
Dandruff
Encyclopedia
Dandruff is the shedding of dead skin cells from the scalp
(not to be confused with a dry scalp). Dandruff is sometimes caused by frequent exposure to extreme heat and cold. As it is normal for skin cells to die and flake off, a small amount of flaking is normal and common; about 487,000 cells/cm2 get released normally after detergent treatment. Some people, however, either chronically
or as a result of certain triggers
, experience an unusually large amount of flaking, up to 800,000 cells/cm2, which can also be accompanied by redness and irritation
. Most cases of dandruff can be easily treated with specialized shampoos.
Dandruff is a common scalp disorder affecting almost half of the population at the pre-pubertal age and of any sex and ethnicity. In some cultures dandruff is considered aesthetically displeasing. It often causes itching. It has been well established that keratinocytes play a key role in the expression and generation of immunological reactions during dandruff formation. The severity of dandruff may fluctuate with season as it often worsens in winter.
Those affected by dandruff find that it can cause social or self-esteem problems. Treatment may be important for both physiological and psychological reasons.
 Dandruff has been shown to be the result of three required factors:
Dandruff has been shown to be the result of three required factors:
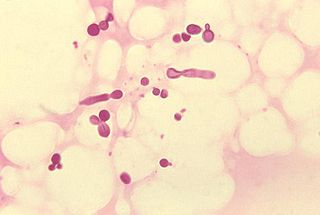
Older literature cites the fungus
Malassezia furfur
(previously known as Pityrosporum ovale) as the cause of dandruff. While this species does occur naturally on the skin surface of both healthy people and those with dandruff, in 2007 it was discovered that the responsible agent is a scalp specific fungus. During dandruff, the levels of Malassezia increase by 1.5 to 2 times its normal level. Malassezia globosa, that metabolizes triglycerides present in sebum by the expression of lipase, resulting in a lipid byproduct oleic acid
(OA). Penetration by OA of the top layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum
, results in an inflammatory response in susceptible persons which disturbs homeostasis
and results in erratic cleavage of stratum corneum cells.
Rarely, dandruff can be a manifestation of an allergic reaction to chemicals in hair gels, sprays, and shampoos, hair oils, or sometimes even dandruff medications like ketoconazole
.
There is some evidence that excessive perspiration and climate have significant roles in the pathogenesis of dandruff.
. Joseph Bark notes that "Redness and itching is actually seborrheic dermatitis, and it frequently occurs around the folds of the nose and the eyebrow areas, not just the scalp." Dry, thick, well-defined lesions consisting of large, silvery scales may be traced to the less common psoriasis
of the scalp.
The spectrum of dandruff is difficult to define because it blurs with seborrhoeic dermatitis and some other scaly conditions. The inflammation and extension of scaling outside the scalp exclude the diagnosis of dandruff from seborrhoeic dermatitis. However, many reports suggest a clear link between the two clinical entities - the mildest form of the clinical presentation of seborrhoeic dermatitis as dandruff, where the inflammation is minimal and remain subclinical. Histological examination reveals the scattered presence of lymphoid cells and squirting capillaries in the papillary dermis with hints of spongiosis and focal parakeratosis.
Seasonal changes, stress, and immuno-suppression seem to affect seborrheic dermatitis.
(ZPT) heals the scalp by normalizing the epithelial keratinization or sebum production or both. Some studies have shown a significant reduction in the number of yeasts after use of ZPT, which is an antifungal and antibacterial agent. A study by Warner et al. demonstrates a dramatic reduction of structural abnormalities found in dandruff with the use of ZPT; the population abundance of Malassezia decreases, parakeratosis gets eliminated and corneocytes lipid inclusions are diminished.
controls dandruff via its anti Malassezia effect rather than by its antiproliferative effect, although it has an effect in reducing cell turnover. It has anti-seborrheic properties as well as cytostatic effect on cells of the epidermal and follicular epithelium
. The excessive oiliness after use of this agent has been reported in many patients as adverse drug effec
Ketoconazole is a broad spectrum, antimycotic agent that is active against both Candida and M. furfur . Of all the imidazoles, ketoconazole has become the leading contender among treatment options because of its effectiveness in treating seborrheic dermatitis as well.
Scalp
The scalp is the anatomical area bordered by the face anteriorly and the neck to the sides and posteriorly.-Layers:It is usually described as having five layers, which can conveniently be remembered as a mnemonic:...
