
Digital down converter
Encyclopedia
Digital signal processing
Digital signal processing is concerned with the representation of discrete time signals by a sequence of numbers or symbols and the processing of these signals. Digital signal processing and analog signal processing are subfields of signal processing...
, a digital down-converter (DDC) converts a digitized real signal centered at an intermediate frequency
Intermediate frequency
In communications and electronic engineering, an intermediate frequency is a frequency to which a carrier frequency is shifted as an intermediate step in transmission or reception. The intermediate frequency is created by mixing the carrier signal with a local oscillator signal in a process called...
(IF) to a baseband
Baseband
In telecommunications and signal processing, baseband is an adjective that describes signals and systems whose range of frequencies is measured from close to 0 hertz to a cut-off frequency, a maximum bandwidth or highest signal frequency; it is sometimes used as a noun for a band of frequencies...
ed complex signal centered at zero frequency. In addition to downconversion, DDC’s typically decimate
Decimation (signal processing)
In digital signal processing, decimation is a technique for reducing the number of samples in a discrete-time signal. The element which implements this technique is referred to as a decimator.Decimation is a two-step process:...
to a lower sampling rate
Sampling rate
The sampling rate, sample rate, or sampling frequency defines the number of samples per unit of time taken from a continuous signal to make a discrete signal. For time-domain signals, the unit for sampling rate is hertz , sometimes noted as Sa/s...
, allowing follow-on signal processing by lower speed processors.
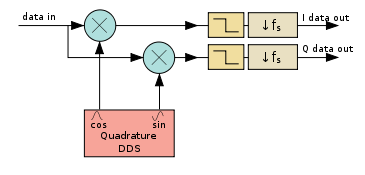
Architecture
A DDC consists of three subcomponents: a direct digital synthesizer (DDS), a low-pass filterLow-pass filter
A low-pass filter is an electronic filter that passes low-frequency signals but attenuates signals with frequencies higher than the cutoff frequency. The actual amount of attenuation for each frequency varies from filter to filter. It is sometimes called a high-cut filter, or treble cut filter...
(LPF), and a downsampler
Downsampling
In signal processing, downsampling is the process of reducing the sampling rate of a signal. This is usually done to reduce the data rate or the size of the data....
(which may be integrated into the low-pass filter).
The DDS generates a complex sinusoid at the intermediate to downconverting by creating a difference signal at the IF minus the DDS frequency, they also upconvert, generating an unwanted signal at the sum of the two frequencies.
Any suitable low-pass filter can be used including FIR
Finite impulse response
A finite impulse response filter is a type of a signal processing filter whose impulse response is of finite duration, because it settles to zero in finite time. This is in contrast to infinite impulse response filters, which have internal feedback and may continue to respond indefinitely...
, IIR
IIR
IIR may refer to* IIR Holdings, a human capital development company acquired by Informa* Indo-Iranian languages* Infinite impulse response...
and CIC filters. The most common choice is a FIR filter for low amounts of decimation (less than ten) or a CIC filter followed by a FIR filter for larger downsampling ratios.
Variations on the DDC
Several variations on the DDC are useful, including many that input a feedback signal into the DDS. These include:- Decision directed carrier recoveryCarrier recoveryA carrier recovery system is a circuit used to estimate and compensate for frequency and phase differences between a received signal's carrier wave and the receiver's local oscillator for the purpose of coherent demodulation....
phase locked loops in which the I and Q are compared to the nearest ideal constellation point of a PSK signal, and the resulting error signal is filtered and fed back into the DDS - A Costas loopCostas loopA Costas loop is a phase-locked loop used for carrier phase recovery from suppressed-carrier modulation signals, such as from double-sideband suppressed carrier signals. It was invented by John P. Costas at General Electric in the 1950s...
in which the I and Q are multiplied and low pass filtered as part of a BPSK/QPSK carrier recovery loop
Implementation
DDC’s are most commonly implemented in logic in field-programmable gate arrayField-programmable gate array
A field-programmable gate array is an integrated circuit designed to be configured by the customer or designer after manufacturing—hence "field-programmable"...
s or application-specific integrated circuit
Application-specific integrated circuit
An application-specific integrated circuit is an integrated circuit customized for a particular use, rather than intended for general-purpose use. For example, a chip designed solely to run a cell phone is an ASIC...
s. While software implementations are also possible, operations in the DDS, multipliers and input stages of the lowpass filters all run at the sampling rate of the input data. This data is commonly taken directly from analog to digital converters (ADC’s) sampling at tens or hundreds of MHz, which is beyond the real time computational capabilities of software processors.
CORDICs
CORDIC
CORDIC is a simple and efficient algorithm to calculate hyperbolic and trigonometric functions...
are an alternative to the use of multipliers in the
implementation of digital down converters.

