
EF hand
Encyclopedia
The EF hand is a helix-loop-helix structural domain found in a large family
of calcium-binding protein
s. The EF-hand motif contains a helix-loop-helix topology, much like the spread thumb and forefinger of the human hand, in which the Ca2+ ions are coordinated by ligands within the loop. It consists of two alpha helices
positioned roughly perpendicular to one another and linked by a short loop region (usually about 12 amino acid
s) that usually binds calcium
ions. The motif takes its name from traditional nomenclature used in describing the protein parvalbumin
, which contains three such motifs and is probably involved in muscle
relaxation via its calcium-binding activity. EF hands also appear in each structural domain of the signaling protein
calmodulin
and in the muscle protein troponin-C.

Additional points:
Protein family
A protein family is a group of evolutionarily-related proteins, and is often nearly synonymous with gene family. The term protein family should not be confused with family as it is used in taxonomy....
of calcium-binding protein
Protein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
s. The EF-hand motif contains a helix-loop-helix topology, much like the spread thumb and forefinger of the human hand, in which the Ca2+ ions are coordinated by ligands within the loop. It consists of two alpha helices
Alpha helix
A common motif in the secondary structure of proteins, the alpha helix is a right-handed coiled or spiral conformation, in which every backbone N-H group donates a hydrogen bond to the backbone C=O group of the amino acid four residues earlier...
positioned roughly perpendicular to one another and linked by a short loop region (usually about 12 amino acid
Amino acid
Amino acids are molecules containing an amine group, a carboxylic acid group and a side-chain that varies between different amino acids. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen...
s) that usually binds calcium
Calcium
Calcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
ions. The motif takes its name from traditional nomenclature used in describing the protein parvalbumin
Parvalbumin
Parvalbumin is a calcium-binding albumin protein with low molecular weight .It has three EF hand motifs and is structurally related to calmodulin and troponin C...
, which contains three such motifs and is probably involved in muscle
Muscle
Muscle is a contractile tissue of animals and is derived from the mesodermal layer of embryonic germ cells. Muscle cells contain contractile filaments that move past each other and change the size of the cell. They are classified as skeletal, cardiac, or smooth muscles. Their function is to...
relaxation via its calcium-binding activity. EF hands also appear in each structural domain of the signaling protein
Cell signaling
Cell signaling is part of a complex system of communication that governs basic cellular activities and coordinates cell actions. The ability of cells to perceive and correctly respond to their microenvironment is the basis of development, tissue repair, and immunity as well as normal tissue...
calmodulin
Calmodulin
Calmodulin is a calcium-binding protein expressed in all eukaryotic cells...
and in the muscle protein troponin-C.
Binding site

- The calcium ion is coordinated in a pentagonal bipyramidal configuration. The six residues involved in the binding are in positions 1, 3, 5, 7, 9 and 12; these residues are denoted by X, Y, Z, -Y, -X and -Z. The invariant Glu or Asp at position 12 provides two oxygens for liganding Ca (bidentate ligand).
- The calcium ion is bound by both protein backbonePeptide bondThis article is about the peptide link found within biological molecules, such as proteins. A similar article for synthetic molecules is being created...
atoms and by amino acid side chainSide chainIn organic chemistry and biochemistry, a side chain is a chemical group that is attached to a core part of the molecule called "main chain" or backbone. The placeholder R is often used as a generic placeholder for alkyl group side chains in chemical structure diagrams. To indicate other non-carbon...
s, specifically those of the acidic amino acid residues, aspartate and glutamate. These residues are negatively charged and will make a charge-interaction with the positively charged calcium ion. The EF hand motif was among the first structural motifs whose sequence requirements were analyzed in detail. Five of the loop residues bind calcium and thus have a strong preference for oxygenOxygenOxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
-containing side chains, especially aspartate and glutamate. The sixth residue in the loop is necessarily glycineGlycineGlycine is an organic compound with the formula NH2CH2COOH. Having a hydrogen substituent as its 'side chain', glycine is the smallest of the 20 amino acids commonly found in proteins. Its codons are GGU, GGC, GGA, GGG cf. the genetic code.Glycine is a colourless, sweet-tasting crystalline solid...
