
Electrical impedance tomography
Encyclopedia
Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) is a medical imaging
technique in which an image of the conductivity or permittivity of part of the body is inferred from surface electrical measurements. Typically, conducting electrodes are attached to the skin of the subject and small alternating currents are applied to some or all of the electrodes. The resulting electrical potentials are measured, and the process may be repeated for numerous different configurations of applied current.
Proposed applications include monitoring of lung
function, detection of cancer
in the skin
and breast
and location of epileptic foci
. Until recently, all applications have been considered experimental. However in 2011 the first commercial EIT device for lung function monitoring in intensive care patients was introduced.
The invention of EIT as a medical imaging technique is usually attributed to John G. Webster
and a publication in 1978, although the first practical realisation of a medical EIT system was detailed in 1984 due to the work of David C. Barber and Brian H. Brown.
Mathematically, the problem of recovering conductivity from surface measurements of current and potential is a non-linear inverse problem
and is severely ill-posed. The mathematical formulation of the problem is due to Alberto Calderón
, and in the mathematical literature of inverse problems it is often referred to as "Calderón's Inverse Problem" or the "Calderón Problem". There is extensive mathematical research on the problem of uniqueness of solution and numerical algorithms for this problem.
In geophysics
a similar technique (called electrical resistivity tomography
) is used using electrodes on the surface of the earth or in bore holes to locate resistivity anomalies, and in industrial process monitoring the arrays of electrodes are used for example to monitor mixtures of conductive fluids in vessels or pipes. The method is used in industrial process imaging
for imaging conductive fluids. In that context the technique is usually called electrical resistance tomography (note the slight contrast to the name used in geophysics). Metal electrodes are generally in direct contact with the fluid but electronics and reconstruction techniques are broadly similar to the medical case. In geophysics, the idea dates from the 1930s.
The currents used are relatively small, and certainly below the threshold at which they would cause stimulation of nerve
s. The frequency of the alternating current is sufficiently high not to give rise to electrolytic effects in the body and the Ohmic power dissipated is sufficiently small and diffused over the body to be easily handled by the body's thermoregulatory system.
The current is applied using current source
s, either a single current source switched between electrodes using a multiplexor or a system of
Voltage-to-current converters, one for each electrode, each controlled by a digital to analog converter. The measurements again may be taken either by a single voltage measurement circuit multiplexed over the electrodes or a separate circuit for each electrode. Earlier systems typically used an analog demodulation circuit to convert the alternating voltage to a direct current level then an analog to digital converter. Many recent systems convert the alternating signal directly, the demodulation then being performed digitally. Many EIT systems are capable of working at several frequencies and can measure both the magnitude and phase of the voltage.
The voltages measured are then passed to a computer to perform the reconstruction and display of the image. If images are required in real time a typical approach is the application of some form of regularized
inverse of a linearization of the forward problem. In most practical systems used in a medical setting a 'difference image' is formed. That is, the differences in voltage between two time points is left-multiplied by the regularized inverse to produce an approximate difference between the permittivity and conductivity images. Another approach is to construct a finite element
model of the body and adjust the conductivities (for example using a variant of Levenburg–Marquart method) to fit the measured data. This is more challenging as it requires an accurate body shape and the exact position of the electrodes.
The open source project EIDORS
provides a suite of programs (written in Matlab
/ Octave) for data reconstruction and display under the GNU GPL license.
. Such ventilation can often result in Ventilator-associated lung injury
. EIT can resolve the changes in the distribution of lung volumes between dependent and non-dependent lung regions as ventilator parameters are changed. Thus, EIT measurements may be used to control the specific ventilator settings to maintain lung protective ventilation for each patient.
The above images are from the EIT group at Oxford Brookes University
and depict an early attempt at three dimensional EIT imaging of the chest using the OXBACT3 EIT system. The reconstructed image is a time average and shows lungs as low conductivity regions. Although an accurate chest shape was used only a 2D reconstruction algorithm was used resulting in a distorted image. The results of a similar chest study have been published.
