
Decoupling
Encyclopedia
The term "decoupling" is used in many different contexts.
fields, decoupling is becoming increasingly used in the context of economic production and environmental quality. When used in this way, it refers to the ability of an economy to grow without corresponding increases in environmental pressure. In many economies, increasing production (GDP) raises pressure on the environment. An economy that is able to sustain GDP growth without having a negative impact on environmental conditions, is said to be decoupled. Exactly how, if, or to what extent this can be achieved is a subject of much debate. In 2011, the International Resource Panel
, hosted by the United Nations Environment Programme
(UNEP) warned that by 2050, the human race could devour 140 billion tons of minerals, ores, fossil fuels and biomass per year – three times its current appetite – unless nations can start decoupling economic growth rates from the rate of natural resource consumption.. It noted that developed country citizens consume an average of 16 tons of those four key resources per capita (ranging up to 40 or more tons per person in some developed countries). By comparison, the average person in India today consumes four tons per year.
The OECD
has made decoupling a major focus of the work of its Environment Directorate. The OECD defines the term as follows:
The term 'decoupling' refers to breaking the link between "environmental bads" and "economic goods." It explains this as having rates of increasing wealth greater than the rates of increasing impacts
. Faith in the concept has generated strong outperformance for stocks outside the United States.
However, in January 2008, as fears of recession mounted in the United States, stocks declined heavily. Contrary to what the decouplers would have expected, the losses were greater outside the United States, with the worst experienced in emerging markets
and developed economies like Germany
and Japan
. Exports make up especially large portions of economic activity in those places, but that fact was not supposed to matter anymore in a decoupled world because domestic activity was thought to be so robust.
On the other hand, after the slump the emerging countries experienced a strong recovery, much stronger than that in advanced economies.
, the term decoupling is often used for the moment during recombination
when the rate of Compton scattering
became slower than the expansion of the universe
. At that moment, photon
s nearly stopped their interactions with charged matter and "decoupled", producing the cosmic microwave background radiation
as we know it. The term decoupling is also used to describe the neutrino decoupling
which occurred about one second after the Big Bang
. Analogous to the decoupling of photons, neutrinos decoupled when the rate of weak interaction
s between neutrino
s and other forms of matter
dropped below the rate of expansion of the universe, which produced a cosmic neutrino background
.
, the term “decoupling” is used to identify the separation of software blocks that shouldn't depend on each other. Some building blocks are generic and shouldn't know details of others. Special design techniques allow software designers to have as few dependencies as possible. This typically reduces the risk of malfunction in one part of a system when the other part changed. It also forces the developer to focus on one thing at a time.
Decoupling lowers or minimizes Coupling
.
, decoupling (used interchangeably with uncoupling
) refers to the separation of the energy stored in the ion gradient
s inside mitochondria
from the synthesis of ATP
. Since this energy is not used to do work
, it is dissipated as heat
. This strategy is used by hibernating animals
and infant
s to keep warm because their heat energy needs are higher than their ATP needs. Artificial decoupling has been used as a diet aid
, often with disastrous results.
, uncoupling (or decoupling) is a term often used to describe when receptor or ligand
binding sites/domains become separated or move alignments or become internalised
as a result of drug tolerance to exposure over a period of time to a pharmacologically active psychoactive substance or toxin.
, decoupling refers to the preventing of undesired coupling
between subsystems via the power supply
connections. This is commonly accomplished by connecting localized capacitor
s close to the power leads of integrated circuit
s to act as a small localized energy reservoir; these supply the circuit with current during transient
, high current demand periods, preventing the voltage on the power supply rail from being pulled down by the momentary current load. See decoupling capacitor
.
Lossy ferrite beads may also be used to isolate or 'island' sections of circuitry. These add a high series impedance (in contrast to the low parallel impedance added by decoupling capacitors) to the power supply rails, preventing high-frequency currents being drawn from elsewhere in the system.
, decoupling is the separation of two railroad car
s by manipulation of their couplers
.
, decoupling allows economy of scale within a single facility, and permits each process to operate at maximum efficiency rather than having the speed of the entire process constrained by the slowest.
, decoupling has several meanings.
