
Differential game
Encyclopedia
In game theory
, differential games are a group of problems related to the modeling and analysis of conflict in the context of a dynamical system. The problem usually consists of two actors, a pursuer and an evader, with conflicting goals. The dynamics of the pursuer and the evader are modeled by systems of differential equations.
Differential games are related closely with optimal control
problems. In an optimal control problem there is single control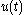 and a single criterion to be optimized; differential game theory generalizes this to two controls
and a single criterion to be optimized; differential game theory generalizes this to two controls 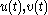 and two criteria, one for each player. Each player attempts to control the state of the system so as to achieve his goal; the system responds to the inputs of both players.
and two criteria, one for each player. Each player attempts to control the state of the system so as to achieve his goal; the system responds to the inputs of both players.
The first to study differential games was Rufus Isaacs
(1951, published 1965) and one of the first games analyzed was the 'homicidal chauffeur game'
.
Differential games have been applied to economics. Recent developments include adding stochasticity to differential games and the derivation of the stochastic feedback Nash equilibrium (SFNE). A recent example is the stochastic differential game of capitalism by Leong and Huang (2010).
Game theory
Game theory is a mathematical method for analyzing calculated circumstances, such as in games, where a person’s success is based upon the choices of others...
, differential games are a group of problems related to the modeling and analysis of conflict in the context of a dynamical system. The problem usually consists of two actors, a pursuer and an evader, with conflicting goals. The dynamics of the pursuer and the evader are modeled by systems of differential equations.
Differential games are related closely with optimal control
Optimal control
Optimal control theory, an extension of the calculus of variations, is a mathematical optimization method for deriving control policies. The method is largely due to the work of Lev Pontryagin and his collaborators in the Soviet Union and Richard Bellman in the United States.-General method:Optimal...
problems. In an optimal control problem there is single control
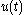 and a single criterion to be optimized; differential game theory generalizes this to two controls
and a single criterion to be optimized; differential game theory generalizes this to two controls 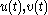 and two criteria, one for each player. Each player attempts to control the state of the system so as to achieve his goal; the system responds to the inputs of both players.
and two criteria, one for each player. Each player attempts to control the state of the system so as to achieve his goal; the system responds to the inputs of both players.The first to study differential games was Rufus Isaacs
Rufus Isaacs (game theorist)
Rufus Philip Isaacs was a game theorist especially prominent in the 1950s and 1960s with his work on differential games.-Biography:...
(1951, published 1965) and one of the first games analyzed was the 'homicidal chauffeur game'
Homicidal chauffeur problem
In game theory, the homicidal chauffeur problem is a mathematical pursuit problem which pits a hypothetical runner, who can only move slowly, but is highly maneuverable, against the driver of a motor vehicle, which is much faster but far less maneuverable, who is attempting to run him down. Both...
.
Differential games have been applied to economics. Recent developments include adding stochasticity to differential games and the derivation of the stochastic feedback Nash equilibrium (SFNE). A recent example is the stochastic differential game of capitalism by Leong and Huang (2010).