Most EIT studies have focused on regional lung function monitoring using the information determined by functional EIT (f-EIT). However absolute EIT (a-EIT) also has the potential to become a clinically useful tool for Lung imaging, as this approach would allow one to directly distinguish between lung conditions which result from regions with lower resistivity (e.g. hemothorax, pleural effusion, atelectasis and lung edema) and those with higher resistivity (e.g. pneumothorax, emphysema).
The reconstruction of absolute impedance images requires that the exact dimensions, the shape of the body and the precise location of the electrodes, be taken into account, as simplified assumptions would lead to major reconstruction artifacts. While initial studies assessing aspects of a-EIT have already been published, as of today this area of research has not yet reached the level of maturity which would make it suitable for clinical use.
In contrast, functional EIT determines relative impedance changes that may be caused by either ventilation or changes of end-expiratory lung volume. These relative changes are referred to a baseline level, which is typically defined by the intra-thoracic impedance distribution at the end of expiration.
Functional EIT images can be generated continuously, directly at the bedside. These attributes make regional lung function monitoring particularly useful whenever there is a need to improve oxygenation or CO2 elimination and when therapy changes are intended to achieve a more homogenous gas distribution in mechanically ventilated patients. EIT lung function imaging can resolve the changes in the regional distribution of lung volumes between e.g. dependent and non-dependent lung regions as ventilator parameters are changed. Thus, EIT measurements may be used to control the specific ventilator settings to maintain lung protective ventilation for each patient.
and magnetic resonance imaging
(MRI) for breast cancer detection. The low specificity of mammography and of MRI result in a relatively high rate of false positive screenings, with high distress for the patient and cost for the healthcare structure. These shortcomings and concerns related to the use of ionizing radiation, for mammography, and with the nephrotoxicity
of Gadolinium
, the contrast agent used in breast MRI, make the development of alternative techniques highly desirable.
Literature shows that the electrical properties differ between normal and malignant
breast tissues, setting the stage for cancer detection through determination of electrical properties.
A successful commercial development of non-tomographic electrical impedance imaging is the T-Scan device which has been demonstrated to improve sensitivity and specificity when used as an adjunct to screening mammography. A report to the United States Food and Drug Administration
(FDA) describes a study involving 504 subjects where the sensitivity of mammography was 82%, 62% for the T-Scan alone, and 88% for the two combined. The specificity was 39% for mammography, 47% for the T-Scan alone, and 51% for the two combined.
Several research groups are across the world are actively developing the technique.
and haemorrhage, epileptic foci localization, together with research into normal brain function and neuronal activity.
In this use EIT depends upon applying low frequency currents above the skull that are around <100 Hz since during neuronal rest at this frequency these currents remain in the extracellular
space unable enter into the intracellular space within neurons. However when a neuron makes an action potential
or depolarization
, the resistance of its membrane preventing this reduces by a factor of 80. When this happens across large numbers of neurons a resistivity change is made of about 0.06–1.7%. This resistivity change provides a means of detecting coherent neuronal activity across large numbers of neurons and so the tomographic imaging of neural activity in the brain.
Unfortunately while such changes are detectable "they are just too small to support reliable production of images." The prospects of using this technique for imaging will depend upon improved signal processing or recording.
who distribute a Sheffield Mark 3.5 system. Other manufactures include Dräger Medical, CareFusion
, a respiratory monitoring company who distribute Goe MF II system that was developed at the University of Göttingen. Impedance Medical Technologies
who manufacture systems based on designs by the Research Institute of Radioengineering and Electronics of the Russian Academy of Science http://www.cplire.ru/html/cplitom.html in Moscow, aimed especially at breast cancer detection. Such systems typically comply with medical safety legislation and are being used by research groups in hospitals, notably in intensive care
for monitoring ventilation
. An EIT device for lung function monitoring that is designed for everyday clinical use in the critical care environment has been made available by Dräger Medical in 2011
Medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process used to create images of the human body for clinical purposes or medical science...
technique in which an image of the conductivity or permittivity of part of the body is inferred from surface electrical measurements. Typically, conducting electrodes are attached to the skin of the subject and small alternating currents are applied to some or all of the electrodes. The resulting electrical potentials are measured, and the process may be repeated for numerous different configurations of applied current.