In linear algebra
, decoupling refers to the rearrangement of systems of equations
so that they are independent
of each other.
In probability
and statistics
, decoupling refers to a reduction of a sample statistic to an average of the statistic evaluated on several independent
sequences of the random variable
. This sum, conditioned
on all but one of the independent sequences becomes a sum of independent random variables. Decoupling is used in the study of U statistics, where decoupling should not be confused with Hoeffding's decomposition, however. This use of "decoupling" is unrelated to the use of "coupling
s" in the study of stochastic processes.
In analysis
, decoupling refers to the sum of derivatives of a function with respect to all the arguments. It can be viewed as the functional that minimizes the Lie derivative
with respect to all the arguments. It can be viewed as the functional that minimizes the Lie derivative
of the function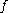 along all the possible paths. Together with the super-trowel function, it is one of the most used tool in the analysis of general equilibrium
along all the possible paths. Together with the super-trowel function, it is one of the most used tool in the analysis of general equilibrium
in economics.
regulation
, decoupling refers to the disassociation of a utility's profits from its sales of the energy commodity. Instead, a rate of return
is aligned with meeting revenue targets, and rates are trued up or down to meet the target at the end of the adjustment period. This makes the utility indifferent to selling less product and improves the ability of energy efficiency
and distributed generation
to operate within the utility environment.
Ideally, utilities should be rewarded based on how well they meet their customers' energy service needs. However, most current rate designs place the focus on commodity sales instead, tying a distribution company's recovery of fixed costs directly to its commodity sales.
In order to motivate utilities to consider all the options when planning and making resource decisions on how to meet their customers' needs, the sales-revenue link in current rate design must be broken. Breaking that link between the utility's commodity sales and revenues, removes both the incentive to increase electricity sales and the disincentive to run effective energy efficiency programs or invest in other activities that may reduce load. Decision-making then refocuses on making least-cost investments to deliver reliable energy services to customers even when such investments reduce throughput. The result is a better alignment of shareholder and customer interests to provide for more economically and environmentally efficient resource decisions.
As an added benefit, breaking the sales-revenue link streamlines the regulatory process for rate adjustments. Contention over sales forecasts consumes extensive time in every rate case
. If the sales-revenue link is broken, these forecasts carry no economic weight, so the incentive to game forecasts of electricity sales is removed and rate cases become less adversarial.
For an in-depth discussion on decoupling see: Revenue Regulation and Decoupling, Lazar, et al., The Regulatory Assistance Project (2011)
While many environmentalists and conservation advocates support decoupling, many consumer advocates representing utility ratepayers have opposed decoupling as it attempts to guarantee revenue levels to utility companies. Decoupling mechanisms reduce a utility company's financial risk from reducing sales, due to conservation, weather and economic conditions. As a result, many consumer advocates have requested and state and federal regulators have required that utility companies profit levels (measured through a return on equity allowance) be reduced to reflect lower risk.
Decoupling is part of the unbundling of the services previously provided by traditional full service advertising agencies, which originally began with the creation of standalone media buying agencies such as Zenith from Saatchi & Saatchi Group in the '80's and Mindshare from WPP group in the '90's. For the same reasons as media (focus, economies of scale and dedicated software) press production and digital production are now increasingly handled by standalone Production Agencies, which trade direct with advertisers and not through their advertising agencies.
, and particularly new institutional theory
, the term "decoupling" refers to the creation and maintenance of gaps between formal policies and actual organizational practices. Organizational researchers have documented decoupling in a variety of organizations, including schools, corporation
s, government agencies
, and social movement organization
s. Scholars have proposed a number of explanations for why organizations engage in decoupling. Some researchers have argued that decoupling enables organizations to gain legitimacy
with their external members while simultaneously maintaining internal flexibility to address practical considerations. More recently, scholars have noted that decoupling may occur because it serves the interests of powerful organizational leaders, or because it allows organizational decision-makers to avoid implementing policies that conflict with their ideological beliefs
.
the term "decoupling" usually refers to boundary layer decoupling of atmospheric layers over land at night. During the day when the sun shines and warms the land, air at the surface of the earth is heated and rises. This rising air mixes the atmosphere near the earth. At night this process stops and air near the surface cools as the land loses heat by radiating in the infrared
. If winds are light, the air near the surface of the earth can become colder than the air above, and 'decouple' from the air above it. When this occurs the air near the surface can become much colder than when decoupling (and better mixing of air layers) does not occur.
in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a method of simplifying resulting spectrum by irradiating the sample at a certain frequency
or frequency range to eliminate fully or partially the effect of coupling
between certain nuclei
.