due to the conformational requirements of the backbone. The remaining residues are typically hydrophobic and form a hydrophobic core that binds the stabilizes the two helices. - Upon binding to Ca2+, this motif may undergo conformational changes that enable Ca2+-regulated functions as seen in Ca2+ effectors such as calmodulin (CaM) and troponin C (TnC) and Ca2+ buffers such as calreticulin and calbindin D9k. While the majority of the known EF-hand Calcium-binding proteins (CaBPs) contain paired EF-hand motifs, CaBP’s with single EF hands have also been discovered in both bacteria and eukaryotes. In addition, “EF-hand-like motifs” have been found in a number of bacteria. Although the coordination properties remain similar with the canonical 29-residue helix-loop-helix EF-hand motif, the EF-hand-like motifs differ from EF-hands in that they contain deviations in the secondary structure of the flanking sequences and/or variation in the length of the Ca2+-coordinating loop.
Prediction

- Pattern (motif signature) search is one of the most straightforward ways to predict continuous EF-hand Ca2+-binding sites in proteins. Based on the sequence alignment results of canonical EF-hand motifs, especially the conserved side chains directly involved in Ca2+ binding, a pattern has been generated to predict canonical EF-hand sites. A prediction servers may be found in the external links section.
Classification
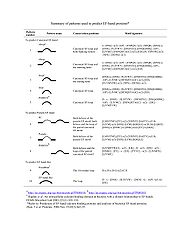
- Since the delineation of the EF-hand motif in 1973, the family of EF-hand proteins has expanded to include at least 66 subfamilies thus far. EF-hand motifs are divided into two major groups:
- Canonical EF-hands as seen in calmodulin (CaM) and the prokaryotic CaM-like protein calerythrin. The 12-residue canonical EF-hand loop binds Ca2+ mainly via sidechain carboxylates or carbonyls (loop sequence positions 1, 3, 5, 12). The residue at the –X axis coordinates the Ca2+ ion through a bridged water molecule. The EF-hand loop has a bidentate ligand (Glu or Asp) at axis –Z.
- Pseudo EF-hands exclusively found in the N-termini of S100 and S100-like proteins. The 14-residue pseudo EF-hand loop chelates Ca2+ primarily via backbone carbonyls (positions 1, 4, 6, 9).
Additional points:

- EF-hand-like proteins with diversified flanking structural elements around the Ca2+-binding loop have been reported in bacteria and viruses. These prokaryotic EF-hand-like proteins are widely implicated in Ca2+ signaling and homeostasis in bacteria. They contain flexible lengths of Ca2+-binding loops that differ from the EF-hand motifs. However, their coordination properties resemble classical EF-hand motifs.
- For example, the semi-continuous Ca2+-binding site in D-galactose-binding protein (GBP) contains a nine-residue loop. The Ca2+ ion is coordinated by seven protein oxygen atoms, five of which are from the loop mimicking the canonical EF-loop whereas the other two are from the carboxylate group of a distant Glu.
- Another example is a novel domain named Excalibur (extracellular Ca2+-binding region) isolated from Bacillus subtilis. This domain has a conserved 10-residue Ca2+-binding loop strikingly similar to the canonical 12-residue EF-hand loop.
- The diversity of the structure of the flanking region is illustrated by the discovery of EF-hand-like domains in bacterial proteins. For example, a helix-loop-strand instead of the helix-loop-helix structure is in periplasmic galactose-binding protein (Salmonella typhimurium) or alginate-binding protein (SphingomonasSphingomonasSphingomonas was defined in 1990 as a group of Gram-negative, rod-shaped, chemoheterotrophic, strictly aerobic bacteria. They possess ubiquinone 10 as their major respiratory quinone, contain glycosphingolipids instead of lipopolysaccharide in their cell envelopes, and typically produce...
sp.); the entering helix is missing in protective antigen (Bacillus anthracisBacillus anthracisBacillus anthracis is the pathogen of the Anthrax acute disease. It is a Gram-positive, spore-forming, rod-shaped bacterium, with a width of 1-1.2µm and a length of 3-5µm. It can be grown in an ordinary nutrient medium under aerobic or anaerobic conditions.It is one of few bacteria known to...
) or dockerin (Clostridium thermocellumClostridium thermocellumClostridium thermocellum is an anaerobic, thermophilic bacterium. C. thermocellum has garnered research interest due to its cellulolytic and ethanologenic abilities, being capable of directly converting a cellulosic substrate into ethanol. This makes it useful in converting biomass into a usable...
).
