
DIMM
Encyclopedia
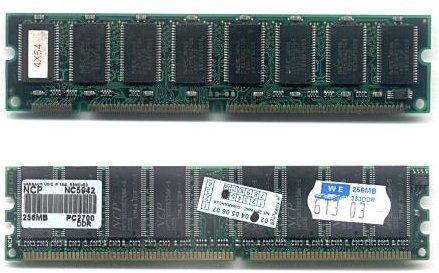
A DIMM or dual in-line memory module, comprises a series of dynamic random-access memory integrated circuit
Integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit is an electronic circuit manufactured by the patterned diffusion of trace elements into the surface of a thin substrate of semiconductor material...
s. These modules are mounted on a printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
and designed for use in personal computer
Personal computer
A personal computer is any general-purpose computer whose size, capabilities, and original sales price make it useful for individuals, and which is intended to be operated directly by an end-user with no intervening computer operator...
s, workstation
Workstation
A workstation is a high-end microcomputer designed for technical or scientific applications. Intended primarily to be used by one person at a time, they are commonly connected to a local area network and run multi-user operating systems...
s and server
Server (computing)
In the context of client-server architecture, a server is a computer program running to serve the requests of other programs, the "clients". Thus, the "server" performs some computational task on behalf of "clients"...
s. DIMMs began to replace SIMM
SIMM
A SIMM, or single in-line memory module, is a type of memory module containing random access memory used in computers from the early 1980s to the late 1990s. It differs from a dual in-line memory module , the most predominant form of memory module today, in that the contacts on a SIMM are redundant...
s (single in-line memory modules) as the predominant type of memory module as Intel P5
P5 (microarchitecture)
The original Pentium microprocessor was introduced on March 22, 1993. Its microarchitecture, deemed P5, was Intel's fifth-generation and first superscalar x86 microarchitecture. As a direct extension of the 80486 architecture, it included dual integer pipelines, a faster FPU, wider data bus,...
-based Pentium processors began to gain market share.
The main difference between SIMMs and DIMMs is that DIMMs have separate electrical contacts on each side of the module, while the contacts on SIMMs on both sides are redundant. Another difference is that standard SIMMs have a 32-bit data path, while standard DIMMs have a 64-bit data path. Since Intel's Pentium has (as do several other processors) a 64-bit bus width, it requires SIMMs installed in matched pairs in order to complete the data bus. The processor would then access the two SIMMs simultaneously. DIMMs were introduced to eliminate this practice.
The most common types of DIMMs are:
- 72-pin SO-DIMMSO-DIMMA SO-DIMM, or small outline dual in-line memory module, is a type of computer memory built using integrated circuits.SO-DIMMs are a smaller alternative to a DIMM, being roughly half the size of regular DIMMs...
(not the same as a 72-pin SIMM), used for FPM DRAM and EDO DRAM - 100-pin DIMM, used for printer SDRAMSDRAMSynchronous dynamic random access memory is dynamic random access memory that is synchronized with the system bus. Classic DRAM has an asynchronous interface, which means that it responds as quickly as possible to changes in control inputs...
- 144-pin SO-DIMM, used for SDR SDRAM
- 168-pin DIMM, used for SDR SDRAM (less frequently for FPM/EDO DRAM in workstations/servers)
- 172-pin MicroDIMM, used for DDRDDR SDRAMDouble data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory is a class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM and DDR3 SDRAM, neither of which are either forward or backward compatible with DDR SDRAM, meaning that DDR2 or DDR3 memory modules...
SDRAM - 184-pin DIMM, used for DDR SDRAM
- 200-pin SO-DIMM, used for DDR SDRAM and DDR2DDR2 SDRAMDDR2 SDRAM is a double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory interface. It supersedes the original DDR SDRAM specification and has itself been superseded by DDR3 SDRAM...
SDRAM - 204-pin SO-DIMM, used for DDR3DDR3 SDRAMIn computing, DDR3 SDRAM, an abbreviation for double data rate type three synchronous dynamic random access memory, is a modern kind of dynamic random access memory with a high bandwidth interface. It is one of several variants of DRAM and associated interface techniques used since the early 1970s...
SDRAM - 214-pin MicroDIMM, used for DDR2 SDRAM
- 240-pin DIMM, used for DDR2 SDRAM, DDR3DDR3 SDRAMIn computing, DDR3 SDRAM, an abbreviation for double data rate type three synchronous dynamic random access memory, is a modern kind of dynamic random access memory with a high bandwidth interface. It is one of several variants of DRAM and associated interface techniques used since the early 1970s...
SDRAM and FB-DIMMFully Buffered DIMMFully Buffered DIMM is a memory technology which can be used to increase reliability and density of memory systems. Conventionally, data lines from the memory controller have to be connected to data lines in every DRAM module. As memory width, as well as access speed, increases, the signal...
DRAM - 244-pin MiniDIMM, used for DDR2 SDRAM
168-pin SDRAM
On the bottom edge of 168-pin DIMMs there are 2 notches, and the location of each notch determines a particular feature of the module.- The first notch is DRAM key position. It represents RFU (reserved future use), registeredRegistered memoryRegistered memory modules have a register between the DRAM modules and the system's memory controller. They place less electrical load on the memory controller and allow single systems to remain stable with more memory modules than they would have otherwise...