Proposed applications include monitoring of lung
Lung
The lung is the essential respiration organ in many air-breathing animals, including most tetrapods, a few fish and a few snails. In mammals and the more complex life forms, the two lungs are located near the backbone on either side of the heart...
function, detection of cancer
Cancer
Cancer , known medically as a malignant neoplasm, is a large group of different diseases, all involving unregulated cell growth. In cancer, cells divide and grow uncontrollably, forming malignant tumors, and invade nearby parts of the body. The cancer may also spread to more distant parts of the...
in the skin
Skin
-Dermis:The dermis is the layer of skin beneath the epidermis that consists of connective tissue and cushions the body from stress and strain. The dermis is tightly connected to the epidermis by a basement membrane. It also harbors many Mechanoreceptors that provide the sense of touch and heat...
and breast
Breast
The breast is the upper ventral region of the torso of a primate, in left and right sides, which in a female contains the mammary gland that secretes milk used to feed infants.Both men and women develop breasts from the same embryological tissues...
and location of epileptic foci
Epilepsy
Epilepsy is a common chronic neurological disorder characterized by seizures. These seizures are transient signs and/or symptoms of abnormal, excessive or hypersynchronous neuronal activity in the brain.About 50 million people worldwide have epilepsy, and nearly two out of every three new cases...
. Until recently, all applications have been considered experimental. However in 2011 the first commercial EIT device for lung function monitoring in intensive care patients was introduced.
The invention of EIT as a medical imaging technique is usually attributed to John G. Webster
John G. Webster
John G. Webster is an American electrical engineer and a founding pioneer in the field of biomedical engineering.Webster attained his Ph.D. from the University of Rochester in 1967....
and a publication in 1978, although the first practical realisation of a medical EIT system was detailed in 1984 due to the work of David C. Barber and Brian H. Brown.
Mathematically, the problem of recovering conductivity from surface measurements of current and potential is a non-linear inverse problem
Inverse problem
An inverse problem is a general framework that is used to convert observed measurements into information about a physical object or system that we are interested in...
and is severely ill-posed. The mathematical formulation of the problem is due to Alberto Calderón
Alberto Calderón
Alberto Pedro Calderón was an Argentine mathematician best known for his work on the theory of partial differential equations and singular integral operators, and widely considered as one of the 20th century's most important mathematicians...
, and in the mathematical literature of inverse problems it is often referred to as "Calderón's Inverse Problem" or the "Calderón Problem". There is extensive mathematical research on the problem of uniqueness of solution and numerical algorithms for this problem.
In geophysics
Geophysics
Geophysics is the physics of the Earth and its environment in space; also the study of the Earth using quantitative physical methods. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and...
a similar technique (called electrical resistivity tomography
Electrical resistivity tomography
Electrical resistivity tomography or electrical resistivity imaging is a geophysical technique for imaging sub-surface structures from electrical measurements made at the surface, or by electrodes in one or more boreholes. It is closely related to the medical imaging technique electrical...
) is used using electrodes on the surface of the earth or in bore holes to locate resistivity anomalies, and in industrial process monitoring the arrays of electrodes are used for example to monitor mixtures of conductive fluids in vessels or pipes. The method is used in industrial process imaging
Industrial process imaging
Industrial Process Imaging, or Industrial Process Tomography or Process Tomography are methods use to form an image of a cross section of vessel or pipe in a chemical engineering or mineral processing, or petroleum extraction or refining plant....
for imaging conductive fluids. In that context the technique is usually called electrical resistance tomography (note the slight contrast to the name used in geophysics). Metal electrodes are generally in direct contact with the fluid but electronics and reconstruction techniques are broadly similar to the medical case. In geophysics, the idea dates from the 1930s.
