
Early Byzantine mosaics in the Middle East
Encyclopedia
Christian
A Christian is a person who adheres to Christianity, an Abrahamic, monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth as recorded in the Canonical gospels and the letters of the New Testament...
mosaics created between the 4th and the 8th centuries in ancient Syria
Syria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
, Palestine
Palestine
Palestine is a conventional name, among others, used to describe the geographic region between the Mediterranean Sea and the Jordan River, and various adjoining lands....
and Egypt
Egypt
Egypt , officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, Arabic: , is a country mainly in North Africa, with the Sinai Peninsula forming a land bridge in Southwest Asia. Egypt is thus a transcontinental country, and a major power in Africa, the Mediterranean Basin, the Middle East and the Muslim world...
when the area belonged to the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
. The eastern provinces of the Eastern Roman and later the Byzantine Empire
Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire was the Eastern Roman Empire during the periods of Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, centred on the capital of Constantinople. Known simply as the Roman Empire or Romania to its inhabitants and neighbours, the Empire was the direct continuation of the Ancient Roman State...
s inherited a strong artistic tradition from Late Antiquity
Late Antiquity
Late Antiquity is a periodization used by historians to describe the time of transition from Classical Antiquity to the Middle Ages, in both mainland Europe and the Mediterranean world. Precise boundaries for the period are a matter of debate, but noted historian of the period Peter Brown proposed...
. The tradition of making mosaics was carried on in the Umayyad
Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate was the second of the four major Arab caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. It was ruled by the Umayyad dynasty, whose name derives from Umayya ibn Abd Shams, the great-grandfather of the first Umayyad caliph. Although the Umayyad family originally came from the...
era until the end of the 8th century. The great majority of these works of art were later destroyed but archeological excavations unearthed many surviving examples.
The Madaba region
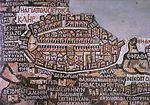
The single most important piece of Byzantine Christian mosaic art in the East is the Madaba MapMadaba Map
The Madaba Map is part of a floor mosaic in the early Byzantine church of Saint George at Madaba, Jordan. The Madaba Map is a map of the Middle East. Part of it contains the oldest surviving original cartographic depiction of the Holy Land and especially Jerusalem...
, made between 542 and 570 as the floor of the church of Saint George at Madaba
Madaba
Madaba , is the capital city of Madaba Governorate of Jordan, which has a population of about 60,000. Madaba is the fifth most populous town in Jordan. It is best known for its Byzantine and Umayyad mosaics, especially a large Byzantine-era mosaic map of The Holy Land...
, Jordan
Jordan
Jordan , officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan , Al-Mamlaka al-Urduniyya al-Hashemiyya) is a kingdom on the East Bank of the River Jordan. The country borders Saudi Arabia to the east and south-east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north and the West Bank and Israel to the west, sharing...
. It was rediscovered in 1894. The Madaba Map is the oldest surviving cartographic depiction of the Holy Land
Holy Land
The Holy Land is a term which in Judaism refers to the Kingdom of Israel as defined in the Tanakh. For Jews, the Land's identifiction of being Holy is defined in Judaism by its differentiation from other lands by virtue of the practice of Judaism often possible only in the Land of Israel...
. It depicts an area from Lebanon
Lebanon
Lebanon , officially the Republic of LebanonRepublic of Lebanon is the most common term used by Lebanese government agencies. The term Lebanese Republic, a literal translation of the official Arabic and French names that is not used in today's world. Arabic is the most common language spoken among...
in the north to the Nile Delta
Nile Delta
The Nile Delta is the delta formed in Northern Egypt where the Nile River spreads out and drains into the Mediterranean Sea. It is one of the world's largest river deltas—from Alexandria in the west to Port Said in the east, it covers some 240 km of Mediterranean coastline—and is a rich...
in the south, and from the Mediterranean Sea
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean surrounded by the Mediterranean region and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Anatolia and Europe, on the south by North Africa, and on the east by the Levant...
in the west to the Eastern Desert
Arabian Desert
The Arabian Desert is a vast desert wilderness stretching from Yemen to the Persian Gulf and Oman to Jordan and Iraq. It occupies most of the Arabian Peninsula, with an area of...
. The largest and most detailed element of the topographic depiction is Jerusalem, at the center of the map. The map is enriched with many naturalistic features, like animals, fishing boats, bridges and palm trees.
