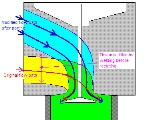
Cylinder head porting
Encyclopedia
Cylinder head porting refers to the process of modifying the intake and exhaust ports of an internal combustion engine
to improve the quality and quantity of the air flow. Cylinder head
s, as manufactured, are usually suboptimal due to design and manufacturing constraints. Porting the heads provides the finely detailed attention required to bring the engine to the highest level of efficiency. More than any other single factor, the porting process is responsible for the high power output of modern engines.
This process can be applied to a standard racing engine to optimize its power output as well as to a production engine to turn it into a racing engine, to enhance its power output for daily use or to alter its power output characteristics to suit a particular application.
Daily human experience with air gives the impression that air is light and nearly non-existent as we move slowly through it. However, an engine running at high speed experiences a totally different substance. In that context, air can be thought of as thick, sticky, elastic, gooey and heavy (see viscosity
). Pumping it is a major problem for engines running at speed so head porting helps to alleviate this.
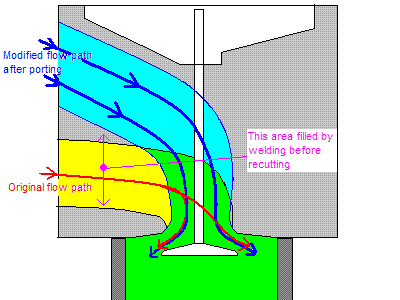
, the original port wall material can be carefully reshaped by hand with die grinder
s or by numerically controlled milling machines. For major modifications the ports must be welded up or similarly built up to add material where none existed.
 The Ford two-liter shown above in stock trim was capable of delivering 115 horsepower
The Ford two-liter shown above in stock trim was capable of delivering 115 horsepower
@5500 rpm for a BMEP
of 136 psi. Contrast this with the Pro Stock
ports shown below.
This aftermarket racing GM Pro Stock head was capable of 1300 horsepower@8500 rpm with a BMEP
of 238psi. Since BMEP is an excellent efficiency measure and closely related to volumetric efficiency
, the aftermarket Pro Stock head is vastly better than the stock Ford. In fact a BMEP of 238 puts it near the top of the racing engine world. It is close to the limit for a naturally aspirated gas burning engines. For four-valve/cylinder engines the BMEP limit is about 265 psi.
Of course cam
profiles, engine rpm, engine height constraints and other limitations play a role in this difference as well but the difference in port design is a major factor.

. On the exhaust ports the opposite condition exists and one can control the geometry down stream of the highest speed section, namely the valve seat
. This allows the possibility of good pressure recovery and is the reason exhaust ports flow better than intake ports of equal size.
Accepting the expansion into the cylinder loss as unavoidable, the rest of the port becomes that much more important. The critical areas are those that pass the most air at the highest speed for the longest time.
The valve seat configuration on the port and on the valve together form one of the most critical areas. The highest speed within the port is at or near the valve seat for most or all the duration of the cycle. After that, the throat area and short turn radius become critical at higher lifts in the middle of the cycle. The valve seat and valve head angles require careful study in each design.
The bowl area and the rest of the length of the port have important functions in controlling some of the dynamic behavior of the waves that traverse the system as well as setting up the air for a good entry to the throat. Shape, cross section, volume, cylinder swirl or tumble, and surface finish must be considered together with the overall design of the rest of the engine and vehicle to achieve good results.
The port is shaped to allow the maximum use of the available cross sectional area as the flow velocity should be optimized for the conditions the engine is expected to encounter. Well-shaped ports have few dead spots.
Some typical losses and their sources on a small block Chevrolet intake port.
1. Expansion exiting valve to cylinder 31%
2. Expansion, 30° (bowl) 19%
3. Short turn radius bend 17%
4. Expansion, 25° (valve seat entry) 12%
5. Bend at valve guide 11%
6. Expansion behind valve guide 4%
7. Wall friction 4% *
(For sand cast
surfaces. This falls to 3% for smooth surfaces)
8. Contraction at push rod 2%
Total = 100%
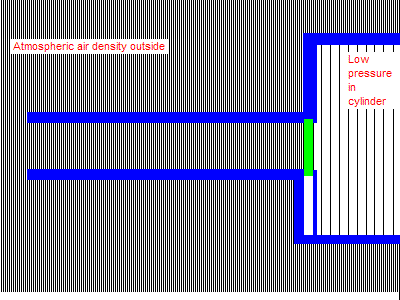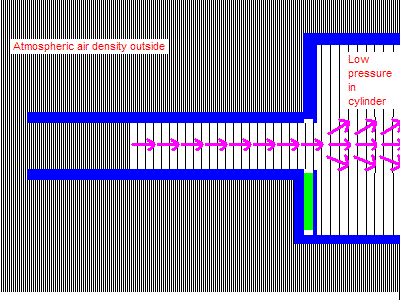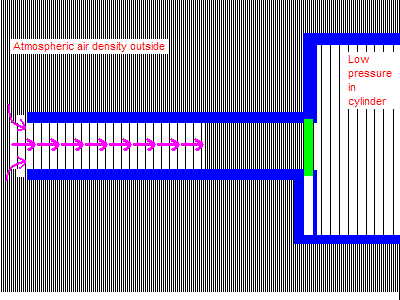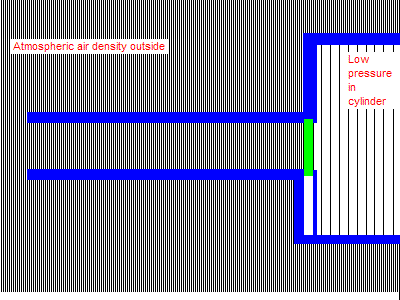 When the valve opens, the air doesn’t flow in, it decompresses into the low-pressure region below it. All the air on the upstream side of the moving disturbance boundary is completely isolated and unaffected by what happens on the downstream side. The air at the runner entrance does not move until the wave reaches all the way to the end. It is only then that the entire runner can begin to flow. Up until that point all that can happen is the higher pressure gas filling the volume of the runner decompresses or expands into the low-pressure region advancing up the runner. (Once the low pressure wave reaches the open end of the runner it reverses sign, the inrushing air forces a high pressure wave down the runner. Not shown in this animation.)