- Among all the structures reported to date, the majority of EF-hand motifs are paired either between two canonical or one pseudo and one canonical motifs. For proteins with odd numbers of EF-hands, such as the penta-EF-hand calpain, EF-hand motifs were coupled through homo- or hetero-dimerization. The recently-identified EF-hand containing ER Ca2+ sensor protein, stromal interaction molecule 1 and 2 (STIM1, STIM2), has been shown to contain a Ca2+-binding canonical EF-hand motif that pairs with an immediate, downstream atypical "hidden" non-Ca2+-binding EF-hand. Single EF-hand motifs can serve as protein-docking modules: for example, the single EF hand in the NKD1 and NKD2 proteins binds the Dishevelled (DVL1, DVL2, DVL3) proteins.
- Functionally, the EF-hands can be divided into two classes: 1) signaling proteins and 2) buffering/transport proteins. The first group is the largest and includes the most well-known members of the family such as calmodulin, troponin C and S100B. These proteins typically undergo a calcium-dependent conformational change which opens a target binding site. The latter group is represented by calbindin D9k and do not undergo calcium dependent conformational changes.
Examples
Humans proteins containing this domain include:- ACTN1ACTN1Alpha-actinin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTN1 gene.-Interactions:Actinin, alpha 1 has been shown to interact with PDLIM1, Collagen, type XVII, alpha 1, CDK5R1, Zyxin, Protein kinase N1, GIPC1, SSX2IP and CDK5R2....
; ACTN2; ACTN3ACTN3Alpha-actinin-3, also known as alpha-actinin skeletal muscle isoform 3 or F-actin cross-linking protein, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ACTN3 gene....
; ACTN4; APBA2BPAPBA2BPN-terminal EF-hand calcium-binding protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NECAB3 gene.-Further reading:...
; AYTL1; AYTL2 - C14orf143; CABP1; CABP2; CABP3; CABP4; CABP5; CABP7; CALB1; CALB2; CALM2CALM2Calmodulin 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALM2 gene.- Further reading :...
; CALM3CALM3Calmodulin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALM3 gene.-Further reading:...
; CALML3CALML3Calmodulin-like protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALML3 gene.-Further reading:...
; CALML4; CALML5CALML5Calmodulin-like protein 5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALML5 gene.-Further reading:...
; CALML6; CALN1CALN1Calcium-binding protein 8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CALN1 gene.-Further reading:...
; CALUCaluCalu is an Etruscan chthonic deity, often equated with the Etruscan equivalent to the Greek Hades, Aita. He is identified by his wolf attributes, such as a wolf-like appearance or a human with a wolf-skin cap....
; CAPN1CAPN1Calpain-1 catalytic subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN1 gene.-External Links:* The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors:...
; CAPN11; CAPN2CAPN2Calpain-2 catalytic subunit is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN2 gene.-External Links:* The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors:...
; CAPN3CAPN3Calpain-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN3 gene.-External links:* The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors: ** LOVD mutation database:...
; CAPN9CAPN9Calpain-9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPN9 gene.-External Links:* The MEROPS online database for peptidases and their inhibitors:...
; CAPNS1CAPNS1Calpain small subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPNS1 gene.-Further reading:...
; CAPNS2; CAPSCAPS (gene)Calcyphosin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CAPS gene.-Further reading:...
; CAPS2; CAPSLCaPSLCaPSL is a printer command language/page description language used by early Canon printers including the LBP-8III series and supported on LBP-8IV printers. This language was discontinued, with later Canon printers implementing PCL. It was also called LIPS or LIPS4....
; CBARA1CBARA1Calcium-binding atopy-related autoantigen 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CBARA1 gene.-Further reading:...
; CETN1CETN1Centrin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CETN1 gene. It belongs to the centrin family of proteins.-Further reading:...
; CETN2CETN2Centrin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CETN2 gene. It belongs to the centrin family of proteins.-Interactions:CETN2 has been shown to interact with XPC.-Further reading:...
; CETN3CETN3Centrin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CETN3 gene. It belongs to the centrin family of proteins.-Further reading:...
; CHPCHP (gene)Calcium binding protein P22, also known as CHP, is a human gene.-Interactions:CHP has been shown to interact with Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 1 and Sodium-hydrogen antiporter 3.-Further reading:...
; CHP2; CIB1CIB1Calcium and integrin-binding protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CIB1 gene.-Interactions:CIB1 has been shown to interact with RAC3, PSEN2, DNA-PKcs, UBR5 and CD61.-Further reading:...
