
Deinking
Encyclopedia
Deinking is the industrial process
of removing printing ink from paperfibers
of recycled paper to make deinked pulp.
The key in the deinking process is the ability to detach ink from the fibers. This is achieved by a combination of mechanical action and chemical means. In Europe the most common process is froth flotation
deinking.
Paper is one of the main targets for recycling
. A concern about recycling wood pulp
paper is that the fibers are degraded with each cycle and after being recycled 4–6 times the fibers become too short and weak to be useful in making paper.
, linen
and cotton
. It was not until the introduction of wood pulp
in 1843 that paper production was not dependent on recycled materials.
Recycling of used paper
before the industrialisation
of paper production, rag paper was recycled to make low-grade board
. A process for removing printing inks from recycled paper was invented by German jurist Justus Claproth
in 1774. He practiced together with German paper producer Johann Engelhard Schmid. Today this method is called deinking.
First in the 1950s and 1960s the use of recycled fibres from paper made of wood pulp begun to pick up and was mainly used in packaging paper and paperboard. In the 1950s the froth flotation
technique was adapted for deinking recycled paper. Use of recovered paper increased in the 1970s mainly in graphic and hygenic papers and accelerated in the 1980s. The annual growth in use of recovered paper increased by 6 % between 1980 and 1996. The use of virgin fibres only increased 2 % in the sametime period. In 1997 the recovered paper production was 42 % of the total paper production.
.svg.png)
Recycled paper can be used to make paper of the same or lower quality than it was originally. The sorted paper is baled and shipped to a papermill. The pulpmill uses waste paper grade according to the paper quality they want to make.
to the pulper
. Many extraneous materials are readily removed. Twine, strapping, etc. are removed from the hydropulper by a "ragger". Metal straps and staples can be screened out or removed by a magnet. Film-backed pressure sensitive tape stays intact: the PSA adhesive and the backing are both removed together.
The pulper chops the paper to smaller pieces, water and chemicals are added. Normally the pH
is adjusted to 8,5 - 10,0. Normal deinking chemicals are:
After pulping the mixture is a slurry
. The slurry goes to screening.
, with either slots or holes, are used to remove contaminants that are larger than pulp fibers.
Materials which are more difficult to remove include wax coatings on corrugated cartons and stickies
, soft rubbery particles which can make deposits and contaminate the recycled paper. Stickies can originate from book bindings, hot melt adhesives, PSA adhesive
s from paper labels, laminating adhesives of reinforced gummed tapes
, etc.
. Several processes are used, most commonly flotation or washing.
uses peroxide
s or hydrosulfites
to increase the brightness
of the pulp. The bleaching methods are similar for mechanical pulp, but the goal is to make the fiber brighter.
.
Temperature control important as this affects the stickyness of stickies
.
Industrial process
Industrial processes are procedures involving chemical or mechanical steps to aid in the manufacture of an item or items, usually carried out on a very large scale. Industrial processes are the key components of heavy industry....
of removing printing ink from paperfibers
Fiber crop
Fiber crops are field crops grown for their fibers, which are traditionally used to make paper, cloth, or rope. The fibers may be chemically modified, like in viscose or cellophane...
of recycled paper to make deinked pulp.
The key in the deinking process is the ability to detach ink from the fibers. This is achieved by a combination of mechanical action and chemical means. In Europe the most common process is froth flotation
Froth flotation
Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in several processing industries...
deinking.
Paper is one of the main targets for recycling
Paper recycling
Paper recycling is the process of recovering waste paper and remaking it into new paper products. There are three categories of paper that can be used as feedstocks for making recycled paper: mill broke, pre-consumer waste, and post-consumer waste. Mill broke is paper trimmings and other paper...
. A concern about recycling wood pulp
Wood pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibres from wood, fibre crops or waste paper. Wood pulp is the most common raw material in papermaking.-History:...
paper is that the fibers are degraded with each cycle and after being recycled 4–6 times the fibers become too short and weak to be useful in making paper.
