
Edith Bolling Wilson
Encyclopedia
Edith Bolling Galt Wilson (October 15, 1872 – December 28, 1961), second wife of U.S. President
Woodrow Wilson
, was First Lady of the United States
from 1915 to 1921. She has been labeled "the Secret President" and "the first woman to run the government" for the role she played when her husband suffered prolonged and disabling illness after a stroke
in October 1919. Some even refer to her as "the first female president of the United States
."
, the daughter of William Holcombe Bolling, a circuit court judge, and Sarah "Sallie" Spears (White) Bolling, Edith was a descendant of the Plantagenets, of colonial Virginia
settlers and the famous Native American
, Pocahontas
, through Pocahontas' granddaughter Jane Rolfe Bolling
. Her paternal great-grandmother, Catherine Payne Bolling, was the daughter of Martha Dandridge Payne, whose father Nathaniel West Dandrige was a first cousin of Martha Dandridge Custis, wife of George Washington. She was the seventh of eleven children.
She attended private girls' schools in Virginia and Martha Washington College (a precursor of Emory and Henry College
) to study music. While visiting her married sister in Washington, D.C.
, Edith met Norman Galt, a prosperous jeweler; in 1896 they were married. For 12 years she lived as a contented young matron in the capital, with vacations abroad. However, her personal life was not without tragedy: she gave birth to a son in 1903 who lived only for a few days (the difficult birth also left her unable to bear additional children), and in 1908 her husband died unexpectedly. Edith Bolling Galt then chose a manager who operated the family's jewelry firm with financial success.
at the White House
by Helen Bones, the president's cousin and official White House hostess since the death of Ellen Wilson, the president's first wife. A man who depended on female companionship, Wilson took an instant liking to Mrs. Galt, who was charming, intelligent, and plumply pretty. His admiration grew swiftly into love. In proposing to her, he made the poignant statement that "in this place time is not measured by weeks, or months, or years, but by deep human experiences..."
They had been a romantic item for such a short period of time that Washington wags were quick to poke fun at the marriage. As one joke went, when Edith Galt heard the President propose marriage, she nearly fell out of bed. Additionally, a typographical error in a Washington newspaper was much closer to the mark than intended. Prior to their marriage, an item meant to describe the president's social evening at a local theater with Mrs. Galt included the phrase "rather than paying attention to the play the President spent the evening entertaining Mrs. Galt." What was printed in the first run of the Washington Post was the phrase "rather than paying attention to the play the President spent the evening entering Mrs. Galt." [emphasis added] The first run of the paper was recalled, but a few copies were not recovered and are now highly prized collectibles.
Complicating matters were rumors, apparently groundless, that Wilson had been cheating on his first wife, or that he and Mrs. Galt had actually murdered the First Lady. Distressed at the effect all this might be having on his fiancée, Wilson offered Mrs. Galt the opportunity to back out of their engagement. She spurned the offer, replying that she would stand by him not for duty, pity or honor, but for love.
President Wilson, aged 58, married Edith Bolling Galt, aged 43, on December 18, 1915, at the home of the bride in Washington, D.C. The wedding, a small affair attended by 40 guests, was performed jointly by the Reverend Dr. James H. Taylor of Central Presbyterian Church and the Reverend Dr. Herbert Scott Smith of St. Margaret's Episcopal Church, pastors of the groom and bride respectively. The couple honeymooned two weeks in Hot Springs, Virginia and at The Greenbrier
in White Sulphur Springs, West Virginia
.
In 1916, the Swiss-born American artist Adolfo Müller-Ury
(1862–1947) was commissioned by Colonel Edward M. House
to paint a portrait of Mrs. Wilson, which he did in the White House. The painting always hung in the President's bedroom, but when Mrs. Wilson died she left it to the White House, and a copy was made to hang in the Woodrow Wilson House Museum.
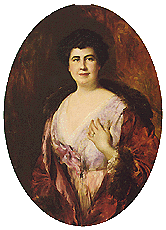 As First Lady during World War I, Mrs. Wilson observed gasless Sundays, meatless Mondays, and wheatless Wednesdays to set an example for the federal rationing effort. Similarly, she set sheep to graze on the White House lawn rather than waste manpower in mowing it and auctioned off their wool for the benefit of the American Red Cross
As First Lady during World War I, Mrs. Wilson observed gasless Sundays, meatless Mondays, and wheatless Wednesdays to set an example for the federal rationing effort. Similarly, she set sheep to graze on the White House lawn rather than waste manpower in mowing it and auctioned off their wool for the benefit of the American Red Cross
.