; CIB2; CIB3; CIB4; CRNN - DGKADGKADiacylglycerol kinase alpha is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGKA gene.-External links:* in PROSITE...
; DGKBDGKBDiacylglycerol kinase beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGKB gene.-Further reading:...
; DGKGDGKGDiacylglycerol kinase gamma is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the DGKG gene.-Further reading:...
; DSTDystoninBullous pemphigoid antigen 1, isoforms 1/2/3/4/5/8 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the DST gene.-Interactions:Dystonin has been shown to interact with Collagen, type XVII, alpha 1, DCTN1 and Erbin.-Further reading:...
; DUOX1DUOX1Dual oxidase 1, also known as DUOX1 or ThOX1 , is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the DUOX1 gene. DUOX1 was first identified in the mammalian thyroid gland. In humans, two isoforms are found; hDUOX1 and hDUOX2...
; DUOX2DUOX2Dual oxidase 2, also known as DUOX2 or ThOX2 is an enzyme which in humans is encoded by the DUOX2 gene. Dual oxidase is an enzyme that was first identified in the mammalian thyroid gland. In humans, two isoforms are found; hDUOX1 and hDUOX2... - EFCAB1; EFCAB2; EFCAB4A; EFCAB4B; EFCAB6EFCAB6EF-hand calcium-binding domain-containing protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EFCAB6 gene.-Interactions:EFCAB6 has been shown to interact with PARK7 and Androgen receptor.-Further reading:...
; EFCBP1; EFCBP2EFCBP2N-terminal EF-hand calcium-binding protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NECAB2 gene.-Further reading:...
; EFHA1; EFHA2; EFHB; EFHC1EFHC1EF-hand domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EFHC1 gene.-Further reading:...
; EFHD1; EFHD2; EPS15EPS15Epidermal growth factor receptor substrate 15 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPS15 gene.-Interactions:EPS15 has been shown to interact with REPS2, HGS, EPN1, CRK and HRB.-Further reading:...
; EPS15L1EPS15L1Epidermal growth factor receptor substrate 15-like 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the EPS15L1 gene.-Interactions:EPS15L1 has been shown to interact with HRB.-Further reading:... - FKBP10FKBP10FK506-binding protein 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FKBP10 gene.-Further reading:...
; FKBP14; FKBP7; FKBP9FKBP9FK506-binding protein 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FKBP9 gene.-Further reading:...
; FKBP9L; FREQFreqFreq is a 1985 album by English singer and musician Robert Calvert.It was recorded during the time of the UK miners' strike and in between the songs it features snippets of field recordings by Calvert with miners on a picket line, with Calvert displaying his sympathy for their cause.The lyrics...
; FSTL1FSTL1Follistatin-related protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the FSTL1 gene.-Further reading:...
; FSTL5 - GCAGCA (gene)Grancalcin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the GCA gene.-Interactions:GCA has been shown to interact with SRI.-Further reading:...
; GPD2; GUCA1AGUCA1AGuanylyl cyclase-activating protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GUCA1A gene.-Further reading:...
; GUCA1BGUCA1BGuanylyl cyclase-activating protein 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the GUCA1B gene.-External links:*...
; GUCA1C - hippocalcinHippocalcinHippocalcin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HPCA gene.Hippocalcin is a calcium-binding protein that belongs to the neuronal calcium sensor family of proteins. It is expressed in mammalian brains especially in the hippocampus...
; HPCAL1HPCAL1Hippocalcin-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the HPCAL1 gene.-Further reading:...
; HPCAL4HPCAL4Hippocalcin like 4, also known as HPCAL4, is a human gene.-Further reading:...
; HZGJ - IFPSIFPSIFPS was a financial modeling language created by professor Gerald R. Wagner and his students of the University of Texas at Austin in the late 1970s. IFPS was marketed by Execucom, an Austin-based company started by Wagner...
; ITSN1ITSN1Intersectin-1 is a protein that, in humans, is encoded by the ITSN1 gene.-Interactions:ITSN1 has been shown to interact with SNAP-25, SOS1, SCAMP1 and CDC42.-Further reading:...
; ITSN2ITSN2Intersectin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ITSN2 gene.-Interactions:ITSN2 has been shown to interact with Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein.-Further reading:...
