunate events or to maximize the realization of opportunities...
and billing
Invoice
An invoice or bill is a commercial document issued by a seller to the buyer, indicating the products, quantities, and agreed prices for products or services the seller has provided the buyer. An invoice indicates the buyer must pay the seller, according to the payment terms...
. In the USA in 2001, California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
's flawed regulation
Regulation
Regulation is administrative legislation that constitutes or constrains rights and allocates responsibilities. It can be distinguished from primary legislation on the one hand and judge-made law on the other...
of retail competition led to the California electricity crisis
California electricity crisis
The California electricity crisis, also known as the Western U.S. Energy Crisis of 2000 and 2001 was a situation in which California had a shortage of electricity caused by market manipulations and illegal shutdowns of pipelines by Texas energy consortiums...
and left incumbent retailers subject to high spot prices but without the ability to hedge against these (see Manifesto on The Californian Electricity Crisis). In the UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
a retailer, Independent Energy, with a large customer base went bust when it could not collect the money due from customers.
New technology
Event-driven SOA
Event-driven SOA is a form of service-oriented architecture , combining the intelligence and proactiveness of event-driven architecture with the organizational capabilities found in service offerings...
is available and has been piloted by the US Department of Energy that may be better suited to real-time market pricing. A potential use of event-driven SOA
Event-driven SOA
Event-driven SOA is a form of service-oriented architecture , combining the intelligence and proactiveness of event-driven architecture with the organizational capabilities found in service offerings...
could be a virtual electricity market where home clothes dryers can bid on the price of the electricity they use in a real-time market pricing system. The real-time market price and control system could turn home electricity
Electricity
Electricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
customers into active participants in managing the power grid and their monthly utility bills. Customers can set limits on how much they would pay for electricity to run a clothes dryer, for example, and electricity providers willing to transmit power at that price would be alerted over the grid and could sell the electricity to the dryer.
On one side, consumer devices can bid for power based on how much the owner of the device were willing to pay, set ahead of time by the consumer. On the other side, suppliers can enter bids automatically from their electricity generators, based on how much it would cost to start up and run the generators. Further, the electricity suppliers could perform real-time market analysis
Market analysis
A market analysis studies the attractiveness and the dynamics of a special market within a special industry. It is part of the industry analysis and this in turn of the global environmental analysis. Through all these analyses the chances, strengths, weaknesses and risks of a company can be...
to determine return-on-investment
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
for optimizing profitability or reducing end-user cost of goods
Cost of goods sold
Cost of goods sold refers to the inventory costs of those goods a business has sold during a particular period. Costs are associated with particular goods using one of several formulas, including specific identification, first-in first-out , or average cost...
.
Event-driven SOA
Event-driven SOA
Event-driven SOA is a form of service-oriented architecture , combining the intelligence and proactiveness of event-driven architecture with the organizational capabilities found in service offerings...
software could allow homeowners to customize many different types of electricity devices found within their home to a desired level of comfort or economy. The event-driven software could also automatically respond to changing electricity prices, in as little as five-minute intervals. For example, to reduce the home owner's electricity usage in peak periods (when electricity is most expensive), the software could automatically lower the target temperature of the thermostat on the central heating system (in winter) or raise the target temperature of the thermostat on the central cooling system (in summer).
Electricity market experience
In the main, experience in the introduction of wholesale and retail competition has been mixed. Many regional markets have achieved some success and the ongoing trend continues to be towards deregulation and introduction of competition. However in 2000/2001 major failures such as the California electricity crisisCalifornia electricity crisis
The California electricity crisis, also known as the Western U.S. Energy Crisis of 2000 and 2001 was a situation in which California had a shortage of electricity caused by market manipulations and illegal shutdowns of pipelines by Texas energy consortiums...
and the Enron debacle
Timeline of the Enron scandal
-1985:Kenneth Lay seized control in 1985 of HNG/Internorth created by the merger of Houston Natural Gas and the much larger and more diversified InterNorth, which combined four natural gas pipeline companies, Northern Natural Gas, Transwestern Pipeline, Florida Gas Transmission, and Houston...
caused a slow down in the pace of change and in some regions an increase in market regulation and reduction in competition. However, this trend is widely regarded as a temporary one against the longer term trend towards more open and competitive markets.
Notwithstanding the favorable light in which market solutions are viewed conceptually, the "missing money" problem has to date proved intractable. If electricity prices were to move to the levels needed to incent new merchant (i.e., market-based) transmission and generation, the costs to consumers would be politically difficult.
