
Development geography
Encyclopedia
Development geography is the study of the earth
's geography
with reference to the standard of living
and quality of life
of its human inhabitants. In this context, development is a process of change that affects people's lives. It may involve an improvement in the quality of life as perceived by the people undergoing change. However, development is not always a positive process. Gunder Frank commented on the global economic forces that lead to the development of underdevelopment. This is covered in his dependency theory
.
In development geography, geographers study spatial patterns in development. They try to find by what characteristics they can measure development by looking at economic, political and social
factors. They seek to understand both the geographical causes and consequences of varying development. Studies compare More Economically Developed Countries (MEDCs) with Less Economically Developed Countries (LEDCs). Additionally variations within countries are looked at such as the differences between northern
and southern Italy, the Mezzogiorno.
Within development geography, sustainable development
is also studied in an attempt to understand how to meet the needs of the present without compromising the needs of future generations to meet their own needs.
Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun, and the densest and fifth-largest of the eight planets in the Solar System. It is also the largest of the Solar System's four terrestrial planets...
's geography
Geography
Geography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
with reference to the standard of living
Standard of living
Standard of living is generally measured by standards such as real income per person and poverty rate. Other measures such as access and quality of health care, income growth inequality and educational standards are also used. Examples are access to certain goods , or measures of health such as...
and quality of life
Quality of life
The term quality of life is used to evaluate the general well-being of individuals and societies. The term is used in a wide range of contexts, including the fields of international development, healthcare, and politics. Quality of life should not be confused with the concept of standard of...
of its human inhabitants. In this context, development is a process of change that affects people's lives. It may involve an improvement in the quality of life as perceived by the people undergoing change. However, development is not always a positive process. Gunder Frank commented on the global economic forces that lead to the development of underdevelopment. This is covered in his dependency theory
Dependency theory
Dependency theory or dependencia theory is a body of social science theories predicated on the notion that resources flow from a "periphery" of poor and underdeveloped states to a "core" of wealthy states, enriching the latter at the expense of the former...
.
In development geography, geographers study spatial patterns in development. They try to find by what characteristics they can measure development by looking at economic, political and social
Social
The term social refers to a characteristic of living organisms...
factors. They seek to understand both the geographical causes and consequences of varying development. Studies compare More Economically Developed Countries (MEDCs) with Less Economically Developed Countries (LEDCs). Additionally variations within countries are looked at such as the differences between northern
Italy
Italy , officially the Italian Republic languages]] under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. In each of these, Italy's official name is as follows:;;;;;;;;), is a unitary parliamentary republic in South-Central Europe. To the north it borders France, Switzerland, Austria and...
and southern Italy, the Mezzogiorno.
Within development geography, sustainable development
Sustainable development
Sustainable development is a pattern of resource use, that aims to meet human needs while preserving the environment so that these needs can be met not only in the present, but also for generations to come...
is also studied in an attempt to understand how to meet the needs of the present without compromising the needs of future generations to meet their own needs.
Quantitative indicators
Quantitative indicators are numerical indications of development.- Economic indicators include GNPGNPGross National Product is the market value of all products and services produced in one year by labor and property supplied by the residents of a country...
(Gross National Product) per capita, unemploymentUnemploymentUnemployment , as defined by the International Labour Organization, occurs when people are without jobs and they have actively sought work within the past four weeks...
rates, energy consumptionWorld energy resources and consumption]World energy consumption in 2010: over 5% growthEnergy markets have combined crisis recovery and strong industry dynamism. Energy consumption in the G20 soared by more than 5% in 2010, after the slight decrease of 2009. This strong increase is the result of two converging trends...
and percentage of GNP in primary industries. Of these, GNP per capita is the most used as it measures the value of all the goods and services produced in a country, excluding those produced by foreign companies, hence measuring the economic and industrial development of the country. However, using GNP per capita also has many problems.- It does not take into account the distribution of the money which can often be extremely unequal as in the UAE where oil money has been collected by a rich elite and has not flowed to the bulk of the country.
- GNP does not measure whether the money produced is actually improving people's lives and this is important because in many MEDCs where there are large increases in wealth over time but only small increases in happiness.