History
Before the invention of the paper machine in 1799 the most common fibre source was recycled fibres from used textiles, called rags. Hence the name rag paper. The rags were from hempHemp
Hemp is mostly used as a name for low tetrahydrocannabinol strains of the plant Cannabis sativa, of fiber and/or oilseed varieties. In modern times, hemp has been used for industrial purposes including paper, textiles, biodegradable plastics, construction, health food and fuel with modest...
, linen
Linen
Linen is a textile made from the fibers of the flax plant, Linum usitatissimum. Linen is labor-intensive to manufacture, but when it is made into garments, it is valued for its exceptional coolness and freshness in hot weather....
and cotton
Cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective capsule, around the seeds of cotton plants of the genus Gossypium. The fiber is almost pure cellulose. The botanical purpose of cotton fiber is to aid in seed dispersal....
. It was not until the introduction of wood pulp
Wood pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibres from wood, fibre crops or waste paper. Wood pulp is the most common raw material in papermaking.-History:...
in 1843 that paper production was not dependent on recycled materials.
Recycling of used paper
Paper recycling
Paper recycling is the process of recovering waste paper and remaking it into new paper products. There are three categories of paper that can be used as feedstocks for making recycled paper: mill broke, pre-consumer waste, and post-consumer waste. Mill broke is paper trimmings and other paper...
before the industrialisation
Industrialisation
Industrialization is the process of social and economic change that transforms a human group from an agrarian society into an industrial one...
of paper production, rag paper was recycled to make low-grade board
Paperboard
Paperboard is a thick paper based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker than paper. According to ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a basis weight above 224 g/m2, but there are exceptions. Paperboard can be single...
. A process for removing printing inks from recycled paper was invented by German jurist Justus Claproth
Justus Claproth
Justus Claproth was a German jurist and inventor of the deinking process of recycled paper....
in 1774. He practiced together with German paper producer Johann Engelhard Schmid. Today this method is called deinking.
First in the 1950s and 1960s the use of recycled fibres from paper made of wood pulp begun to pick up and was mainly used in packaging paper and paperboard. In the 1950s the froth flotation
Froth flotation
Froth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in several processing industries...
technique was adapted for deinking recycled paper. Use of recovered paper increased in the 1970s mainly in graphic and hygenic papers and accelerated in the 1980s. The annual growth in use of recovered paper increased by 6 % between 1980 and 1996. The use of virgin fibres only increased 2 % in the sametime period. In 1997 the recovered paper production was 42 % of the total paper production.
Deinking process
.svg.png)
Sorting
Waste paper may contain a mixture of different paper types made of mixtures of different paperfibers. These must be sorted before processed. Broke (paper waste from paper production) is normally used directly in the papermachine.- Office waste (OW)
- Old magazine paperMagazine paper-Manufacture:Magazine papers are made on paper machines from pulp. The pulp may be recycled, mechanical or chemical depending on the magazine quality...
s (OMG) - Old newsprintNewspaperA newspaper is a scheduled publication containing news of current events, informative articles, diverse features and advertising. It usually is printed on relatively inexpensive, low-grade paper such as newsprint. By 2007, there were 6580 daily newspapers in the world selling 395 million copies a...
(ONP) - PaperboardPaperboardPaperboard is a thick paper based material. While there is no rigid differentiation between paper and paperboard, paperboard is generally thicker than paper. According to ISO standards, paperboard is a paper with a basis weight above 224 g/m2, but there are exceptions. Paperboard can be single...
- Corrugated fiberboard
Recycled paper can be used to make paper of the same or lower quality than it was originally. The sorted paper is baled and shipped to a papermill. The pulpmill uses waste paper grade according to the paper quality they want to make.
Debaling
The bales are opened and large foreign objects are sorted out on the conveyor beltConveyor belt
A conveyor belt consists of two or more pulleys, with a continuous loop of material - the conveyor belt - that rotates about them. One or both of the pulleys are powered, moving the belt and the material on the belt forward. The powered pulley is called the drive pulley while the unpowered pulley...
to the pulper
Pulper
In agriculture, a pulper is a machine designed to remove pulp i.e. the soft flesh from agricultural produce. For example, in coffee growing the ripe, red cherries are picked from the coffee bushes and prior to fermentation and later drying the soft pulp needs to be removed...
