Crest factor
Encyclopedia
The crest factor or peak-to-average ratio (PAR) or peak-to-average power ratio (PAPR) is a measurement of a waveform
, calculated from the peak amplitude of the waveform divided by the RMS
value of the waveform.
It is therefore a dimensionless quantity
. While this quotient is most simply expressed by a positive rational number
, in commercial products it is also commonly stated as the ratio of two whole numbers, e.g., 2:1. In signal processing applications it is often expressed in decibels (dB)
.
The minimum possible crest factor is 1, 1:1 or 0 dB.
s:
Notes:
1. crest factors specified for QPSK, QAM, WCDMA are typical factors needed for reliable communication, not the theoretical crest factors which can be larger.
(Note the waveform factor of the half wave sine wave rectified signal should be 2.22 not 1.11)
level to the time
-averaged power level in an electrical circuit. This quantity is known as the peak-to-average ratio (p/a r or PAR). Such meters are used as a quick means to identify degraded telephone
channels.
Par meters are very sensitive to envelope delay distortion. They may also be used for idle channel
noise
, nonlinear distortion
, and amplitude-distortion measurements.
The peak-to-average ratio can be determined for many signal parameters, such as voltage, current, power, frequency
, and phase
.
Waveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
, calculated from the peak amplitude of the waveform divided by the RMS
Root mean square
In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids...
value of the waveform.

It is therefore a dimensionless quantity
Dimensionless quantity
In dimensional analysis, a dimensionless quantity or quantity of dimension one is a quantity without an associated physical dimension. It is thus a "pure" number, and as such always has a dimension of 1. Dimensionless quantities are widely used in mathematics, physics, engineering, economics, and...
. While this quotient is most simply expressed by a positive rational number
Rational number
In mathematics, a rational number is any number that can be expressed as the quotient or fraction a/b of two integers, with the denominator b not equal to zero. Since b may be equal to 1, every integer is a rational number...
, in commercial products it is also commonly stated as the ratio of two whole numbers, e.g., 2:1. In signal processing applications it is often expressed in decibels (dB)
Decibel
The decibel is a logarithmic unit that indicates the ratio of a physical quantity relative to a specified or implied reference level. A ratio in decibels is ten times the logarithm to base 10 of the ratio of two power quantities...
.
The minimum possible crest factor is 1, 1:1 or 0 dB.
Examples
This table provides values for some normalized waveformWaveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
s:
| Wave type | Waveform | Peak magnitude Magnitude (mathematics) The magnitude of an object in mathematics is its size: a property by which it can be compared as larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind; in technical terms, an ordering of the class of objects to which it belongs.... (normalized) | RMS Root mean square In mathematics, the root mean square , also known as the quadratic mean, is a statistical measure of the magnitude of a varying quantity. It is especially useful when variates are positive and negative, e.g., sinusoids... value | Crest factor | Crest factor (dB) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC Direct current Direct current is the unidirectional flow of electric charge. Direct current is produced by such sources as batteries, thermocouples, solar cells, and commutator-type electric machines of the dynamo type. Direct current may flow in a conductor such as a wire, but can also flow through... |
1 | 1 | 1 | 0.0 dB | |
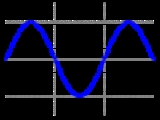
| Sine wave Sine wave The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields... |
 |
1 |  |
 |
3.01 dB |
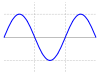
| Full-wave rectified sine | 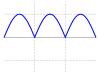 |
1 | 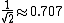 |
 |
3.01 dB |
| Half-wave rectified sine |  |
1 |  |
 |
6.02 dB |
| Triangle wave Triangle wave A triangle wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform named for its triangular shape.Like a square wave, the triangle wave contains only odd harmonics... |
 |
1 | 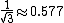 |
 |
4.77 dB |
| Square wave Square wave A square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels... |
 |
1 | 1 | 1 | 0 dB |
| PWM Pulse-width modulation Pulse-width modulation , or pulse-duration modulation , is a commonly used technique for controlling power to inertial electrical devices, made practical by modern electronic power switches.... -Signal |
1 |  |
 |
 dB dB |
|
| QPSK | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 dB | |
| 8VSB 8VSB 8VSB is the modulation method used for broadcast in the ATSC digital television standard. ATSC and 8VSB modulation is used primarily in North America; in contrast, the DVB-T standard uses COFDM.... |
6.5–8.1 dB | ||||
| 64QAM | 1 |  |
 |
3.7 dB | |
 -QAM -QAM |
1 |  |
 |
4.8 dB | |
| WCDMA downlink carrier | 10.6 dB | ||||
| OFDM | ~12 dB | ||||
| GMSK | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 dB |
Notes:
1. crest factors specified for QPSK, QAM, WCDMA are typical factors needed for reliable communication, not the theoretical crest factors which can be larger.