One of the earliest examples of Byzantine mosaic art in the region can be found on Mount Nebo
Mount Nebo (Jordan)
Mount Nebo is an elevated ridge that is approximately 817 meters above sea level, in what is now western Jordan. The view from the summit provides a panorama of the Holy Land and, to the north, a more limited one of the valley of the River Jordan...
, a place of pilgrimage in the Byzantine era where Moses
Moses
Moses was, according to the Hebrew Bible and Qur'an, a religious leader, lawgiver and prophet, to whom the authorship of the Torah is traditionally attributed...
died. Among the many 6th century mosaics in the church complex in an area known as Siyagha (discovered after 1933) the most interesting one is located in the baptistery. The intact floor mosaic in the Byzantine monastery, built on the foundations of an even earlier chapel from the third or fourth century CE, was laid down in circa 530. It covers an area of 9 x 3 m and depicts the monastic pastime of wine-making, as well as hunters, with a rich assortment of Middle Eastern flora and fauna.
The Church of Sts. Lot and Procopius was founded in 567 in Nebo village under Mount Nebo (now Khirbet Mukhayyat). Its floor mosaic depicts everyday activities like grape harvest. Another two spectacular mosaics were discovered in the ruined Church of Preacher John nearby. One of the mosaics was placed above the other one which was completely covered and unknown until the modern restoration. The figures on the older mosaic have thus escaped the iconoclasts.
The town of Madaba
Madaba
Madaba , is the capital city of Madaba Governorate of Jordan, which has a population of about 60,000. Madaba is the fifth most populous town in Jordan. It is best known for its Byzantine and Umayyad mosaics, especially a large Byzantine-era mosaic map of The Holy Land...
remained an important center of mosaic making during the 5-8th centuries. In the Church of the Apostles even the name of the master mosaicist, Salomios was also recorded (from 568). In the middle of the main panel Thalassa, goddess of the sea, can be seen surrounded by fishes and other sea creatures. Native Middle Eastern birds, mammals, plants and fruits were also added. The Church of Prophet Elijah was built in 607. Its carpet-like central panel in the nave framed by a row of medaillons depicting native animals. Mosaic was used as a decoration not only for churches but for rich private residences like the Hippolytos Hall and the Burnt Palace (both from the early 6th century). They follow the classical Roman tradition with mythological and allegorical scenes like the Four Seasons, Phaedra and Hippolytos, Venus and Adonis, the Three Graces and the city goddesses of Madaba, Rome and Gregoria (in the Hippolytos Hall); hunting scenes, fight of a bull and a lion (in the Burnt Palace).
.jpg)
The early 7th century church complex of Tell Mar Elias
Tell Mar Elias
Tell Mar Elias is a hill in the Ajlun region of North Jordan. The site, northwest of Ajlun, has long been identified with Tishbe, mentioned in the Bible as the hometown or region of the Prophet Elijah ....
, the birth place of Prophet Elijah, (in present-day Jordan
Jordan
Jordan , officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan , Al-Mamlaka al-Urduniyya al-Hashemiyya) is a kingdom on the East Bank of the River Jordan. The country borders Saudi Arabia to the east and south-east, Iraq to the north-east, Syria to the north and the West Bank and Israel to the west, sharing...
, near Ajlun) was discovered in 1999. The floor of the cruciform main church is decorated with wonderfully intact, multi-colored mosaics with floral and geometric motifs (flowers, leaves, scrolls, braided patterns, amphorae) without any representations of animals or humans. One large mosaic floor inscription in white letters on a red background says that the presbyter Saba and his wife offered the church to God as an expression of their faith, in the year 622.
Another holy place, Bethany Beyond the Jordan (Al Maghtas), the scene of the baptism of Jesus
Baptism of Jesus
The baptism of Jesus marks the beginning of Jesus Christ's public ministry. This event is recorded in the Canonical Gospels of Matthew, Mark and Luke. In John 1:29-33 rather than a direct narrative, the Baptist bears witness to the episode...