When the valve opens, the air doesn’t flow in, it decompresses into the low-pressure region below it. All the air on the upstream side of the moving disturbance boundary is completely isolated and unaffected by what happens on the downstream side. The air at the runner entrance does not move until the wave reaches all the way to the end. It is only then that the entire runner can begin to flow. Up until that point all that can happen is the higher pressure gas filling the volume of the runner decompresses or expands into the low-pressure region advancing up the runner. (Once the low pressure wave reaches the open end of the runner it reverses sign, the inrushing air forces a high pressure wave down the runner. Not shown in this animation.)
Conversely, the closing of the valve does not immediately stop flow at the runner entrance, which continues completely unaffected until the signal that the valve closed reaches it. The closing valve causes a buildup of pressure that travels up the runner as a positive wave. The runner entrance continues to flow at full speed, forcing the pressure to rise until the signal reaches the entrance. This very considerable pressure rise can be seen on the graph below, it rises far above atmospheric pressure.
It is this phenomenon that enables the so-called “ram tuning” to occur and it is what is being “tuned” by tuned intake and exhaust systems. The principle is the same as in the water hammer
effect so well known to plumbers. The speed that the signal can travel is the speed of sound
within the runner.
This is why port/runner volumes are so important; the volumes of successive parts of the port/runner control the flow during all transition periods. That is, any time a change occurs in the cylinder - whether positive or negative - such as when the piston reaches maximum speed.
This point occurs at different points depending on the length of the connecting rod
and the throw of the crank
, and varies with the connecting rod ratio (rod/stroke). For normal automotive design this point is almost always between 69 and 79 degrees ATDC, with higher rod ratios favoring the later position. It only occurs at 1/2 stroke (90 degrees) with a connecting rod of infinite length.
The wave/flow activity in a real engine is vastly more complex than this but the principle is the same.
At first glance this wave travel might seem to be blindingly fast and not very significant but a few calculations shows the opposite is true.
In an intake runner at room temperature the sonic speed is about 1100 feet per second (335.3 m/s) and traverses a 12 inches (304.8 mm) port/runner in 0.9 milliseconds. The engine using this system, running at 8500 rpm, takes a very considerable 46 crank degrees before any signal from the cylinder can reach the runner end (assuming no movement of the air in the runner). 46 degrees, during which nothing but the volume of the port/runner supplies the demands of the cylinder. This not only applies to the initial signal but to any and every change in the pressure or vacuum developed in the cylinder.
Why couldn’t we just use a shorter runner so the delay is not so great? The answer lies at the end of the cycle when that big long runner now continues to flow at full speed disregarding the rising pressure in the cylinder and providing pressure to the cylinder when it is needed most. The runner length also controls the timing of the returning waves and cannot be altered. A shorter runner would flow earlier but also would die earlier while returning the positive waves much too quickly and those waves would be weaker. The key is to find the optimum balance of all the factors for the engine requirements.
Further complicating the system is the fact that the piston dome, the signal source, continually moves. First moving down the cylinder, thus increasing the distance the signal must travel. Then moving back up at the end of the intake cycle when the valve is still open past BDC
. The signals coming from the piston dome, after the initial runner flow has been established, must fight upstream against whatever velocity has been developed at that instant, delaying it further. The signals developed by the piston do not have a clean path up the runner either. Large portions of it bounce off the rest of the combustion chamber
and resonate inside the cylinder until an average pressure is reached. Also, temperature variations due to the changing pressures and absorption from hot engine parts cause changes in the local sonic velocity.
When the valve closes, it causes a pile up of gas giving rise to a strong positive wave that must travel up the runner. The wave activity in the port/runner does not stop but continues to reverberate for some time. When the valve next opens, the remaining waves influence the next cycle.
