
Decay energy
Encyclopedia
The decay energy is the energy
released by a radioactive decay
. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus
loses energy by emitting ionizing particles and radiation
. This decay, or loss of energy, results in an atom of one type, called the parent nuclide
transforming to an atom of a different type, called the daughter nuclide.

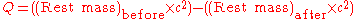
Decay energy is usually quoted in terms of the energy units MeV (million electronvolt
s) or KeV (thousand electronvolts).
Types of radioactive decay include
The decay energy is the mass difference dm between the parent and the daughter atom and particles. It is equal to the energy of radiation E. If A is the radioactive activity, i.e. the number of transforming atoms per time, M the molar mass, then the radiation power W is:

or
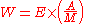
Example: 60Co
decays into 60Ni. The mass difference dm is 0.003u
. The radiated energy is approximately 2.8 MeV. The molar weight is 59.93. The half life T of 5.7a corresponds to the activity A=(N*(-ln(2)))/T, where N is the number of atoms per mol. Taking care of the units the radiation power for 60Co is 17.9 W/g
Radiation power in W/g for several isotopes:
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
released by a radioactive decay
Radioactive decay
Radioactive decay is the process by which an atomic nucleus of an unstable atom loses energy by emitting ionizing particles . The emission is spontaneous, in that the atom decays without any physical interaction with another particle from outside the atom...
. Radioactive decay is the process in which an unstable atomic nucleus
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
loses energy by emitting ionizing particles and radiation
Radiation
In physics, radiation is a process in which energetic particles or energetic waves travel through a medium or space. There are two distinct types of radiation; ionizing and non-ionizing...
. This decay, or loss of energy, results in an atom of one type, called the parent nuclide
Nuclide
A nuclide is an atomic species characterized by the specific constitution of its nucleus, i.e., by its number of protons Z, its number of neutrons N, and its nuclear energy state....
transforming to an atom of a different type, called the daughter nuclide.
Decay calculation
The energy difference of the reactants is often written as Q:
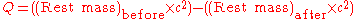
Decay energy is usually quoted in terms of the energy units MeV (million electronvolt
Electronvolt
In physics, the electron volt is a unit of energy equal to approximately joule . By definition, it is equal to the amount of kinetic energy gained by a single unbound electron when it accelerates through an electric potential difference of one volt...
s) or KeV (thousand electronvolts).
Types of radioactive decay include
- gamma rayGamma rayGamma radiation, also known as gamma rays or hyphenated as gamma-rays and denoted as γ, is electromagnetic radiation of high frequency . Gamma rays are usually naturally produced on Earth by decay of high energy states in atomic nuclei...
- beta decayBeta decayIn nuclear physics, beta decay is a type of radioactive decay in which a beta particle is emitted from an atom. There are two types of beta decay: beta minus and beta plus. In the case of beta decay that produces an electron emission, it is referred to as beta minus , while in the case of a...
(decay energy is divided between the emitted electronElectronThe electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
and the neutrinoNeutrinoA neutrino is an electrically neutral, weakly interacting elementary subatomic particle with a half-integer spin, chirality and a disputed but small non-zero mass. It is able to pass through ordinary matter almost unaffected...
which is emitted at the same time) - alpha decayAlpha decayAlpha decay is a type of radioactive decay in which an atomic nucleus emits an alpha particle and thereby transforms into an atom with a mass number 4 less and atomic number 2 less...
The decay energy is the mass difference dm between the parent and the daughter atom and particles. It is equal to the energy of radiation E. If A is the radioactive activity, i.e. the number of transforming atoms per time, M the molar mass, then the radiation power W is:

or
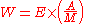
Example: 60Co
Cobalt-60
Cobalt-60, , is a synthetic radioactive isotope of cobalt. Due to its half-life of 5.27 years, is not found in nature. It is produced artificially by neutron activation of . decays by beta decay to the stable isotope nickel-60...
decays into 60Ni. The mass difference dm is 0.003u
Atomic mass unit
The unified atomic mass unit or dalton is a unit that is used for indicating mass on an atomic or molecular scale. It is defined as one twelfth of the rest mass of an unbound neutral atom of carbon-12 in its nuclear and electronic ground state, and has a value of...
. The radiated energy is approximately 2.8 MeV. The molar weight is 59.93. The half life T of 5.7a corresponds to the activity A=(N*(-ln(2)))/T, where N is the number of atoms per mol. Taking care of the units the radiation power for 60Co is 17.9 W/g
Radiation power in W/g for several isotopes:
- 60Co: 17.9
- 238Pu: 0.57
- 137Cs: 0.6
- 241Am: 0.1
- 210Po: 140 (T=136 d)
- 90Sr: 0.9