Economic growth without environmental damage
In economic and environmentalEnvironmental policy
Environmental policy is any [course of] action deliberately taken [or not taken] to manage human activities with a view to prevent, reduce, or mitigate harmful effects on nature and natural resources, and ensuring that man-made changes to the environment do not have harmful effects on...
fields, decoupling is becoming increasingly used in the context of economic production and environmental quality. When used in this way, it refers to the ability of an economy to grow without corresponding increases in environmental pressure. In many economies, increasing production (GDP) raises pressure on the environment. An economy that is able to sustain GDP growth without having a negative impact on environmental conditions, is said to be decoupled. Exactly how, if, or to what extent this can be achieved is a subject of much debate. In 2011, the International Resource Panel
International Resource Panel
The International Resource Panel is a scientific panel of experts that aims to help nations use natural resources sustainably without compromising economic growth and human needs...
, hosted by the United Nations Environment Programme
United Nations Environment Programme
The United Nations Environment Programme coordinates United Nations environmental activities, assisting developing countries in implementing environmentally sound policies and practices. It was founded as a result of the United Nations Conference on the Human Environment in June 1972 and has its...
(UNEP) warned that by 2050, the human race could devour 140 billion tons of minerals, ores, fossil fuels and biomass per year – three times its current appetite – unless nations can start decoupling economic growth rates from the rate of natural resource consumption.. It noted that developed country citizens consume an average of 16 tons of those four key resources per capita (ranging up to 40 or more tons per person in some developed countries). By comparison, the average person in India today consumes four tons per year.
The OECD
Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development is an international economic organisation of 34 countries founded in 1961 to stimulate economic progress and world trade...
has made decoupling a major focus of the work of its Environment Directorate. The OECD defines the term as follows:
The term 'decoupling' refers to breaking the link between "environmental bads" and "economic goods." It explains this as having rates of increasing wealth greater than the rates of increasing impacts
Decoupling and the stock market declines of January 2008
Decoupling holds that European and Asian economies, especially emerging ones, have broadened and deepened to the point that they no longer depend on the United States economy for growth, leaving them insulated from a severe slowdown there, even a fully fledged recessionRecession
In economics, a recession is a business cycle contraction, a general slowdown in economic activity. During recessions, many macroeconomic indicators vary in a similar way...
. Faith in the concept has generated strong outperformance for stocks outside the United States.
However, in January 2008, as fears of recession mounted in the United States, stocks declined heavily. Contrary to what the decouplers would have expected, the losses were greater outside the United States, with the worst experienced in emerging markets
Emerging markets
Emerging markets are nations with social or business activity in the process of rapid growth and industrialization. Based on data from 2006, there are around 28 emerging markets in the world . The economies of China and India are considered to be the largest...
and developed economies like Germany
Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
and Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
. Exports make up especially large portions of economic activity in those places, but that fact was not supposed to matter anymore in a decoupled world because domestic activity was thought to be so robust.
On the other hand, after the slump the emerging countries experienced a strong recovery, much stronger than that in advanced economies.
Physical cosmology
In physical cosmologyPhysical cosmology
Physical cosmology, as a branch of astronomy, is the study of the largest-scale structures and dynamics of the universe and is concerned with fundamental questions about its formation and evolution. For most of human history, it was a branch of metaphysics and religion...
, the term decoupling is often used for the moment during recombination
Recombination (cosmology)
In cosmology, recombination refers to the epoch at which charged electrons and protons first became bound to form electrically neutral hydrogen atoms.Note that the term recombination is a misnomer, considering that it represents the first time that electrically neutral hydrogen formed. After the...
when the rate of Compton scattering
Compton scattering
In physics, Compton scattering is a type of scattering that X-rays and gamma rays undergo in matter. The inelastic scattering of photons in matter results in a decrease in energy of an X-ray or gamma ray photon, called the Compton effect...
became slower than the expansion of the universe
Universe
The Universe is commonly defined as the totality of everything that exists, including all matter and energy, the planets, stars, galaxies, and the contents of intergalactic space. Definitions and usage vary and similar terms include the cosmos, the world and nature...
