Drainage research
Encyclopedia
Drainage research is the study of agricultural drainage
systems and their effects to arrive at optimal system design.
 Agricultural land drainage
Agricultural land drainage
has agricultural
, environmental
, hydrological
, engineering
, economical
, social
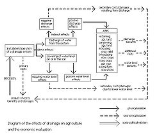
and socio-political aspects (Figure 1).
All these aspects can be subject of drainage research.
The aim (objective, target) of agricultural land drainage is the optimized agricultural production related to:
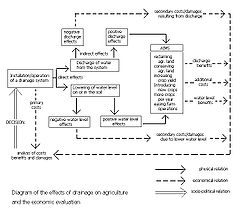
 The role of targets, criterion, environmental, and hydrological factors is illustrated in Figure 2.
The role of targets, criterion, environmental, and hydrological factors is illustrated in Figure 2.
In this figure criterion factors are factors influenced by drainage on the one hand and the agricultural performance on the other.
An example of a criterion factor is the depth of the water table
:
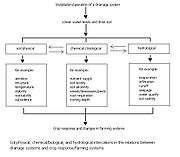 The underlying processes in the optimization (as in the insert of Figure 2) are manifold. The processes can be grouped into mutually dependent soil physical
The underlying processes in the optimization (as in the insert of Figure 2) are manifold. The processes can be grouped into mutually dependent soil physical
, soil chemical/biological
, and hydrological
processes (Figure 3):
Examples of processes can be found in.
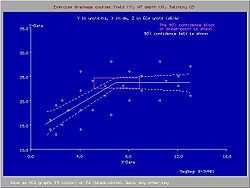 In drainage research the collection and analysis of field data is important.
In drainage research the collection and analysis of field data is important.
In dealing with field data one must expect considerable random variation owing to the large number of natural processes involved and the large variability of plant and soil properties and hydrological conditions.
An example of a relation between crop yield and depth of water table subject to random natural variation is shown in the attached graph. The graph was made with the SegReg program, see segmented regression
.
When analysing field data with random variation a proper application of statistical principles
like in regression
and frequency analysis
is necessary.
the salts brought into the soil with the irrigation water to prevent soil salination
.
Agro-hydro-salinity and leaching models like SaltMod
may be helpful to determine the drainage requirement.
Drainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of surface and sub-surface water from an area. Many agricultural soils need drainage to improve production or to manage water supplies.-Early history:...
systems and their effects to arrive at optimal system design.
Aspects to be covered

Drainage
Drainage is the natural or artificial removal of surface and sub-surface water from an area. Many agricultural soils need drainage to improve production or to manage water supplies.-Early history:...
has agricultural
Agriculture
Agriculture is the cultivation of animals, plants, fungi and other life forms for food, fiber, and other products used to sustain life. Agriculture was the key implement in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that nurtured the...
, environmental
Natural environment
The natural environment encompasses all living and non-living things occurring naturally on Earth or some region thereof. It is an environment that encompasses the interaction of all living species....
, hydrological
Hydrology (agriculture)
Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
, engineering
Engineering
Engineering is the discipline, art, skill and profession of acquiring and applying scientific, mathematical, economic, social, and practical knowledge, in order to design and build structures, machines, devices, systems, materials and processes that safely realize improvements to the lives of...
, economical
Economy
An economy consists of the economic system of a country or other area; the labor, capital and land resources; and the manufacturing, trade, distribution, and consumption of goods and services of that area...
, social
Social
The term social refers to a characteristic of living organisms...
and socio-political aspects (Figure 1).
All these aspects can be subject of drainage research.
The aim (objective, target) of agricultural land drainage is the optimized agricultural production related to:
- reclamation of agricultural land
- conservationSoil conservationSoil conservation is a set of management strategies for prevention of soil being eroded from the Earth’s surface or becoming chemically altered by overuse, acidification, salinization or other chemical soil contamination...
of agricultural land - optimizationOptimization (mathematics)In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
of crop yieldCrop yieldIn agriculture, crop yield is not only a measure of the yield of cereal per unit area of land under cultivation, yield is also the seed generation of the plant itself... - crop diversificationAgricultural diversificationIn the agricultural context, diversification can be regarded as the re-allocation of some of a farm's productive resources, such as land, capital, farm equipment and paid labour, into new activities...
- cropping intensification
- optimization of farmFarmA farm is an area of land, or, for aquaculture, lake, river or sea, including various structures, devoted primarily to the practice of producing and managing food , fibres and, increasingly, fuel. It is the basic production facility in food production. Farms may be owned and operated by a single...
operations.
Systems analysis

