Effective temperature
Encyclopedia
The effective temperature of a body such as a star or planet is the temperature
of a black body
that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation
. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's temperature when the body's emissivity
curve (as a function of wavelength
) is not known.
 The effective temperature of a star
The effective temperature of a star
is the temperature of a black body
with the same luminosity per surface area ( ) as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law
) as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law 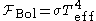 . Notice that the total (bolometric
. Notice that the total (bolometric
) luminosity of a star is then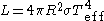 , where
, where 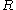 is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightforward. More rigorously the effective temperature corresponds to the temperature at the radius that is defined by the Rosseland optical depth. The effective temperature and the bolometric luminosity are the two fundamental physical parameters needed to place a star on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram
is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightforward. More rigorously the effective temperature corresponds to the temperature at the radius that is defined by the Rosseland optical depth. The effective temperature and the bolometric luminosity are the two fundamental physical parameters needed to place a star on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram
. Both effective temperature and bolometric luminosity actually depend on the chemical composition of a star.
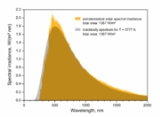
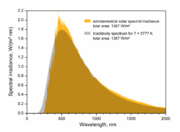
The effective temperature of our Sun is around 5780 kelvin
s (K).
Stars actually have a temperature gradient, going from their central core up to the atmosphere. The "core temperature" of the sun—the temperature at the centre of the sun where nuclear reactions take place—is estimated to be 15 000 000 K.
The color index
of a star indicates its temperature from the very cool—by stellar standards, that is—red M stars that radiate heavily in the infrared
to the very blue O stars that radiate largely in the ultraviolet
. The effective temperature of a star indicates the amount of heat that the star radiates per unit of surface area. From the warmest surfaces to the coolest is the sequence of star types
known as O, B, A, F, G, K, and M.
A red star could be a tiny red dwarf
, a star of feeble energy production and a small surface or a bloated giant or even supergiant
star such as Antares
or Betelgeuse
, either of which generates far greater energy but passes it through a surface so large that the star radiates little per unit of surface area. A star near the middle of the spectrum, such as the modest Sun
or the giant Capella
radiates more heat per unit of surface area than the feeble red dwarf stars or the bloated supergiants, but much less than such a white or blue star as Vega
or Rigel
.
can be calculated by equating the power received by the planet with the power emitted by a blackbody of temperature T.
Take the case of a planet at a distance D from the star, of luminosity
L.
Assuming the star radiates isotropically and that the planet is a long way from the star, the power absorbed by the planet is given by treating the planet as a disc of radius r, which intercepts some of the power which is spread over the surface of a sphere of radius D. We also allow the planet to reflect some of the incoming radiation by incorporating a parameter called the albedo
. An albedo of 1 means that all the radiation is reflected, an albedo of 0 means all of it is absorbed. The expression for absorbed power is then:
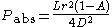
The next assumption we can make is that the entire planet is at the same temperature T, and that the planet radiates as a blackbody. The Stefan–Boltzmann law gives an expression for the power radiated by the planet:

Equating these two expressions and rearranging gives an expression for the effective temperature:

Note that the planet's radius has cancelled out of the final expression.
The effective temperature for Jupiter
is 112 K and 51 Pegasi b
(Bellerophon) is 1258 K. The actual temperature depends on albedo
, atmosphere
, and internal heating. The actual temperature from spectroscopic analysis for HD 209458 b
(Osiris) is 1130 K, but the black body temperature is 1359 K. The internal heating within Jupiter of 40 K combined with the effective temperature of 112 K results in a total of 152 K as the actual temperature.
Temperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
of a black body
Black body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
that would emit the same total amount of electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation
Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that exhibits wave-like behavior as it travels through space...
. Effective temperature is often used as an estimate of a body's temperature when the body's emissivity
Emissivity
The emissivity of a material is the relative ability of its surface to emit energy by radiation. It is the ratio of energy radiated by a particular material to energy radiated by a black body at the same temperature...
curve (as a function of wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
) is not known.
Star

