
Correspondence rules
Encyclopedia
In quantum mechanics
, correspondence rules refers to the principle of replacing physical quantities with operators.
Such replacements include energy and momentum, which can be derived informally from taking the time and space derivities of the plane wave
function. These show a similarity to the heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Examples of correspondence rules
Quantum mechanics
Quantum mechanics, also known as quantum physics or quantum theory, is a branch of physics providing a mathematical description of much of the dual particle-like and wave-like behavior and interactions of energy and matter. It departs from classical mechanics primarily at the atomic and subatomic...
, correspondence rules refers to the principle of replacing physical quantities with operators.
Such replacements include energy and momentum, which can be derived informally from taking the time and space derivities of the plane wave
Plane wave
In the physics of wave propagation, a plane wave is a constant-frequency wave whose wavefronts are infinite parallel planes of constant peak-to-peak amplitude normal to the phase velocity vector....
function. These show a similarity to the heisenberg uncertainty principle.
Examples of correspondence rules
| quantity | operator | See equation |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Energy In physics, energy is an indirectly observed quantity. It is often understood as the ability a physical system has to do work on other physical systems... (Hamiltonian Hamiltonian (quantum mechanics) In quantum mechanics, the Hamiltonian H, also Ȟ or Ĥ, is the operator corresponding to the total energy of the system. Its spectrum is the set of possible outcomes when one measures the total energy of a system... ) |
 |
Sc |
| Momentum Momentum In classical mechanics, linear momentum or translational momentum is the product of the mass and velocity of an object... |
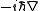 |
Continuity equation Continuity equation A continuity equation in physics is a differential equation that describes the transport of a conserved quantity. Since mass, energy, momentum, electric charge and other natural quantities are conserved under their respective appropriate conditions, a variety of physical phenomena may be described... |

