
Direct Part Marking
Encyclopedia
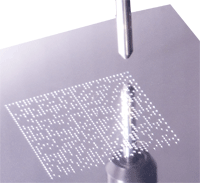
Barcode
A barcode is an optical machine-readable representation of data, which shows data about the object to which it attaches. Originally barcodes represented data by varying the widths and spacings of parallel lines, and may be referred to as linear or 1 dimensional . Later they evolved into rectangles,...
. This is done to allow the tracking of parts through the full life cycle
Product life cycle management
Product life-cycle management is the succession of strategies used by business management as a product goes through its life-cycle. The conditions in which a product is sold changes over time and must be managed as it moves through its succession of stages.Product life-cycle Like human beings,...
.
The interpretation of 'permanent' often depends on the context the part is used. In the aerospace
Aerospace
Aerospace comprises the atmosphere of Earth and surrounding space. Typically the term is used to refer to the industry that researches, designs, manufactures, operates, and maintains vehicles moving through air and space...
industry an aircraft part may be in service for over 30 years. Within telecom and computer industries the life cycle may only last a few years.
DPM is often used by automotive, aerospace, and electronic manufacturers to facilitate a reliable identification of their parts. This can assist in data logging for safety, warranty issues and satisfy regulatory requirements. Also the United States Department of Defense
United States Department of Defense
The United States Department of Defense is the U.S...
demands a physical mark on tangible assets in conjunction with the Item Unique Identification
IUID
Item Unique IDentification is an asset identification system instituted by the United States Department of Defense to uniquely identify a discrete tangible item or asset and distinguish it from other like and/or unlike tangible items...
.
Barcode Types
There are many ways to encode an information to a machine-readable code. The preferred codes are the Data MatrixData Matrix
A Data Matrix code is a two-dimensional matrix barcode consisting of black and white "cells" or modules arranged in either a square or rectangular pattern. The information to be encoded can be text or raw data. Usual data size is from a few bytes up to 1556 bytes. The length of the encoded data...
and the QR Code
QR Code
A QR code is a type of matrix barcode first designed for the automotive industry. More recently, the system has become popular outside of the industry due to its fast readability and comparatively large storage capacity. The code consists of black modules arranged in a square pattern on a white...
. Data Matrix is used by Motorola. It is also preferred by NASA
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration is the agency of the United States government that is responsible for the nation's civilian space program and for aeronautics and aerospace research...
to mark parts. In the automotive industries also the QR Code
QR Code
A QR code is a type of matrix barcode first designed for the automotive industry. More recently, the system has become popular outside of the industry due to its fast readability and comparatively large storage capacity. The code consists of black modules arranged in a square pattern on a white...
is used. This is founded in the fact that this code was initially developed by Denso Wave
DENSO
is a global automotive components manufacturer headquartered in the city of Kariya, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. Established December 16, 1949 as , in 1996 the company became DENSO Corporation worldwide...
(a global automotive components manufacturer) for tracking parts in vehicle manufacturing.
Marking Methods
Methods to produce a permanent mark on parts are:- Abrasive blastingAbrasive blastingAbrasive blasting is the operation of forcibly propelling a stream of abrasive material against a surface under high pressure to smooth a rough surface, roughen a smooth surface, shape a surface, or remove surface contaminants. A pressurized fluid, typically air, or a centrifugal wheel is used to...
- Adhesive dispensing
- CastCastingIn metalworking, casting involves pouring liquid metal into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowing it to cool and solidify. The solidified part is also known as a casting, which is ejected or broken out of the mold to complete the process...
, forgeForgeA forge is a hearth used for forging. The term "forge" can also refer to the workplace of a smith or a blacksmith, although the term smithy is then more commonly used.The basic smithy contains a forge, also known as a hearth, for heating metals...
or moldMoldMolds are fungi that grow in the form of multicellular filaments called hyphae. Molds are not considered to be microbes but microscopic fungi that grow as single cells called yeasts... - Dot peen
- ScribeScribeA scribe is a person who writes books or documents by hand as a profession and helps the city keep track of its records. The profession, previously found in all literate cultures in some form, lost most of its importance and status with the advent of printing...
- Electro-chemical etching
- EmbroideryEmbroideryEmbroidery is the art or handicraft of decorating fabric or other materials with needle and thread or yarn. Embroidery may also incorporate other materials such as metal strips, pearls, beads, quills, and sequins....
- EngravingEngravingEngraving is the practice of incising a design on to a hard, usually flat surface, by cutting grooves into it. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an intaglio printing plate, of copper or another metal, for printing...
/milling - Laser markingLaser engravingLaser engraving, or laser marking, is the practice of using lasers to engrave or mark an object. The technique does not involve the use of inks, nor does it involve tool bits which contact the engraving surface and wear out...
- LaserShot peeing
- Lique metal jet
- StencilStencilA stencil is a thin sheet of material, such as paper, plastic, or metal, with letters or a design cut from it, used to produce the letters or design on an underlying surface by applying pigment through the cut-out holes in the material. The key advantage of a stencil is that it can be reused to...
(mechanical cut, photo process, laser cut)
Other methods like manual metal stamp, vibro-etch and embossing were not suitable to successfully apply micro size (1/32- to 15/64-inch square), high density machine-readable symbols.
Marking Method Selection Factors
The marking method depends on a number of different factors:- Part function
Non-intrusive marking methods are recommended for parts used in safety critical applications like aircraft engines or high pressure and high stress systems. - Part geometry
It is more difficult to place a Data Matrix on a curved surface than it is on a flat surface. - Surface
Highly polished metal surfaces should be textured to reduce glare prior to marking. The textured area should extend one symbol width beyond the borders of marking. - Part Size
When a 2D Symbol is used, the size of the part is not a relevant factor as the available marking area is reduced to below 1/4 inch square. - Operating environment / age life
It should be controlled, if the used marking method can survive in its intended environment and remain readable for the life cycle of the part. - Surface roughnessSurfaceIn mathematics, specifically in topology, a surface is a two-dimensional topological manifold. The most familiar examples are those that arise as the boundaries of solid objects in ordinary three-dimensional Euclidean space R3 — for example, the surface of a ball...
/ Finish
A rough surface is more challenging for a 2D barcode as the data elements can be recognized appropriately. The surface roughness levels should be limited to 8 micro-inches for dot-peen marking, laser and scribe systems can make a readable mark in rougher surfaces. The laser systems burn a "quiet zone" first and then the 2D code. The scribe method provides a high resolution 2D mark that readily readable in most cast surfaces. - Surface thickness
Surface thickness must be taken into account when applying intrusive markings to prevent deformation or excessive weakening of the part. In most applications the marking depth should not exceed 1/10 the thickness of the part.

