
Dilution (equation)
Encyclopedia
Dilution is a reduction in the concentration
of a chemical (gas, vapor, solution). It is the process of reducing the concentration of a solute
in solution
, usually simply by mixing with more solvent
. To dilute a solution means to add more solvent without the addition of more solute. The resulting solution is thoroughly mixed so as to ensure that all parts of the solution are identical.
The same direct relationship
applies to gas
es and vapor
s diluted in air for example. Although, thorough mixing of gases and vapors may not be as easily accomplished.
For example, if there are 10 grams of salt (the solute) dissolved in 1 litre of water (the solvent), this solution has a certain salt concentration/molarity. If one adds 1 litre of water to this solution the salt concentration is reduced. The diluted solution still contains 10 grams of salt/(0.171 mole
s of NaCl).
Mathematically this relationship can be shown in the equation
:
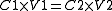
Where:
C1 = Concentration/molarity 1
V1 = Volume 1
C2 = Concentration/molarity 2
V2 = Volume 2
concentration in a room.
Sometimes the equation is also written as:
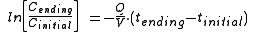 where tinitial = 0
where tinitial = 0
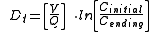
Dt = Time required; the unit of time used is the same as is used for Q.
V = Air or gas volume of the closed space or room in cubic feet, cubic meters or liter
s
Q = Ventilation rate into or out of the room in cubic feet per minute, cubic meters per hour or liters per second
Cinitial = Initial concentration of a vapor inside the room measured in ppm
Cending = Final reduced concentration of the vapor inside the room in ppm
has to be used.

Where the ventilation rate has been adjusted by a mixing factor K.
C = concentration of a gas
G = generation rate
V = room volume
Q' = adjusted ventilation rate of the volume
Concentration
In chemistry, concentration is defined as the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Four types can be distinguished: mass concentration, molar concentration, number concentration, and volume concentration...
of a chemical (gas, vapor, solution). It is the process of reducing the concentration of a solute
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
in solution
Solution
In chemistry, a solution is a homogeneous mixture composed of only one phase. In such a mixture, a solute is dissolved in another substance, known as a solvent. The solvent does the dissolving.- Types of solutions :...
, usually simply by mixing with more solvent
Solvent
A solvent is a liquid, solid, or gas that dissolves another solid, liquid, or gaseous solute, resulting in a solution that is soluble in a certain volume of solvent at a specified temperature...
. To dilute a solution means to add more solvent without the addition of more solute. The resulting solution is thoroughly mixed so as to ensure that all parts of the solution are identical.
The same direct relationship
Direct relationship
In mathematics and statistics, a positive or direct relationship is a relationship between two variables in which change in one variable is associated with a change in the other variable in the same direction. For example all linear relationships with a positive slope are direct relationships...
applies to gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es and vapor
Vapor
A vapor or vapour is a substance in the gas phase at a temperature lower than its critical point....
s diluted in air for example. Although, thorough mixing of gases and vapors may not be as easily accomplished.
For example, if there are 10 grams of salt (the solute) dissolved in 1 litre of water (the solvent), this solution has a certain salt concentration/molarity. If one adds 1 litre of water to this solution the salt concentration is reduced. The diluted solution still contains 10 grams of salt/(0.171 mole
Mole (unit)
The mole is a unit of measurement used in chemistry to express amounts of a chemical substance, defined as an amount of a substance that contains as many elementary entities as there are atoms in 12 grams of pure carbon-12 , the isotope of carbon with atomic weight 12. This corresponds to a value...
s of NaCl).
Mathematically this relationship can be shown in the equation
Equation
An equation is a mathematical statement that asserts the equality of two expressions. In modern notation, this is written by placing the expressions on either side of an equals sign , for examplex + 3 = 5\,asserts that x+3 is equal to 5...
:
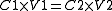
Where:
C1 = Concentration/molarity 1
V1 = Volume 1
C2 = Concentration/molarity 2
V2 = Volume 2
Basic Room Purge Equation
The Basic Room Purge Equation, is used in industrial hygiene. It determines the time required to reduce a known vapor concentration existing in a closed space to a lower vapor concentration. The equation can only be applied when the purged volume of vapor or gas is replaced with "clean" air or gas. For example, the equation can be used to calculate the time required at a certain ventilation rate to reduce a high carbon monoxideCarbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide , also called carbonous oxide, is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas that is slightly lighter than air. It is highly toxic to humans and animals in higher quantities, although it is also produced in normal animal metabolism in low quantities, and is thought to have some normal...
concentration in a room.

Sometimes the equation is also written as:
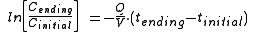 where tinitial = 0
where tinitial = 0Dt = Time required; the unit of time used is the same as is used for Q.
V = Air or gas volume of the closed space or room in cubic feet, cubic meters or liter
Litér
- External links :*...
s
Q = Ventilation rate into or out of the room in cubic feet per minute, cubic meters per hour or liters per second
Cinitial = Initial concentration of a vapor inside the room measured in ppm
Cending = Final reduced concentration of the vapor inside the room in ppm
Dilution Ventilation Equation
The Basic Room Purge Equation can be used only for purge scenarios. In a scenario where a liquid continuously evaporates from a container in a ventilated room, a differential equationDifferential equation
A differential equation is a mathematical equation for an unknown function of one or several variables that relates the values of the function itself and its derivatives of various orders...
has to be used.

Where the ventilation rate has been adjusted by a mixing factor K.

C = concentration of a gas
G = generation rate
V = room volume
Q' = adjusted ventilation rate of the volume
Welding
The dilution in welding terms is defined as the weight of the base metal melted divided by the total weight of the weld metal. For example, if we have a dilution of 0.40, the fraction of the weld metal that came from the consumable electrode is 0.60.See also
- Displacement ventilationDisplacement ventilationDisplacement ventilation is an room air distribution strategy where conditioned outdoor air is supplied at floor level and extracted above the occupied zone, usually at ceiling height.- System design :...
- Reaction rateReaction rateThe reaction rate or speed of reaction for a reactant or product in a particular reaction is intuitively defined as how fast or slow a reaction takes place...
- Partial molar quantities

