
DEMO
Encyclopedia
DEMO is a proposed nuclear fusion
power plant
that is intended to build upon the expected success of the ITER
experimental nuclear fusion reactor. Whereas ITER's goal is to produce 500 megawatt
s of fusion power
for at least 500 seconds, the goal of DEMO will be to produce at least four times that much fusion power on a continual basis. Moreover, while ITER's goal is to produce 10 times as much power as is required for breakeven, DEMO's goal is to produce 25 times as much power. DEMO's 2 to 4 gigawatts of thermal output will be on the scale of a modern electric power
plant. Also notably, DEMO is intended to be the first fusion reactor to generate electrical power. Earlier experiments, such as ITER, merely dissipate the thermal power they produce into the atmosphere as steam.
To achieve its goals, DEMO must have linear dimensions about
15% larger than ITER and a plasma
density about 30% greater than ITER. As a prototype
commercial
fusion reactor
DEMO could make fusion energy (which does not have the problems associated with fossil fuel
s or fission
energy) available by 2033. Subsequent commercial fusion reactors could be built for nearly a quarter of the cost of DEMO if things go according to plan.
While fusion reactors like ITER and DEMO will not produce transuranic wastes, some of the components of the ITER and DEMO reactors will become radioactive due to neutron
s impinging upon them. Careful material choice will mean that the wastes produced in this way will have much shorter half lives than the waste from fission reactors, with wastes remaining harmful for less than one century. The process of manufacturing tritium currently produces long-lived waste, but both ITER and DEMO will produce their own tritium, dispensing with the fission reactor currently used for this purpose.
PROTO
is a beyond DEMO experiment, part of European Commission long-term strategy for research of fusion energy. PROTO would act as a prototype power station, taking in any remaining technology refinements, and demonstrating electricity generation on a commercial basis. It is only expected after DEMO, meaning a post-2050 timeline, and may or may not be a second part of DEMO/PROTO experiment. This might possibly make PROTO the first commercial nuclear fusion
power plant
in the world.
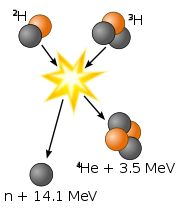
When deuterium
and tritium
fuse, the two nuclei
come together to form a helium
nucleus (an alpha particle
) and a high-energy neutron
.
DEMO will be constructed once designs which solve the many problems of current fusion reactors are engineered. These problems include: containing the plasma fuel at high temperatures, maintaining a great enough density of reacting ions, and capturing high-energy neutrons from the reaction without melting the walls of the reactor.
Once fusion has begun, high-energy
neutrons will pour out of the plasma, not affected by the strong magnetic fields (see neutron flux
). Since the neutrons receive the majority of the energy from the fusion, they will be the fusion reactor's source of energy output.
The DEMO project is planned to build upon and improve the concepts of ITER. Since it is only proposed at this time, many of the details, including heating methods and the method for the capture of high-energy neutrons, are still undetermined.
Nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process by which two or more atomic nuclei join together, or "fuse", to form a single heavier nucleus. This is usually accompanied by the release or absorption of large quantities of energy...
power plant
Power station
A power station is an industrial facility for the generation of electric energy....
that is intended to build upon the expected success of the ITER
ITER
ITER is an international nuclear fusion research and engineering project, which is currently building the world's largest and most advanced experimental tokamak nuclear fusion reactor at Cadarache in the south of France...
experimental nuclear fusion reactor. Whereas ITER's goal is to produce 500 megawatt
Watt
The watt is a derived unit of power in the International System of Units , named after the Scottish engineer James Watt . The unit, defined as one joule per second, measures the rate of energy conversion.-Definition:...
s of fusion power
Fusion power
Fusion power is the power generated by nuclear fusion processes. In fusion reactions two light atomic nuclei fuse together to form a heavier nucleus . In doing so they release a comparatively large amount of energy arising from the binding energy due to the strong nuclear force which is manifested...
for at least 500 seconds, the goal of DEMO will be to produce at least four times that much fusion power on a continual basis. Moreover, while ITER's goal is to produce 10 times as much power as is required for breakeven, DEMO's goal is to produce 25 times as much power. DEMO's 2 to 4 gigawatts of thermal output will be on the scale of a modern electric power
Electric power
Electric power is the rate at which electric energy is transferred by an electric circuit. The SI unit of power is the watt.-Circuits:Electric power, like mechanical power, is represented by the letter P in electrical equations...
plant. Also notably, DEMO is intended to be the first fusion reactor to generate electrical power. Earlier experiments, such as ITER, merely dissipate the thermal power they produce into the atmosphere as steam.
