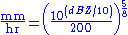.gif)
DBZ (meteorology)
Encyclopedia
Meteorology
Meteorology is the interdisciplinary scientific study of the atmosphere. Studies in the field stretch back millennia, though significant progress in meteorology did not occur until the 18th century. The 19th century saw breakthroughs occur after observing networks developed across several countries...
measure of equivalent reflectivity
Reflectivity
In optics and photometry, reflectivity is the fraction of incident radiation reflected by a surface. In general it must be treated as a directional property that is a function of the reflected direction, the incident direction, and the incident wavelength...
(Z) of a radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
signal reflected off a remote object. The reference level for Z is 1 mm6 m−3, which is equal to 1 μm3. It is related to the number of drops per unit volume and the sixth power of drop diameter.
Reflectivity of a cloud
Cloud
A cloud is a visible mass of liquid droplets or frozen crystals made of water and/or various chemicals suspended in the atmosphere above the surface of a planetary body. They are also known as aerosols. Clouds in Earth's atmosphere are studied in the cloud physics branch of meteorology...
is dependent on the number and type of hydrometeors, which includes rain, snow, and hail, and the hydrometeors' size. A large number of small hydrometeors will reflect the same as one large hydrometeor. The signal returned to the radar
Radar
Radar is an object-detection system which uses radio waves to determine the range, altitude, direction, or speed of objects. It can be used to detect aircraft, ships, spacecraft, guided missiles, motor vehicles, weather formations, and terrain. The radar dish or antenna transmits pulses of radio...
will be equivalent in both situations, so a group of small hydrometeors is virtually indistinguishable from one large hydrometeor on the resulting radar image.
A meteorologist can determine the difference between one large hydrometeor and a group of small hydrometeors as well as the type of hydrometeor through knowledge of local weather condition contexts.
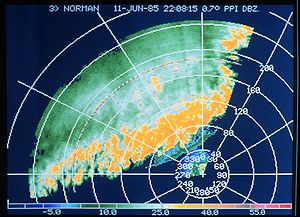
One dBZ-scale of rain:
- >65 Extreme
- 46-65 heavy
- 24-45 moderate
- 8-23 light
- 0-8 Barely anything
dBZ values can be converted to rainfall rates in millimetres per hour using this formula: