Corporate Average Fuel Economy
Encyclopedia
The Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) are regulation
s in the United States
, first enacted by the U.S. Congress in 1975, and intended to improve the average fuel economy
of cars
and light truck
s (truck
s, van
s and sport utility vehicle
s) sold in the US in the wake of the 1973 Arab Oil Embargo. Historically, it is the sales-weighted harmonic mean
fuel economy, expressed in miles per US gallon (mpg), of a manufacturer's fleet of current model year
passenger cars or light trucks with a gross vehicle weight rating
(GVWR) of 8,500 pounds (3,856 kg) or less, manufactured for sale in the US. If the average fuel economy of a manufacturer's annual fleet of vehicle production falls below the defined standard, the manufacturer must pay a penalty
, currently $5.50 USD per 0.1 mpg under the standard, multiplied by the manufacturer's total production for the U.S. domestic market. In addition, a Gas Guzzler Tax
is levied on individual passenger car models (but not trucks, vans, minivans, or SUVs) that get less than 22.5 miles per US gallon.
Starting in 2011 the CAFE standards are newly expressed as mathematical functions depending on vehicle "footprint", a measure of vehicle size determined by multiplying the vehicle’s wheelbase by its average track width.
CAFE footprint requirements are set up such that a vehicle with a bigger footprint has a lower fuel economy requirement than a vehicle with a smaller footprint. For example, the 2012 Honda Fit
has a footprint of 40 sq ft (3.7 m²) must achieve fuel economy (as measured for CAFE) of 36 miles per US gallon, equivalent to a published fuel economy of 27 miles per US gallon, while a Ford F-150 with its footprint of 65–75 sq ft (6–7 m2) must achieve CAFE fuel economy of 22 miles per US gallon, i.e., 17 miles per US gallon published.
CAFE has separate standards for "passenger cars" and "light trucks", despite the majority of "light trucks" actually being used as passenger cars. The market share of "light trucks" grew steadily from 9.7% in 1979 to 47% in 2001 and remained in 50% numbers up to 2011.
More than 500,000 vehicles in the 1999 model year exceeded the 8500 lb (3,855.5 kg) GVWR cutoff and were thus omitted from CAFE calculations.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
(NHTSA) regulates CAFE standards and the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) measures vehicle fuel efficiency. US Congress specifies that CAFE standards must be set at the "maximum feasible level" given consideration for:
Historically, the EPA has encouraged consumers to buy more fuel efficient vehicles, while the NHTSA expressed concerns that smaller, more fuel efficient vehicles may lead to increased traffic fatalities.
Thus higher fuel efficiency was associated with lower traffic safety, intertwining the issues of fuel economy
, road-traffic safety
, air pollution
, and climate change
. In the mid 2000s, increasing safety of smaller cars and the poor safety record of light trucks began to reverse this association. Nevertheless, the on-road vehicle fleets in the US and Canada have the lowest overall average fuel economy among first world
nations: 25 miles per US gallon in the US, versus 45 miles per US gallon in the European Union
and higher in Japan
(2008). Furthermore, despite pervasive opinion that larger and heavier (and therefore relatively fuel-uneconomical) vehicles are safer, the US traffic fatality rate—and its trend over time—is worse than that of other first world
nations.
wrote a report on the effects of the CAFE standard. The report's conclusions include a finding that in the absence of CAFE, and with no other fuel economy regulation substituted, motor vehicle fuel consumption would have been approximately 14 percent higher than it actually was in 2002. One cost of this increase in fuel economy is a possible increase in fatalities, estimated to be 1,300 to 2,600 increased fatalities in 1993, albeit with certain of the committee members dissenting.
A plot of average overall vehicle fuel economy (CAFE) for new model year passenger cars, the required by law CAFE standard target fuel economy value (CAFE standard) for new model year passenger cars, and fuel prices, adjusted for inflation, shows that there has been little variation over the past 20 years. Within this period, there are three distinct periods of fuel economy change:
before returning to 1986 levels in 1990. These are following by an extended period during which the passenger car CAFE standard, the observed average passenger car fuel economy, and the price of gasoline remained stable, and finally a period starting about 2003 when prices rose dramatically and fuel economy has slowly responded.
Simple economics would predict that an increase in gasoline prices would lead in the long run to an increase in the average fuel economy of the US passenger car fleet, and that a drop in gasoline prices would be associated with a reduction in the average fuel economy of the entire US fleet. There is some evidence that this happened with an increase in market share of lower fuel economy light trucks and SUVs and decline in passenger car sales, as a percentage of total fleet sales, as car buying trends changed during the 1990s, the impact of which is not reflected in this chart.