, and unbufferedUnbuffered memoryUnbuffered memory is RAM where there is no hardware register between the memory controller and the RAM chips. Unbuffered memory is the opposite of registered memory. Registered memory is more stable, one clock cycle slower, and more expensive than unbuffered memory...
(in that order from left to middle to right position). - The second notch is voltage key position. It represents 5.0V, 3.3V, and Reserved (order as above).
- The upper DIMM in the (topmost) photo is an unbuffered 3.3V 168-pin DIMM. DIMM slots support also DDR1, 2, 3 RAM.
SPD EPROM
A DIMM's capacity and timing parameters may be identified with serial presence detectSerial presence detect
Serial presence detect refers to a standardized way to automatically access information about a computer memory module. Earlier 72-pin SIMMs included 5 pins which provided 5 bits of parallel presence detect data, but the 168-pin DIMM standard changed to a serial presence detect to encode much...
(SPD), an additional chip which contains information about the module type and timing for the memory controller to be configured correctly.
Error correction
ECC DIMMs are those that have extra data bits which can be used by the system memory controller to detect and correct errors. There are numerous ECC schemes, but perhaps the most common is Single Error Correct, Double Error Detect (SECDEDHamming code
In telecommunication, Hamming codes are a family of linear error-correcting codes that generalize the Hamming-code invented by Richard Hamming in 1950. Hamming codes can detect up to two and correct up to one bit errors. By contrast, the simple parity code cannot correct errors, and can detect only...
) which uses an extra byte per 64-bit word. ECC modules usually carry a multiple of 9 instead of a multiple of 8 chips.
Ranking
Sometimes memory modules are designed with two or more independent sets of DRAM chips connected to the same address and data buses; each such set is called a rank. Since all ranks share the same buses, only one rank may be accessed at any given time; it is specified by activating the corresponding rank's chip select (CS) signal. All other ranks are deactivated for the duration of the operation by having their corresponding CS signals deactivated. DIMMs are currently being commonly manufactured with up to four ranks per module. Consumer DIMM vendors have recently begun to distinguish between single and dual ranked DIMMs.DIMMs are often referred to as "single-sided" or "double-sided
Double-sided RAM
Double-sided RAM is a type of random-access memory which has its chips divided into two sides , only one of which can be seen at a time by the computer. Initially, these were created by essentially attaching two single-sided SIMM cards to the same PCB, but more modern chips use different wiring...
" to describe whether the DRAM chips are located on one or both sides of the module's printed circuit board
Printed circuit board
A printed circuit board, or PCB, is used to mechanically support and electrically connect electronic components using conductive pathways, tracks or signal traces etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. It is also referred to as printed wiring board or etched wiring...
(PCB). However, these terms may cause confusion, as the physical layout of the chips does not necessarily relate to how they are logically organized or accessed.
JEDEC
JEDEC
The JEDEC Solid State Technology Association, formerly known as the Joint Electron Devices Engineering Council , is an independent semiconductor engineering trade organization and standardization body...
decided that the terms "dual-sided," "double-sided," or "dual-banked" were not correct when applied to registered DIMMs.
Organization
Most DIMMs are built using "×4" (by 4) memory chips or "×8" (by 8) memory chips with 9 chips per side. "×4" or "×8" refer to the data width of the DRAM chips in bits.In the case of the "×4"-registered DIMMs, the data width per side is 36 bits; therefore, the memory controller
Memory controller
The memory controller is a digital circuit which manages the flow of data going to and from the main memory. It can be a separate chip or integrated into another chip, such as on the die of a microprocessor...
(which requires 72 bits) needs to address both sides at the same time to read or write the data it needs. In this case, the two-sided module is single-ranked.
For "×8"-registered DIMMs, each side is 72 bits wide, so the memory controller only addresses one side at a time (the two-sided module is dual-ranked).
Speeds
For various technologies, there are certain bus and device clock frequencies that are standardized. There is also a decided nomenclature for each of these speeds for each type.SDR SDRAM DIMMs
- These first synchronous registered DRAM DIMMs had the same bus frequency for data, address and control lines.
- PC66 = 66 MHz
- PC100 = 100 MHz
- PC133 = 133 MHz
DDR SDRAM
DDR SDRAM
Double data rate synchronous dynamic random access memory is a class of memory integrated circuits used in computers. DDR SDRAM has been superseded by DDR2 SDRAM and DDR3 SDRAM, neither of which are either forward or backward compatible with DDR SDRAM, meaning that DDR2 or DDR3 memory modules...
(DDR1) DIMMs
- DIMMs based on Double Data Rate (DDR) DRAM have data but not the strobe at double the rate of the clock. This is achieved by clocking on both the rising and falling edge of the data strobes.