. Many extraneous materials are readily removed. Twine, strapping, etc. are removed from the hydropulper by a "ragger". Metal straps and staples can be screened out or removed by a magnet. Film-backed pressure sensitive tape stays intact: the PSA adhesive and the backing are both removed together.
Pulping
Pulpers are either batch, which uses a tub with a high shear rotor, or continuous, using a long, perforated drum. Drum pulpers are very expensive but have the advantage of not breaking up contaminants, thus giving cleaner end product.The pulper chops the paper to smaller pieces, water and chemicals are added. Normally the pH
PH
In chemistry, pH is a measure of the acidity or basicity of an aqueous solution. Pure water is said to be neutral, with a pH close to 7.0 at . Solutions with a pH less than 7 are said to be acidic and solutions with a pH greater than 7 are basic or alkaline...
is adjusted to 8,5 - 10,0. Normal deinking chemicals are:
- pH control: sodium silicateSodium silicateSodium silicate is the common name for a compound sodium metasilicate, Na2SiO3, also known as water glass or liquid glass. It is available in aqueous solution and in solid form and is used in cements, passive fire protection, refractories, textile and lumber processing, and automobiles...
and/or sodium hydroxide - Bleaching: hydrogen peroxideHydrogen peroxideHydrogen peroxide is the simplest peroxide and an oxidizer. Hydrogen peroxide is a clear liquid, slightly more viscous than water. In dilute solution, it appears colorless. With its oxidizing properties, hydrogen peroxide is often used as a bleach or cleaning agent...
- CalciumCalciumCalcium is the chemical element with the symbol Ca and atomic number 20. It has an atomic mass of 40.078 amu. Calcium is a soft gray alkaline earth metal, and is the fifth-most-abundant element by mass in the Earth's crust...
ionIonAn ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
source: hard waterHard waterHard water is water that has high mineral content . Hard water has high concentrations of Ca2+ and Mg2+ ions. Hard water is generally not harmful to one's health but can pose serious problems in industrial settings, where water hardness is monitored to avoid costly breakdowns in boilers, cooling...
, lime or calcium chlorideCalcium chlorideCalcium chloride, CaCl2, is a salt of calcium and chlorine. It behaves as a typical ionic halide, and is solid at room temperature. Common applications include brine for refrigeration plants, ice and dust control on roads, and desiccation... - Collector: fatty acidFatty acidIn chemistry, especially biochemistry, a fatty acid is a carboxylic acid with a long unbranched aliphatic tail , which is either saturated or unsaturated. Most naturally occurring fatty acids have a chain of an even number of carbon atoms, from 4 to 28. Fatty acids are usually derived from...
, fatty acid emulsionEmulsionAn emulsion is a mixture of two or more liquids that are normally immiscible . Emulsions are part of a more general class of two-phase systems of matter called colloids. Although the terms colloid and emulsion are sometimes used interchangeably, emulsion is used when both the dispersed and the...
, fatty acid soapSoapIn chemistry, soap is a salt of a fatty acid.IUPAC. "" Compendium of Chemical Terminology, 2nd ed. . Compiled by A. D. McNaught and A. Wilkinson. Blackwell Scientific Publications, Oxford . XML on-line corrected version: created by M. Nic, J. Jirat, B. Kosata; updates compiled by A. Jenkins. ISBN...
and/or organo-modified siloxaneSiloxaneA siloxane is any chemical compound composed of units of the form R2SiO, where R is a hydrogen atom or a hydrocarbon group. They belong to the wider class of organosilicon compounds....
After pulping the mixture is a slurry
Slurry
A slurry is, in general, a thick suspension of solids in a liquid.-Examples of slurries:Examples of slurries include:* Lahars* A mixture of water and cement to form concrete* A mixture of water, gelling agent, and oxidizers used as an explosive...
. The slurry goes to screening.