; KCNIP1KCNIP1Kv channel-interacting protein 1 also known as KChIP1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNIP1 gene.- Function :This gene encodes a member of the family of voltage-gated potassium channel-interacting proteins , which belong to the recoverin branch of the EF-hand superfamily...
; KCNIP2KCNIP2Kv channel-interacting protein 2 also known as KChIP2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNIP2 gene.- Function :This gene encodes a member of the family of voltage-gated potassium channel-interacting proteins , which belong to the recoverin branch of the EF-hand superfamily...
; KCNIP3; KCNIP4KCNIP4Kv channel-interacting protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the KCNIP4 gene....
; KIAA1799 - LCP1LCP1Plastin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the LCP1 gene.-Further reading:...
- MACF1MACF1Microtubule-actin cross-linking factor 1, isoforms 1/2/3/5 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MACF1 gene.-Further reading:...
; MRLC2; MRLC3; MST133; MYL1MYL1Myosin light chain 3, skeletal muscle isoform is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYL1 gene.-Further reading:...
; MYL2MYL2Myosin regulatory light chain 2, ventricular/cardiac muscle isoform is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYL2 gene.- External links :* * Info with links in the...
; MYL5; MYL6BMYL6BMyosin light chain 6B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYL6B gene.-Further reading:...
; MYL7MYL7Myosin regulatory light chain 2, atrial isoform is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYL7 gene.-Further reading:...
; MYL9MYL9Myosin regulatory light polypeptide 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the MYL9 gene.- Function :Myosin, a structural component of muscle, consists of two heavy chains and four light chains. The protein encoded by this gene is a myosin light chain that may regulate muscle contraction by...
; MYLC2PL; MYLPF - NCALD; NINNinNin may refer to:* Nine Inch Nails, an American industrial rock band* NIN , a Serbian political magazine* NIN , the Sumerian sign for lady* NIN , a human gene* Nion or Nin, a letter in the Ogham alphabet...
; NKD1; NKD2; NLP; NOX5NOX5NADPH oxidase, EF-hand calcium binding domain 5, also known as NOX5, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the NOX5 gene.- Function :NOX5 is a novel NADPH oxidase that generates superoxide....
; NUCB1NUCB1Nucleobindin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUCB1 gene.-Further reading:...
; NUCB2NUCB2Nucleobindin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the NUCB2 gene.-Interactions:NUCB2 has been shown to interact with NDN.-Further reading:... - OCM
- PDCD6PDCD6Programmed cell death protein 6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PDCD6 gene.-Interactions:PDCD6 has been shown to interact with ASK1, PDCD6IP, Fas receptor, ANXA11 and PEF1.-Further reading:...
; PEF1PEF1Peflin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PEF1 gene.-Further reading:...
; PKD2; PLCD1PLCD11-phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase delta-1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PLCD1 gene.PLCd1 is essential to maintain homeostasis of the skin.-External links:*...
; PLCD4PLCD41-phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase delta-4 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PLCD4 gene....
; PLCH1; PLCH2; PLS1; PLS3PLS3Plastin-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PLS3 gene.-Further reading:...
; PP1187; PPEF1PPEF1Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase with EF-hands 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPEF1 gene.-Interactions:PPEF1 has been shown to interact with Calmodulin 1.-Further reading:...
; PPEF2; PPP3R1PPP3R1Calcineurin subunit B type 1 also known as protein phosphatase 2B regulatory subunit 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPP3R1 gene.- Clinical significance :...
; PPP3R2PPP3R2Calcineurin subunit B type 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PPP3R2 gene.-Further reading:...
; PRKCSHPRKCSHGlucosidase 2 subunit beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PRKCSH gene.-Further reading:...
; PVALB - RAB11FIP3RAB11FIP3Rab11 family-interacting protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RAB11FIP3 gene.-Interactions:RAB11FIP3 has been shown to interact with RAB11A.-Further reading:...
; RASEF; RASGRP; RASGRP1RASGRP1RAS guanyl-releasing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RASGRP1 gene.- Function :RAS guanyl nucleotide-releasing protein is a member of a family of genes characterized by the presence of a Ras superfamily guanine nucleotide exchange factor domain...
; RASGRP2RASGRP2RAS guanyl-releasing protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RASGRP2 gene.-Further reading:...
; RASGRP3RASGRP3Ras guanyl-releasing protein 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RASGRP3 gene.-Further reading:...
; RCN1RCN1Reticulocalbin-1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RCN1 gene.-Further reading:...