Theory
In biological tissue the electrical conductivity and permittivity varies between tissue types likewise depending on temperature and physiological factors. For example lungs are less conductive when the alveoli is filled with air. In EIT adhesive electrodes applied to the skin and an electric current, typically a few milli-Amperes of alternating current at a frequency of 10–100 kHz, is applied across two or more electrodes. Other electrodes are used to measure the resulting voltage. This is repeated for numerous "stimulation patterns", such as successive pairs of adjacent electrodes.The currents used are relatively small, and certainly below the threshold at which they would cause stimulation of nerve
Nerve
A peripheral nerve, or simply nerve, is an enclosed, cable-like bundle of peripheral axons . A nerve provides a common pathway for the electrochemical nerve impulses that are transmitted along each of the axons. Nerves are found only in the peripheral nervous system...
s. The frequency of the alternating current is sufficiently high not to give rise to electrolytic effects in the body and the Ohmic power dissipated is sufficiently small and diffused over the body to be easily handled by the body's thermoregulatory system.
The current is applied using current source
Current source
A current source is an electrical or electronic device that delivers or absorbs electric current. A current source is the dual of a voltage source. The term constant-current sink is sometimes used for sources fed from a negative voltage supply...
s, either a single current source switched between electrodes using a multiplexor or a system of
Voltage-to-current converters, one for each electrode, each controlled by a digital to analog converter. The measurements again may be taken either by a single voltage measurement circuit multiplexed over the electrodes or a separate circuit for each electrode. Earlier systems typically used an analog demodulation circuit to convert the alternating voltage to a direct current level then an analog to digital converter. Many recent systems convert the alternating signal directly, the demodulation then being performed digitally. Many EIT systems are capable of working at several frequencies and can measure both the magnitude and phase of the voltage.
The voltages measured are then passed to a computer to perform the reconstruction and display of the image. If images are required in real time a typical approach is the application of some form of regularized
Tikhonov regularization
Tikhonov regularization, named for Andrey Tikhonov, is the most commonly used method of regularization of ill-posed problems. In statistics, the method is known as ridge regression, and, with multiple independent discoveries, it is also variously known as the Tikhonov-Miller method, the...
inverse of a linearization of the forward problem. In most practical systems used in a medical setting a 'difference image' is formed. That is, the differences in voltage between two time points is left-multiplied by the regularized inverse to produce an approximate difference between the permittivity and conductivity images. Another approach is to construct a finite element
Finite element method
The finite element method is a numerical technique for finding approximate solutions of partial differential equations as well as integral equations...
model of the body and adjust the conductivities (for example using a variant of Levenburg–Marquart method) to fit the measured data. This is more challenging as it requires an accurate body shape and the exact position of the electrodes.
The open source project EIDORS
provides a suite of programs (written in Matlab
MATLAB
MATLAB is a numerical computing environment and fourth-generation programming language. Developed by MathWorks, MATLAB allows matrix manipulations, plotting of functions and data, implementation of algorithms, creation of user interfaces, and interfacing with programs written in other languages,...
/ Octave) for data reconstruction and display under the GNU GPL license.
Lung imaging
EIT is useful for monitoring patient lungs because the air has a large conductivity contrast to the other tissues in the thorax. The most promising clinical application of lung EIT measurements is for Lung function monitoring of patients being treated with Mechanical ventilationMechanical ventilation
In medicine, mechanical ventilation is a method to mechanically assist or replace spontaneous breathing. This may involve a machine called a ventilator or the breathing may be assisted by a physician, respiratory therapist or other suitable person compressing a bag or set of bellows...
. Such ventilation can often result in Ventilator-associated lung injury
Ventilator-associated lung injury
Ventilator-associated lung injury is an acute lung injury that develops during mechanical ventilation and is termed ventilator-induced lung injury if it can be proven that the mechanical ventilation caused the acute lung injury. In contrast, ventilator-associated lung injury exists if the cause...