Cleaning and screening
Centrifugal cleaning is spinning the pulp slurry in a cleaner, causing materials that are denser than pulp fibers to move outward and be rejected. ScreensSieve
A sieve, or sifter, separates wanted elements from unwanted material using a woven screen such as a mesh or net. However, in cooking, especially with flour, a sifter is used to aerate the substance, among other things. A strainer is a type of sieve typically used to separate a solid from a liquid...
, with either slots or holes, are used to remove contaminants that are larger than pulp fibers.
Materials which are more difficult to remove include wax coatings on corrugated cartons and stickies
Stickies (papermaking)
Stickies are tacky substances contained in the paper pulp and process water systems of paper machines. Stickies have a large tendency to make deposits on the processing equipment in certain stages of the papermaking process. Contaminations of paper that that are classified as tacky are also called...
, soft rubbery particles which can make deposits and contaminate the recycled paper. Stickies can originate from book bindings, hot melt adhesives, PSA adhesive
Adhesive
An adhesive, or glue, is a mixture in a liquid or semi-liquid state that adheres or bonds items together. Adhesives may come from either natural or synthetic sources. The types of materials that can be bonded are vast but they are especially useful for bonding thin materials...
s from paper labels, laminating adhesives of reinforced gummed tapes
Adhesive tape
Adhesive tape is one of many varieties of backing materials coated with an adhesive. Several types of adhesives can be used.-Types:Pressure sensitive tape...
, etc.
Deinking stage
In the deinking stage the goal is to release and remove the hydrophobic contaminants from the recycled paper. The contaminants are mostly printing ink and stickiesStickies (papermaking)
Stickies are tacky substances contained in the paper pulp and process water systems of paper machines. Stickies have a large tendency to make deposits on the processing equipment in certain stages of the papermaking process. Contaminations of paper that that are classified as tacky are also called...
. Several processes are used, most commonly flotation or washing.
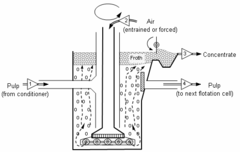
- Flotation deinking

- Froth flotationFroth flotationFroth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in several processing industries...
was adapted from the flotation process used in the mining industry in the 1960s. It is the most common deinking process in EuropeEuropeEurope is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
used to recover recycled paper. Often most of the collector is added to the inlet of the flotation. The process temperatures are normally in the range 45 - 55 °C. Air is blown into the pulp suspensionSuspension (chemistry)In chemistry, a suspension is a heterogeneous fluid containing solid particles that are sufficiently large for sedimentation. Usually they must be larger than 1 micrometer. The internal phase is dispersed throughout the external phase through mechanical agitation, with the use of certain...
. The collector has affinityChemical affinityIn chemical physics and physical chemistry, chemical affinity is the electronic property by which dissimilar chemical species are capable of forming chemical compounds...
both to the ink particles and air bubbles, causing them to attach. The air bubbles lift the ink to the surface and form a thick froth that can be removed. Normally the setup is a two stage system with 3, 4 or 5 flotation cells in series. Flotation deinking is very effective in removing ink particles larger than about 10 µm.
- Wash deinking
- Wash deinking consists of a washing stage where dispersantDispersantA dispersant or a dispersing agent or a plasticizer or a superplasticizer is either a non-surface active polymer or a surface-active substance added to a suspension, usually a colloid, to improve the separation of particles and to prevent settling or clumping...
s are added to wash out the printing inks. When the pulp slurry is dewateredDewateringDewatering is the removal of water from solid material or soil by wet classification, centrifugation, filtration, or similar solid-liquid separation processes, such as removal of residual liquid from a filter cake by a filter press as part of various industrial processes.Construction dewatering,...
(thickened), the medium to fine particles are washWashWash may refer to:* Arroyo , also called a wash, a dry creek bed or gulch that temporarily fills with water after a heavy rain* WASH, a water, sanitation and hygiene advocacy campaign initiated by the Water Supply and Sanitation Collaborative Council...
ed out. This process is most useful for removing particles smaller than about 30 µm, like water-based inks, fillers, coating particles, fines and micro stickiesStickies (papermaking)Stickies are tacky substances contained in the paper pulp and process water systems of paper machines. Stickies have a large tendency to make deposits on the processing equipment in certain stages of the papermaking process. Contaminations of paper that that are classified as tacky are also called...