To achieve its goals, DEMO must have linear dimensions about
15% larger than ITER and a plasma
Plasma (physics)
In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
density about 30% greater than ITER. As a prototype
Prototype
A prototype is an early sample or model built to test a concept or process or to act as a thing to be replicated or learned from.The word prototype derives from the Greek πρωτότυπον , "primitive form", neutral of πρωτότυπος , "original, primitive", from πρῶτος , "first" and τύπος ,...
commercial
Commerce
While business refers to the value-creating activities of an organization for profit, commerce means the whole system of an economy that constitutes an environment for business. The system includes legal, economic, political, social, cultural, and technological systems that are in operation in any...
fusion reactor
Nuclear reactor
A nuclear reactor is a device to initiate and control a sustained nuclear chain reaction. Most commonly they are used for generating electricity and for the propulsion of ships. Usually heat from nuclear fission is passed to a working fluid , which runs through turbines that power either ship's...
DEMO could make fusion energy (which does not have the problems associated with fossil fuel
Fossil fuel
Fossil fuels are fuels formed by natural processes such as anaerobic decomposition of buried dead organisms. The age of the organisms and their resulting fossil fuels is typically millions of years, and sometimes exceeds 650 million years...
s or fission
Nuclear fission
In nuclear physics and nuclear chemistry, nuclear fission is a nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of an atom splits into smaller parts , often producing free neutrons and photons , and releasing a tremendous amount of energy...
energy) available by 2033. Subsequent commercial fusion reactors could be built for nearly a quarter of the cost of DEMO if things go according to plan.
While fusion reactors like ITER and DEMO will not produce transuranic wastes, some of the components of the ITER and DEMO reactors will become radioactive due to neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
s impinging upon them. Careful material choice will mean that the wastes produced in this way will have much shorter half lives than the waste from fission reactors, with wastes remaining harmful for less than one century. The process of manufacturing tritium currently produces long-lived waste, but both ITER and DEMO will produce their own tritium, dispensing with the fission reactor currently used for this purpose.
PROTO
Proto
Proto- is a prefix meaning "first".Proto may also refer to:- Organizations :* Proto , a tool company , now a division of Stanley Black & Decker...
is a beyond DEMO experiment, part of European Commission long-term strategy for research of fusion energy. PROTO would act as a prototype power station, taking in any remaining technology refinements, and demonstrating electricity generation on a commercial basis. It is only expected after DEMO, meaning a post-2050 timeline, and may or may not be a second part of DEMO/PROTO experiment. This might possibly make PROTO the first commercial nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is the process by which two or more atomic nuclei join together, or "fuse", to form a single heavier nucleus. This is usually accompanied by the release or absorption of large quantities of energy...
power plant
Power station
A power station is an industrial facility for the generation of electric energy....
in the world.
Timeline
The following timetable was presented at the IAEA Fusion Energy Conference in 2004 by Prof. Sir Chris Llewellyn Smith. These dates are conceptual and as such are subject to change.- Conceptual design is to be complete by 2017
- Engineering design is to be complete by 2024
- The first 'Construction Phase' is to last from 2024 to 2033
- The first phase of operation is to last from 2033 to 2038
- The plant is then to be expanded/updated
- The second phase of operation is to last from 2040 onwards
How the reactor will work

When deuterium
Deuterium
Deuterium, also called heavy hydrogen, is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in of hydrogen . Deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% of all naturally occurring hydrogen in Earth's oceans, while the most common isotope ...
and tritium
Tritium
Tritium is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. The nucleus of tritium contains one proton and two neutrons, whereas the nucleus of protium contains one proton and no neutrons...
fuse, the two nuclei
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
come together to form a helium
Helium
Helium is the chemical element with atomic number 2 and an atomic weight of 4.002602, which is represented by the symbol He. It is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-toxic, inert, monatomic gas that heads the noble gas group in the periodic table...
nucleus (an alpha particle
Alpha particle
Alpha particles consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium nucleus, which is classically produced in the process of alpha decay, but may be produced also in other ways and given the same name...