- PC1600 = 200 MHz data & strobe / 100 MHz clock for address and control
- PC2100 = 266 MHz data & strobe / 133 MHz clock for address and control
- PC2700 = 333 MHz data & strobe / 166 MHz clock for address and control
- PC3200 = 400 MHz data & strobe / 200 MHz clock for address and control
DDR2 SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM
DDR2 SDRAM is a double data rate synchronous dynamic random-access memory interface. It supersedes the original DDR SDRAM specification and has itself been superseded by DDR3 SDRAM...
DIMMs
- DIMMs based on Double Data Rate 2 (DDR2) DRAM also have data and data strobe frequencies at double the rate of the clock. This is achieved by clocking on both the rising and falling edge of the data strobes. The power consumption and voltage of DDR2 is significantly lower than DDR(1) at the same speed.
- PC2-3200 = 400 MHz data & strobe / 200 MHz clock for address and control
- PC2-4200 = 533 MHz data & strobe / 266 MHz clock for address and control
- PC2-5300 = 667 MHz data & strobe / 333 MHz clock for address and control
- PC2-6400 = 800 MHz data & strobe / 400 MHz clock for address and control
- PC2-8500 = 1066 MHz data & strobe / 533 MHz clock for address and control
DDR3 SDRAM
DDR3 SDRAM
In computing, DDR3 SDRAM, an abbreviation for double data rate type three synchronous dynamic random access memory, is a modern kind of dynamic random access memory with a high bandwidth interface. It is one of several variants of DRAM and associated interface techniques used since the early 1970s...
DIMMs
- DIMMs based on Double Data Rate 3(DDR3) DRAM have data and strobe frequencies at double the rate of the clock. This is achieved by clocking on both the rising and falling edge of the data strobes. The power consumption and voltage of DDR3 is lower than DDR2 of the same speed.
- PC3-6400 = 800 MHz data & strobe / 400 MHz clock for address and control
- PC3-8500 = 1066 MHz data & strobe / 533 MHz clock for address and control
- PC3-10600 = 1333 MHz data & strobe / 667 MHz clock for address and control
- PC3-12800 = 1600 MHz data & strobe / 800 MHz clock for address and control
- PC3-14900 = 1866 MHz data & strobe / 933 MHz clock for address and control
- PC3-17000 = 2133 MHz data & strobe / 1066 MHz clock for address and control
Form factors
Several form factors are commonly used in DIMMs. Single Data Rate (SDR) SDRAM DIMMs commonly came in two main heights: 1.7-inch and 1.5-inch. When 1U rackmount servers started becoming popular, these form factor Registered DIMMs had to plug into angled DIMM sockets to fit in the 1.75" high box. To alleviate this issue, the next standards of DDR DIMMs were created with a "Low Profile" (LP) height of ~1.2". These fit into vertical DIMM sockets for a 1U platform. With the advent of blade servers, the LP form factor DIMMs have once again been often angled to fit in these space-constrained boxes. This led to the development of the Very Low Profile (VLP) form factor DIMM with a height of ~.72" (18.3 mm). The DDR3 JEDEC standard for VLP DIMM height is 18.75mm. These will fit vertically in ATCAAdvanced Telecommunications Computing Architecture
Advanced Telecommunications Computing Architecture is the largest specification effort in the history of the PCI Industrial Computer Manufacturers Group , with more than 100 companies participating. Known as AdvancedTCA, the official specification designation PICMG 3.x was ratified by the PICMG...
systems. Other DIMM form factors include the SO-DIMM, the Mini-DIMM and the VLP Mini-DIMM.
See also
- Dual in-line packageDual in-line packageIn microelectronics, a dual in-line package is an electronic device package with a rectangular housing and two parallel rows of electrical connecting pins. The package may be through-hole mounted to a printed circuit board or inserted in a socket.A DIP is usually referred to as a DIPn, where n is...
(DIP) - Rambus in-line memory moduleRDRAMDirect Rambus DRAM or DRDRAM is a type of synchronous dynamic RAM. RDRAM was developed by Rambus inc., in the mid-1990s as a replacement for then-prevalent DIMM SDRAM memory architecture....
(RIMM) - Single in-line memory module (SIMM)
- Single in-line packageSingle in-line packageA single in-line package is an electronic device package which has one row of connecting pins. It is not as popular as the dual in-line package which contain two rows of pins, but has been used for packaging RAM chips and multiple resistors with a common pin. SIPs group RAM chips together on a...
(SIP) - SO-DIMMSO-DIMMA SO-DIMM, or small outline dual in-line memory module, is a type of computer memory built using integrated circuits.SO-DIMMs are a smaller alternative to a DIMM, being roughly half the size of regular DIMMs...
- Zig-zag in-line packageZig-zag in-line packageThe zig-zag in-line package or ZIP was a short-lived packaging technology for integrated circuits, particularly dynamic RAM chips. It was intended as a replacement for dual in-line packaging . A ZIP is an integrated circuit encapsulated in a slab of plastic, measuring about 3 mm x 30 mm...
(ZIP) - Memory GeometryMemory geometryIn the design of modern personal computers, memory geometry describes the internal structure of random-access memory. Memory geometry is of concern to consumers upgrading their computers, since older memory controllers may not be compatible with later products...