Though the new First Lady had sound qualifications for the role of hostess, the social aspect of the administration was overshadowed by war in Europe
and abandoned after the United States formally entered the conflict in 1917. Edith Wilson submerged her own life in her husband's, trying to keep him fit under tremendous strain. She accompanied him to Europe when the Allies conferred on terms of peace, the first such trip for a U.S. President while in office, and played a political role, being compared, in some circles, to royalty.
Her most significant contribution as First Lady, however, was her service as steward of the executive branch following the president's stroke
in September 1919.
 Following his attendance at the Paris Peace Conference
Following his attendance at the Paris Peace Conference
which began in January 1919, Wilson returned to campaign for Senate approval of the peace treaty and the League of Nations
Covenant. However, his health failed in October, when a stroke left him partly paralyzed. The United States never did ratify the Treaty of Versailles
nor join the League of Nations, which had initially been Wilson's concept. This is attributed to the facts that isolationist sentiment was strong and some of the articles in the League's charter conflicted with the United States Constitution, rather than any failure of Wilson to promote his position.
His constant attendant, Edith Wilson took over many routine duties and details of government. She carefully screened all matters of state and decided which were important enough to bring to the bedridden president. "I studied every paper sent from the different Secretaries or Senators," she wrote later of her role, "and tried to digest and present in tabloid form the things that, despite my vigilance, had to go to the President. I, myself, never made a single decision regarding the disposition of public affairs. The only decision that was mine was what was important and what was not, and the very important decision of when to present matters to my husband."
Edith also strongly opposed allowing Vice President
Thomas R. Marshall
to assume the powers of the presidency. She selected matters for her husband's attention and let everything else go to the heads of departments or remain in abeyance. In My Memoir, published in 1939, she called her role a "stewardship" and stated emphatically that her husband's doctors had urged that course upon her. Others, however, disagreed with her version of events and called it revisionism. One historian, Phyllis Levin, a former reporter for the New York Times, wrote, Edith Wilson was "a woman of narrow views and formidable determination" and blamed her for numerous diplomatic failures that occurred during her husband's incapacitation. However, she has also been praised for successes during her time as unofficial acting president.
.
She died of congestive heart failure
at the age of 89, on December 28, 1961, on what would have been Wilson's 105th birthday. On the day of her death, she was to have been the guest of honor at the dedication ceremony for the Woodrow Wilson Bridge
across the Potomac River
between Maryland
and Virginia
. She was buried next to the president at the Washington Cathedral.
Mrs. Wilson left her home to the National Trust for Historic Preservation
to be made into a museum honoring her husband. The Woodrow Wilson House opened as a museum in 1964.
served her well as First Lady and that her birthplace and childhood home will become the conduit by which public awareness will be built honoring the Bolling name, her contributions to this country, the institution of the presidency, and for the example she set for women then and now.
|-
President of the United States
The President of the United States of America is the head of state and head of government of the United States. The president leads the executive branch of the federal government and is the commander-in-chief of the United States Armed Forces....
Woodrow Wilson
Woodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was the 28th President of the United States, from 1913 to 1921. A leader of the Progressive Movement, he served as President of Princeton University from 1902 to 1910, and then as the Governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913...
, was First Lady of the United States
First Lady of the United States
First Lady of the United States is the title of the hostess of the White House. Because this position is traditionally filled by the wife of the president of the United States, the title is most often applied to the wife of a sitting president. The current first lady is Michelle Obama.-Current:The...
from 1915 to 1921. She has been labeled "the Secret President" and "the first woman to run the government" for the role she played when her husband suffered prolonged and disabling illness after a stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
in October 1919. Some even refer to her as "the first female president of the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
."
Early life
Born Edith White Bolling in Wytheville, VirginiaWytheville, Virginia
Wytheville is a town in Wythe County, Virginia, United States. The population was 8,211 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Wythe County. The town is home to a Chautauqua Festival, held the third weekend in June every year since 1985...