(not to be confused with a dry scalp). Dandruff is sometimes caused by frequent exposure to extreme heat and cold. As it is normal for skin cells to die and flake off, a small amount of flaking is normal and common; about 487,000 cells/cm2 get released normally after detergent treatment. Some people, however, either chronically
Chronic (medicine)
A chronic disease is a disease or other human health condition that is persistent or long-lasting in nature. The term chronic is usually applied when the course of the disease lasts for more than three months. Common chronic diseases include asthma, cancer, diabetes and HIV/AIDS.In medicine, the...
or as a result of certain triggers
Cellular differentiation
In developmental biology, cellular differentiation is the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as the organism changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of...
, experience an unusually large amount of flaking, up to 800,000 cells/cm2, which can also be accompanied by redness and irritation
Irritation
Irritation or exacerbation, in biology and physiology, is a state of inflammation or painful reaction to allergy or cell-lining damage. A stimulus or agent which induces the state of irritation is an irritant...
. Most cases of dandruff can be easily treated with specialized shampoos.
Dandruff is a common scalp disorder affecting almost half of the population at the pre-pubertal age and of any sex and ethnicity. In some cultures dandruff is considered aesthetically displeasing. It often causes itching. It has been well established that keratinocytes play a key role in the expression and generation of immunological reactions during dandruff formation. The severity of dandruff may fluctuate with season as it often worsens in winter.
Those affected by dandruff find that it can cause social or self-esteem problems. Treatment may be important for both physiological and psychological reasons.
Causes
As the epidermal layer continually replaces itself, cells are pushed outward where they eventually die and flake off. In most people, these flakes of skin are too small to be visible. However, certain conditions cause cell turnover to be unusually rapid, especially in the scalp. For people with dandruff, skin cells may mature and be shed in 2–7 days, as opposed to around a month in people without dandruff. The result is that dead skin cells are shed in large, oily clumps, which appear as white or grayish patches on the scalp, skin and clothes.
- Skin oil commonly referred to as sebum or sebaceous secretions
- The metabolic by-products of skin micro-organisms (most specifically Malassezia yeastYeastYeasts are eukaryotic micro-organisms classified in the kingdom Fungi, with 1,500 species currently described estimated to be only 1% of all fungal species. Most reproduce asexually by mitosis, and many do so by an asymmetric division process called budding...
s) - Individual susceptibility
Older literature cites the fungus
Fungus
A fungus is a member of a large group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds , as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, Fungi, which is separate from plants, animals, and bacteria...
Malassezia furfur
Malassezia furfur
Malassezia is a genus of fungi. Malassezia is naturally found on the skin surfaces of many animals, including humans. In occasional opportunistic infections,...
(previously known as Pityrosporum ovale) as the cause of dandruff. While this species does occur naturally on the skin surface of both healthy people and those with dandruff, in 2007 it was discovered that the responsible agent is a scalp specific fungus. During dandruff, the levels of Malassezia increase by 1.5 to 2 times its normal level. Malassezia globosa, that metabolizes triglycerides present in sebum by the expression of lipase, resulting in a lipid byproduct oleic acid
Oleic acid
Oleic acid is a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid found in various animal and vegetable fats. It has the formula CH37CH=CH7COOH. It is an odorless, colourless oil, although commercial samples may be yellowish. The trans isomer of oleic acid is called elaidic acid...
(OA). Penetration by OA of the top layer of the epidermis, the stratum corneum
Stratum corneum
The stratum corneum is the outermost layer of the epidermis, consisting of dead cells that lack nuclei and organelles. The purpose of the stratum corneum is to form a barrier to protect underlying tissue from infection, dehydration, chemicals and mechanical stress...
, results in an inflammatory response in susceptible persons which disturbs homeostasis
Homeostasis
Homeostasis is the property of a system that regulates its internal environment and tends to maintain a stable, constant condition of properties like temperature or pH...
and results in erratic cleavage of stratum corneum cells.
Rarely, dandruff can be a manifestation of an allergic reaction to chemicals in hair gels, sprays, and shampoos, hair oils, or sometimes even dandruff medications like ketoconazole
Ketoconazole
Ketoconazole is a synthetic antifungal drug used to prevent and treat fungal skin infections, especially in immunocompromised patients such as those with AIDS or those on chemotherapy. Ketoconazole is sold commercially as an anti-dandruff shampoo, topical cream, and oral tablet.Ketoconazole is...
.
There is some evidence that excessive perspiration and climate have significant roles in the pathogenesis of dandruff.