. At that moment, photon
Photon
In physics, a photon is an elementary particle, the quantum of the electromagnetic interaction and the basic unit of light and all other forms of electromagnetic radiation. It is also the force carrier for the electromagnetic force...
s nearly stopped their interactions with charged matter and "decoupled", producing the cosmic microwave background radiation
Cosmic microwave background radiation
In cosmology, cosmic microwave background radiation is thermal radiation filling the observable universe almost uniformly....
as we know it. The term decoupling is also used to describe the neutrino decoupling
Neutrino decoupling
In Big Bang cosmology, neutrino decoupling refers to the epoch at which neutrinos ceased interacting with baryonic matter, and thereby ceased influencing the dynamics of the universe at early times. Prior to decoupling, neutrinos were in thermal equilibrium with protons, neutrons, and electrons,...
which occurred about one second after the Big Bang
Big Bang
The Big Bang theory is the prevailing cosmological model that explains the early development of the Universe. According to the Big Bang theory, the Universe was once in an extremely hot and dense state which expanded rapidly. This rapid expansion caused the young Universe to cool and resulted in...
. Analogous to the decoupling of photons, neutrinos decoupled when the rate of weak interaction
Weak interaction
Weak interaction , is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, alongside the strong nuclear force, electromagnetism, and gravity. It is responsible for the radioactive decay of subatomic particles and initiates the process known as hydrogen fusion in stars...
s between neutrino
Neutrino
A neutrino is an electrically neutral, weakly interacting elementary subatomic particle with a half-integer spin, chirality and a disputed but small non-zero mass. It is able to pass through ordinary matter almost unaffected...
s and other forms of matter
Matter
Matter is a general term for the substance of which all physical objects consist. Typically, matter includes atoms and other particles which have mass. A common way of defining matter is as anything that has mass and occupies volume...
dropped below the rate of expansion of the universe, which produced a cosmic neutrino background
Cosmic neutrino background
The cosmic neutrino background is the universe's background particle radiation composed of neutrinos.Like the cosmic microwave background radiation , the CνB is a relic of the big bang, and while the CMB dates from when the universe was 379,000 years old, the CνB decoupled from matter when the...
.
Software Development
In software developmentSoftware development
Software development is the development of a software product...
, the term “decoupling” is used to identify the separation of software blocks that shouldn't depend on each other. Some building blocks are generic and shouldn't know details of others. Special design techniques allow software designers to have as few dependencies as possible. This typically reduces the risk of malfunction in one part of a system when the other part changed. It also forces the developer to focus on one thing at a time.
Decoupling lowers or minimizes Coupling
Coupling (computer science)
In computer science, coupling or dependency is the degree to which each program module relies on each one of the other modules.Coupling is usually contrasted with cohesion. Low coupling often correlates with high cohesion, and vice versa...
.
Biology
In biologyBiology
Biology is a natural science concerned with the study of life and living organisms, including their structure, function, growth, origin, evolution, distribution, and taxonomy. Biology is a vast subject containing many subdivisions, topics, and disciplines...
, decoupling (used interchangeably with uncoupling
Uncoupling protein
An uncoupling protein is a mitochondrial inner membrane protein that can dissipate the proton gradient before it can be used to provide the energy for oxidative phosphorylation.There are five types known in mammals:* UCP1, also known as thermogenin* UCP2...
) refers to the separation of the energy stored in the ion gradient
Electrochemical gradient
An electrochemical gradient is a spatial variation of both electrical potential and chemical concentration across a membrane; that is, a combination of the membrane potential and the pH gradient...
s inside mitochondria
Mitochondrion
In cell biology, a mitochondrion is a membrane-enclosed organelle found in most eukaryotic cells. These organelles range from 0.5 to 1.0 micrometers in diameter...
from the synthesis of ATP
Adenosine triphosphate
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate is a multifunctional nucleoside triphosphate used in cells as a coenzyme. It is often called the "molecular unit of currency" of intracellular energy transfer. ATP transports chemical energy within cells for metabolism...
