
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2
Encyclopedia
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 also known as cell division protein kinase 2 is an enzyme
that in humans is encoded by the CDK2 gene
.
encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase
family of Ser/Thr protein kinases
. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae
cdc28, and S. pombe
cdc2, also known as Cdk1
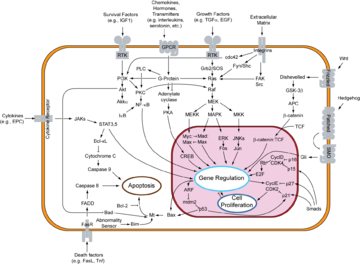
in humans. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinase
complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase of the cell cycle
, and is essential for the G1/S transition
. This protein associates with and is regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin E
or A
. Cyclin E binds G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase while binding with Cyclin A is required to progress through the S phase.
Its activity is also regulated by phosphorylation
.
Two alternatively spliced variants and multiple transcription initiation sites of this gene have been reported.
The role of this protein in G1-S transition has been recently questioned as cells lacking Cdk2 are reported to have no problem during this transition.
) and p27Kip1 (CDKN1B
). Drugs that inhibit Cdk2 and arrest the cell cycle, such as GW8510, may reduce the sensitivity of the epithelium to many cell cycle-active antitumor agents and, therefore, represent a strategy for prevention of chemotherapy-induced alopecia
.
cell types, expression of the CDK2 gene is regulated by the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor
.
with Retinoblastoma-like protein 2
, Retinoblastoma-like protein 1
, Flap structure-specific endonuclease 1
, CEBPA
, BRCA1
, PPM1B
, Cyclin A1, Cyclin E1
, SKP2
, PPP2CA
, ORC1L, CDK2AP1
, CDKN3
, CDKN1B
and P21
.
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
that in humans is encoded by the CDK2 gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
.
Function
The proteinProtein
Proteins are biochemical compounds consisting of one or more polypeptides typically folded into a globular or fibrous form, facilitating a biological function. A polypeptide is a single linear polymer chain of amino acids bonded together by peptide bonds between the carboxyl and amino groups of...
encoded by this gene is a member of the cyclin-dependent kinase
Cyclin-dependent kinase
thumb|350px|Schematic of the cell cycle. outer ring: I=[[Interphase]], M=[[Mitosis]]; inner ring: M=Mitosis; G1=[[G1 phase|Gap phase 1]]; S=[[S phase|Synthesis]]; G2=[[G2 phase|Gap phase 2]]...
family of Ser/Thr protein kinases
Serine/threonine-specific protein kinase
Serine/threonine protein kinases phosphorylate the OH group of serine or threonine .At least 125 of the 500+ human protein kinases are serine/threonine kinases .-Regulation:...
. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae
Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a species of yeast. It is perhaps the most useful yeast, having been instrumental to baking and brewing since ancient times. It is believed that it was originally isolated from the skin of grapes...
cdc28, and S. pombe
Schizosaccharomyces pombe
Schizosaccharomyces pombe, also called "fission yeast", is a species of yeast. It is used as a model organism in molecular and cell biology. It is a unicellular eukaryote, whose cells are rod-shaped. Cells typically measure 3 to 4 micrometres in diameter and 7 to 14 micrometres in length...
cdc2, also known as Cdk1
Cdk1
Cyclin dependent kinase 1 also known as Cdk1 or cell division control protein 2 homolog is a highly conserved protein that functions as a serine/threonine kinase, and is a key player in cell cycle regulation. It has been highly studied in the budding yeast S. cerevisiae, and the fission yeast S....
in humans. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent kinase
Cyclin-dependent kinase
thumb|350px|Schematic of the cell cycle. outer ring: I=[[Interphase]], M=[[Mitosis]]; inner ring: M=Mitosis; G1=[[G1 phase|Gap phase 1]]; S=[[S phase|Synthesis]]; G2=[[G2 phase|Gap phase 2]]...
complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase of the cell cycle
Cell cycle
The cell cycle, or cell-division cycle, is the series of events that takes place in a cell leading to its division and duplication . In cells without a nucleus , the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission...
, and is essential for the G1/S transition
G1/S transition
The G1/S transition is a stage in the cell cycle at the boundary between the G1 phase and the S phase.It is a "point of no return" beyond which the cell is committed to dividing; in yeast this is called START and in multicellular eukaryotes it is termed the restriction point....
. This protein associates with and is regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin E
Cyclin E
Cyclin E is a member of the cyclin family.Cyclin E binds to G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase. The Cyclin E/CDK2 complex phosphorylates p27Kip1 , tagging it for degradation, thus promoting expression of Cyclin A, allowing progression to S phase....
or A
Cyclin A
Cyclin A is a member of the cyclin family.Cyclin A binds to S phase Cdk2 and is required for the cell to progress through the S phase. Cyclin A/ Cdk2 is inhibited by the complex p21CIP.-External links:*...
. Cyclin E binds G1 phase Cdk2, which is required for the transition from G1 to S phase while binding with Cyclin A is required to progress through the S phase.