- The figure rarely takes into account the unofficial economy, which includes subsistence agriculture and cash-in-hand or unpaid work, which is often substantial in LEDCs. In LEDCs it is often too expensive to accurately collect this data and some governments intentionally or unintentionally release inaccurate figures.
- The figure is usually given in US dollars which due to changing currency exchange rates can distort the money's true street value so it is often converted using purchasing power parityPurchasing power parityIn economics, purchasing power parity is a condition between countries where an amount of money has the same purchasing power in different countries. The prices of the goods between the countries would only reflect the exchange rates...
(PPP) in which the actual comparative purchasing power of the money in the country is calculated.
- Social indications include access to clean water and sanitationSanitationSanitation is the hygienic means of promoting health through prevention of human contact with the hazards of wastes. Hazards can be either physical, microbiological, biological or chemical agents of disease. Wastes that can cause health problems are human and animal feces, solid wastes, domestic...
(which indicate the level of infrastructure developed in the country) and adult literacyLiteracyLiteracy has traditionally been described as the ability to read for knowledge, write coherently and think critically about printed material.Literacy represents the lifelong, intellectual process of gaining meaning from print...
rate, measuring the resources the government has to meet the needs of the people. - Demographic indicators include the birth rateBirth rateCrude birth rate is the nativity or childbirths per 1,000 people per year . Another word used interchangeably with "birth rate" is "natality". When the crude birth rate is subtracted from the crude death rate, it reveals the rate of natural increase...
, death rate and fertility rate, which indicate the level of industrialization.- Health indicators (a sub-factor of demographic indicators) include nutritionNutritionNutrition is the provision, to cells and organisms, of the materials necessary to support life. Many common health problems can be prevented or alleviated with a healthy diet....
(calories per day, calories from protein, percentage of population with malnutrition), infant mortalityInfant mortalityInfant mortality is defined as the number of infant deaths per 1000 live births. Traditionally, the most common cause worldwide was dehydration from diarrhea. However, the spreading information about Oral Re-hydration Solution to mothers around the world has decreased the rate of children dying...
and population per doctor, which indicate the availability of healthcare and sanitationSanitationSanitation is the hygienic means of promoting health through prevention of human contact with the hazards of wastes. Hazards can be either physical, microbiological, biological or chemical agents of disease. Wastes that can cause health problems are human and animal feces, solid wastes, domestic...
facilities in a country.
- Health indicators (a sub-factor of demographic indicators) include nutrition
- Environmental indications include how much a country does for the environment.
Composite indicators
- In the table below GDP stands for gross domestic product, which is generally taken to be equal to GNP.
- Other composite measures include the PQLI (Physical Quality of Life Index) which was a precursor to the HDI which used infant mortality rate instead of GNP per capita and rated countries from 0 to 100. It was calculated by assigning each country a score of 0 to 100 for each indicator compared with other countries in the world. The average of these three numbers makes the PQLI of a country.
- The HPIHuman Poverty IndexThe Human Poverty Index is an indication of the standard of living in a country, developed by the United Nations . For highly developed countries, the UN considers that it can better reflect the extent of deprivation compared to the Human Development Index....
(Human Poverty Index) is used to calculate the percentage of people in a country who live in relative poverty. In order to better differentiate the number of people in abnormally poor living conditions the HPI-1 is used in developing countries, and the HPI-2 is used in developed countries. The HPI-1 is calculated based on the percentage of people not expected to survive to 40, the adult illiteracy rate, the percentage of people without access to safe water, health services and the percentage of children under 5 who are underweight. The HPI-2 is calculated based on the percentage of people who do not survive to 60, the adult functional illiteracyFunctional illiteracyFunctional illiteracy is a term used to describe reading and writing skills that are inadequate "to manage daily living and employment tasks that require reading skills beyond a basic level." Functional illiteracy is contrasted with illiteracy in the strict sense, meaning the inability to read or...
rate and the percentage of people living below 50% of median personal disposable income. - The GDIGender-related Development IndexThe Gender-related Development Index and the Gender Empowerment Measure were introduced in 1995 in the Human Development Report written by the United Nations Development Program. The aim of these measurements was to add a gender-sensitive dimension to the HDI. The first measurement that they...