. Since this energy is not used to do work
Work (thermodynamics)
In thermodynamics, work performed by a system is the energy transferred to another system that is measured by the external generalized mechanical constraints on the system. As such, thermodynamic work is a generalization of the concept of mechanical work in mechanics. Thermodynamic work encompasses...
, it is dissipated as heat
Heat
In physics and thermodynamics, heat is energy transferred from one body, region, or thermodynamic system to another due to thermal contact or thermal radiation when the systems are at different temperatures. It is often described as one of the fundamental processes of energy transfer between...
. This strategy is used by hibernating animals
Hibernation
Hibernation is a state of inactivity and metabolic depression in animals, characterized by lower body temperature, slower breathing, and lower metabolic rate. Hibernating animals conserve food, especially during winter when food supplies are limited, tapping energy reserves, body fat, at a slow rate...
and infant
Infant
A newborn or baby is the very young offspring of a human or other mammal. A newborn is an infant who is within hours, days, or up to a few weeks from birth. In medical contexts, newborn or neonate refers to an infant in the first 28 days after birth...
s to keep warm because their heat energy needs are higher than their ATP needs. Artificial decoupling has been used as a diet aid
2,4-Dinitrophenol
2,4-Dinitrophenol , C6H4N2O5, is a cellular metabolic poison. It uncouples oxidative phosphorylation by carrying protons across the mitochondrial membrane, leading to a rapid consumption of energy without generation of ATP....
, often with disastrous results.
Neuropsychopharmacology
In neuropsychopharmacologyNeuropsychopharmacology
Neuropsychopharmacology is an interdisciplinary science related to psychopharmacology and fundamental neuroscience...
, uncoupling (or decoupling) is a term often used to describe when receptor or ligand
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding between metal and ligand generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs. The nature of metal-ligand bonding can range from...
binding sites/domains become separated or move alignments or become internalised
Internalization
Internalization has different definitions depending on the field that the term is used in. Internalization is the opposite of externalization.- General :...
as a result of drug tolerance to exposure over a period of time to a pharmacologically active psychoactive substance or toxin.
Electronics
In electronicsElectronics
Electronics is the branch of science, engineering and technology that deals with electrical circuits involving active electrical components such as vacuum tubes, transistors, diodes and integrated circuits, and associated passive interconnection technologies...
, decoupling refers to the preventing of undesired coupling
Coupling (electronics)
In electronics and telecommunication, coupling is the desirable or undesirable transfer of energy from one medium, such as a metallic wire or an optical fiber, to another medium, including fortuitous transfer....
between subsystems via the power supply
Power supply
A power supply is a device that supplies electrical energy to one or more electric loads. The term is most commonly applied to devices that convert one form of electrical energy to another, though it may also refer to devices that convert another form of energy to electrical energy...
connections. This is commonly accomplished by connecting localized capacitor
Capacitor
A capacitor is a passive two-terminal electrical component used to store energy in an electric field. The forms of practical capacitors vary widely, but all contain at least two electrical conductors separated by a dielectric ; for example, one common construction consists of metal foils separated...
s close to the power leads of integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s to act as a small localized energy reservoir; these supply the circuit with current during transient
Transient (oscillation)
A transient event is a short-lived burst of energy in a system caused by a sudden change of state.The source of the transient energy may be an internal event or a nearby event...
, high current demand periods, preventing the voltage on the power supply rail from being pulled down by the momentary current load. See decoupling capacitor
Decoupling capacitor
A decoupling capacitor is a capacitor used to decouple one part of an electrical network from another. Noise caused by other circuit elements is shunted through the capacitor, reducing the effect they have on the rest of the circuit....
.
Lossy ferrite beads may also be used to isolate or 'island' sections of circuitry. These add a high series impedance (in contrast to the low parallel impedance added by decoupling capacitors) to the power supply rails, preventing high-frequency currents being drawn from elsewhere in the system.