, the daughter of William Holcombe Bolling, a circuit court judge, and Sarah "Sallie" Spears (White) Bolling, Edith was a descendant of the Plantagenets, of colonial Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
settlers and the famous Native American
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans in the United States are the indigenous peoples in North America within the boundaries of the present-day continental United States, parts of Alaska, and the island state of Hawaii. They are composed of numerous, distinct tribes, states, and ethnic groups, many of which survive as...
, Pocahontas
Pocahontas
Pocahontas was a Virginia Indian notable for her association with the colonial settlement at Jamestown, Virginia. She was the daughter of Chief Powhatan, the head of a network of tributary tribal nations in Tidewater Virginia...
, through Pocahontas' granddaughter Jane Rolfe Bolling
Jane Rolfe
Jane Rolfe was the granddaughter of Pocahontas and the English colonist John Rolfe, ....
. Her paternal great-grandmother, Catherine Payne Bolling, was the daughter of Martha Dandridge Payne, whose father Nathaniel West Dandrige was a first cousin of Martha Dandridge Custis, wife of George Washington. She was the seventh of eleven children.
She attended private girls' schools in Virginia and Martha Washington College (a precursor of Emory and Henry College
Emory and Henry College
Emory & Henry College, known as E&H, Emory, or the College, is a private liberal arts college located in Emory, Virginia, United States. The campus comprises of Washington County, Virginia, which is part of the mountain region of Southwest Virginia...
) to study music. While visiting her married sister in Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C.
Washington, D.C., formally the District of Columbia and commonly referred to as Washington, "the District", or simply D.C., is the capital of the United States. On July 16, 1790, the United States Congress approved the creation of a permanent national capital as permitted by the U.S. Constitution....
, Edith met Norman Galt, a prosperous jeweler; in 1896 they were married. For 12 years she lived as a contented young matron in the capital, with vacations abroad. However, her personal life was not without tragedy: she gave birth to a son in 1903 who lived only for a few days (the difficult birth also left her unable to bear additional children), and in 1908 her husband died unexpectedly. Edith Bolling Galt then chose a manager who operated the family's jewelry firm with financial success.
Marriage and early First Ladyship
In March 1915, the widow Galt was introduced to U.S. President Woodrow WilsonWoodrow Wilson
Thomas Woodrow Wilson was the 28th President of the United States, from 1913 to 1921. A leader of the Progressive Movement, he served as President of Princeton University from 1902 to 1910, and then as the Governor of New Jersey from 1911 to 1913...
at the White House
White House
The White House is the official residence and principal workplace of the president of the United States. Located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., the house was designed by Irish-born James Hoban, and built between 1792 and 1800 of white-painted Aquia sandstone in the Neoclassical...
by Helen Bones, the president's cousin and official White House hostess since the death of Ellen Wilson, the president's first wife. A man who depended on female companionship, Wilson took an instant liking to Mrs. Galt, who was charming, intelligent, and plumply pretty. His admiration grew swiftly into love. In proposing to her, he made the poignant statement that "in this place time is not measured by weeks, or months, or years, but by deep human experiences..."
They had been a romantic item for such a short period of time that Washington wags were quick to poke fun at the marriage. As one joke went, when Edith Galt heard the President propose marriage, she nearly fell out of bed. Additionally, a typographical error in a Washington newspaper was much closer to the mark than intended. Prior to their marriage, an item meant to describe the president's social evening at a local theater with Mrs. Galt included the phrase "rather than paying attention to the play the President spent the evening entertaining Mrs. Galt." What was printed in the first run of the Washington Post was the phrase "rather than paying attention to the play the President spent the evening entering Mrs. Galt." [emphasis added] The first run of the paper was recalled, but a few copies were not recovered and are now highly prized collectibles.
Complicating matters were rumors, apparently groundless, that Wilson had been cheating on his first wife, or that he and Mrs. Galt had actually murdered the First Lady. Distressed at the effect all this might be having on his fiancée, Wilson offered Mrs. Galt the opportunity to back out of their engagement. She spurned the offer, replying that she would stand by him not for duty, pity or honor, but for love.