The increase in annual costs to consumers in New England
New England
New England is a region in the northeastern corner of the United States consisting of the six states of Maine, New Hampshire, Vermont, Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and Connecticut...
alone were calculated at $3 billion during the recent FERC hearings on the NEPOOL market structure. Several mechanisms that are intended to incent new investment where it is most needed by offering enhanced capacity payments (but only in zones where generation is projected to be short) have been proposed for NEPOOL, PJM
PJM Interconnection
PJM Interconnection LLC is a Regional Transmission Organization which is part of the Eastern Interconnection grid operating an electric transmission system serving all or parts of Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Kentucky, Maryland, Michigan, New Jersey, North Carolina, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Tennessee,...
and NYPOOL, and go under the generic heading of "locational capacity" or LICAP (the PJM version currently [May 2006] under FERC review is called the "Reliability Pricing Model", or "RPM"). There is substantial doubt as to whether any of these mechanisms will in fact incent new investment, given the regulatory risk and chronic instability of the market rules in US systems, and there are substantial concerns that the result will instead be to increase revenues to incumbent generators, and costs to consumers, in the constrained areas.
See also
- Availability based tariffAvailability based tariffAvailability Based Tariff is a frequency based pricing mechanism for electric power. The ABT falls under electricity market mechanisms to charge and regulate power to achieve short term and long term network stability as well as incentives and dis-incentives to market participants against...
- CEGBCEGBThe Central Electricity Generating Board was the cornerstone of the British electricity industry for almost 40 years; from 1957, to privatisation in the 1990s....
- ElectricityElectricityElectricity is a general term encompassing a variety of phenomena resulting from the presence and flow of electric charge. These include many easily recognizable phenomena, such as lightning, static electricity, and the flow of electrical current in an electrical wire...
- Electrical utility
- Energy demand managementEnergy demand managementEnergy demand management, also known as demand side management , is the modification of consumer demand for energy through various methods such as financial incentives and education...
- Distributed generationDistributed generationDistributed generation, also called on-site generation, dispersed generation, embedded generation, decentralized generation, decentralized energy or distributed energy, generates electricity from many small energy sources....
- Electricity generationElectricity generationElectricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
- Electricity liberalizationElectricity liberalizationElectricity liberalization refers to the liberalization of electricity markets. As electricity supply is a natural monopoly, this entails complex and costly systems of regulation to enforce a system of competition....
- Electricity transmission
- Electricity tariffElectricity tariffElectricity pricing varies widely from country to country, and may vary signicantly from locality to locality within a particular country. There are many reasons that account for these differences in price...
- Future energy development
- Independent System Operator
- Load ProfileLoad profileIn electrical engineering, a load profile is a graph of the variation in the electrical load versus time. A load profile will vary according to customer type , temperature and holiday seasons....
- National Grid (UK)
- Negawatt PowerNegawatt powerNegawatt power is a theoretical unit of power representing an amount of energy saved. The energy saved is a direct result of energy conservation or increased efficiency. The term was coined by the Chief Scientist of the Rocky Mountain Institute and environmentalist, Amory Lovins in 1989. Negawatts...
- NERC TagNERC TagA NERC Tag, also commonly referred to as an E-Tag, represents a transaction on the North American bulk electricity market scheduled to flow within, between or across electric utility company territories...
- North American Electric Reliability Corporation
- Power qualityPower qualityPower quality is the set of limits of electrical properties that allows electrical systems to function in their intended manner without significant loss of performance or life. The term is used to describe electric power that drives an electrical load and the load's ability to function properly...
- Tres Amigas SuperStation
- Voltage dropVoltage dropVoltage drop is the reduction in voltage in the passive elements of an electrical circuit. Voltage drops across conductors, contacts, connectors and source internal resistances are undesired as they reduce the supplied voltage while voltage drops across loads and other electrical and electronic...
- Vehicle-to-gridVehicle-to-gridVehicle-to-grid describes a system in which plug-in electric vehicles, such as electric cars and plug-in hybrids , communicate with the power grid to sell demand response services by either delivering electricity into the grid or by throttling their charging rate.Vehicle-to-grid can be used with...
- Cost of electricity by sourceCost of electricity by sourceThe cost of electricity generated by different sources measures the cost of generating electricity including initial capital, return on investment, as well as the costs of continuous operation, fuel, and maintenance...
Further reading
- A 2006 World Bank report on Water, Electricity, and the effect of utility subsidies on the poor
- Financial Transmission Rights and Transmission Congestion Contracts http://www.financialtransmissionrights.com/
- Insight into the historic performance of the Reserve Capacity Mechanism - Independent Market Operator of Western Australia
Reserve Capacity Mechanism Review Report
- The EU energy sector inquiry that shows up current impediments for competition in the electricity industry in Europe The EU energy sector inquiry - final report 10 January 2007
- Article by Severin Borenstein on the Trouble with Electricity Markets
- David Cay Johnston, "Competitive Era Fails to Shrink Electric Bills", NYT October 15, 2006
- Lewis Evans, Richard B Meade, "Alternating Currents or Counter-Revolution? Contemporary Electricity Reform in New Zealand", Victoria University Press, 2006.
- Freedom Energy Logistics http://felpower.com
- Czech electricity market overview - Year report on the electricity market (technical report) and Expected balance report http://www.ote-cr.cz/about/anual-report