, was excavated after 1994. Floor mosaics were discovered in the 5-6th century Church of the Arch, the Church of the Trinity and also the 5th century Rhotorios Monastery (with Greek inscriptions). The floor here was covered by a colored mosaic with a frame and cross marks depicted with geometrical designs. On the other side of the lower Jordan Valley
Jordan Valley (Middle East)
The Jordan Valley forms part of the larger Jordan Rift Valley. It is 120 kilometers long and 15 kilometers wide, where it runs from Lake Tiberias in the north to northern Dead Sea in the south. It runs for an additional 155 kilometer south of the Dead Sea to Aqaba, an area also known as Wadi...
another church was discovered in Khirbet el-Beiyudat (ancient Archelais
Archelais
Archelaïs is a Catholic titular see. The original diocese was in Palestine, with its see twelve miles west of the Jordan River. Its episcopal list is given in Gams ....
). According to inscriptions its floor was paved with mosaics during the 560s.
The monastic complex above Lot’s Cave (near the southern end of the Dead Sea
Dead Sea
The Dead Sea , also called the Salt Sea, is a salt lake bordering Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank to the west. Its surface and shores are below sea level, the lowest elevation on the Earth's surface. The Dead Sea is deep, the deepest hypersaline lake in the world...
), which was uncovered after 1988, contained five mosaics, one dated April 606, another May 691.
Another important mosaic site around Madaba is ancient Esbus, present-day Tell Hesban where two Byzantine churches have been discovered. Both churches produced impressive remains of mosaic floors which is not surprising given the fact that Esbus was an ecclesiastical center with its own bishop. Particularly interesting is the nilotic mosaic of the presbytery of the North Church where the mosaicists have created a motif of a turtledove set on a nest made of an imaginary flower. Christian mosaics were also discovered in other settlements in the surroundings of Madaba like Ma'in and Massuh, testifying the widespread popularity of the craft in Byzantine times and the importance of the Madaba area as an artistic center. The church at Massuh has two layers of floor mosaics. The lower one, from the 6th century, has no iconoclastic damage, while the upper layer, from the 7th century, was systematically altered by iconoclasts. Figures were carefully replaced by crosses, or floral and architectural motifs.

Egypt
Important Justinian era mosaics decorated the Saint Catherine's MonasterySaint Catherine's Monastery, Mount Sinai
Saint Catherine's Monastery lies on the Sinai Peninsula, at the mouth of a gorge at the foot of Mount Sinai in the city of Saint Catherine in Egypt's South Sinai Governorate. The monastery is Orthodox and is a UNESCO World Heritage Site...
on Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai
Mount Sinai , also known as Mount Horeb, Mount Musa, Gabal Musa , Jabal Musa meaning "Moses' Mountain", is a mountain near Saint Catherine in the Sinai Peninsula of Egypt. A mountain called Mount Sinai is mentioned many times in the Book of Exodus in the Torah and the Bible as well as the Quran...
. Generally wall mosaics have not survived in the region because of the destruction of buildings but the St. Catherine's Monastery is exceptional. On the upper wall Moses
Moses
Moses was, according to the Hebrew Bible and Qur'an, a religious leader, lawgiver and prophet, to whom the authorship of the Torah is traditionally attributed...
is shown in two panels on a landscape background. In the apse we can see the Transfiguration of Jesus
Transfiguration of Jesus
The Transfiguration of Jesus is an event reported in the New Testament in which Jesus is transfigured and becomes radiant upon a mountain. The Synoptic Gospels describe it, and 2 Peter 1:16-18 refers to it....
on a golden background. The apse is surrounded with bands containing medallions of apostles and prophets, and two contemporary figure, "Abbot Longinos" and "John the Deacon". The mosaic was probably created in 565/6.
The Holy Land
Jerusalem with its many holy places probably had the highest concentration of mosaic-covered churches but very few of them survived the subsequent waves of destructions. The present remains do not do justice to the original richness of the city. The most important is the so-called "Armenian Mosaic" which was discovered in 1894 near the Damascus GateDamascus Gate
Damascus Gate is the main entrance to the Old City of Jerusalem. It is located in the wall on the city's northwest side where the highway leads out to Nablus, and from there, in times past, to the capital of Syria, Damascus; as such, its modern English name is Damascus Gate, and its modern Hebrew...