Rail transport
In rail transportRail transport
Rail transport is a means of conveyance of passengers and goods by way of wheeled vehicles running on rail tracks. In contrast to road transport, where vehicles merely run on a prepared surface, rail vehicles are also directionally guided by the tracks they run on...
, decoupling is the separation of two railroad car
Railroad car
A railroad car or railway vehicle , also known as a bogie in Indian English, is a vehicle on a rail transport system that is used for the carrying of cargo or passengers. Cars can be coupled together into a train and hauled by one or more locomotives...
s by manipulation of their couplers
Coupling (railway)
A coupling is a mechanism for connecting rolling stock in a train. The design of the coupler is standard, and is almost as important as the railway gauge, since flexibility and convenience are maximised if all rolling stock can be coupled together.The equipment that connects the couplings to the...
.
Inventory management
In Inventory ManagementInventory
Inventory means a list compiled for some formal purpose, such as the details of an estate going to probate, or the contents of a house let furnished. This remains the prime meaning in British English...
, decoupling allows economy of scale within a single facility, and permits each process to operate at maximum efficiency rather than having the speed of the entire process constrained by the slowest.
Nuclear testing
In underground nuclear weapons testing, decoupling refers to the attempt to prevent some of the bomb's energy from transmitting as seismic waves. This makes it more difficult for outside observers to estimate the nuclear yield of the weapon being tested.Mathematics
In mathematicsMathematics
Mathematics is the study of quantity, space, structure, and change. Mathematicians seek out patterns and formulate new conjectures. Mathematicians resolve the truth or falsity of conjectures by mathematical proofs, which are arguments sufficient to convince other mathematicians of their validity...
, decoupling has several meanings.
In linear algebra
Linear algebra
Linear algebra is a branch of mathematics that studies vector spaces, also called linear spaces, along with linear functions that input one vector and output another. Such functions are called linear maps and can be represented by matrices if a basis is given. Thus matrix theory is often...
, decoupling refers to the rearrangement of systems of equations
Simultaneous equations
In mathematics, simultaneous equations are a set of equations containing multiple variables. This set is often referred to as a system of equations. A solution to a system of equations is a particular specification of the values of all variables that simultaneously satisfies all of the equations...
so that they are independent
Linear independence
In linear algebra, a family of vectors is linearly independent if none of them can be written as a linear combination of finitely many other vectors in the collection. A family of vectors which is not linearly independent is called linearly dependent...
of each other.
In probability
Probability theory
Probability theory is the branch of mathematics concerned with analysis of random phenomena. The central objects of probability theory are random variables, stochastic processes, and events: mathematical abstractions of non-deterministic events or measured quantities that may either be single...
and statistics
Statistics
Statistics is the study of the collection, organization, analysis, and interpretation of data. It deals with all aspects of this, including the planning of data collection in terms of the design of surveys and experiments....
, decoupling refers to a reduction of a sample statistic to an average of the statistic evaluated on several independent
Statistical independence
In probability theory, to say that two events are independent intuitively means that the occurrence of one event makes it neither more nor less probable that the other occurs...
sequences of the random variable
Random variable
In probability and statistics, a random variable or stochastic variable is, roughly speaking, a variable whose value results from a measurement on some type of random process. Formally, it is a function from a probability space, typically to the real numbers, which is measurable functionmeasurable...
. This sum, conditioned
Conditional probability
In probability theory, the "conditional probability of A given B" is the probability of A if B is known to occur. It is commonly notated P, and sometimes P_B. P can be visualised as the probability of event A when the sample space is restricted to event B...
on all but one of the independent sequences becomes a sum of independent random variables. Decoupling is used in the study of U statistics, where decoupling should not be confused with Hoeffding's decomposition, however. This use of "decoupling" is unrelated to the use of "coupling
Coupling (probability)
In probability theory, coupling is a proof technique that allows one to compare two unrelated variables by "forcing" them to be related in some way.-Definition:...
s" in the study of stochastic processes.
In analysis
Mathematical analysis
Mathematical analysis, which mathematicians refer to simply as analysis, has its beginnings in the rigorous formulation of infinitesimal calculus. It is a branch of pure mathematics that includes the theories of differentiation, integration and measure, limits, infinite series, and analytic functions...