 The graph above shows the intake runner pressure over 720 crank degrees of an engine with a 7 inches (177.8 mm) intake port/runner running at 4500 rpm, which is its torque
The graph above shows the intake runner pressure over 720 crank degrees of an engine with a 7 inches (177.8 mm) intake port/runner running at 4500 rpm, which is its torque
peak (close to maximum cylinder filling and BMEP for this engine). The two pressure traces are taken from the valve end (blue) and the runner entrance (red). The blue line rises sharply as the intake valve closes. This causes a pile up of air, which becomes a positive wave reflected back up the runner and the red line shows that wave arriving at the runner entrance later. Note how the suction wave during cylinder filling is delayed even more by having to fight upstream against the inrushing air and the fact that the piston is further down the bore, increasing the distance.
The goal of tuning is to arrange the runners and valve timing so that there is a high-pressure wave in the port during the opening of the intake valve to get flow going quickly and then to have a second high pressure wave arrive just before valve closing so the cylinder fills as much as possible. The first wave is what is left in the runner from the previous cycle, while the second is primarily created during the current cycle by the suction wave changing sign at the runner entrance and arriving back at the valve in time for valve closing. The factors involved are often contradictory and requires a careful balancing act to work. When it does work, it is possible to see volumetric efficiencies of 140%, similar to that of a decent supercharger
, but it only occurs over a limited RPM range.
, which can alter the flow path noticeably, possibly increasing flow. This is similar to what the dimples on a golf ball
do. Flow bench
testing shows that the difference between a mirror finished intake port and a rough textured port is typically less than 1%. The difference between a smooth to the touch port and an optically mirrored surface is not measurable by ordinary means. Exhaust ports may be smooth finished because of the dry gas flow and in the interest of minimizing exhaust by-product build-up. A 300 - 400 Grit finish followed by a light buff is generally accepted to be representative of a near optimal finish for exhaust gas ports.
The reason that polished ports are not advantageous from a flow standpoint is that at the interface between the metal wall and the air, the air speed is ZERO (see boundary layer
and laminar flow
). This is due to the wetting
action of the air and indeed all fluids. The first layer of molecules adheres to the wall and does not move significantly. The rest of the flow field must shear past, which develops a velocity profile (or gradient) across the duct. For surface roughness to impact flow appreciably, the high spots must be high enough to protrude into the faster moving air toward the center. Only a very rough surface does this.

The ports are responsible for sweeping as much exhaust out of the cylinder as possible and refilling it with as much fresh mixture as possible without a large amount of the fresh mixture also going out the exhaust. This takes careful and subtle timing and aiming of all the transfer ports.
Since two-strokes are very dependent on wave dynamics, their power band
s tend to be narrow. While struggling to get maximum power, care must always be taken to ensure that the power profile does not get too sharp and hard to control.
Two-stroke port duration is often expressed as a function of time/area. This integrates the continually changing open port area with the duration. Wider ports increase time/area without increasing duration while higher ports increase both.
In addition to time area, the relationship between all the port timings strongly determine the power characteristics of the engine.
Although four-strokes have this problem, two-strokes rely much more heavily on wave action in the intake and exhaust systems. The two-stroke port design has strong effects on the wave timing and strength.
The flow of heat in the engine is heavily dependent on the porting layout. Cooling passages must be routed around ports. Every effort must be made to keep the incoming charge from heating up but at the same time many parts are cooled primarily by that incoming fuel/air mixture. When ports take up too much space on the cylinder wall, the ability of the piston to transfer its heat through the walls to the coolant is hampered. As ports get more radical, some areas of the cylinder get thinner, which can then overheat.
A piston ring
must ride on the cylinder wall smoothly with good contact to avoid mechanical stress and assist in piston cooling. In radical port designs, the ring has minimal contact in the lower stroke area, which can suffer extra wear. The mechanical shocks induced during the transition from partial to full cylinder contact can shorten the life of the ring considerably. Very wide ports allow the ring to bulge out into the port, exacerbating the problem.
The piston must also contact the wall for cooling purposes but also must transfer the side thrust of the power stroke. Ports must be designed so that the piston can transfer these forces and heat to the cylinder wall while minimizing flex and shock to the piston.
Engine configuration can be influenced by port design. This is primarily a factor in multi-cylinder engines. Engine width can be excessive for even two cylinder engines of certain designs. Rotary disk valve engines with wide sweeping transfers can be so wide as to be impractical as a parallel twin. The V-twin and fore-and-aft engine designs are used to control overall width.
Engine sealing ability, cylinder, piston and piston ring life all depend on reliable contact between cylinder and piston/piston ring so any cylinder distortion reduces power and engine life. This distortion can be caused by uneven heating, local cylinder weakness, or mechanical stresses. Exhaust ports that have long passages in the cylinder casting conduct large amounts of heat to one side of the cylinder while on the other side the cool intake may be cooling the opposite side. The thermal distortion resulting from the uneven expansion reduces both power and durability although careful design can minimize the problem.