. It depicts a vine with many branches and grape clusters, which springs from a vase. Populating the vine's branches are peacocks, ducks, storks, pigeons, an eagle, a partridge, and a parrot in a cage. The inscription reads: "For the memory and salvation of all those Armenians whose name the Lord knows." The symbolism of the mosaic indicates that the room was used to remember the dead as a mortuary chapel. In the Dominus Flevit Church
Dominus Flevit Church
Dominus Flevit is a Roman Catholic church located on the Mount of Olives immediately facing the Old City of Jerusalem.- History :Dominus Flevit, which translates from Latin as "The Lord Wept", was fashioned in the shape of a teardrop to symbolize the tears of Christ...
on Mount Olives a 7th century Byzantine chapel was unearthed in 1955. The floor is richly decorated with intersecting circles and pictures of fruit, leaves, flowers, and fish. A Greek inscription mentions Simon, who "decorated this place of prayer in honor of Jesus". In the nearby Church of the Agony (built originally in the last decades of the 4th century) a colorful mosaic floor was discovered in 1920 which follows a geometric design. Fragments of a similar geometric mosaic floor were preserved in the Basilica of St. Stephen (outside the Damascus Gate) which was built by Empress Aelia Eudocia
Aelia Eudocia
Aelia Eudocia Augusta was the wife of Theodosius II, and a prominent historical figure in understanding the rise of Christianity during the beginning of the Byzantine Empire. Eudocia lived in a world where Greek paganism and Christianity were still coming together...
in the first half of the 5th century.

Monastery of the Cross
The Monastery of the Cross is a monastery near the Nayot neighborhood of Jerusalem, Israel. It is located in the Valley of the Cross, below the Israel Museum and the Knesset.- History :...
a section of the elaborate 5th century mosaic floor survived, incorporating pictures of peacocks, plants and geometric patterns. Early Byzantine mosaics were preserved in the Church of John the Baptist in Ein Kerem
Ein Kerem
Ein Kerem , lit. “Spring of the Vineyard”, and - ‘Ein Kārem), is an ancient village of the Jerusalem District and now a neighbourhood in southwest of Jerusalem. According to Christian tradition, John the Baptist was born in Ein Kerem, leading to the establishment of many churches and monasteries....
, the Beit Jimal Monastery
Beit Jimal Monastery
Beit Jimal is a Catholic monastery, established by Salesian monks in 1919. The monastery is located in the Judean hills next to the city of Beit Shemesh. There are actually two separate monasteries, one for men and a second for women, as well as a small and well-appointed church, called St. Stephen...
(in the 5th century the Church of the Tomb of St. Stephen, mosaics discovered in 1916), the Church of the Seat of Mary (Kathisma) (from the 5-8th centuries, floral and geometric designs, cornucopiae, discovered in 1992-7) and the lower church at Shepherds' Field (or Beit Sahour
Beit Sahour
Beit Sahour is a Palestinian town east of Bethlehem under the administration of the Palestinian National Authority...
, the Greek Orthodox site, a floor including crosses, and therefore must predate 427). An exceptionally well preserved, carpet-like mosaic floor was uncovered in 1949 in Bethany, the early Byzantine church of the Lazarium which was built between 333 and 390. Because of its purely geometrical pattern, the church floor is to be grouped with other mosaics of the time in Palestine and neighboring areas, especially the Constantinian mosaics in the central nave at Bethlehem. A second church was built above the older one during the 6th century with another more simple geometric mosaic floor. In 2003 during the construction works of the Israeli security barrier in Abu Dis
Abu Dis
Abu Dis is a Palestinian town in the Jerusalem Governorate, bordering Jerusalem. Abu Dis is due east of the Jerusalem municipal border. According to the Palestinian Central Bureau of Statistics , the town had a population of approximately 12,100 in mid-year 2006.-Ottoman era:Abu Dis was one of the...
workers damaged the remains of a Byzantine monastery which was subsequently excavated. The monastery church had an elaborate mosaic floor decorated with images of animals including a deer and an octopus.
Ruins of three Byzantine churches were discovered in the village of Beit Jibrin (ancient Eleutheropolis). One was decorated with an exquisite mosaic depicting the four seasons but it was defaced during the 1948 Arab-Israeli War
1948 Arab-Israeli War
The 1948 Arab–Israeli War, known to Israelis as the War of Independence or War of Liberation The war commenced after the termination of the British Mandate for Palestine and the creation of an independent Israel at midnight on 14 May 1948 when, following a period of civil war, Arab armies invaded...
