
Dichroic prism
Encyclopedia
Prism (optics)
In optics, a prism is a transparent optical element with flat, polished surfaces that refract light. The exact angles between the surfaces depend on the application. The traditional geometrical shape is that of a triangular prism with a triangular base and rectangular sides, and in colloquial use...
that splits light
Light
Light or visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, and is responsible for the sense of sight. Visible light has wavelength in a range from about 380 nanometres to about 740 nm, with a frequency range of about 405 THz to 790 THz...
into two beams of differing wavelength
Wavelength
In physics, the wavelength of a sinusoidal wave is the spatial period of the wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.It is usually determined by considering the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase, such as crests, troughs, or zero crossings, and is a...
(colour). They are usually constructed of one or more glass prisms with dichroic
Dichroism
Dichroism has two related but distinct meanings in optics. A dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths , or one in which light rays having different polarizations are absorbed by different amounts.The original meaning of...
optical coating
Optical coating
An optical coating is one or more thin layers of material deposited on an optical component such as a lens or mirror, which alters the way in which the optic reflects and transmits light. One type of optical coating is an antireflection coating, which reduces unwanted reflections from surfaces, and...
s that selectively reflect or transmit light depending on the light's wavelength. That is, certain surfaces within the prism act as dichroic filter
Dichroic filter
A dichroic filter, thin-film filter, or interference filter is a very accurate color filter used to selectively pass light of a small range of colors while reflecting other colors. By comparison, dichroic mirrors and dichroic reflectors tend to be characterized by the color of light that they...
s. These are used as beam splitter
Beam splitter
A beam splitter is an optical device that splits a beam of light in two. It is the crucial part of most interferometers.In its most common form, a rectangle, it is made from two triangular glass prisms which are glued together at their base using Canada balsam...
s in many optical instrument
Optical instrument
An optical instrument either processes light waves to enhance an image for viewing, or analyzes light waves to determine one of a number of characteristic properties.-Image enhancement:...
s. (See dichroism
Dichroism
Dichroism has two related but distinct meanings in optics. A dichroic material is either one which causes visible light to be split up into distinct beams of different wavelengths , or one in which light rays having different polarizations are absorbed by different amounts.The original meaning of...
for the etymology of the term.)
One common application of dichroic prisms is in some camcorder
Camcorder
A camcorder is an electronic device that combines a video camera and a video recorder into one unit. Equipment manufacturers do not seem to have strict guidelines for the term usage...
s and high-quality digital camera
Digital camera
A digital camera is a camera that takes video or still photographs, or both, digitally by recording images via an electronic image sensor. It is the main device used in the field of digital photography...
s. A trichroic prism assembly is a combination of two dichroic prisms which are used to split an image into red
Red
Red is any of a number of similar colors evoked by light consisting predominantly of the longest wavelengths of light discernible by the human eye, in the wavelength range of roughly 630–740 nm. Longer wavelengths than this are called infrared , and cannot be seen by the naked eye...
, green
Green
Green is a color, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 520–570 nanometres. In the subtractive color system, it is not a primary color, but is created out of a mixture of yellow and blue, or yellow and cyan; it is considered...
, and blue
Blue
Blue is a colour, the perception of which is evoked by light having a spectrum dominated by energy with a wavelength of roughly 440–490 nm. It is considered one of the additive primary colours. On the HSV Colour Wheel, the complement of blue is yellow; that is, a colour corresponding to an equal...
components so they can be separately detected on three CCD arrays
Charge-coupled device
A charge-coupled device is a device for the movement of electrical charge, usually from within the device to an area where the charge can be manipulated, for example conversion into a digital value. This is achieved by "shifting" the signals between stages within the device one at a time...
.
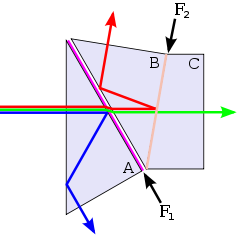
A possible layout for the device is shown in the diagram. A light beam enters the first prism (A) and the blue component of the beam is reflected from a low-pass filter
Filter (optics)
Optical filters are devices which selectively transmit light of different wavelengths, usually implemented as plane glass or plastic devices in the optical path which are either dyed in the mass or have interference coatings....
coating (F1) that reflects blue light (high-frequency), but transmits longer wavelengths (lower frequencies). The blue beam undergoes total internal reflection
Total internal reflection
Total internal reflection is an optical phenomenon that happens when a ray of light strikes a medium boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to the normal to the surface. If the refractive index is lower on the other side of the boundary and the incident angle is...
from the front of prism A and exits it through a side face. The remainder of the beam enters the second prism (B) and is split by a second filter coating (F2) that reflects red light but transmits shorter wavelengths. The red beam is also totally internally reflected due to a small air-gap between prisms A and B. The remaining green component of the beam travels through prism C.
The trichroic prism assembly can be used in reverse to combine red, green and blue beams into a coloured image, and is used in this way in some projector devices. Assemblies with more than 3 beams are possible.
Advantages of dichroic prism color separation
When used for color separation in an imaging system this method has some advantages over other methods, like a Bayer filterBayer filter
A Bayer filter mosaic is a color filter array for arranging RGB color filters on a square grid of photosensors. Its particular arrangement of color filters is used in most single-chip digital image sensors used in digital cameras, camcorders, and scanners to create a color image...
. Most of those characteristics derive from the usage of dichroic filters
Dichroic filter
A dichroic filter, thin-film filter, or interference filter is a very accurate color filter used to selectively pass light of a small range of colors while reflecting other colors. By comparison, dichroic mirrors and dichroic reflectors tend to be characterized by the color of light that they...
and are in common with those.
- No light is absorbed, all light being directed to one of the output beams.
- Better color separation than with most other filters.
- Easy to fabricate for any combination of pass bands.
Disadvantages of dichroic prism color separation
- Since a dichroic prism uses dichroic filters, the exact bandpass of each filter depends on the light incidence angle.
- Maximum lens numerical apertureNumerical apertureIn optics, the numerical aperture of an optical system is a dimensionless number that characterizes the range of angles over which the system can accept or emit light. By incorporating index of refraction in its definition, NA has the property that it is constant for a beam as it goes from one...
might be restricted due to the geometry of the optical path inside the assembly. - The exact bandpass depends on the lens numerical aperture, since this factor changes the average light incidence angle in the filters.
- Since some of the glass surfaces are at an angle against the incident beam some polarization by reflection effects can result.