The turbulence remaining in the cylinder after transfer persists into the combustion phase to help burning speed. Unfortunately good scavenging flow is slower and less turbulent.
is the stock in trade of the head porter and are used with a variety of carbide cutters, grinding wheel
s and abrasive cartridges. The complex and sensitive shapes required in porting necessitate a good degree of artistic skill with a hand tool.
Until recently, CNC machining
was used only to provide the basic shape of the port but hand finishing was usually still required because some areas of the port were not accessible to a CNC tool. New developments in CNC machining now allow this process to be fully automated with the assistance of CAD/CAM software. 5-Axis CNC controls using specialized fixtures like tilting rotary tables allow the cutting tool full access to the entire port. The combination of CNC and CAM software give the porter full control over the port shape and surface finish.
Measurement of the interior of the ports is difficult but must be done accurately. Sheet metal templates are made up, taking the shape from an experimental port, for both cross-sectional and lengthwise shape. Inserted in the port these templates are then used as a guide for shaping the final port. Even a slight error might cause a loss in flow so measurement must be as accurate as possible. Confirmation of the final port shape and automated replication of the port is now done using digitizing. Digitizing is where a probe scans the entire shape of the port collecting data that can then be used by CNC machine tools and CAD/CAM software programs to model and cut the desired port shape. This replication process usually produces ports that flow within 1% of each other. This kind of accuracy, repeatability, time has never before been possible. What used to take 18hrs. or more now takes less than 3hrs.
Valves and valve seats are ground with special equipment designed for this purpose.
involved in porting is counter-intuitive and complex. Successfully optimizing ports requires an air flow bench
, a thorough knowledge of the principles involved, and engine simulation software.
Although a large portion of porting knowledge has been accumulated by individuals using "cut and try" methods over time, the tools and knowledge now exist to develop a porting design with a measure of certainty. Porting by inexperienced individuals without a full understanding of the fluid dynamics
of the process still continues but the results are spotty and the process is expensive and time consuming with many more failures than successes.
Internal combustion engine
The internal combustion engine is an engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer in a combustion chamber. In an internal combustion engine, the expansion of the high-temperature and high -pressure gases produced by combustion apply direct force to some component of the engine...
to improve the quality and quantity of the air flow. Cylinder head
Cylinder head
In an internal combustion engine, the cylinder head sits above the cylinders on top of the cylinder block. It closes in the top of the cylinder, forming the combustion chamber. This joint is sealed by a head gasket...
s, as manufactured, are usually suboptimal due to design and manufacturing constraints. Porting the heads provides the finely detailed attention required to bring the engine to the highest level of efficiency. More than any other single factor, the porting process is responsible for the high power output of modern engines.
This process can be applied to a standard racing engine to optimize its power output as well as to a production engine to turn it into a racing engine, to enhance its power output for daily use or to alter its power output characteristics to suit a particular application.
Daily human experience with air gives the impression that air is light and nearly non-existent as we move slowly through it. However, an engine running at high speed experiences a totally different substance. In that context, air can be thought of as thick, sticky, elastic, gooey and heavy (see viscosity
Viscosity
Viscosity is a measure of the resistance of a fluid which is being deformed by either shear or tensile stress. In everyday terms , viscosity is "thickness" or "internal friction". Thus, water is "thin", having a lower viscosity, while honey is "thick", having a higher viscosity...
). Pumping it is a major problem for engines running at speed so head porting helps to alleviate this.
Port modifications
When a modification is decided upon through careful flow testing with an air flow benchAir flow bench
An air flow bench is a device used for testing the internal aerodynamic qualities of an engine component and is related to the more familiar wind tunnel.Used primarily for testing the intake and exhaust ports of cylinder heads of internal combustion engines...
, the original port wall material can be carefully reshaped by hand with die grinder
Die grinder
A die grinder is a handheld power tool used to grind, sand, hone, polish, or machine material, typically metal but also plastic or wood. They are usually pneumatically driven, although versions with electric and flexible shaft drive also exist...
s or by numerically controlled milling machines. For major modifications the ports must be welded up or similarly built up to add material where none existed.


Horsepower
Horsepower is the name of several units of measurement of power. The most common definitions equal between 735.5 and 750 watts.Horsepower was originally defined to compare the output of steam engines with the power of draft horses in continuous operation. The unit was widely adopted to measure the...
@5500 rpm for a BMEP
Mean effective pressure
The mean effective pressure is a quantity related to the operation of an reciprocating engine and is a valuable measure of an engine's capacity to do work that is independent of engine displacement. When quoted as an indicated mean effective pressure or imep , it may be thought of as the average...
of 136 psi. Contrast this with the Pro Stock
Pro Stock
Pro Stock Drag Racing is a class of drag racing featuring 'Factory Hot-Rods'. The class can be known as "all motor," as the cars cannot use artificial induction such as turbocharging, supercharging, or nitrous oxide, and there are very strict rules governing the modifications allowed to the...
ports shown below.