. The other church north of the wadi was excavated in 1941-1942. Its floor mosaic have octagons with representations of birds, quadrupeds, and scenes from the story of Jonah
Jonah
Jonah is the name given in the Hebrew Bible to a prophet of the northern kingdom of Israel in about the 8th century BC, the eponymous central character in the Book of Jonah, famous for being swallowed by a fish or a whale, depending on translation...
depicting the prophet being thrown out of the boat or resting. In nearby Emmaus Nicopolis
Emmaus Nicopolis
Emmaus Nicopolis was the Roman name for a city associated with the Emmaus of the New Testament, where Jesus is said to have appeared after his death and resurrection. In the modern age, the site was the location of the Palestinian Arab village of Imwas, near the Latrun junction, between Jerusalem...
two Byzantine basilicas were built in the 6-7th centuries above the house of Cleopas
Cleopas
Cleopas was a figure of early Christianity, one of the two disciples who encountered Jesus during the Road to Emmaus appearance in the Gospel of ....
, which was venerated by Christians as the place of the breaking of bread by the risen Christ. Both were decorated with mosaic floors. In the northern nave of the southern basilica, a nilotic mosaic portrayed birds, animals and flowers. In Abu Gosh a 5th century mosaic floor was preserved in the modern Church of the Ark of the Covenant.

Judean desert
The Judaean Desert is a desert in Israel and the West Bank that lies east of Jerusalem and descends to the Dead Sea. It stretches from the northeastern Negev to the east of Beit El, and is marked by terraces with escarpments. It ends in a steep escarpment dropping to the Dead Sea and the Jordan...
also decorated their monasteries with mosaic floors. The Monastery of Martyrius
Monastery of Martyrius
The Monastery of Martyrius, now located in the center of the Israeli settlement and city of Ma'ale Adumim, east of Jerusalem, was one of the most important centres of monastic life in the Judean Desert during the Byzantine period.-History:...
was founded in the end of the 5th century and it was re-discovered in 1982-85. The most important work of art here is the intact geometric mosaic floor of the refectory although the severely damaged church floor was similarly rich. The mosaics in the church of the nearby Monastery of Euthymius are of later date (discovered in 1930). They were laid down in the Umayyad era, after a devastating earthquake in 659. Two six pointed stars and a red chalice are the most important surviving features. The church floor was later replaced with rough opus sectile (probably by the Crusaders). In 1995-99 two large Byzantine churches were discovered in Khirbet Yattir (ancient Iethira) in the southern part of the Judean Desert. They belonged to monastic communities and were paved with beautiful mosaics in the 6-7th centuries. Two phases can be distinguished in the mosaic floor of Church C. The earlier was decorated with four birds and medallions of vines while the later one was divided into 23 strips which contain magical symbols and holy names. The dedicatory inscription dates this mosaic to the year 631/32.
The most important Byzantine mosaics in Samaria
Samaria
Samaria, or the Shomron is a term used for a mountainous region roughly corresponding to the northern part of the West Bank.- Etymology :...
were discovered in Shilo where three basilicas were uncovered. The large mosaic floor of the Church of the Ark (completed in 420, re-discovered in 2006) contains geometric designs, flora representations and three Greek inscriptions, among them a salute to the residents of Seilun (Shilo).
Galilee
Two mosaic sites were discovered in the vicinity of modern-day NahariyaNahariya
Nahariya is the northernmost coastal city in Israel, with an estimated population of 51,200.-History:Nahariya was founded by German Jewish immigrants from the Fifth Aliyah in the 1930s...
in Western Galilee. One that now belongs to moshav Shavei Tzion
Shavei Tzion
Shavei Tzion is a moshav shitufi in northern Israel. Located between Acre and Nahariya and covering 2,000 dunams, it falls under the jurisdiction of Mateh Asher Regional Council. In 2006 it had a population of 654....
was a 5-6th century church that stood immediately on the seashore. The main motifs of its carpet-like, decorative floor are red swastikas on white background. The other church is located on a hill called Khirbet Ittaim. The tri-apsidal basilica was built in 555 by the bishop of Tyre and was destroyed in 614 by the Persians. The remarkable mosaic floor has figurative scenes like a hunter attacking a tiger in the south apse, a man with a horse, a sitting man playing a flute and two beautiful peacocks drinking from the fountain of life.
In 1940 a 6th century Byzantine church was discovered in present-day Hanita
Hanita
Hanita is a kibbutz in northern Israel. Located in the western Galilee approximately 15 kilometres northeast of Nahariya, it falls under the jurisdiction of Mateh Asher Regional Council. In 2011 it had a population of 500....