In the case of passenger cars, US average fuel economy did not fall as economic theory would predict, suggesting that CAFE standards maintained the higher fuel economy of the passenger car fleet during the long period from the end of the 1979 energy crisis
to the rise of gasoline prices in the early 2000s. Most recently, fuel economy has increased about one mpg from 2006 to 2007. This increase is due primarily to increased fuel efficiency of imported cars. Similarly, Simple Economics predicts that due to the US's large percentage consumption of the world's oil supply, that increasing fuel economy would drive down the gasoline prices that US consumers would otherwise have to pay—reductions
in petroleum demand in the United States helped create the collapse of OPEC
market power in 1986.
The "CAFE" and "CAFE standard" shown here only regards new model passenger car fuel economy and target fuel economy (respectively) rather than the overall US fuel economy average which tends to be dominated by used vehicles manufactured in previous years, new model light truck CAFE standards, light truck CAFE averages, or aggregate data.
, not a simple arithmetic mean
(average) – namely, the reciprocal of the average of the reciprocal values. For a fleet composed of four different kinds of vehicle A, B, C and D, produced in numbers nA, nB, nC and nD, with fuel economies fA, fB, fC and fD, the CAFE would be:
For example, a fleet of 4 vehicles getting 15, 13, 17, and 100 mpg has a CAFE of slightly less than 19 mpg:
While the arithmetic mean fuel economy of the fleet is just over 36 mpg:
The harmonic mean captures the fuel economy of driving each car in the fleet for the same number of miles, while the arithmetic mean captures the fuel economy of driving each car using the same amount of gas (i.e. the 13 mpg vehicle would travel 13 miles (20.9 km) with one gallon while the 100 mpg vehicle would travel 100 miles).
For the purposes of CAFE, a manufacturer's car output is divided into a domestic fleet (vehicles with more than 75 percent U.S., Canadian
or post-NAFTA
Mexican
content) and a foreign fleet (everything else). Each of these fleets must separately meet the requirements. The two-fleet requirement was developed by the United Automobile Workers (UAW) as a means to ensure job creation in the US. The UAW successfully lobbied
Congress to write this provision into the enabling legislation – and continues to advocate this position. The two fleet rule for light trucks was removed in 1996.
For the fuel economy calculation for alternative fuel
vehicles, a gallon of alternative fuel is deemed to contain 15% fuel (which is approximately the amount of gasoline in a gallon of E85)
as an incentive to develop alternative fuel vehicles. The mileage for dual-fuel vehicles, such as E85 capable models, is computed as the average of its alternative fuel rating—divided by 0.15 (equal to multiplying by 6.666) -- and its gasoline rating. Thus an E85-capable vehicle that gets 15 mpg on E-85 and 25 mpg on gasoline might logically be rated at 20 mpg. But in fact the average, for CAFE purposes, despite perhaps only one percent of the fuel used in E85-capable vehicles is actually E85, is computed as 100 mpg for E-85 and the standard 25 mpg for gasoline, or 62.5 mpg. However, the total increase in a manufacturer's average fuel economy rating due to dual-fueled vehicles cannot exceed 1.2mpg. Section 32906 reduces the increase due to dual-fueled vehicles to 0 through 2020.
Manufacturers are also allowed to earn CAFE "credits" in any year they exceed CAFE requirements, which they may use to offset deficiencies in other years. CAFE credits can be applied to the three years before or after the year in which they are earned. The reason for this flexibility is so manufacturers are penalized only for persistent failure to meet the requirements, not for transient non-compliance due to market conditions.
and the Ford Excursion
. From 1979-1991, separate standards were established for two wheel drive (2WD) and four wheel drive (4WD) light trucks, but for most of this period, car makers were allowed to choose between these separate standards or a combined standard to be applied to the entire fleet of light trucks they sold that model year. In 1980 and 1981, respectively, a manufacturer whose light truck fleet was powered exclusively by basic engines which were not also used in passenger cars could meet standards of 14 mpg and 14.5 mpg.
Since 1980, the traditional Japanese manufacturers have increased their combined fleet average fuel economy by 1.6 miles per gallon according to the March 30, 2009 Summary of Fuel Economy Performance published annually by NHTSA. During this time, they also increased their sales in the US by 221%. The traditional European manufacturers actually decreased their fleet average fuel economy by 2 miles per gallon while increasing their sales volume by 91%. The traditional US manufacturers, Chrysler, Ford and General Motors, increased their fleet average fuel economy by 4.1 miles per gallon since 1980 according to the latest government figures. During this time the sales of US manufacturers decreased by 29%.