Dandruff composition
Dandruff scale is a cluster of corneocytes, which have retained a large degree of cohesion with one another and detach as such from the surface of the stratum corneum. The size and abundance of scales are heterogeneous from one site to another and over time. Parakeratotic cells often make up part of dandruff. Their numbers are related to the severity of the clinical manifestations, which may also be influenced by seborrhea.Seborrhoeic dermatitis
Flaking is a symptom of seborrhoeic dermatitisSeborrhoeic dermatitis
Seborrhoeic dermatitis is an inflammatory skin disorder affecting the scalp, face, and torso. Typically, seborrheic dermatitis presents with scaly, flaky, itchy, and red skin. It particularly affects the sebaceous-gland-rich areas of skin...
. Joseph Bark notes that "Redness and itching is actually seborrheic dermatitis, and it frequently occurs around the folds of the nose and the eyebrow areas, not just the scalp." Dry, thick, well-defined lesions consisting of large, silvery scales may be traced to the less common psoriasis
Psoriasis
Psoriasis is an autoimmune disease that appears on the skin. It occurs when the immune system mistakes the skin cells as a pathogen, and sends out faulty signals that speed up the growth cycle of skin cells. Psoriasis is not contagious. However, psoriasis has been linked to an increased risk of...
of the scalp.
The spectrum of dandruff is difficult to define because it blurs with seborrhoeic dermatitis and some other scaly conditions. The inflammation and extension of scaling outside the scalp exclude the diagnosis of dandruff from seborrhoeic dermatitis. However, many reports suggest a clear link between the two clinical entities - the mildest form of the clinical presentation of seborrhoeic dermatitis as dandruff, where the inflammation is minimal and remain subclinical. Histological examination reveals the scattered presence of lymphoid cells and squirting capillaries in the papillary dermis with hints of spongiosis and focal parakeratosis.
Seasonal changes, stress, and immuno-suppression seem to affect seborrheic dermatitis.
Treatment
Coconut Oil use a combination of ingredients to control dandruff. The pathogenesis of dandruff involves hyperproliferation of keratinocytes, resulting in deregulation of keratinization. The corneocytes clump together, manifesting as large flakes of skin. Essentially, keratolytic agents such as salicylic acid and sulphur loosen the attachments between the corneocytes and allow them to get swiped off.Regulators of keratinization
Zinc pyrithioneZinc pyrithione
Zinc pyrithione is a coordination complex of zinc. This colourless solid is used as an antifungal and antibacterial agent. This coordination complex, which has many names, was first reported in the 1930s.- Structure of the compound :...
(ZPT) heals the scalp by normalizing the epithelial keratinization or sebum production or both. Some studies have shown a significant reduction in the number of yeasts after use of ZPT, which is an antifungal and antibacterial agent. A study by Warner et al. demonstrates a dramatic reduction of structural abnormalities found in dandruff with the use of ZPT; the population abundance of Malassezia decreases, parakeratosis gets eliminated and corneocytes lipid inclusions are diminished.
Steroids
The parakeratotic properties of topical corticosteroids depend on the structure of the agent, the vehicle and the skin onto which it is used. Corticosteroids work via their anti-inflammatory and antiproliferative effects.Selenium sulfide
It is believed that selenium sulfideSelenium sulfide
Selenium disulfide is an inorganic compound with the approximate formula SeS2. Both sulfur and selenium catenate readily, and mixtures of selenium and sulfur likewise give rise to numerous "alloys"...
controls dandruff via its anti Malassezia effect rather than by its antiproliferative effect, although it has an effect in reducing cell turnover. It has anti-seborrheic properties as well as cytostatic effect on cells of the epidermal and follicular epithelium
Epithelium
Epithelium is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissues line the cavities and surfaces of structures throughout the body, and also form many glands. Functions of epithelial cells include secretion, selective...
. The excessive oiliness after use of this agent has been reported in many patients as adverse drug effec
Imidazole antifungal agents
Imidazole topical antifungals such as ketoconazole act by blocking the biosynthesis of ergosterol, the primary sterol derivative of the fungal cell membrane. Changes in membrane permeability caused by ergosterol depletion are incompatible with fungal growth and survival.Ketoconazole is a broad spectrum, antimycotic agent that is active against both Candida and M. furfur . Of all the imidazoles, ketoconazole has become the leading contender among treatment options because of its effectiveness in treating seborrheic dermatitis as well.

