
Direct simulation Monte Carlo
Encyclopedia
Direct Simulation Monte Carlo (DSMC) method uses probabilistic (Monte Carlo
) simulation
to solve the Boltzmann equation
for finite Knudsen number
fluid
flows.
The DSMC method was proposed by Prof. Graeme Bird, Emeritus Professor of Aeronautics, University of Sydney. DSMC is a numerical method for modeling rarefied gas flows, in which the mean free path
of a molecule is of the same order (or greater) than a representative physical length scale (i.e. the Knudsen number
Kn is greater than 1). In supersonic and hypersonic flows rarefaction is characterized by Tsein's parameter, which is equivalent to the product of Knudsen number and Mach number (KnM) or M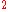 /Re, where Re is the Reynolds number. In these rarefied flows, the Navier-Stokes equations
/Re, where Re is the Reynolds number. In these rarefied flows, the Navier-Stokes equations
can be inaccurate. The DSMC method has been extended to model continuum flows (Kn < 1) and the results can be compared with Navier stokes solutions.
The DSMC method models fluid flows using simulation molecule
s which represent a large number of real molecules in a probabilistic simulation to solve the Boltzmann equation. Molecules are moved through a simulation of physical space in a realistic manner that is directly coupled to physical time such that unsteady flow characteristics can be modeled. Intermolecular collisions and molecule-surface collisions are calculated using probabilistic, phenomenological
models. Common collision models include the Hard Sphere model, the Variable Hard Sphere (VHS) model, and the Variable Soft Sphere (VSS) model. The fundamental assumption of the DSMC method is that the molecular movement and collision phases can be decoupled over time periods that are smaller than the mean collision time.
Currently the DSMC method has been applied to the solution of flows ranging from estimation of the Space Shuttle
re-entry aerodynamics, to the modeling micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS
).
Monte Carlo method
Monte Carlo methods are a class of computational algorithms that rely on repeated random sampling to compute their results. Monte Carlo methods are often used in computer simulations of physical and mathematical systems...
) simulation
Simulation
Simulation is the imitation of some real thing available, state of affairs, or process. The act of simulating something generally entails representing certain key characteristics or behaviours of a selected physical or abstract system....
to solve the Boltzmann equation
Boltzmann equation
The Boltzmann equation, also often known as the Boltzmann transport equation, devised by Ludwig Boltzmann, describes the statistical distribution of one particle in rarefied gas...
for finite Knudsen number
Knudsen number
The Knudsen number is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the molecular mean free path length to a representative physical length scale. This length scale could be, for example, the radius of a body in a fluid...
fluid
Fluid
In physics, a fluid is a substance that continually deforms under an applied shear stress. Fluids are a subset of the phases of matter and include liquids, gases, plasmas and, to some extent, plastic solids....
flows.
The DSMC method was proposed by Prof. Graeme Bird, Emeritus Professor of Aeronautics, University of Sydney. DSMC is a numerical method for modeling rarefied gas flows, in which the mean free path
Mean free path
In physics, the mean free path is the average distance covered by a moving particle between successive impacts which modify its direction or energy or other particle properties.-Derivation:...
of a molecule is of the same order (or greater) than a representative physical length scale (i.e. the Knudsen number
Knudsen number
The Knudsen number is a dimensionless number defined as the ratio of the molecular mean free path length to a representative physical length scale. This length scale could be, for example, the radius of a body in a fluid...
Kn is greater than 1). In supersonic and hypersonic flows rarefaction is characterized by Tsein's parameter, which is equivalent to the product of Knudsen number and Mach number (KnM) or M
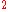 /Re, where Re is the Reynolds number. In these rarefied flows, the Navier-Stokes equations
/Re, where Re is the Reynolds number. In these rarefied flows, the Navier-Stokes equationsNavier-Stokes equations
In physics, the Navier–Stokes equations, named after Claude-Louis Navier and George Gabriel Stokes, describe the motion of fluid substances. These equations arise from applying Newton's second law to fluid motion, together with the assumption that the fluid stress is the sum of a diffusing viscous...
can be inaccurate. The DSMC method has been extended to model continuum flows (Kn < 1) and the results can be compared with Navier stokes solutions.
The DSMC method models fluid flows using simulation molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s which represent a large number of real molecules in a probabilistic simulation to solve the Boltzmann equation. Molecules are moved through a simulation of physical space in a realistic manner that is directly coupled to physical time such that unsteady flow characteristics can be modeled. Intermolecular collisions and molecule-surface collisions are calculated using probabilistic, phenomenological
Phenomenology (science)
The term phenomenology in science is used to describe a body of knowledge that relates empirical observations of phenomena to each other, in a way that is consistent with fundamental theory, but is not directly derived from theory. For example, we find the following definition in the Concise...
models. Common collision models include the Hard Sphere model, the Variable Hard Sphere (VHS) model, and the Variable Soft Sphere (VSS) model. The fundamental assumption of the DSMC method is that the molecular movement and collision phases can be decoupled over time periods that are smaller than the mean collision time.
Currently the DSMC method has been applied to the solution of flows ranging from estimation of the Space Shuttle
Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle was a manned orbital rocket and spacecraft system operated by NASA on 135 missions from 1981 to 2011. The system combined rocket launch, orbital spacecraft, and re-entry spaceplane with modular add-ons...
re-entry aerodynamics, to the modeling micro-electro-mechanical systems (MEMS
Microelectromechanical systems
Microelectromechanical systems is the technology of very small mechanical devices driven by electricity; it merges at the nano-scale into nanoelectromechanical systems and nanotechnology...
).
DSMC Software
Multiple implementations of the DSMC method exist:- DS1V, DS2V and DS3V are the original DSMC programs writen by Prof. Bird. These programs have a visual user interface that can be used for configuration and post processing.
- dsmcFoam is a DSMC solver for 2D and 3D flows. dsmcFoam is part of the open source CFD package OpenFOAMOpenFOAMOpenFOAM is a C++ toolbox for the development of customized numerical solvers, and pre-/post-processing utilities for the solution of continuum mechanics problems, including computational fluid dynamics . The code is released as free and open source software under the GNU General Public License...
. - MONACO is a DSMC solver developed by Prof. Iain Boyd's group at the University of MichiganUniversity of MichiganThe University of Michigan is a public research university located in Ann Arbor, Michigan in the United States. It is the state's oldest university and the flagship campus of the University of Michigan...
. - PI-DSMC is a commercial DSMC software package for 2D and 3D flows.
- SMILE (Statistical Modeling in Low-density Environment) is a general purpose 2D/3D parallel DSMC software system developed since 1998 by Computational Aerodynamics Laboratory (L7) at the Khristianovich Institute of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics, Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences. SMILE has been the principle aerodynamic analysis tool for high-altitude stages of reentry of the Mir Space Station as well as many other Russian and European space vehicle projects.
- MGDS is a fully 3D DSMC solver incorporating three level adaptive mesh refinement and a cut cell algorithm developed by Prof. Tom Schwartzentruber's group at the University of MinnesotaUniversity of MinnesotaThe University of Minnesota, Twin Cities is a public research university located in Minneapolis and St. Paul, Minnesota, United States. It is the oldest and largest part of the University of Minnesota system and has the fourth-largest main campus student body in the United States, with 52,557...
.
External links
- Direct Simulation Monte Carlo Method: Visual Simulation Programs created by GA Bird.
- DSMC Demo Applet
- Course material on DSMC (part of Computational Physics tutorial by Franz J. Vesely, University of Vienna)
- Course material on DSMC and recent developments (given at IPAM UCLA by Lorenzo Pareschi, University of Ferrara)
- PI-DSMC homepage