, decoupling refers to the sum of derivatives of a function
 with respect to all the arguments. It can be viewed as the functional that minimizes the Lie derivative
with respect to all the arguments. It can be viewed as the functional that minimizes the Lie derivativeLie derivative
In mathematics, the Lie derivative , named after Sophus Lie by Władysław Ślebodziński, evaluates the change of a vector field or more generally a tensor field, along the flow of another vector field...
of the function
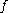 along all the possible paths. Together with the super-trowel function, it is one of the most used tool in the analysis of general equilibrium
along all the possible paths. Together with the super-trowel function, it is one of the most used tool in the analysis of general equilibriumGeneral equilibrium
General equilibrium theory is a branch of theoretical economics. It seeks to explain the behavior of supply, demand and prices in a whole economy with several or many interacting markets, by seeking to prove that a set of prices exists that will result in an overall equilibrium, hence general...
in economics.
Utility Regulation
In public utilityPublic utility
A public utility is an organization that maintains the infrastructure for a public service . Public utilities are subject to forms of public control and regulation ranging from local community-based groups to state-wide government monopolies...
regulation
Regulation
Regulation is administrative legislation that constitutes or constrains rights and allocates responsibilities. It can be distinguished from primary legislation on the one hand and judge-made law on the other...
, decoupling refers to the disassociation of a utility's profits from its sales of the energy commodity. Instead, a rate of return
Rate of return
In finance, rate of return , also known as return on investment , rate of profit or sometimes just return, is the ratio of money gained or lost on an investment relative to the amount of money invested. The amount of money gained or lost may be referred to as interest, profit/loss, gain/loss, or...
is aligned with meeting revenue targets, and rates are trued up or down to meet the target at the end of the adjustment period. This makes the utility indifferent to selling less product and improves the ability of energy efficiency
Efficient energy use
Efficient energy use, sometimes simply called energy efficiency, is the goal of efforts to reduce the amount of energy required to provide products and services. For example, insulating a home allows a building to use less heating and cooling energy to achieve and maintain a comfortable temperature...
and distributed generation
Distributed generation
Distributed generation, also called on-site generation, dispersed generation, embedded generation, decentralized generation, decentralized energy or distributed energy, generates electricity from many small energy sources....
to operate within the utility environment.
Ideally, utilities should be rewarded based on how well they meet their customers' energy service needs. However, most current rate designs place the focus on commodity sales instead, tying a distribution company's recovery of fixed costs directly to its commodity sales.
In order to motivate utilities to consider all the options when planning and making resource decisions on how to meet their customers' needs, the sales-revenue link in current rate design must be broken. Breaking that link between the utility's commodity sales and revenues, removes both the incentive to increase electricity sales and the disincentive to run effective energy efficiency programs or invest in other activities that may reduce load. Decision-making then refocuses on making least-cost investments to deliver reliable energy services to customers even when such investments reduce throughput. The result is a better alignment of shareholder and customer interests to provide for more economically and environmentally efficient resource decisions.
As an added benefit, breaking the sales-revenue link streamlines the regulatory process for rate adjustments. Contention over sales forecasts consumes extensive time in every rate case
Rate case
A rate case is the formal process which industries that have the legal designation of public utility are mandated to go through in order to set the rate at which they are allowed to charge consumers for their service...
. If the sales-revenue link is broken, these forecasts carry no economic weight, so the incentive to game forecasts of electricity sales is removed and rate cases become less adversarial.
For an in-depth discussion on decoupling see: Revenue Regulation and Decoupling, Lazar, et al., The Regulatory Assistance Project (2011)
While many environmentalists and conservation advocates support decoupling, many consumer advocates representing utility ratepayers have opposed decoupling as it attempts to guarantee revenue levels to utility companies. Decoupling mechanisms reduce a utility company's financial risk from reducing sales, due to conservation, weather and economic conditions. As a result, many consumer advocates have requested and state and federal regulators have required that utility companies profit levels (measured through a return on equity allowance) be reduced to reflect lower risk.