In late 2007, CAFE standards received their first overhaul in more than 30 years. On December 19, President Bush signed into law the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
, which requires in part that automakers boost fleetwide gas mileage to 35 mpg by the year 2020. This requirement applies to all passenger automobiles, including "light trucks." Politicians had faced increased public pressure to raise CAFE standards; a July 2007 poll conducted in 30 congressional districts in seven states revealed 84-90% in favor of legislating mandatory increases.
Overall fuel economy for both cars and light trucks in the U.S. market reached its highest level in 1987, when manufacturers managed 26.2 mpg (8.98 L/100 km). The average in 2004 was 24.6 mpg. In that time, vehicles increased in size from an average of 3,220 pounds to 4,066 pounds (1,461 kg to 1,844 kg), in part due to an increase in truck ownership during that time from 28% to 53%.
A number of manufacturers choose to pay CAFE penalties rather than attempt to comply with the regulations. As of model year
2006, BMW
, DaimlerChrysler
, Volkswagen
, Ferrari
, Porsche
and Maserati
failed to meet CAFE requirements.
For the 2008 model year, Mercedes-Benz had the lowest fleet average while Lotus had the highest.
signed the Energy Independence and Security Act. This Act aims at improving vehicle fuel economy. The Act set a goal for the national fuel economy standard of 35 miles per gallon (mpg) by 2020. This would increase the fuel economy standards by 40 percent and save the United States billions of gallons of fuel. This standard is the first standard that has been set above the Corporate Average Fuel Economy standards (CAFE) since it was created in 1975.
CAFE standards since 1975 have increased very slowly till date. In 1978, the CAFE standard for passenger cars was 18.0mpg. At the time of the signing of the Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA) in 2007, the standard for passenger cars was 27.5mpg which was the same as the standard that was set in 1990. This has been the peak standard for passenger cars. This peak standard was first set in 1985 and then it was lowered to 26mpg in 1986 and got back to the peak again in 1990. The combined standard for light trucks experienced a much more gradual increase from 17.5mpg in 1982 to 22.2mpg in 2007. The light truck Average Fuel Economy Standards for model years (MY) 2005 to 2007 were 21.0mpg for MY2005, 21.6mpg for MY2006 and 22.2mpg for MY2007.
In 2006, the rule making for light trucks for model years 2008 - 2011 included a reform to the structure for CAFE standards for light truck and gave manufacturers the option for model years 2008-2010 to comply with the reformed standard or to comply with the unreformed standard. The reformed standard was based on the vehicle foot print. The unreformed standard for 2008 was set to be 22.5mpg.
To achieve the target of 35mpg authorized under EISA for the combined fleet of passenger cars and light truck for MY2020, NHTSA is required to continue raising the CAFE standards.In determining a new CAFE standard, NHTSA must assess the environmental impacts of each new standard and the effect of this standard on employment. With the EISA, NHTSA needed to take new analysis including taking a fresh look at the potential impacts under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and assessing whether or not the impacts are significant within the meaning of NEPA.
NHTSA has to issue its new standards eighteen months before the model year for fleet. According to NHTSA report, in order to achieve this industry wide combined fleet of at least 35mpg, NHTSA must set new standards well in advance of the model year so as to provide the automobile manufacturers with lead time enough to make extensive necessary changes in their automobiles. The EISA also called for a reform where the standards set by the Transportation Department would be are “attribute based” so as to ensure that the safety of vehicles is not compromised for higher standards.
These new flexibilities were implemented by regulation on March 23, 2009 in the Final Rule for 2011 Model Year Passenger Cars and Light Trucks.
Calculations using official CAFE data, and the newly proposed credit trading flexibility contained in the September 28, 2009 Notice of Proposed Rulemaking show that ninety-eight percent of the benefit derived from just the cross fleet credit trading provision flows to Toyota. According to these calculations 75% of the benefit from the two new CAFE credit trading provisions, cross fleet trading and 5-year carry-forward, falls to foreign manufacturers. Toyota can use the provision to avoid or reduce compliance on average by 0.69 mpg per year through 2020,
The estimated value of the CAFE exemption gained by Toyota is $2.5 billion; Honda’s benefit is worth $0.8 billion, and Nissan’s benefit is valued at $0.9 billion in reduced CAFE compliance costs. Foreign companies gained $5.5 billion in benefits compared with the $1.8 billion that went to the Detroit Three.