) and a high-energy neutron
Neutron
The neutron is a subatomic hadron particle which has the symbol or , no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton. With the exception of hydrogen, nuclei of atoms consist of protons and neutrons, which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons. The number of...
.
- + → + + 17.6 MeV
DEMO will be constructed once designs which solve the many problems of current fusion reactors are engineered. These problems include: containing the plasma fuel at high temperatures, maintaining a great enough density of reacting ions, and capturing high-energy neutrons from the reaction without melting the walls of the reactor.
- The activation energy for fusion is very large because the protonProtonThe proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s in each nucleus strongly repel one another; they are both positively chargedElementary chargeThe elementary charge, usually denoted as e, is the electric charge carried by a single proton, or equivalently, the absolute value of the electric charge carried by a single electron. This elementary charge is a fundamental physical constant. To avoid confusion over its sign, e is sometimes called...
. In order to fuse, the nuclei must be within 1 femtometreFemtometreThe femtometre is an SI unit of length equal to 10-15 metres. This distance can also be called fermi and was so named in honour of Enrico Fermi and is often encountered in nuclear physics as a characteristic of this scale...
(1 × 10−15 metres) of each other, which is achievable using very high temperatures. - DEMO, a tokamakTokamakA tokamak is a device using a magnetic field to confine a plasma in the shape of a torus . Achieving a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that move around the torus in a helical shape...
reactor, requires both dense plasma and high temperatures for the fusion reaction to be sustained. - High temperatures give the nuclei enough energy to overcome their electrostatic repulsion. This requires temperatures in the region of 100,000,000 °C, perhaps using energy from microwaves, ionIonAn ion is an atom or molecule in which the total number of electrons is not equal to the total number of protons, giving it a net positive or negative electrical charge. The name was given by physicist Michael Faraday for the substances that allow a current to pass between electrodes in a...
beams, or neutral beam injection. - Containment vessels melt at these temperatures, so the plasmaPlasma (physics)In physics and chemistry, plasma is a state of matter similar to gas in which a certain portion of the particles are ionized. Heating a gas may ionize its molecules or atoms , thus turning it into a plasma, which contains charged particles: positive ions and negative electrons or ions...
is to be kept away from the walls using magnetic confinement.
Once fusion has begun, high-energy
Energy
In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems...
neutrons will pour out of the plasma, not affected by the strong magnetic fields (see neutron flux
Neutron flux
The neutron flux is a quantity used in reactor physics corresponding to the total length travelled by all neutrons per unit time and volume . The neutron fluence is defined as the neutron flux integrated over a certain time period....
). Since the neutrons receive the majority of the energy from the fusion, they will be the fusion reactor's source of energy output.
- The tokamakTokamakA tokamak is a device using a magnetic field to confine a plasma in the shape of a torus . Achieving a stable plasma equilibrium requires magnetic field lines that move around the torus in a helical shape...
containment vessel will have a lining composed of ceramic or composite tiles containing tubes in which low-temperature liquid lithiumLithiumLithium is a soft, silver-white metal that belongs to the alkali metal group of chemical elements. It is represented by the symbol Li, and it has the atomic number 3. Under standard conditions it is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly...
will flow. - Lithium readily absorbs high-speed neutrons to form helium and tritium.
- The lithium is processed to remove the helium and tritium.
- The deuterium and tritium are added in carefully measured amounts to the plasma.
- This increase in temperature is passed on to (pressurized) liquid waterWaterWater is a chemical substance with the chemical formula H2O. A water molecule contains one oxygen and two hydrogen atoms connected by covalent bonds. Water is a liquid at ambient conditions, but it often co-exists on Earth with its solid state, ice, and gaseous state . Water also exists in a...
in a sealed, pressurized pipe. - The hot water from the pipe will be used to boil water under lower pressure in a heat exchangerHeat exchangerA heat exchanger is a piece of equipment built for efficient heat transfer from one medium to another. The media may be separated by a solid wall, so that they never mix, or they may be in direct contact...
. - The steam from the heat exchanger will be used to drive the turbine of a generator, to create an electrical current.
The DEMO project is planned to build upon and improve the concepts of ITER. Since it is only proposed at this time, many of the details, including heating methods and the method for the capture of high-energy neutrons, are still undetermined.