President Wilson, aged 58, married Edith Bolling Galt, aged 43, on December 18, 1915, at the home of the bride in Washington, D.C. The wedding, a small affair attended by 40 guests, was performed jointly by the Reverend Dr. James H. Taylor of Central Presbyterian Church and the Reverend Dr. Herbert Scott Smith of St. Margaret's Episcopal Church, pastors of the groom and bride respectively. The couple honeymooned two weeks in Hot Springs, Virginia and at The Greenbrier
The Greenbrier
The Greenbrier is a Forbes four-star and AAA Five Diamond Award winning luxury resort located just outside the town of White Sulphur Springs in Greenbrier County, West Virginia, United States....
in White Sulphur Springs, West Virginia
White Sulphur Springs, West Virginia
White Sulphur Springs is a city in Greenbrier County, West Virginia, United States. The population was 2,444 at the 2010 census.-Geography:White Sulphur Springs is located at ....
.
In 1916, the Swiss-born American artist Adolfo Müller-Ury
Adolfo Müller-Ury
Adolfo Muller-Ury was a Swiss-born American portrait painter and impressionistic painter of roses and still life.-Heritage and early life in Switzerland:...
(1862–1947) was commissioned by Colonel Edward M. House
Edward M. House
Edward Mandell House was an American diplomat, politician, and presidential advisor. Commonly known by the title of Colonel House, although he had no military experience, he had enormous personal influence with U.S...
to paint a portrait of Mrs. Wilson, which he did in the White House. The painting always hung in the President's bedroom, but when Mrs. Wilson died she left it to the White House, and a copy was made to hang in the Woodrow Wilson House Museum.
Hostessing and the First World War
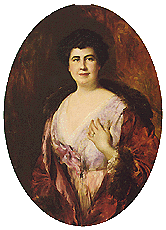
American Red Cross
The American Red Cross , also known as the American National Red Cross, is a volunteer-led, humanitarian organization that provides emergency assistance, disaster relief and education inside the United States. It is the designated U.S...
.
Though the new First Lady had sound qualifications for the role of hostess, the social aspect of the administration was overshadowed by war in Europe
World War I
World War I , which was predominantly called the World War or the Great War from its occurrence until 1939, and the First World War or World War I thereafter, was a major war centred in Europe that began on 28 July 1914 and lasted until 11 November 1918...
and abandoned after the United States formally entered the conflict in 1917. Edith Wilson submerged her own life in her husband's, trying to keep him fit under tremendous strain. She accompanied him to Europe when the Allies conferred on terms of peace, the first such trip for a U.S. President while in office, and played a political role, being compared, in some circles, to royalty.
Her most significant contribution as First Lady, however, was her service as steward of the executive branch following the president's stroke
Stroke
A stroke, previously known medically as a cerebrovascular accident , is the rapidly developing loss of brain function due to disturbance in the blood supply to the brain. This can be due to ischemia caused by blockage , or a hemorrhage...
in September 1919.
Unofficial acting presidency

Paris Peace Conference, 1919
The Paris Peace Conference was the meeting of the Allied victors following the end of World War I to set the peace terms for the defeated Central Powers following the armistices of 1918. It took place in Paris in 1919 and involved diplomats from more than 32 countries and nationalities...
which began in January 1919, Wilson returned to campaign for Senate approval of the peace treaty and the League of Nations
League of Nations
The League of Nations was an intergovernmental organization founded as a result of the Paris Peace Conference that ended the First World War. It was the first permanent international organization whose principal mission was to maintain world peace...
Covenant. However, his health failed in October, when a stroke left him partly paralyzed. The United States never did ratify the Treaty of Versailles
Treaty of Versailles
The Treaty of Versailles was one of the peace treaties at the end of World War I. It ended the state of war between Germany and the Allied Powers. It was signed on 28 June 1919, exactly five years after the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand. The other Central Powers on the German side of...
nor join the League of Nations, which had initially been Wilson's concept. This is attributed to the facts that isolationist sentiment was strong and some of the articles in the League's charter conflicted with the United States Constitution, rather than any failure of Wilson to promote his position.
