
Electrical efficiency
Encyclopedia
The efficiency of an entity (a device
, component
, or system
) in electronics
and electrical engineering
is defined as useful power output divided by the total electrical power consumed (a fractional expression
), typically denoted by the Greek letter small Eta (η).
Machine
A machine manages power to accomplish a task, examples include, a mechanical system, a computing system, an electronic system, and a molecular machine. In common usage, the meaning is that of a device having parts that perform or assist in performing any type of work...
, component
Electronic component
An electronic component is a basic electronic element and may be available in a discrete form having two or more electrical terminals . These are intended to be connected together, usually by soldering to a printed circuit board, in order to create an electronic circuit with a particular function...
, or system
System
System is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
) in electronics
Electronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
and electrical engineering
Electrical engineering
Electrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
is defined as useful power output divided by the total electrical power consumed (a fractional expression
Expression (mathematics)
In mathematics, an expression is a finite combination of symbols that is well-formed according to rules that depend on the context. Symbols can designate numbers , variables, operations, functions, and other mathematical symbols, as well as punctuation, symbols of grouping, and other syntactic...
), typically denoted by the Greek letter small Eta (η).
-

Efficiency of typical electrical devices
Efficiency should not be confused with effectivenessEffectivenessEffectiveness is the capability of producing a desired result. When something is deemed effective, it means it has an intended or expected outcome, or produces a deep, vivid impression.-Etymology:...
: a system that wastes most of its input power but produces exactly what it is meant to is effective but not efficient. The term "efficiency" makes sense only in reference to the wanted effect. A light bulb, for example, might have 2% efficiency at emitting light yet still be 98% efficient at heating a room (In practice it is nearly 100% efficient at heating a room because the light energy will also be converted to heat eventually, apart from the small fraction that leaves through the windows). An electronic amplifierElectronic amplifierAn electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude...
that delivers 10 watts of power to its load (e.g., a loudspeakerLoudspeakerA loudspeaker is an electroacoustic transducer that produces sound in response to an electrical audio signal input. Non-electrical loudspeakers were developed as accessories to telephone systems, but electronic amplification by vacuum tube made loudspeakers more generally useful...
), while drawing 20 watts of power from a power source is 50% efficient. (10/20 × 100% = 50%)
- Electric kettle: more than 90% (comparatively little heat energy is lost during the 2 to 3 minutes a kettle takes to boil water).
- A four-quadrant gateFour-quadrant gateA four-quadrant gate is a type of boom barrier gate protecting a grade crossing.It has a gate mechanism on both sides of the tracks for both directions of automotive traffic...
is highly effective, yet it has an electrical efficiency close to 0%. - An electric fire is 100% efficient in terms of converting electrical energy into the desired result, i.e., heating.
Efficiency of devices at point of maximum power transfer
As a result of the maximum power theoremMaximum power theoremIn electrical engineering, the maximum power transfer theorem states that, to obtain maximum external power from a source with a finite internal resistance, the resistance of the load must be equal to the resistance of the source as viewed from the output terminals...
, devices transfer maximum power to a load when running at 50% electrical efficiency. This occurs when the load resistance (of the device in question) is equal to the internal Thevenin equivalentThévenin's theoremIn circuit theory, Thévenin's theorem for linear electrical networks states that any combination of voltage sources, current sources, and resistors with two terminals is electrically equivalent to a single voltage source V and a single series resistor R. For single frequency AC systems the theorem...
resistance of the power source. This is valid only for non-reactive source and load impedances.
Efficiency of light bulbs
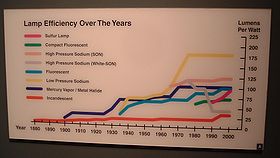
- Incandescent light bulbIncandescent light bulbThe incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe makes light by heating a metal filament wire to a high temperature until it glows. The hot filament is protected from air by a glass bulb that is filled with inert gas or evacuated. In a halogen lamp, a chemical process...
: about 2%. - Compact fluorescent lampCompact fluorescent lampA compact fluorescent lamp , also called compact fluorescent light, energy-saving light, and compact fluorescent tube, is a fluorescent lamp designed to replace an incandescent lamp; some types fit into light fixtures formerly used for incandescent lamps...
: about 7%-9%. - White light-emitting diodeLight-emitting diodeA light-emitting diode is a semiconductor light source. LEDs are used as indicator lamps in many devices and are increasingly used for other lighting...
(LED) about 4%-18%.