Its activity is also regulated by phosphorylation
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation is the addition of a phosphate group to a protein or other organic molecule. Phosphorylation activates or deactivates many protein enzymes....
.
Two alternatively spliced variants and multiple transcription initiation sites of this gene have been reported.
The role of this protein in G1-S transition has been recently questioned as cells lacking Cdk2 are reported to have no problem during this transition.
Inhibitors
Known CDK inhibitors are p21Cip1 (CDKN1AP21
p21 / WAF1 also known as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 or CDK-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDKN1A gene located on chromosome 6 .- Function :...
) and p27Kip1 (CDKN1B
CDKN1B
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDKN1B gene. It encodes a protein which belongs to the Cip/Kip family of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor proteins. The encoded protein binds to and prevents the activation of cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D-CDK4...
). Drugs that inhibit Cdk2 and arrest the cell cycle, such as GW8510, may reduce the sensitivity of the epithelium to many cell cycle-active antitumor agents and, therefore, represent a strategy for prevention of chemotherapy-induced alopecia
Alopecia
Alopecia means loss of hair from the head or body. Alopecia can mean baldness, a term generally reserved for pattern alopecia or androgenic alopecia. Compulsive pulling of hair can also produce hair loss. Hairstyling routines such as tight ponytails or braids may induce Traction alopecia. Both...
.
Gene regulation
In melanocyticMelanocyte
-External links: - "Eye: fovea, RPE" - "Integument: pigmented skin"...
cell types, expression of the CDK2 gene is regulated by the Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor
Microphthalmia-associated transcription factor is a basic helix-loop-helix leucine zipper transcription factor involved in melanocyte and osteoclast development.-Clinical significance:...
.
Interactions
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 has been shown to interactProtein-protein interaction
Protein–protein interactions occur when two or more proteins bind together, often to carry out their biological function. Many of the most important molecular processes in the cell such as DNA replication are carried out by large molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein...
with Retinoblastoma-like protein 2
Retinoblastoma-like protein 2
Retinoblastoma-like protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBL2 gene.-Interactions:Retinoblastoma-like protein 2 has been shown to interact with HDAC1, C-Raf, RBBP8, Cyclin E1, Prohibitin, Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, BRF1 and BRCA1....
, Retinoblastoma-like protein 1
Retinoblastoma-like protein 1
Retinoblastoma-like 1 , also known as RBL1, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the RBL1 gene.- Function :The protein encoded by this gene is similar in sequence and possibly function to the product of the retinoblastoma 1 gene...
, Flap structure-specific endonuclease 1
Flap structure-specific endonuclease 1
Flap endonuclease 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the FEN1 gene.-Interactions:Flap structure-specific endonuclease 1 has been shown to interact with Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, EP300, Werner syndrome ATP-dependent helicase, Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein A1, Cyclin A2, PCNA,...
, CEBPA
CEBPA
CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein alpha is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CEBPA gene.-Interactions:CEBPA has been shown to interact with Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 and Cyclin-dependent kinase 4.- External links :*...
, BRCA1
BRCA1
BRCA1 is a human caretaker gene that produces a protein called breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein, responsible for repairing DNA. The first evidence for the existence of the gene was provided by the King laboratory at UC Berkeley in 1990...
, PPM1B
PPM1B
Protein phosphatase 1B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPM1B gene.-Interactions:PPM1B has been shown to interact with IKBKG, IKK2, Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, Cyclin-dependent kinase 6, CHUK and MAP3K7.-Further reading:...
, Cyclin A1, Cyclin E1
Cyclin E1
G1/S-specific cyclin-E1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CCNE1 gene.-Interactions:Cyclin E1 has been shown to interact with Retinoblastoma-like protein 2, Cdk1, CDC25A, Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, SMARCA4, CDKN1B, HERC5, CUL3 and P21....
, SKP2
SKP2
S-phase kinase-associated protein 2 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the SKP2 gene.- Function :This gene encodes a member of the F-box protein family which is characterized by an approximately 40 amino acid motif, the F-box domain...
, PPP2CA
PPP2CA
Serine/threonine-protein phosphatase 2A catalytic subunit alpha isoform is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the PPP2CA gene.-Interactions:...
, ORC1L, CDK2AP1
CDK2AP1
Cyclin-dependent kinase 2-associated protein 1 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDK2AP1 gene.-Interactions:CDK2AP1 has been shown to interact with Cyclin-dependent kinase 2.-Further reading:...
, CDKN3
CDKN3
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 3 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDKN3 gene.-Interactions:CDKN3 has been shown to interact with Cyclin-dependent kinase 2, Cdk1 and MS4A3.-Further reading:...
, CDKN1B
CDKN1B
Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CDKN1B gene. It encodes a protein which belongs to the Cip/Kip family of cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor proteins. The encoded protein binds to and prevents the activation of cyclin E-CDK2 or cyclin D-CDK4...
and P21
P21
p21 / WAF1 also known as cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1 or CDK-interacting protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the CDKN1A gene located on chromosome 6 .- Function :...
.