Digital multimeters
Crest factor is an important parameter to understand when trying to take accurate measurements of low frequency signals. For example, given a certain digital multimeter with an AC accuracy of 0.03 % (always specified for sine waves) with an additional error of 0.2 % for crest factors between 1.414 and 5, then the total error for measuring a triangular wave (crest factor = 1.73) is 0.03 % + 0.2 % = 0.23 %. In acoustics, crest factor is usually expressed in decibels. For example, for a sine wave the 1.414 ratio is 20 log(1.414) or 3 dB. Most ambient noise has a crest factor of around 10 dB while impulsive sounds such as gunshots can have crest factors of over 30 dB.(Note the waveform factor of the half wave sine wave rectified signal should be 2.22 not 1.11)
Peak-to-average ratio (PAR) meter
A peak-to-average ratio meter (Par meter) is a device used to measure the ratio of the peak powerPower (physics)
In physics, power is the rate at which energy is transferred, used, or transformed. For example, the rate at which a light bulb transforms electrical energy into heat and light is measured in watts—the more wattage, the more power, or equivalently the more electrical energy is used per unit...
level to the time
Time
Time is a part of the measuring system used to sequence events, to compare the durations of events and the intervals between them, and to quantify rates of change such as the motions of objects....
-averaged power level in an electrical circuit. This quantity is known as the peak-to-average ratio (p/a r or PAR). Such meters are used as a quick means to identify degraded telephone
Telephone
The telephone , colloquially referred to as a phone, is a telecommunications device that transmits and receives sounds, usually the human voice. Telephones are a point-to-point communication system whose most basic function is to allow two people separated by large distances to talk to each other...
channels.
Par meters are very sensitive to envelope delay distortion. They may also be used for idle channel
Channel (communications)
In telecommunications and computer networking, a communication channel, or channel, refers either to a physical transmission medium such as a wire, or to a logical connection over a multiplexed medium such as a radio channel...
noise
Noise
In common use, the word noise means any unwanted sound. In both analog and digital electronics, noise is random unwanted perturbation to a wanted signal; it is called noise as a generalisation of the acoustic noise heard when listening to a weak radio transmission with significant electrical noise...
, nonlinear distortion
Nonlinear distortion
Nonlinear distortion is a term used to describe the phenomenon of a non-linear relationship between the "input" and "output" signals of - for example - an electronic device.-Model:...
, and amplitude-distortion measurements.
The peak-to-average ratio can be determined for many signal parameters, such as voltage, current, power, frequency
Frequency
Frequency is the number of occurrences of a repeating event per unit time. It is also referred to as temporal frequency.The period is the duration of one cycle in a repeating event, so the period is the reciprocal of the frequency...
, and phase
Phase (waves)
Phase in waves is the fraction of a wave cycle which has elapsed relative to an arbitrary point.-Formula:The phase of an oscillation or wave refers to a sinusoidal function such as the following:...
.
Applications
- Electrical engineeringElectrical engineeringElectrical engineering is a field of engineering that generally deals with the study and application of electricity, electronics and electromagnetism. The field first became an identifiable occupation in the late nineteenth century after commercialization of the electric telegraph and electrical...
— for describing the quality of an AC power waveform - VibrationOscillationOscillation is the repetitive variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value or between two or more different states. Familiar examples include a swinging pendulum and AC power. The term vibration is sometimes used more narrowly to mean a mechanical oscillation but sometimes...
analysis — for estimating the amount of impact wearWearIn materials science, wear is erosion or sideways displacement of material from its "derivative" and original position on a solid surface performed by the action of another surface....
in a bearingBearing (mechanical)A bearing is a device to allow constrained relative motion between two or more parts, typically rotation or linear movement. Bearings may be classified broadly according to the motions they allow and according to their principle of operation as well as by the directions of applied loads they can... - RadioRadioRadio is the transmission of signals through free space by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space...
and audioAudio frequencyAn audio frequency or audible frequency is characterized as a periodic vibration whose frequency is audible to the average human...
electronics — for estimating the headroom required in a signal chain- MusicMusicMusic is an art form whose medium is sound and silence. Its common elements are pitch , rhythm , dynamics, and the sonic qualities of timbre and texture...
has a widely-varying crest factor. Typical values for a processed mix are around 4–8 (which corresponds to 12–18 dB of headroom, usually involving audio level compressionAudio level compressionDynamic range compression, also called DRC or simply compression reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds by narrowing or "compressing" an audio signal's dynamic range...
), and 8–10 for an unprocessed recording (18–20 dB).
- Music
- PhysiologyPhysiologyPhysiology is the science of the function of living systems. This includes how organisms, organ systems, organs, cells, and bio-molecules carry out the chemical or physical functions that exist in a living system. The highest honor awarded in physiology is the Nobel Prize in Physiology or...
— for analysing the sound of snoringSnoringSnoring is the vibration of respiratory structures and the resulting sound, due to obstructed air movement during breathing while sleeping. In some cases the sound may be soft, but in other cases, it can be loud and unpleasant...
External links
- Definition of peak-to-average ratio – ATIS (Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions) Telecom Glossary 2K
- Definition of crest factor – ATIS (Alliance for Telecommunications Industry Solutions) Telecom Glossary 2K