His constant attendant, Edith Wilson took over many routine duties and details of government. She carefully screened all matters of state and decided which were important enough to bring to the bedridden president. "I studied every paper sent from the different Secretaries or Senators," she wrote later of her role, "and tried to digest and present in tabloid form the things that, despite my vigilance, had to go to the President. I, myself, never made a single decision regarding the disposition of public affairs. The only decision that was mine was what was important and what was not, and the very important decision of when to present matters to my husband."
Edith also strongly opposed allowing Vice President
Vice president
A vice president is an officer in government or business who is below a president in rank. The name comes from the Latin vice meaning 'in place of'. In some countries, the vice president is called the deputy president...
Thomas R. Marshall
Thomas R. Marshall
Thomas Riley Marshall was an American Democratic politician who served as the 28th Vice President of the United States under Woodrow Wilson...
to assume the powers of the presidency. She selected matters for her husband's attention and let everything else go to the heads of departments or remain in abeyance. In My Memoir, published in 1939, she called her role a "stewardship" and stated emphatically that her husband's doctors had urged that course upon her. Others, however, disagreed with her version of events and called it revisionism. One historian, Phyllis Levin, a former reporter for the New York Times, wrote, Edith Wilson was "a woman of narrow views and formidable determination" and blamed her for numerous diplomatic failures that occurred during her husband's incapacitation. However, she has also been praised for successes during her time as unofficial acting president.
Later years
In 1921 Mrs. Wilson retired with the former president to their comfortable home on S Street in Washington, D.C., nursing him until his death three years later. She later served as director of the Woodrow Wilson Foundation. Her memoir appeared in 1938. In 1961, she attended the inaugural of President John F. KennedyJohn F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald "Jack" Kennedy , often referred to by his initials JFK, was the 35th President of the United States, serving from 1961 until his assassination in 1963....
.
She died of congestive heart failure
Congestive heart failure
Heart failure often called congestive heart failure is generally defined as the inability of the heart to supply sufficient blood flow to meet the needs of the body. Heart failure can cause a number of symptoms including shortness of breath, leg swelling, and exercise intolerance. The condition...
at the age of 89, on December 28, 1961, on what would have been Wilson's 105th birthday. On the day of her death, she was to have been the guest of honor at the dedication ceremony for the Woodrow Wilson Bridge
Woodrow Wilson Bridge
The Woodrow Wilson Memorial Bridge is a bascule bridge that spans the Potomac River between the independent city of Alexandria, Virginia and Oxon Hill in Prince George's County, Maryland, United States. While over the water near the Virginia shore, it crosses the southern tip of the District of...
across the Potomac River
Potomac River
The Potomac River flows into the Chesapeake Bay, located along the mid-Atlantic coast of the United States. The river is approximately long, with a drainage area of about 14,700 square miles...
between Maryland
Maryland
Maryland is a U.S. state located in the Mid Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware to its east...
and Virginia
Virginia
The Commonwealth of Virginia , is a U.S. state on the Atlantic Coast of the Southern United States. Virginia is nicknamed the "Old Dominion" and sometimes the "Mother of Presidents" after the eight U.S. presidents born there...
. She was buried next to the president at the Washington Cathedral.
Mrs. Wilson left her home to the National Trust for Historic Preservation
National Trust for Historic Preservation
The National Trust for Historic Preservation is an American member-supported organization that was founded in 1949 by congressional charter to support preservation of historic buildings and neighborhoods through a range of programs and activities, including the publication of Preservation...
to be made into a museum honoring her husband. The Woodrow Wilson House opened as a museum in 1964.
Birthplace Foundation
The Edith Bolling Wilson Birthplace Foundation’s goal is to share how Edith Bolling’s humble beginnings in Wytheville, VirginiaWytheville, Virginia
Wytheville is a town in Wythe County, Virginia, United States. The population was 8,211 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Wythe County. The town is home to a Chautauqua Festival, held the third weekend in June every year since 1985...
served her well as First Lady and that her birthplace and childhood home will become the conduit by which public awareness will be built honoring the Bolling name, her contributions to this country, the institution of the presidency, and for the example she set for women then and now.
External links
- http://www.edithbollingwilson.org
- Original text based on White House biography
- Edith Wilson: The Secret President
- Edith Wilson at Findagrave.com
|-