. Among the mainly decorative motifs of its mosaic floor there are two animal scenes: a boar grazing on a field and a hare eating grapes (the latter is very uncommon). Both are considered a symbol of redemption.
The mosaic decoration of the Church of the Annunciation
Church of the Annunciation
The Church of the Annunciation , sometimes also referred to as the Basilica of the Annunciation is a church in Nazareth, in modern-day northern Israel.-History:...
in Nazareth
Nazareth
Nazareth is the largest city in the North District of Israel. Known as "the Arab capital of Israel," the population is made up predominantly of Palestinian Arab citizens of Israel...
, which was one of the great Constantinian basilicas of the Holy Land, was totally destroyed during the centuries together with much of the basilica. Archeological evidences prove that prior to the mid-4th century another small church stood on the site. A mosaic inscription referring to Deacon Conon survived of this building. The existence of a large Byzantine church on the site of the present-day Sisters of Nazareth convent was proven in 2006-2007. This church was architecturally complex and elaborately decorated, it was floored with polychrome mosaic (of which only very scant remains survived) and also had polychrome wall mosaics. Further mosaic-floored Byzantine buildings were located to the south of the church. This evidence indicates that Byzantine Nazareth contained two large churches dominating its centre, with other mosaic-floored and colonnaded masonry structures around them. As such the town had to be an important Byzantine pilgrimage centre. On the top of nearby Mount Tabor
Mount Tabor
-Places:*Mount Tabor, a hill in Israel near Nazareth believed by many to be the site of the Transfiguration of ChristIn the United States:*Mount Tabor, Indiana, an unincorporated community...
which was venerated as the place of the Transfiguration of Christ another great church was built before 422. A small portion of its mosaic floor survived.
The Monastery of Lady Mary near Bet She'an
Bet She'an
is a city in the North District of Israel which has played an important role historically due to its geographical location at the junction of the Jordan River Valley and Jezreel Valley...
was established in 567. Many rooms and the church itself was decorated with mosaic among them a great zodiac, a circle of 12 figures representing the months, with the sun god Helios and the moon goddess Selene in the centre. Similar mosaic zodiacs were found in contemporary Jewish synagogues. Other mosaics represent vine tendrils, hunters, animals and birds.
Petra and the desert

Mosaic art also flourished in Christian Petra
Petra
Petra is a historical and archaeological city in the Jordanian governorate of Ma'an that is famous for its rock cut architecture and water conduits system. Established sometime around the 6th century BC as the capital city of the Nabataeans, it is a symbol of Jordan as well as its most visited...
where three Byzantine churches were discovered. The most important one was uncovered in 1990. It is known that the walls were also covered with golden glass mosaics but only the floor panels survived as usual. The mosaic of the seasons in the southern aisle is from this first building period from the middle of the 5th century. In the first half of the 6th century the mosaics of the northern aisle and the eastern end of the southern aisle were installed. They depict native as well as exotic or mythological animals, and personifications of the Seasons, Ocean, Earth and Wisdom.
Mosaic covered churches prove that the towns along the Nabatean spice road in the Negev Desert flourished in the Christian era. In Mamshit
Mamshit
Mamshit is the Nabataean city of Memphis. In the Nabataean period, Mamshit was an important station on Incense Road, running from the Idumean Mountains, through the Arabah and Ma'ale Akrabim, and on to Beer-Sheva or to Hebron and Jerusalem. The city covers and is the smallest but best restored...
two great churches survived. The Eastern Church (or Church of the Martyrs) was probably built in the late 4th century and has a geometric floor with crosses. The mosaics of the Western (or Nile) Church are more elaborate depicting birds, fruit basket, swastikas and flowers. An inscription in a medallion reads: "God, save your servant Nilus, lover of Jesus, who founded this building. Preserve him and his household."
Several mosaics were discovered around Gaza
Gaza
Gaza , also referred to as Gaza City, is a Palestinian city in the Gaza Strip, with a population of about 450,000, making it the largest city in the Palestinian territories.Inhabited since at least the 15th century BC,...
which was an important centre of Christianity during the Byzantine era. The most publicized of these discoveries were made in 1917 by Australian troops fighting against the Ottomans at Shellal
Shellal
Shellal is a small ancient village on the banks of the Nile, south of Aswan in Egypt. It was the traditional north frontier of the Nubian region with both the Egyptian Empire and the Roman Empire. During the period of ancient Egypt it was a very important quarry area for granite production...