In this figure criterion factors are factors influenced by drainage on the one hand and the agricultural performance on the other.
An example of a criterion factor is the depth of the water table
Water table
The water table is the level at which the submarine pressure is far from atmospheric pressure. It may be conveniently visualized as the 'surface' of the subsurface materials that are saturated with groundwater in a given vicinity. However, saturated conditions may extend above the water table as...
:
- A drainage system influences this depth; the relation between drainage system design and depth of water table is mainly physical and can be described by drainage equationsWatertable controlWatertable control is the practice of controlling the water table in agricultural land by subsurface drainage with proper criteria to improve the crop production.- Description and definitions :...
, in which the drainage requirements are to be found from a water balanceHydrology (agriculture)Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
. - The depth of the water table as a criterion factor needs to be translated into a criterion index to be given a numerical value that represents the behavior of the water table on the one hand and that can be related to the target (e.g. crop production) on the other hand.
- The relation between criterion index and target can often be optimizedOptimization (mathematics)In mathematics, computational science, or management science, mathematical optimization refers to the selection of a best element from some set of available alternatives....
, the maximum value providing the ultimate aim while the corresponding value of the criterion index can be used as an agricultural drainage criterion in the design procedure.
Crop response processes

Soil physics
Soil physics is the study of soil physical properties and processes. It is applied to management and prediction under natural and managed ecosystems. Soil physics deals with the dynamics of physical soil components and their phases as solids, liquids, and gases. It draws on the principles of...
, soil chemical/biological
Soil chemistry
Soil chemistry is the study of the chemical characteristics of soil. Soil chemistry is affected by mineral composition, organic matter and environmental factors.-History:...
, and hydrological
Hydrology (agriculture)
Agricultural hydrology is the study of water balance components intervening in agricultural water management, notably in irrigation and drainage.-Water balance components:...
processes (Figure 3):
- The soil physical processes include soil aerationAerationAeration is the process by which air is circulated through, mixed with or dissolved in a liquid or substance.-Aeration of liquids:-Methods:Aeration of liquids is achieved by:...
, soil structureSoil structureSoil structure is determined by how individual soil granules clump or bind together and aggregate, and therefore, the arrangement of soil pores between them...
, soil stability, and soil temperatureTemperatureTemperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot... - The chemical processes include soil salinity, soil acidityAcid sulfate soilAcid sulfate soils are naturally occurring soils, sediments or organic substrates that are formed under waterlogged conditions. These soils contain iron sulfide minerals or their oxidation products. In an undisturbed state below the water table, acid sulfate soils are benign...
and soil alkalinity. - The hydrological processes include evaporationEvaporationEvaporation is a type of vaporization of a liquid that occurs only on the surface of a liquid. The other type of vaporization is boiling, which, instead, occurs on the entire mass of the liquid....
, runoffSurface runoffSurface runoff is the water flow that occurs when soil is infiltrated to full capacity and excess water from rain, meltwater, or other sources flows over the land. This is a major component of the water cycle. Runoff that occurs on surfaces before reaching a channel is also called a nonpoint source...
, and soil salinity.
Examples of processes can be found in.
Field data

In dealing with field data one must expect considerable random variation owing to the large number of natural processes involved and the large variability of plant and soil properties and hydrological conditions.
An example of a relation between crop yield and depth of water table subject to random natural variation is shown in the attached graph. The graph was made with the SegReg program, see segmented regression
Segmented regression
Segmented regression is a method in regression analysis in which the independent variable is partitioned into intervals and a separate line segment is fit to each interval. Segmented or piecewise regression analysis can also be performed on multivariate data by partitioning the various independent...
.
When analysing field data with random variation a proper application of statistical principles
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
like in regression
Regression analysis
In statistics, regression analysis includes many techniques for modeling and analyzing several variables, when the focus is on the relationship between a dependent variable and one or more independent variables...
and frequency analysis
Frequency analysis
In cryptanalysis, frequency analysis is the study of the frequency of letters or groups of letters in a ciphertext. The method is used as an aid to breaking classical ciphers....
is necessary.
Soil salinity control
In irrigated lands, subsurface drainage may be required to leachLeaching (agriculture)
In agriculture, leaching refers to the loss of water-soluble plant nutrients from the soil, due to rain and irrigation. Soil structure, crop planting, type and application rates of fertilizers, and other factors are taken into account to avoid excessive nutrient loss.Leaching may also refer to ...
the salts brought into the soil with the irrigation water to prevent soil salination
Soil salination
Soil salinity is the salt content in the soil.- Causes of soil salinity :Salt-affected soils are caused by excess accumulation of salts, typically most pronounced at the soil surface. Salts can be transported to the soil surface by capillary transport from a salt laden water table and then...
.
Agro-hydro-salinity and leaching models like SaltMod
SaltMod
SaltMod is computer program for the prediction of the salinity of soil moisture, groundwater and drainage water, the depth of the watertable, and the drain discharge in irrigated agricultural lands, using different hydrologic conditions, varying water management options, including the use of...
may be helpful to determine the drainage requirement.
External links
- Website on land drainage : http://www.waterlog.info
- Articles on agricultural land drainage : http://www.waterlog.info/articles.htm
- Frequently asked questions about drainage : http://www.waterlog.info/faqs.htm
- Case studies on land drainage : http://www.waterlog.info/annrep.htm
- Software on land drainage : http://www.waterlog.info/software.htm