 The CAFE rules for trucks were officially amended at the end of March 2006. However, the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals has overturned the rules, returning them to NHTSA, stating that the rules must be made stricter. These changes would have segmented truck fleets by vehicle size and class as of 2011. All SUVs and passenger vans up to 10,000 pounds GVWR would have had to comply with CAFE standards regardless of size, but pickup truck
The CAFE rules for trucks were officially amended at the end of March 2006. However, the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals has overturned the rules, returning them to NHTSA, stating that the rules must be made stricter. These changes would have segmented truck fleets by vehicle size and class as of 2011. All SUVs and passenger vans up to 10,000 pounds GVWR would have had to comply with CAFE standards regardless of size, but pickup truck
s and cargo
van
s over 8500 pounds gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) would have remained exempt.
Under the new final light truck CAFE standard 2008-2011, fuel economy standards would have been restructured so that they are based on a measure of vehicle size called "footprint," the product of multiplying a vehicle's wheelbase by its track width. A target level of fuel economy would have been established for each increment in footprint using a continuous mathematical formula. Smaller footprint light trucks had higher fuel economy targets and larger trucks lower targets. Manufacturers who made more large trucks would have been allowed to meet a lower overall CAFE target, manufacturers who make more small trucks would have needed to meet a higher standard. Unlike previous CAFE standards there was no requirement for a manufacturer or the industry as a whole to meet any particular overall actual MPG target, since that will depend on the mix of sizes of trucks manufactured and ultimately purchased by consumers. Some critics pointed out that this might have had the unintended consequence
of pushing manufacturers to make ever-larger vehicles to avoid strict economy standards. However, the equation used to calculate the fuel economy target had a built in mechanism that provides an incentive to reduce vehicle size to about 52 square feet (the approximate midpoint of the current light truck fleet.)
The Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals found these new Light Truck rules to be arbitrary and capricious; contrary to the Energy Policy and Conservation Act; incorrectly set a value of zero dollars to the global warming damage caused by truck emissions; failed to set a "backstop" to prevent trucks from emitting more CO2 than in previous years; failed to set standards for vehicles in the 8,500 to 10000 lb (4,535.9 kg) range; that the environmental impact assessment was inadequate, and that the rules may have had significant negative impact on the environment. The court directed NHTSA to prepare a new standard as quickly as possible and to fully evaluate that new standard's impact on the environment.
In addition to the new light truck rules of 2006 and the Ninth Court decision, in December 2007 Congress passed the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
which will affect CAFE standards of both cars and trucks and additionally work trucks and medium and heavy duty on-highway vehicles. This standard requires ratable increases in fuel efficiency during the model years 2011 to 2020 reaching 35 mpg in 2020 for the total fleet of passenger and non-passenger automobiles. In the years 2021 to 2030 the standards requires MPG to be the "maximum feasible" fuel economy. The law allows NHTSA to issue additional requirements for cars and trucks based on the "footprint" model or other mathematical standard. Additionally each manufacturer must meet a minimum standard of the higher of either 27.5 mpg for passenger automobiles or 92% of the projected average for all manufacturers. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
(NHTSA) is directed based on National Academy of Sciences
studies to set medium and heavy-duty truck MPG standards to the "maximum feasible". Additionally the law phases out the mpg credit previously granted to E85
flexible-fuel vehicle
manufacturers and adds in one for biodiesel
, and it adds a requirement that NHTSA publish replacement tire fuel efficiency ratings. The bill also adds support for initial state and local infrastructure for plug-in electric vehicles. How the Ninth Court decision will be reconciled to this new law remains undecided, but if the court issue is resolved and the new law goes into effect and if actual achieved combined corporate CAFE remains at 26.7 mpg until then, then average fleet-wide new vehicle mpg would increase by 0.8 mpg a year starting in 2011.
On April 22, 2008 NHTSA responded to this Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
with proposed new fuel economy standards for cars and trucks effective model year 2011. It is not clear how the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals case will interact with these new rules. The new rules also introduce the "footprint" model for cars as well as trucks, where if a manufacturer makes more large cars and trucks they will be allowed to meet a lower standard for fuel economy. This means that an overall fuel efficiency for a particular manufacturer nor the fleet as a whole cannot be predicted with certainly since it will depend on the actual product mix manufactured. However, if the product mix is as NHTSA predicts, car fuel economy would increase from a current standard of 27.5 mpgU.S. (11.7 km/L) to 31 mpgU.S. (13.2 km/L) in 2011. The new regulations are designed to be "optimized" with respect to a certain set of assumptions which include: gas prices in 2016 will be $2.25 a U.S. gallon (59.4¢/L), all new car purchasers will pay 7% interest rates on their vehicles purchases, and only care about fuel costs for the first 5 years of a vehicle's life, and that the value of global warming is $7 per ton CO2. This corresponds to a global warming
value of $4.31 savings a year per car under the new regulations. Further, the new regulations assume that no advanced hybrids
(Toyota Prius
), plug-in hybrids and extended range electric vehicles (Chevrolet Volt
), electric car
s (Th!nk City
), nor alternative fuel vehicles (Honda Civic GX
) will be used to achieve these fuel economies. The new rules also propose again that California
(and the other States following California's lead) be stripped of their historic right to set their own more stringent automotive air pollution standards.
