Cytorrhysis
Encyclopedia
Cell (biology)
The cell is the basic structural and functional unit of all known living organisms. It is the smallest unit of life that is classified as a living thing, and is often called the building block of life. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos....
's cell wall
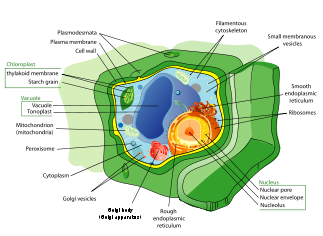
Cell wall
The cell wall is the tough, usually flexible but sometimes fairly rigid layer that surrounds some types of cells. It is located outside the cell membrane and provides these cells with structural support and protection, and also acts as a filtering mechanism. A major function of the cell wall is to...
within plant
Plant
Plants are living organisms belonging to the kingdom Plantae. Precise definitions of the kingdom vary, but as the term is used here, plants include familiar organisms such as trees, flowers, herbs, bushes, grasses, vines, ferns, mosses, and green algae. The group is also called green plants or...
s due to the loss of water through osmosis
Osmosis
Osmosis is the movement of solvent molecules through a selectively permeable membrane into a region of higher solute concentration, aiming to equalize the solute concentrations on the two sides...
. This always follows plasmolysis
Plasmolysis
Plasmolysis is the process in plant cells where the cytoplasm pulls away from the cell wall due to the loss of water through osmosis. The reverse process, cytolysis, can occur if the cell is in a hypotonic solution resulting in a higher external osmotic pressure and a net flow of water into the cell...
. Cytorrhysis will cause a much greater loss of shape and structure.
Usually this is very bad for the cell, resulting in extreme damage and possible death of the cell.
Although the cell wall is not actually destroyed, the vacuole seems to increase in size and finally collapses, releasing its components into the cytosol.The plasma membrane seems to be appressed to the cell wall. Cytorrhysis occurs when the size of the molecules constituting the osmoticum exceeds that of the pores of the cell wall matrix .