(Gender-related Development Index) measures gender equality in a country in terms of life expectancy, literacy rates, school attendance and income.HDI rank Country GDP per capita
(PPP US$)
2008Human development index
(HDI) value
20064 Australia 35,677 0.965 70 Brazil 10,296 0.807 151 Zimbabwe 188 0.513
Qualitative indicators
Qualitative indicators include descriptions of living conditions and people's quality of life. They are useful in analysing features that are not easily calculated or measured in numbers such as freedom, corruption or security, which are mainly non-material benefits.
Geographic variations in development
There is a considerable spatial variation in development rates.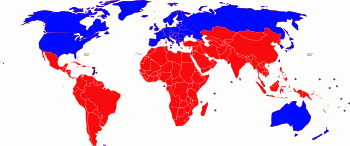
The most famous pattern in development is the North-South divideNorth-South divideThe north–south divide is a socio-economic and political division that exists between the wealthy developed countries, known collectively as "the north", and the poorer developing countries , or "the south." Although most nations comprising the "North" are in fact located in the Northern Hemisphere ,...
. The North-South divide is the divide which separates the rich North or the developed world, from the poor South. This line of division is not as straightforward as it sounds and splits the globe into two main parts. It is also known as the Brandt Line.
The "North" in this divide is regarded as being North America, Europe, Russia, South Korea, Japan, Australia, New Zealand and the like. The countries within this area are generally the more economically developed. The "South" therefore encompasses the remainder of the Southern Hemisphere, mostly consisting of LEDCs. Another possible dividing line is the Tropic of Cancer with the exceptions of Australia and New Zealand. It is critical to understand that the status of countries is far from static and the pattern is likely to become distorted with the fast development of certain southern countries, many of them NICsNewly industrialized countriesThe category of newly industrialized country is a socioeconomic classification applied to several countries around the world by political scientists and economists....
(Newly Industrialised Countries) including India, Thailand, Brazil, Malaysia, Mexico and others. These countries are experiencing sustained fast development on the back of growing manufacturing industries and exports.
Most countries are experiencing significant increases in wealth and standard of living. However there are unfortunate exceptions to this rule. Noticeably some of the former Soviet UnionSoviet UnionThe Soviet Union , officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics , was a constitutionally socialist state that existed in Eurasia between 1922 and 1991....
countries has experienced major disruption of industry in the transition to a market economy. Many African nations have recently experienced reduced GNPs due to wars and the AIDS epidemic, including Angola, Congo, Sierra Leone and others. Arab oil producers rely very heavily on oil exports to support their GDPs so any reduction in oil's market price can lead to rapid decreases in GNP. Countries which rely on only a few exports for much of their income are very vulnerable to changes in the market value of those commodities and are often derogatively called banana republics. Many developing countries do rely on exports of a few primary goods for a large amount of their income (coffee and timber for example), and this can create havoc when the value of these commodities drops, leaving these countries with no way to pay off their debts.
Within countries the pattern is that wealth is more concentrated around urban areas than rural areas. Wealth also tends towards areas with natural resources or in areas that are involved in tertiary (service) industries and trade. This leads to a gathering of wealth around mines and monetary centres such as New York, London and Tokyo.
Aid
MEDCs (More Economically Developed Countries)can give aid to LEDCs (Less Economically Developed Countries). There are several types of aid:- Governmental(Bilateral) aid
- International Organizational (multilateral) aid
- Voluntary aid
- Short-term/emergency aid
- Long-term/sustainable aid
Aid can be given in several ways. Through money, materials, or skilled and learned people (e.g. teachers).
Aid has advantages. Mostly short-term or emergency aid help people in LEDCs to survive a natural (earthquake, tsunami, volcano eruption etc.) or human (civil war etc.) disaster. Aid helps make the recipient country (the country that receives aid) get more developed.
However, aid also has disadvantages. Often aid does not even reach the poorest people. Often money gained from aid is used up to make infrastructures (bridges, roads etc.), which only the rich can use. Also, the recipient country gets more dependant of aid from a donor country (the country giving aid).