. This process is more common when making deinked pulp for tissueFacial tissueFacial tissue and paper handkerchief refers to a class of soft, absorbent, disposable papers that is suitable for use on the face. They are disposable alternatives for cloth handkerchiefs...
. The processing equipment are belt filterBelt filterThe belt filter is an industrial machine, used for solid/liquid separation processes, particularly the dewatering of sludges in the chemical industry, mining and water treatment...
s, pressure belt filters, disk filterDisk filterA disk filter is a type of water filter used primarily in irrigation, similar to a screen filter, except that the filter cartridge is made of a number of disks stacked on top of each other like a pile of poker chips. The water passes through the small grooves in between and the impurities are...
s and static filters. This stage is much more efficient than normal washing / dewatering stages.
- Combined washing and flotation
- High quality deinking of office wastes and other printing papers often commonly uses a combination of washing and flotation.
- Other deinking processes
- Dissolved air flotation (DAF) is used by some mills in the deinking stage and will remove some ink and filler (ash); however, it is mailny used to clarify the process water.
Washing / dewatering
Washing / dewatering (thickening) is a filtration process. Small particles (< 5 µm) are removed by passing water through the pulp.Bleaching
If white paper is desired, bleachingBleaching of wood pulp
Bleaching of wood pulp is the chemical processing carried out on various types of wood pulp to decrease the color of the pulp, so that it becomes whiter. The main use of wood pulp is to make paper where whiteness is an important characteristic...
uses peroxide
Peroxide
A peroxide is a compound containing an oxygen–oxygen single bond or the peroxide anion .The O−O group is called the peroxide group or peroxo group. In contrast to oxide ions, the oxygen atoms in the peroxide ion have an oxidation state of −1.The simplest stable peroxide is hydrogen peroxide...
s or hydrosulfites
Sodium dithionite
Sodium dithionite is a white crystalline powder with a weak sulfurous odor. It is a sodium salt of dithionous acid. Although it is stable under most conditions, it will decompose in hot water and in acid solutions...
to increase the brightness
Brightness
Brightness is an attribute of visual perception in which a source appears to be radiating or reflecting light. In other words, brightness is the perception elicited by the luminance of a visual target...
of the pulp. The bleaching methods are similar for mechanical pulp, but the goal is to make the fiber brighter.
Papermaking
The deinked fiber is made into a new paper product in the same way that virgin wood fiber, see papermakingPapermaking
Papermaking is the process of making paper, a substance which is used universally today for writing and packaging.In papermaking a dilute suspension of fibres in water is drained through a screen, so that a mat of randomly interwoven fibres is laid down. Water is removed from this mat of fibres by...
.
Byproducts
The unusable material left over, mainly ink, plastics, filler and short fibers, is called sludge. The sludge is buried in a landfill, burned to create energy at the paper mill or used as a fertilizer by local farmers.Problems
Water based flexographic printing inks with particle sizes below 5 µm and poor solubility in alkaline conditions may cause problems in deinking, especially in the flotation stage. The solution is to use an extra acidic washing stage.Temperature control important as this affects the stickyness of stickies
Stickies (papermaking)
Stickies are tacky substances contained in the paper pulp and process water systems of paper machines. Stickies have a large tendency to make deposits on the processing equipment in certain stages of the papermaking process. Contaminations of paper that that are classified as tacky are also called...
.
See also
- Paper recyclingPaper recyclingPaper recycling is the process of recovering waste paper and remaking it into new paper products. There are three categories of paper that can be used as feedstocks for making recycled paper: mill broke, pre-consumer waste, and post-consumer waste. Mill broke is paper trimmings and other paper...
- Froth flotationFroth flotationFroth flotation is a process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. This is used in several processing industries...
- Dissolved air flotation
- Environmental issues with paperEnvironmental issues with paperThe environmental impact of paper is significant, which has led to changes in industry and behavior at both business and personal levels. With the use of modern technology such as the printing press and the highly mechanised harvesting of wood, paper has become a cheap commodity. This has led to a...
- Pulp & Paper chemicals