This aftermarket racing GM Pro Stock head was capable of 1300 horsepower@8500 rpm with a BMEP
Mean effective pressure
The mean effective pressure is a quantity related to the operation of an reciprocating engine and is a valuable measure of an engine's capacity to do work that is independent of engine displacement. When quoted as an indicated mean effective pressure or imep , it may be thought of as the average...
of 238psi. Since BMEP is an excellent efficiency measure and closely related to volumetric efficiency
Volumetric efficiency
Volumetric efficiency in internal combustion engine design refers to the efficiency with which the engine can move the charge into and out of the cylinders. More specifically, volumetric efficiency is a ratio of what quantity of fuel and air actually enters the cylinder during induction to the...
, the aftermarket Pro Stock head is vastly better than the stock Ford. In fact a BMEP of 238 puts it near the top of the racing engine world. It is close to the limit for a naturally aspirated gas burning engines. For four-valve/cylinder engines the BMEP limit is about 265 psi.
Of course cam
Cam
A cam is a rotating or sliding piece in a mechanical linkage used especially in transforming rotary motion into linear motion or vice-versa. It is often a part of a rotating wheel or shaft that strikes a lever at one or more points on its circular path...
profiles, engine rpm, engine height constraints and other limitations play a role in this difference as well but the difference in port design is a major factor.

Areas of importance
Considering the flow through the intake port as a whole, the greatest loss must be downstream of the valve due to the lack of pressure recovery (or diffusion). This loss is unavoidable on intake ports due to the nature of the poppet valvePoppet valve
A poppet valve is a valve consisting of a hole, usually round or oval, and a tapered plug, usually a disk shape on the end of a shaft also called a valve stem. The shaft guides the plug portion by sliding through a valve guide...
. On the exhaust ports the opposite condition exists and one can control the geometry down stream of the highest speed section, namely the valve seat
Valve seat
The valve seat in an internal combustion gasoline or diesel engine is the surface against which an intake or an exhaust valve rests during the portion of the engine operating cycle when that valve is closed...
. This allows the possibility of good pressure recovery and is the reason exhaust ports flow better than intake ports of equal size.
Accepting the expansion into the cylinder loss as unavoidable, the rest of the port becomes that much more important. The critical areas are those that pass the most air at the highest speed for the longest time.
The valve seat configuration on the port and on the valve together form one of the most critical areas. The highest speed within the port is at or near the valve seat for most or all the duration of the cycle. After that, the throat area and short turn radius become critical at higher lifts in the middle of the cycle. The valve seat and valve head angles require careful study in each design.
The bowl area and the rest of the length of the port have important functions in controlling some of the dynamic behavior of the waves that traverse the system as well as setting up the air for a good entry to the throat. Shape, cross section, volume, cylinder swirl or tumble, and surface finish must be considered together with the overall design of the rest of the engine and vehicle to achieve good results.
The port is shaped to allow the maximum use of the available cross sectional area as the flow velocity should be optimized for the conditions the engine is expected to encounter. Well-shaped ports have few dead spots.
Some typical losses and their sources on a small block Chevrolet intake port.
1. Expansion exiting valve to cylinder 31%
2. Expansion, 30° (bowl) 19%
3. Short turn radius bend 17%
4. Expansion, 25° (valve seat entry) 12%
5. Bend at valve guide 11%
6. Expansion behind valve guide 4%
7. Wall friction 4% *
(For sand cast
Sand casting
Sand casting, also known as sand molded casting, is a metal casting process characterized by using sand as the mold material.It is relatively cheap and sufficiently refractory even for steel foundry use. A suitable bonding agent is mixed or occurs with the sand...
surfaces. This falls to 3% for smooth surfaces)
8. Contraction at push rod 2%
Total = 100%
Wave dynamics

Conversely, the closing of the valve does not immediately stop flow at the runner entrance, which continues completely unaffected until the signal that the valve closed reaches it. The closing valve causes a buildup of pressure that travels up the runner as a positive wave. The runner entrance continues to flow at full speed, forcing the pressure to rise until the signal reaches the entrance. This very considerable pressure rise can be seen on the graph below, it rises far above atmospheric pressure.
It is this phenomenon that enables the so-called “ram tuning” to occur and it is what is being “tuned” by tuned intake and exhaust systems. The principle is the same as in the water hammer
Water hammer
Water hammer is a pressure surge or wave resulting when a fluid in motion is forced to stop or change direction suddenly . Water hammer commonly occurs when a valve is closed suddenly at an end of a pipeline system, and a pressure wave propagates in the pipe...
effect so well known to plumbers. The speed that the signal can travel is the speed of sound
Speed of sound
The speed of sound is the distance travelled during a unit of time by a sound wave propagating through an elastic medium. In dry air at , the speed of sound is . This is , or about one kilometer in three seconds or approximately one mile in five seconds....
within the runner.