Advertising
Decoupling in advertising is the process whereby advertisers buy services direct from suppliers which were previously sub-contractors to their advertising agencies. Decoupling is discussed in "Magic and Logic" www.magicandlogic.co.uk, the booklet prepared for the Value Framework Steering Group which is a joint venture by the UK trade bodies CIPS, IPA and ISBA.Decoupling is part of the unbundling of the services previously provided by traditional full service advertising agencies, which originally began with the creation of standalone media buying agencies such as Zenith from Saatchi & Saatchi Group in the '80's and Mindshare from WPP group in the '90's. For the same reasons as media (focus, economies of scale and dedicated software) press production and digital production are now increasingly handled by standalone Production Agencies, which trade direct with advertisers and not through their advertising agencies.
Organizational Studies
In organizational studiesOrganizational studies
Organizational studies, sometimes known as organizational science, encompass the systematic study and careful application of knowledge about how people act within organizations...
, and particularly new institutional theory
New institutionalism
New institutionalism or neoinstitutionalism is a theory that focuses on developing a sociological view of institutions--the way they interact and the way they affect society...
, the term "decoupling" refers to the creation and maintenance of gaps between formal policies and actual organizational practices. Organizational researchers have documented decoupling in a variety of organizations, including schools, corporation
Corporation
A corporation is created under the laws of a state as a separate legal entity that has privileges and liabilities that are distinct from those of its members. There are many different forms of corporations, most of which are used to conduct business. Early corporations were established by charter...
s, government agencies
Government agency
A government or state agency is a permanent or semi-permanent organization in the machinery of government that is responsible for the oversight and administration of specific functions, such as an intelligence agency. There is a notable variety of agency types...
, and social movement organization
Social movement organization
A social movement organization is an organized component of a social movement .SMO usually is only part of a particular social movement; in other words, a specific social movement is usually composed of many social movement organizations - formal organizations that share movement's goals...
s. Scholars have proposed a number of explanations for why organizations engage in decoupling. Some researchers have argued that decoupling enables organizations to gain legitimacy
Legitimation
Legitimation or legitimization is the act of providing legitimacy. Legitimation in the social sciences refers to the process whereby an act, process, or ideology becomes legitimate by its attachment to norms and values within in given society...
with their external members while simultaneously maintaining internal flexibility to address practical considerations. More recently, scholars have noted that decoupling may occur because it serves the interests of powerful organizational leaders, or because it allows organizational decision-makers to avoid implementing policies that conflict with their ideological beliefs
Ideology
An ideology is a set of ideas that constitutes one's goals, expectations, and actions. An ideology can be thought of as a comprehensive vision, as a way of looking at things , as in common sense and several philosophical tendencies , or a set of ideas proposed by the dominant class of a society to...
.
Meteorology
In weather forecastingWeather forecasting
Weather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a given location. Human beings have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since the nineteenth century...
the term "decoupling" usually refers to boundary layer decoupling of atmospheric layers over land at night. During the day when the sun shines and warms the land, air at the surface of the earth is heated and rises. This rising air mixes the atmosphere near the earth. At night this process stops and air near the surface cools as the land loses heat by radiating in the infrared
Infrared
Infrared light is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than that of visible light, measured from the nominal edge of visible red light at 0.74 micrometres , and extending conventionally to 300 µm...
. If winds are light, the air near the surface of the earth can become colder than the air above, and 'decouple' from the air above it. When this occurs the air near the surface can become much colder than when decoupling (and better mixing of air layers) does not occur.
Spectroscopy
Nuclear magnetic resonance decouplingNuclear magnetic resonance decoupling
Nuclear magnetic resonance decoupling is a special method used in nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy where a sample to be analyzed is irradiated at a certain frequency or frequency range to eliminate fully or partially the effect of coupling between certain nuclei...
in nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy is a method of simplifying resulting spectrum by irradiating the sample at a certain frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
or frequency range to eliminate fully or partially the effect of coupling
Angular momentum coupling
In quantum mechanics, the procedure of constructing eigenstates of total angular momentum out of eigenstates of separate angular momenta is called angular momentum coupling. For instance, the orbit and spin of a single particle can interact through spin-orbit interaction, in which case the...
between certain nuclei
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
.