. EIT can resolve the changes in the distribution of lung volumes between dependent and non-dependent lung regions as ventilator parameters are changed. Thus, EIT measurements may be used to control the specific ventilator settings to maintain lung protective ventilation for each patient.
 |
 |
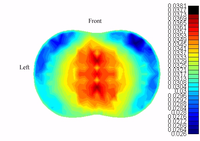 |
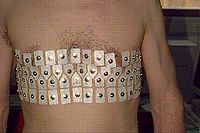
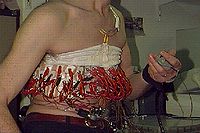
The above images are from the EIT group at Oxford Brookes University
Oxford Brookes University
Oxford Brookes University is a new university in Oxford, England. It was named to honour the school's founding principal, John Brookes. It has been ranked as the best new university by the Sunday Times University Guide 10 years in a row...
and depict an early attempt at three dimensional EIT imaging of the chest using the OXBACT3 EIT system. The reconstructed image is a time average and shows lungs as low conductivity regions. Although an accurate chest shape was used only a 2D reconstruction algorithm was used resulting in a distorted image. The results of a similar chest study have been published.
Most EIT studies have focused on regional lung function monitoring using the information determined by functional EIT (f-EIT). However absolute EIT (a-EIT) also has the potential to become a clinically useful tool for Lung imaging, as this approach would allow one to directly distinguish between lung conditions which result from regions with lower resistivity (e.g. hemothorax, pleural effusion, atelectasis and lung edema) and those with higher resistivity (e.g. pneumothorax, emphysema).
The reconstruction of absolute impedance images requires that the exact dimensions, the shape of the body and the precise location of the electrodes, be taken into account, as simplified assumptions would lead to major reconstruction artifacts. While initial studies assessing aspects of a-EIT have already been published, as of today this area of research has not yet reached the level of maturity which would make it suitable for clinical use.
In contrast, functional EIT determines relative impedance changes that may be caused by either ventilation or changes of end-expiratory lung volume. These relative changes are referred to a baseline level, which is typically defined by the intra-thoracic impedance distribution at the end of expiration.
Functional EIT images can be generated continuously, directly at the bedside. These attributes make regional lung function monitoring particularly useful whenever there is a need to improve oxygenation or CO2 elimination and when therapy changes are intended to achieve a more homogenous gas distribution in mechanically ventilated patients. EIT lung function imaging can resolve the changes in the regional distribution of lung volumes between e.g. dependent and non-dependent lung regions as ventilator parameters are changed. Thus, EIT measurements may be used to control the specific ventilator settings to maintain lung protective ventilation for each patient.
Breast imaging
EIT is being investigated in the field of breast imaging as an alternative/complementary technique to mammographyMammography
Mammography is the process of using low-energy-X-rays to examine the human breast and is used as a diagnostic and a screening tool....
and magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging , nuclear magnetic resonance imaging , or magnetic resonance tomography is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to visualize detailed internal structures...
(MRI) for breast cancer detection. The low specificity of mammography and of MRI result in a relatively high rate of false positive screenings, with high distress for the patient and cost for the healthcare structure. These shortcomings and concerns related to the use of ionizing radiation, for mammography, and with the nephrotoxicity
Nephrotoxicity
Nephrotoxicity is a poisonous effect of some substances, both toxic chemicals and medication, on the kidneys. There are various forms of toxicity. Nephrotoxicity should not be confused with the fact that some medications have a predominantly renal excretion and need their dose adjusted for the...
of Gadolinium
Gadolinium
Gadolinium is a chemical element with the symbol Gd and atomic number 64. It is a silvery-white, malleable and ductile rare-earth metal. It is found in nature only in combined form. Gadolinium was first detected spectroscopically in 1880 by de Marignac who separated its oxide and is credited with...
, the contrast agent used in breast MRI, make the development of alternative techniques highly desirable.
Literature shows that the electrical properties differ between normal and malignant
breast tissues, setting the stage for cancer detection through determination of electrical properties.
A successful commercial development of non-tomographic electrical impedance imaging is the T-Scan device which has been demonstrated to improve sensitivity and specificity when used as an adjunct to screening mammography. A report to the United States Food and Drug Administration
Food and Drug Administration
The Food and Drug Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, one of the United States federal executive departments...
(FDA) describes a study involving 504 subjects where the sensitivity of mammography was 82%, 62% for the T-Scan alone, and 88% for the two combined. The specificity was 39% for mammography, 47% for the T-Scan alone, and 51% for the two combined.
Several research groups are across the world are actively developing the technique.