Discussion
High efficiency is useful in the designDesignDesign as a noun informally refers to a plan or convention for the construction of an object or a system while “to design” refers to making this plan...
of systemSystemSystem is a set of interacting or interdependent components forming an integrated whole....
s that can operate from batteriesBattery (electricity)An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
. Inefficiency has a cost (either the cost paid to the power company or the cost of the required power supplyPower supplyA power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
) to be weighed against the cost of attaining greater efficiency (choosing different components or redesigning the system). Also, any difference in the input and output power probably produces heat within the system (although noiseNoiseIn common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
and other mechanical vibrationOscillationOscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples include a swinging pendulum and AC power. The term vibration is sometimes used more narrowly to mean a mechanical oscillation but sometimes...
s involve at least theoretically separate and generally negligibleNegligibleNegligible refers to the quantities so small that they can be ignored when studying the larger effect. Although related to the more mathematical concepts of infinitesimal, the idea of negligibility is particularly useful in practical disciplines like physics, chemistry, mechanical and electronic...
inefficiencies), and that heat must be removed from the system if it is to remain within its operating temperatureOperating temperatureAn operating temperature is the temperature at which an electrical or mechanical device operates. The device will operate effectively within a specified temperature range which varies based on the device function and application context, and ranges from the minimum operating temperature to the...
range. If the system is in a climate-controlled environment (e.g., a home or office), heat generated may reduce heating costs or increase ventilation and air conditioning costs.
Implications in discussion of power generating equipment
There are two different definitions of caloric value, and the difference between the HCV and LCV definitions causes much confusion when quoters fail to state the convention being used as there is typically a 10% difference between the two methods for a power plant on natural gas.
See also
- BatteryBattery (electricity)An electrical battery is one or more electrochemical cells that convert stored chemical energy into electrical energy. Since the invention of the first battery in 1800 by Alessandro Volta and especially since the technically improved Daniell cell in 1836, batteries have become a common power...
- Eco-actionEco-actionAn eco-action is any action or activity within a program that is intended to have a positive impact on the environment. For this reason it is often used as a synonym for environmental action....
- Electronic amplifierElectronic amplifierAn electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal.It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude...
- List of electronics topics
- Maximum Power TheoremMaximum power theoremIn electrical engineering, the maximum power transfer theorem states that, to obtain maximum external power from a source with a finite internal resistance, the resistance of the load must be equal to the resistance of the source as viewed from the output terminals...
- Micro-SustainabilityMicro-SustainabilityMicro-sustainability focuses on the small environmental actions that when calculated collectively result in a large environmental impact. Micro-sustainability centers on individual efforts, behavior modification and creating attitudinal changes, which result in an environmentally conscious...
- Negawatt powerNegawatt powerNegawatt power is a theoretical unit of power representing an amount of energy saved. The energy saved is a direct result of energy conservation or increased efficiency. The term was coined by the Chief Scientist of the Rocky Mountain Institute and environmentalist, Amory Lovins in 1989. Negawatts...
- Standby powerStandby powerStandby power, also called vampire power, vampire draw, phantom load, or leaking electricity , refers to the electric power consumed by electronic and electrical appliances while they are switched off Standby power, also called vampire power, vampire draw, phantom load, or leaking electricity...
Other measures of efficiency:- Thermal efficiencyThermal efficiencyIn thermodynamics, the thermal efficiency is a dimensionless performance measure of a device that uses thermal energy, such as an internal combustion engine, a boiler, a furnace, or a refrigerator for example.-Overview:...
- Mechanical efficiencyMechanical efficiencyMechanical efficiency measures the effectiveness of a machine in transforming the energy and power that is input to the device into an output force and movement...
- Performance per wattPerformance per wattIn computing, performance per watt is a measure of the energy efficiency of a particular computer architecture or computer hardware. Literally, it measures the rate of computation that can be delivered by a computer for every watt of power consumed....
Efficiency improvement initiatives:- 80 plus80 PLUS80 PLUS is an initiative to promote energy efficiency in computer power supply units . It certifies products that have more than 80% energy efficiency at 20%, 50% and 100% of rated load, and a power factor of 0.9 or greater at 100% load....
- One watt initiativeOne Watt InitiativeThe One Watt Initiative is an energy-saving initiative by the International Energy Agency to reduce standby power-use by any appliance to not more than one watt in 2010, and 0.5 watts in 2013, which has given rise to regulations in many countries and regions.-Standby power:Standby power,...
- Energy starEnergy StarEnergy Star is an international standard for energy efficient consumer products originated in the United States of America. It was first created as a United States government program during the early 1990s, but Australia, Canada, Japan, New Zealand, Taiwan and the European Union have also adopted...
- Mechanical efficiencyMechanical efficiencyMechanical efficiency measures the effectiveness of a machine in transforming the energy and power that is input to the device into an output force and movement...
- Figure of meritFigure of meritA figure of merit is a quantity used to characterize the performance of a device, system or method, relative to its alternatives. In engineering, figures of merit are often defined for particular materials or devices in order to determine their relative utility for an application...
- Heat of combustionHeat of combustionThe heat of combustion is the energy released as heat when a compound undergoes complete combustion with oxygen under standard conditions. The chemical reaction is typically a hydrocarbon reacting with oxygen to form carbon dioxide, water and heat...
- Lower heating value
External links