Star
A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth...
is the temperature of a black body
Black body
A black body is an idealized physical body that absorbs all incident electromagnetic radiation. Because of this perfect absorptivity at all wavelengths, a black body is also the best possible emitter of thermal radiation, which it radiates incandescently in a characteristic, continuous spectrum...
with the same luminosity per surface area (
 ) as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law
) as the star and is defined according to the Stefan–Boltzmann law 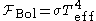 . Notice that the total (bolometric
. Notice that the total (bolometricAbsolute magnitude
Absolute magnitude is the measure of a celestial object's intrinsic brightness. it is also the apparent magnitude a star would have if it were 32.6 light years away from Earth...
) luminosity of a star is then
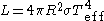 , where
, where 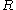 is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightforward. More rigorously the effective temperature corresponds to the temperature at the radius that is defined by the Rosseland optical depth. The effective temperature and the bolometric luminosity are the two fundamental physical parameters needed to place a star on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram
is the stellar radius. The definition of the stellar radius is obviously not straightforward. More rigorously the effective temperature corresponds to the temperature at the radius that is defined by the Rosseland optical depth. The effective temperature and the bolometric luminosity are the two fundamental physical parameters needed to place a star on the Hertzsprung–Russell diagramHertzsprung–Russell diagram
The Hertzsprung–Russell diagram is a scatter graph of stars showing the relationship between the stars' absolute magnitudes or luminosities versus their spectral types or classifications and effective temperatures. Hertzsprung–Russell diagrams are not pictures or maps of the locations of the stars...
. Both effective temperature and bolometric luminosity actually depend on the chemical composition of a star.
The effective temperature of our Sun is around 5780 kelvin
Kelvin
The kelvin is a unit of measurement for temperature. It is one of the seven base units in the International System of Units and is assigned the unit symbol K. The Kelvin scale is an absolute, thermodynamic temperature scale using as its null point absolute zero, the temperature at which all...
s (K).
Stars actually have a temperature gradient, going from their central core up to the atmosphere. The "core temperature" of the sun—the temperature at the centre of the sun where nuclear reactions take place—is estimated to be 15 000 000 K.
The color index
Color index
In astronomy, the color index is a simple numerical expression that determines the color of an object, which in the case of a star gives its temperature...
of a star indicates its temperature from the very cool—by stellar standards, that is—red M stars that radiate heavily in the infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
to the very blue O stars that radiate largely in the ultraviolet
Ultraviolet
Ultraviolet light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays, in the range 10 nm to 400 nm, and energies from 3 eV to 124 eV...
. The effective temperature of a star indicates the amount of heat that the star radiates per unit of surface area. From the warmest surfaces to the coolest is the sequence of star types
Stellar classification
In astronomy, stellar classification is a classification of stars based on their spectral characteristics. The spectral class of a star is a designated class of a star describing the ionization of its chromosphere, what atomic excitations are most prominent in the light, giving an objective measure...
known as O, B, A, F, G, K, and M.
A red star could be a tiny red dwarf
Red dwarf
According to the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram, a red dwarf star is a small and relatively cool star, of the main sequence, either late K or M spectral type....
, a star of feeble energy production and a small surface or a bloated giant or even supergiant
Supergiant
Supergiants are among the most massive stars. They occupy the top region of the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram. In the Yerkes spectral classification, supergiants are class Ia or Ib . They typically have bolometric absolute magnitudes between -5 and -12...
star such as Antares
Antares
Antares is a red supergiant star in the Milky Way galaxy and the sixteenth brightest star in the nighttime sky . Along with Aldebaran, Spica, and Regulus it is one of the four brightest stars near the ecliptic...
or Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse
Betelgeuse, also known by its Bayer designation Alpha Orionis , is the eighth brightest star in the night sky and second brightest star in the constellation of Orion, outshining its neighbour Rigel only rarely...
, either of which generates far greater energy but passes it through a surface so large that the star radiates little per unit of surface area. A star near the middle of the spectrum, such as the modest Sun
Sun
The Sun is the star at the center of the Solar System. It is almost perfectly spherical and consists of hot plasma interwoven with magnetic fields...
or the giant Capella
Capella (star)
Capella is the brightest star in the constellation Auriga, the sixth brightest star in the night sky and the third brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus and Vega. Although it appears to be a single star to the naked eye, it is actually a star system of four stars in...
radiates more heat per unit of surface area than the feeble red dwarf stars or the bloated supergiants, but much less than such a white or blue star as Vega
Vega
Vega is the brightest star in the constellation Lyra, the fifth brightest star in the night sky and the second brightest star in the northern celestial hemisphere, after Arcturus...
or Rigel
Rigel
Rigel is the brightest star in the constellation Orion and the sixth brightest star in the sky, with visual magnitude 0.18...
.
Planet
The effective temperature of a planetPlanet
A planet is a celestial body orbiting a star or stellar remnant that is massive enough to be rounded by its own gravity, is not massive enough to cause thermonuclear fusion, and has cleared its neighbouring region of planetesimals.The term planet is ancient, with ties to history, science,...
can be calculated by equating the power received by the planet with the power emitted by a blackbody of temperature T.
Take the case of a planet at a distance D from the star, of luminosity
Luminosity
Luminosity is a measurement of brightness.-In photometry and color imaging:In photometry, luminosity is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to luminance, which is the density of luminous intensity in a given direction. The SI unit for luminance is candela per square metre.The luminosity function...
L.
Assuming the star radiates isotropically and that the planet is a long way from the star, the power absorbed by the planet is given by treating the planet as a disc of radius r, which intercepts some of the power which is spread over the surface of a sphere of radius D. We also allow the planet to reflect some of the incoming radiation by incorporating a parameter called the albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
. An albedo of 1 means that all the radiation is reflected, an albedo of 0 means all of it is absorbed. The expression for absorbed power is then:
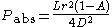
The next assumption we can make is that the entire planet is at the same temperature T, and that the planet radiates as a blackbody. The Stefan–Boltzmann law gives an expression for the power radiated by the planet:

Equating these two expressions and rearranging gives an expression for the effective temperature:

Note that the planet's radius has cancelled out of the final expression.
The effective temperature for Jupiter
Jupiter
Jupiter is the fifth planet from the Sun and the largest planet within the Solar System. It is a gas giant with mass one-thousandth that of the Sun but is two and a half times the mass of all the other planets in our Solar System combined. Jupiter is classified as a gas giant along with Saturn,...
is 112 K and 51 Pegasi b
51 Pegasi b
51 Pegasi b , sometimes though unofficially named Bellerophon, is an extrasolar planet approximately 50 light-years away in the constellation of Pegasus...
(Bellerophon) is 1258 K. The actual temperature depends on albedo
Albedo
Albedo , or reflection coefficient, is the diffuse reflectivity or reflecting power of a surface. It is defined as the ratio of reflected radiation from the surface to incident radiation upon it...
, atmosphere
Atmosphere
An atmosphere is a layer of gases that may surround a material body of sufficient mass, and that is held in place by the gravity of the body. An atmosphere may be retained for a longer duration, if the gravity is high and the atmosphere's temperature is low...
, and internal heating. The actual temperature from spectroscopic analysis for HD 209458 b
HD 209458 b
HD 209458 b is an extrasolar planet that orbits the Solar analog star HD 209458 in the constellation Pegasus, some 150 light-years from Earth's solar system, with evidence of water vapor....
(Osiris) is 1130 K, but the black body temperature is 1359 K. The internal heating within Jupiter of 40 K combined with the effective temperature of 112 K results in a total of 152 K as the actual temperature.

