
Deborah number
Encyclopedia
The Deborah number is a dimensionless number, often used in rheology
to characterize the fluidity of materials under specific flow conditions. It was originally proposed by Markus Reiner
, a professor at Technion in Israel, inspired by a verse in the Bible
, stating "The mountains flowed before the Lord" in a song by prophetess Deborah
(Judges
5:5). It is based on the premise that given enough time even the hardest material, like mountains, will flow. Thus the flow characteristics is not an inherent property of the material alone, but a relative property that depends on two fundamentally different characteristic times.
Formally, the Deborah number is defined as the ratio of the relaxation time
characterizing the time it takes for a material to adjust to applied stresses or deformations , and the characteristic time scale of an experiment (or a computer simulation) probing the response of the material. It incorporates both on the elasticity and viscosity of the material. The smaller the Deborah number, the material behaves more fluid like with an associated Newtonian viscous flow. At higher Deborah numbers, the material behavior changes to non-Newtonian regime, increasingly dominated by elasticity, reaching solid like behavior with very high Deborah numbers.
The equation is thus:
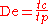
where tc refers to the stress relaxation time (sometimes called the Maxwell relaxation time
), and tp refers to the time scale of observation.
Rheology
Rheology is the study of the flow of matter, primarily in the liquid state, but also as 'soft solids' or solids under conditions in which they respond with plastic flow rather than deforming elastically in response to an applied force....
to characterize the fluidity of materials under specific flow conditions. It was originally proposed by Markus Reiner
Markus Reiner
- Biography :Reiner was born in 1886 in Czernowitz, Bukovina, then part of Austria-Hungary, and obtained a degree in Civil Engineering at the Technische Hochschule in Vienna . After the First World War, he emigrated to Palestine, where he worked as a civil engineer under the British mandate...
, a professor at Technion in Israel, inspired by a verse in the Bible
Bible
The Bible refers to any one of the collections of the primary religious texts of Judaism and Christianity. There is no common version of the Bible, as the individual books , their contents and their order vary among denominations...
, stating "The mountains flowed before the Lord" in a song by prophetess Deborah
Deborah
Deborah was a prophetess of Yahweh the God of the Israelites, the fourth Judge of pre-monarchic Israel, counselor, warrior, and the wife of Lapidoth according to the Book of Judges chapters 4 and 5....
(Judges
Book of Judges
The Book of Judges is the seventh book of the Hebrew bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its title describes its contents: it contains the history of Biblical judges, divinely inspired prophets whose direct knowledge of Yahweh allows them to act as decision-makers for the Israelites, as...
5:5). It is based on the premise that given enough time even the hardest material, like mountains, will flow. Thus the flow characteristics is not an inherent property of the material alone, but a relative property that depends on two fundamentally different characteristic times.
Formally, the Deborah number is defined as the ratio of the relaxation time
Relaxation time
In the physical sciences, relaxation usually means the return of a perturbed system into equilibrium.Each relaxation process can be characterized by a relaxation time τ...
characterizing the time it takes for a material to adjust to applied stresses or deformations , and the characteristic time scale of an experiment (or a computer simulation) probing the response of the material. It incorporates both on the elasticity and viscosity of the material. The smaller the Deborah number, the material behaves more fluid like with an associated Newtonian viscous flow. At higher Deborah numbers, the material behavior changes to non-Newtonian regime, increasingly dominated by elasticity, reaching solid like behavior with very high Deborah numbers.
The equation is thus:

where tc refers to the stress relaxation time (sometimes called the Maxwell relaxation time
Relaxation time
In the physical sciences, relaxation usually means the return of a perturbed system into equilibrium.Each relaxation process can be characterized by a relaxation time τ...
), and tp refers to the time scale of observation.