. The church stood upon a small hill above Wadi Guzze and has an elaborate floor decorated exotic animals in medallions and two beautiful peacocks. It was dated to 561-562 and it is regarded an extraordinary piece of Justinian era mosaic art. A lesser known mosaic of a church was also uncovered during military operations in the summer of 1917 at Umm Jerar, south of Gaza. Two floors have many similarities in design.
In the Barnea district of the port of Ashkelon
Ashkelon
Ashkelon is a coastal city in the South District of Israel on the Mediterranean coast, south of Tel Aviv, and north of the border with the Gaza Strip. The ancient seaport of Ashkelon dates back to the Neolithic Age...
two large Byzantine churches were unearthed. In the first only the remains of glass tesserae prove that its walls were decorated with mosaics while in the other one an almost intact geometric floor survived with three inscriptions dating to years 493 and 498.
Lebanon
As part of ancient SyriaSyria
Syria , officially the Syrian Arab Republic , is a country in Western Asia, bordering Lebanon and the Mediterranean Sea to the West, Turkey to the north, Iraq to the east, Jordan to the south, and Israel to the southwest....
, present-day Lebanon
Lebanon
Lebanon , officially the Republic of LebanonRepublic of Lebanon is the most common term used by Lebanese government agencies. The term Lebanese Republic, a literal translation of the official Arabic and French names that is not used in today's world. Arabic is the most common language spoken among...
shared the same great tradition in Roman and Byzantine mosaic art as neighbouring areas. In the recent past many important finds were brought to light in cities and churches all over the country. An important Byzantine mosaic collection was established in Beiteddine Palace
Beiteddine Palace
Beiteddine Palace is a 19th century palace in Beiteddine, Lebanon. It hosts the annual Beiteddine Festival and the Beiteddine Palace Museum.- History :...
, mostly from discoveries in the coastal town of Jiyyeh (ancient Porphyrion). They date from the 5-6th centuries. The designs are often geometric and stylized but there are also interesting depictions animals, including leopards, gazelles, lions, hares and birds, as well as religious figures.
A big geometric mosaic floor was unearthed in the Church of St John the Baptist in Byblos
Byblos
Byblos is the Greek name of the Phoenician city Gebal . It is a Mediterranean city in the Mount Lebanon Governorate of present-day Lebanon under the current Arabic name of Jubayl and was also referred to as Gibelet during the Crusades...
.
The Umayyad era
The Arab conquest of the Middle EastMiddle East
The Middle East is a region that encompasses Western Asia and Northern Africa. It is often used as a synonym for Near East, in opposition to Far East...
in the 7th century did not break off the art of mosaic making. Arabs learned and accepted the craft as their own and carried on the classical tradition. During the Umayyad era Christianity retained its importance, churches were built and repaired and some of the most important mosaics of the Christian East were made during the 8th century when the region was under Islamic rule.
The mosaics of the Church of St Stephen in ancient Kastron Mefaa (now Umm ar-Rasas) were made in 785 (discovered after 1986). The perfectly preserved mosaic floor is the largest one in Jordan. On the central panel hunting and fishing scenes are depicted while another panel illustrates the most important cities of the region (including Kastron Mefaa, Philadelphia, Madaba, Esbounta, Belemounta, Areopolis, Charac Moaba, Jerusalem, Nablus, Caesarea and Gaza). The frame of the mosaic is especially decorative. Six mosaic masters signed the work: Staurachios from Esbus, Euremios, Elias, Constantinus, Germanus and Abdela. It overlays another, damaged, mosaic floor of the earlier (587) "Church of Bishop Sergius." Another four churches were excavated nearby with traces of mosaic decoration.
The mosaic floors of the Acropolis Church at Ma’in (ancient Belemounta), dated by an inscription to 719–20 include depictions of 11 buildings representing cities in the Holy Land, as identified by Greek toponyms. All figures were damaged by iconoclasts and carefully replaced with various motifs.
The last great mosaics in Madaba were made in 767 in the Church of the Virgin Mary (discovered in 1887). It is a masterpiece of the geometric style with a Greek inscription in the central medallion.
With the fall of the Umayyad dynasty in 750 the Middle East went through deep cultural changes. No great mosaics were made after the end of the 8th century and the majority of churches gradually fell into disrepair and were eventually destroyed. The tradition of mosaic making died out among the Christians and also in the Islamic community.