This is why port/runner volumes are so important; the volumes of successive parts of the port/runner control the flow during all transition periods. That is, any time a change occurs in the cylinder - whether positive or negative - such as when the piston reaches maximum speed.
This point occurs at different points depending on the length of the connecting rod
Connecting rod
In a reciprocating piston engine, the connecting rod or conrod connects the piston to the crank or crankshaft. Together with the crank, they form a simple mechanism that converts linear motion into rotating motion....
and the throw of the crank
Crankshaft
The crankshaft, sometimes casually abbreviated to crank, is the part of an engine which translates reciprocating linear piston motion into rotation...
, and varies with the connecting rod ratio (rod/stroke). For normal automotive design this point is almost always between 69 and 79 degrees ATDC, with higher rod ratios favoring the later position. It only occurs at 1/2 stroke (90 degrees) with a connecting rod of infinite length.
The wave/flow activity in a real engine is vastly more complex than this but the principle is the same.
At first glance this wave travel might seem to be blindingly fast and not very significant but a few calculations shows the opposite is true.
In an intake runner at room temperature the sonic speed is about 1100 feet per second (335.3 m/s) and traverses a 12 inches (304.8 mm) port/runner in 0.9 milliseconds. The engine using this system, running at 8500 rpm, takes a very considerable 46 crank degrees before any signal from the cylinder can reach the runner end (assuming no movement of the air in the runner). 46 degrees, during which nothing but the volume of the port/runner supplies the demands of the cylinder. This not only applies to the initial signal but to any and every change in the pressure or vacuum developed in the cylinder.
Why couldn’t we just use a shorter runner so the delay is not so great? The answer lies at the end of the cycle when that big long runner now continues to flow at full speed disregarding the rising pressure in the cylinder and providing pressure to the cylinder when it is needed most. The runner length also controls the timing of the returning waves and cannot be altered. A shorter runner would flow earlier but also would die earlier while returning the positive waves much too quickly and those waves would be weaker. The key is to find the optimum balance of all the factors for the engine requirements.
Further complicating the system is the fact that the piston dome, the signal source, continually moves. First moving down the cylinder, thus increasing the distance the signal must travel. Then moving back up at the end of the intake cycle when the valve is still open past BDC
Dead centre
In a reciprocating engine, the dead centre is the position of a piston in which it is farthest from, or nearest to, the crankshaft. The former is known as top dead centre while the latter is known as bottom dead centre ....
. The signals coming from the piston dome, after the initial runner flow has been established, must fight upstream against whatever velocity has been developed at that instant, delaying it further. The signals developed by the piston do not have a clean path up the runner either. Large portions of it bounce off the rest of the combustion chamber
Combustion chamber
A combustion chamber is the part of an engine in which fuel is burned.-Internal combustion engine:The hot gases produced by the combustion occupy a far greater volume than the original fuel, thus creating an increase in pressure within the limited volume of the chamber...
and resonate inside the cylinder until an average pressure is reached. Also, temperature variations due to the changing pressures and absorption from hot engine parts cause changes in the local sonic velocity.
When the valve closes, it causes a pile up of gas giving rise to a strong positive wave that must travel up the runner. The wave activity in the port/runner does not stop but continues to reverberate for some time. When the valve next opens, the remaining waves influence the next cycle.

Torque
Torque, moment or moment of force , is the tendency of a force to rotate an object about an axis, fulcrum, or pivot. Just as a force is a push or a pull, a torque can be thought of as a twist....
peak (close to maximum cylinder filling and BMEP for this engine). The two pressure traces are taken from the valve end (blue) and the runner entrance (red). The blue line rises sharply as the intake valve closes. This causes a pile up of air, which becomes a positive wave reflected back up the runner and the red line shows that wave arriving at the runner entrance later. Note how the suction wave during cylinder filling is delayed even more by having to fight upstream against the inrushing air and the fact that the piston is further down the bore, increasing the distance.
The goal of tuning is to arrange the runners and valve timing so that there is a high-pressure wave in the port during the opening of the intake valve to get flow going quickly and then to have a second high pressure wave arrive just before valve closing so the cylinder fills as much as possible. The first wave is what is left in the runner from the previous cycle, while the second is primarily created during the current cycle by the suction wave changing sign at the runner entrance and arriving back at the valve in time for valve closing. The factors involved are often contradictory and requires a careful balancing act to work. When it does work, it is possible to see volumetric efficiencies of 140%, similar to that of a decent supercharger
Supercharger
A supercharger is an air compressor used for forced induction of an internal combustion engine.The greater mass flow-rate provides more oxygen to support combustion than would be available in a naturally aspirated engine, which allows more fuel to be burned and more work to be done per cycle,...
, but it only occurs over a limited RPM range.
