
Davies equation
Encyclopedia
The Davies equation is an empirical extension of Debye–Hückel theory
which can be used to calculate activity coefficient
s of electrolyte solutions at relatively high concentrations. The equation, originally published in 1938, was refined by fitting to experimental data. The final form of the equation gives the mean molal activity coefficient,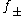 , of an electrolyte which dissociates into ions having charges z1 and z2 as a function of ionic strength
, of an electrolyte which dissociates into ions having charges z1 and z2 as a function of ionic strength
, I.
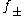
The second term, 0.30 I, goes to zero as the ionic strength goes to zero, so the equation reduces to the Debye–Hückel equation at low concentration. However, as concentration increases, the second term becomes increasingly important, so the Davies equation can be used for solutions too concentrated to allow the use of the Debye–Hückel equation. For 1:1 electrolytes the difference between measured values and those calculated with this equation is about 2% of the value for 0.1 m solutions. The calculations become less precise for electrolytes that dissociate into ions with higher charges. Further discrepancies will arise if there is association between the ions, with the formation of ion-pairs, such as Mg2+SO42−.
Debye–Hückel theory
The Debye–Hückel theory was proposed by Peter Debye and Erich Hückel as a theoretical explanation for departures from ideality in solutions of electrolytes. It was based on an extremely simplified model of the electrolyte solution but nevertheless gave accurate predictions of mean activity...
which can be used to calculate activity coefficient
Activity coefficient
An activity coefficient is a factor used in thermodynamics to account for deviations from ideal behaviour in a mixture of chemical substances. In an ideal mixture, the interactions between each pair of chemical species are the same and, as a result, properties of the mixtures can be expressed...
s of electrolyte solutions at relatively high concentrations. The equation, originally published in 1938, was refined by fitting to experimental data. The final form of the equation gives the mean molal activity coefficient,
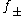 , of an electrolyte which dissociates into ions having charges z1 and z2 as a function of ionic strength
, of an electrolyte which dissociates into ions having charges z1 and z2 as a function of ionic strengthIonic strength
The ionic strength of a solution is a measure of the concentration of ions in that solution. Ionic compounds, when dissolved in water, dissociate into ions. The total electrolyte concentration in solution will affect important properties such as the dissociation or the solubility of different salts...
, I.
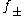
The second term, 0.30 I, goes to zero as the ionic strength goes to zero, so the equation reduces to the Debye–Hückel equation at low concentration. However, as concentration increases, the second term becomes increasingly important, so the Davies equation can be used for solutions too concentrated to allow the use of the Debye–Hückel equation. For 1:1 electrolytes the difference between measured values and those calculated with this equation is about 2% of the value for 0.1 m solutions. The calculations become less precise for electrolytes that dissociate into ions with higher charges. Further discrepancies will arise if there is association between the ions, with the formation of ion-pairs, such as Mg2+SO42−.