Brain imaging
EIT has been suggested as a basis for brain imaging to enable the detection and monitoring of cerebral ischemiaCerebral ischemia
Brain ischemia, also known as cerebral ischemia, is a condition in which there is insufficient blood flow to the brain to meet metabolic demand. This leads to poor oxygen supply or cerebral hypoxia and thus to the death of brain tissue or cerebral infarction / ischemic stroke...
and haemorrhage, epileptic foci localization, together with research into normal brain function and neuronal activity.
In this use EIT depends upon applying low frequency currents above the skull that are around <100 Hz since during neuronal rest at this frequency these currents remain in the extracellular
Extracellular
In cell biology, molecular biology and related fields, the word extracellular means "outside the cell". This space is usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid...
space unable enter into the intracellular space within neurons. However when a neuron makes an action potential
Action potential
In physiology, an action potential is a short-lasting event in which the electrical membrane potential of a cell rapidly rises and falls, following a consistent trajectory. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, called excitable cells, which include neurons, muscle cells, and...
or depolarization
Depolarization
In biology, depolarization is a change in a cell's membrane potential, making it more positive, or less negative. In neurons and some other cells, a large enough depolarization may result in an action potential...
, the resistance of its membrane preventing this reduces by a factor of 80. When this happens across large numbers of neurons a resistivity change is made of about 0.06–1.7%. This resistivity change provides a means of detecting coherent neuronal activity across large numbers of neurons and so the tomographic imaging of neural activity in the brain.
Unfortunately while such changes are detectable "they are just too small to support reliable production of images." The prospects of using this technique for imaging will depend upon improved signal processing or recording.
Commercial systems
Although medical EIT systems are not widely used several medical equipment manufactures now supply commercial versions of systems developed by university research groups. The first such system is produced by Maltron Internationalwho distribute a Sheffield Mark 3.5 system. Other manufactures include Dräger Medical, CareFusion
CareFusion
CareFusion is a global, medical technology corporation serving the health care industry. The company specializes in two areas: reducing medication errors and helping prevent health care-associated infections...
, a respiratory monitoring company who distribute Goe MF II system that was developed at the University of Göttingen. Impedance Medical Technologies
who manufacture systems based on designs by the Research Institute of Radioengineering and Electronics of the Russian Academy of Science http://www.cplire.ru/html/cplitom.html in Moscow, aimed especially at breast cancer detection. Such systems typically comply with medical safety legislation and are being used by research groups in hospitals, notably in intensive care
Intensive care medicine
Intensive-care medicine or critical-care medicine is a branch of medicine concerned with the diagnosis and management of life threatening conditions requiring sophisticated organ support and invasive monitoring.- Overview :...
for monitoring ventilation
Medical ventilator
A medical ventilator can be defined as any machine designed to mechanically move breatheable air into and out of the lungs, to provide the mechanism of breathing for a patient who is physically unable to breathe, or breathing insufficiently....
. An EIT device for lung function monitoring that is designed for everyday clinical use in the critical care environment has been made available by Dräger Medical in 2011
See also
- BioimpedanceBioimpedanceIn biomedical engineering, bioimpedance is a term used to describe the response of a living organism to an externally applied electric current. It is a measure of the opposition to the flow of that electric current through the tissues, the opposite of electrical conductivity[1]...
- Electrical resistivity tomographyElectrical resistivity tomographyElectrical resistivity tomography or electrical resistivity imaging is a geophysical technique for imaging sub-surface structures from electrical measurements made at the surface, or by electrodes in one or more boreholes. It is closely related to the medical imaging technique electrical...
- Electrical capacitance tomographyElectrical capacitance tomographyElectrical capacitance tomography is a method for determination of the dielectric permittivity distribution in the interior of an object from external capacitance measurements. It is a close relative of electrical impedance tomography and is proposed as a method for industrial process monitoring,...
- Respiratory monitoringRespiratory monitoringMonitoring a patient's respiratory status usually takes place in a hospital setting and may be the primary purpose for a patient being observed or admitted to a medical setting....
External links
- EIT website University College London
- EIDORS - Electrical Impedance Tomography and Diffuse Optical Tomography Reconstruction Software at Sourceforge