The "Porting and Polishing" myth
It is popularly held that enlarging the ports to the maximum possible size and applying a mirror finish is what porting is. However that is not so. Some ports may be enlarged to their maximum possible size (in keeping with the highest level of aerodynamic efficiency) but those engines are highly developed very high speed units where the actual size of the ports has become a restriction. Larger ports flow more fuel/air at higher RPM's but sacrifice torque at lower RPM's due to lower fuel/air velocity. A mirror finish of the port does not provide the increase that intuition suggests. In fact, within intake systems, the surface is usually deliberately textured to a degree of uniform roughness to encourage fuel deposited on the port walls to evaporate quickly. A rough surface on selected areas of the port may also alter flow by energizing the boundary layerBoundary layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is that layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface where effects of viscosity of the fluid are considered in detail. In the Earth's atmosphere, the planetary boundary layer is the air layer near the ground affected by diurnal...
, which can alter the flow path noticeably, possibly increasing flow. This is similar to what the dimples on a golf ball
Golf ball
A golf ball is a ball designed to be used in the game of golf.Under the Rules of Golf, a golf ball weighs no more than 1.620 oz , has a diameter not less than 1.680 in , and performs within specified velocity, distance, and symmetry limits...
do. Flow bench
Air flow bench
An air flow bench is a device used for testing the internal aerodynamic qualities of an engine component and is related to the more familiar wind tunnel.Used primarily for testing the intake and exhaust ports of cylinder heads of internal combustion engines...
testing shows that the difference between a mirror finished intake port and a rough textured port is typically less than 1%. The difference between a smooth to the touch port and an optically mirrored surface is not measurable by ordinary means. Exhaust ports may be smooth finished because of the dry gas flow and in the interest of minimizing exhaust by-product build-up. A 300 - 400 Grit finish followed by a light buff is generally accepted to be representative of a near optimal finish for exhaust gas ports.
The reason that polished ports are not advantageous from a flow standpoint is that at the interface between the metal wall and the air, the air speed is ZERO (see boundary layer
Boundary layer
In physics and fluid mechanics, a boundary layer is that layer of fluid in the immediate vicinity of a bounding surface where effects of viscosity of the fluid are considered in detail. In the Earth's atmosphere, the planetary boundary layer is the air layer near the ground affected by diurnal...
and laminar flow
Laminar flow
Laminar flow, sometimes known as streamline flow, occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between the layers. At low velocities the fluid tends to flow without lateral mixing, and adjacent layers slide past one another like playing cards. There are no cross currents...
). This is due to the wetting
Wetting
Wetting is the ability of a liquid to maintain contact with a solid surface, resulting from intermolecular interactions when the two are brought together. The degree of wetting is determined by a force balance between adhesive and cohesive forces.Wetting is important in the bonding or adherence of...
action of the air and indeed all fluids. The first layer of molecules adheres to the wall and does not move significantly. The rest of the flow field must shear past, which develops a velocity profile (or gradient) across the duct. For surface roughness to impact flow appreciably, the high spots must be high enough to protrude into the faster moving air toward the center. Only a very rough surface does this.

Two-stroke porting
In addition to all the considerations given to a four-stroke engine port, two-stroke engine ports have additional ones:- Scavenging quality/purity
The ports are responsible for sweeping as much exhaust out of the cylinder as possible and refilling it with as much fresh mixture as possible without a large amount of the fresh mixture also going out the exhaust. This takes careful and subtle timing and aiming of all the transfer ports.
- Power band width
Since two-strokes are very dependent on wave dynamics, their power band
Power band
The power band of an engine or electric motor refers to the range of operating speeds under which an the engine or motor is able to operate efficiently...
s tend to be narrow. While struggling to get maximum power, care must always be taken to ensure that the power profile does not get too sharp and hard to control.
- Time area
Two-stroke port duration is often expressed as a function of time/area. This integrates the continually changing open port area with the duration. Wider ports increase time/area without increasing duration while higher ports increase both.
- Timing
In addition to time area, the relationship between all the port timings strongly determine the power characteristics of the engine.
- Wave Dynamic considerations
Although four-strokes have this problem, two-strokes rely much more heavily on wave action in the intake and exhaust systems. The two-stroke port design has strong effects on the wave timing and strength.
- Heat flow
The flow of heat in the engine is heavily dependent on the porting layout. Cooling passages must be routed around ports. Every effort must be made to keep the incoming charge from heating up but at the same time many parts are cooled primarily by that incoming fuel/air mixture. When ports take up too much space on the cylinder wall, the ability of the piston to transfer its heat through the walls to the coolant is hampered. As ports get more radical, some areas of the cylinder get thinner, which can then overheat.
- Piston ring durability.
A piston ring
Piston ring
A piston ring is a split ring that fits into a groove on the outer diameter of a piston in a reciprocating engine such as an internal combustion engine or steam engine.The three main functions of piston rings in reciprocating engines are:...
must ride on the cylinder wall smoothly with good contact to avoid mechanical stress and assist in piston cooling. In radical port designs, the ring has minimal contact in the lower stroke area, which can suffer extra wear. The mechanical shocks induced during the transition from partial to full cylinder contact can shorten the life of the ring considerably. Very wide ports allow the ring to bulge out into the port, exacerbating the problem.