; RCN2RCN2Reticulocalbin-2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RCN2 gene.-Further reading:...
; RCN3; RCV1; RCVRN; REPS1REPS1RalBP1-associated Eps domain-containing protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the REPS1 gene.-Further reading:...
; RHBDL3; RHOT1RHOT1Mitochondrial Rho GTPase 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RHOT1 gene.-Further reading:...
; RHOT2RHOT2Mitochondrial Rho GTPase 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the RHOT2 gene.-Function:The gene homolog of RHOT2 in yeast codes for a protein called Gem1 that has been shown to be part of a complex of proteins that functions at points of contact between the endoplasmic reticulum and...
; RPTNRPTNRPTN is a gene that encodes repetin.Repetin is an extracellular epidermal matrix protein.It is one of the genes that differ between present-day humans and neandertals....
; RYR2; RYR3RYR3Ryanodine receptor 3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RYR3 gene. The protein encoded by this gene is both a calcium channel and a receptor for the plant alkaloid ryanodine. RYR3 along with RYR1 control the resting calcium ion concentration in skeletal muscle.... - S100A1S100A1S100 calcium-binding protein A1, also known as S100A1, is a protein which in humans is encoded by the S100A1 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene is a member of the S100 family of proteins containing 2 EF-hand calcium-binding motifs...
; S100A11S100A11Protein S100-A11 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100A11 gene.-Interactions:S100A11 has been shown to interact with Nucleolin and S100B.-Further reading:...
; S100A12S100A12Protein S100-A12 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100A12 gene.-Further reading:...
; S100A6S100A6Protein S100-A6 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100A6 gene.-Interactions:S100A6 has been shown to interact with S100B and SUGT1.-Further reading:...
; S100A8; S100A9S100A9Protein S100-A9 also known as migration inhibitory factor-related protein 14 or calgranulin-B is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100A9 gene.- Function :...
; S100BS100BS100 calcium binding protein B or S100B is a protein of the S-100 protein family.S100 proteins are localized in the cytoplasm and nucleus of a wide range of cells, and involved in the regulation of a number of cellular processes such as cell cycle progression and differentiation...
; S100GS100GProtein S100-G is a protein that in humans is encoded by the S100G gene.-Further reading:...
; S100Z; SCAMC-2; SCGNSCGNSecretagogin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SCGN gene.-Further reading:...
; SCN5ASCN5AThe Nav1.5 is a sodium ion channel protein that in humans is encoded by the SCN5A gene. Mutations in the gene are associated with long QT syndrome type 3 , Brugada syndrome, primary cardiac conduction disease and idiopathic ventricular fibrillation....
; SDF4SDF445 kDa calcium-binding protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SDF4 gene.-Further reading:...
; SLC25A12SLC25A12Calcium-binding mitochondrial carrier protein Aralar1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SLC25A12 gene.-Further reading:...
; SLC25A13; SLC25A23; SLC25A24; SLC25A25; SPATA21; SPTA1SPTA1Spectrin alpha chain, erythrocyte is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPTA1 gene.-Interactions:Spectrin, alpha 1 has been shown to interact with Abl gene.-Further reading:...
; SPTAN1SPTAN1Spectrin alpha chain, brain is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SPTAN1 gene.The spectrins are a family of widely-distributed cytoskeletal proteins which are involved in actin crosslinking. The protein enocoded by this gene is a spectrin alpha-chain which heterodimerizes with...
; SRISRI (gene)Sorcin is a protein that in humans is encoded by the SRI gene.-Interactions:SRI has been shown to interact with Ryanodine receptor 2, ANXA7 and GCA.-Further reading:... - TBC1D9TBC1D9TBC1 domain family member 9 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TBC1D9 gene.-Further reading:...
; TBC1D9B; TCHH; TESC; TNNC1; TNNC2TNNC2Troponin C, skeletal muscle is a protein that in humans is encoded by the TNNC2 gene.-Further reading:... - USP32
- VSNL1VSNL1Visinin-like protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the VSNL1 gene.-Further reading:...
- ZZEF1
See also
- Another distinct calcium-binding motif composed of alpha helices is the dockerin domainDockerinDockerin is a protein domain found in the Cellulosome cellular structure. It is part of endoglucanase enzymes. The dockerin's binding partner is the cohesin domain. This interaction is essential to the construction of the Cellulosome complex . The Dockerin domain has two in-tandem repeats of a...
.