- Piston skirt durability
The piston must also contact the wall for cooling purposes but also must transfer the side thrust of the power stroke. Ports must be designed so that the piston can transfer these forces and heat to the cylinder wall while minimizing flex and shock to the piston.
- Engine configuration
Engine configuration can be influenced by port design. This is primarily a factor in multi-cylinder engines. Engine width can be excessive for even two cylinder engines of certain designs. Rotary disk valve engines with wide sweeping transfers can be so wide as to be impractical as a parallel twin. The V-twin and fore-and-aft engine designs are used to control overall width.
- Cylinder distortion
Engine sealing ability, cylinder, piston and piston ring life all depend on reliable contact between cylinder and piston/piston ring so any cylinder distortion reduces power and engine life. This distortion can be caused by uneven heating, local cylinder weakness, or mechanical stresses. Exhaust ports that have long passages in the cylinder casting conduct large amounts of heat to one side of the cylinder while on the other side the cool intake may be cooling the opposite side. The thermal distortion resulting from the uneven expansion reduces both power and durability although careful design can minimize the problem.
- Combustion turbulence
The turbulence remaining in the cylinder after transfer persists into the combustion phase to help burning speed. Unfortunately good scavenging flow is slower and less turbulent.
Methods
The die grinderDie grinder
A die grinder is a handheld power tool used to grind, sand, hone, polish, or machine material, typically metal but also plastic or wood. They are usually pneumatically driven, although versions with electric and flexible shaft drive also exist...
is the stock in trade of the head porter and are used with a variety of carbide cutters, grinding wheel
Grinding wheel
A grinding wheel is an expendable wheel that is composed of an abrasive compound used for various grinding and abrasive machining operations...
s and abrasive cartridges. The complex and sensitive shapes required in porting necessitate a good degree of artistic skill with a hand tool.
Until recently, CNC machining
Machining
Conventional machining is a form of subtractive manufacturing, in which a collection of material-working processes utilizing power-driven machine tools, such as saws, lathes, milling machines, and drill presses, are used with a sharp cutting tool to physical remove material to achieve a desired...
was used only to provide the basic shape of the port but hand finishing was usually still required because some areas of the port were not accessible to a CNC tool. New developments in CNC machining now allow this process to be fully automated with the assistance of CAD/CAM software. 5-Axis CNC controls using specialized fixtures like tilting rotary tables allow the cutting tool full access to the entire port. The combination of CNC and CAM software give the porter full control over the port shape and surface finish.
Measurement of the interior of the ports is difficult but must be done accurately. Sheet metal templates are made up, taking the shape from an experimental port, for both cross-sectional and lengthwise shape. Inserted in the port these templates are then used as a guide for shaping the final port. Even a slight error might cause a loss in flow so measurement must be as accurate as possible. Confirmation of the final port shape and automated replication of the port is now done using digitizing. Digitizing is where a probe scans the entire shape of the port collecting data that can then be used by CNC machine tools and CAD/CAM software programs to model and cut the desired port shape. This replication process usually produces ports that flow within 1% of each other. This kind of accuracy, repeatability, time has never before been possible. What used to take 18hrs. or more now takes less than 3hrs.
Valves and valve seats are ground with special equipment designed for this purpose.
Summary
The internal aerodynamicsAerodynamics
Aerodynamics is a branch of dynamics concerned with studying the motion of air, particularly when it interacts with a moving object. Aerodynamics is a subfield of fluid dynamics and gas dynamics, with much theory shared between them. Aerodynamics is often used synonymously with gas dynamics, with...
involved in porting is counter-intuitive and complex. Successfully optimizing ports requires an air flow bench
Air flow bench
An air flow bench is a device used for testing the internal aerodynamic qualities of an engine component and is related to the more familiar wind tunnel.Used primarily for testing the intake and exhaust ports of cylinder heads of internal combustion engines...
, a thorough knowledge of the principles involved, and engine simulation software.
Although a large portion of porting knowledge has been accumulated by individuals using "cut and try" methods over time, the tools and knowledge now exist to develop a porting design with a measure of certainty. Porting by inexperienced individuals without a full understanding of the fluid dynamics
Fluid dynamics
In physics, fluid dynamics is a sub-discipline of fluid mechanics that deals with fluid flow—the natural science of fluids in motion. It has several subdisciplines itself, including aerodynamics and hydrodynamics...
of the process still continues but the results are spotty and the process is expensive and time consuming with many more failures than successes.
External links
- Free demo engine simulator used to generate graph above
- Cylinder head porting techniques
- The Brzezinski "UnderCover" Cast Iron Cylinder Head Porting Technique
- A 5-axis CNC cylinder head porting machine in action.
- An Overview of Power Sport Cylinder and Head Port and Polish.
- A number of articles about porting.
- Kinematic Models for Design Digital Library (KMODDL) - Movies and photos of hundreds of working mechanical-systems models at Cornell University. Also includes an e-book library of classic texts on mechanical design and engineering.