On January 26, 2009, President Barack Obama directed the Department of Transportation to review relevant legal, technological, and scientific considerations associated with establishing more stringent fuel economy standards, and to finalize the 2011 model year standard by the end of March. This single-model year standard was issued March 27, 2009 and is about one mpg lower than the fuel economy standards previously recommended under the Bush Administration. "These standards are important steps in the nation's quest to achieve energy independence and bring more fuel efficient vehicles to American families," said Secretary LaHood. The new standards will raise the industry-wide combined average to 27.3 miles per US gallon (11.6 km/L) (a 2 miles per US gallon increase over the 2010 model year average), as estimated by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). It will save about 887000000 U.S.gal of fuel and reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 8.3 million metric tons. This 2011 single-year standard will use an attribute-based system, which sets fuel economy standards for individual vehicle models, based on the "footprint" model. Secretary LaHood also noted that work on the multi-year fuel economy plan for model years after 2011 is already well underway. The review will include an evaluation of fuel saving technologies, market conditions and future product plans from the manufacturers. The effort will be coordinated with interested stakeholders and other federal agencies, including the Environmental Protection Agency. The news rules were immediately challenged in court again by the Center for Biological Diversity as not addressing the inadequacies found by the previous court rulings. The interaction between these future rules, the collapse of the auto industry in the United States, the listing by EPA on March 20, 2009 of CO2 as a global warming pollution dangerous to human welfare, and the willingness indicated by environmental groups to apply once again to the courts for a ruling that these standards are inadequate, again left the future of fuel economy standards in the United States in doubt.
On May 19, 2009 President Barack Obama
proposed a new national fuel economy program which adopts uniform federal standards to regulate both fuel economy and greenhouse gas emissions while preserving the legal authorities of DOT, EPA and California. The program covers model year 2012 to model year 2016 and ultimately requires an average fuel economy standard of 35.5 mpgus in 2016 (of 39 miles per gallon for cars and 30 mpg for trucks), a jump from the current average for all vehicles of 25 miles per gallon. Obama said, "The status quo
is no longer acceptable." The result is a projected reduction in oil consumption of approximately 1.8 Goilbbl over the life of the program and a projected total reduction in greenhouse gas
emissions of approximately 900 million metric tons. Ten car companies and the UAW embraced the national program because it provides certainty and predictability to 2016 and includes flexibilities that will significantly reduce the cost of compliance. Stated goals for the program included: saving consumers money over the long term in increased fuel efficiency, preserving consumer choice—the new rules do not dictate the size of cars, trucks and SUVs that manufacturers can produce; rather it requires that all sizes of vehicles become more energy efficient, reduced air pollution in the form of greenhouse gas emissions and other conventional pollutants, one national policy for all automakers, instead of three standards (a DOT standard, an EPA standard and a California standard that would apply to 13 other states), and industry desires: clarity, predictability and certainty concerning the rules while giving them flexibility on how to meet the expected outcomes and the lead time they need to innovate. The new policy will result in yearly 5% increases in efficiency from 2012 through 2016, 1.8 Goilbbl of oil saved cumulatively over the lifetime of the program and significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to taking 177 million of today's cars off the road.
There are a large number of technologies that manufacturers can apply to improve fuel efficiency short of implementing hybrid
or plug-in hybrid technologies. Applied aggressively, at a cost of several thousand dollars per vehicle, the Union of Concerned Scientists
estimates that these technologies can almost double MPG.
Some technologies, such as four valves per cylinder, are already widely applied in cars, but not trucks. Manufacturers dispute how effective these technologies are, their retail price, and how willing customers are to pay for these improvements. Payback
on these improvements is highly dependent on fuel prices.
On July 29, 2011 President Obama announced a historic agreement with thirteen major automakers to pursue the next phase in the Administration’s national vehicle program, increasing fuel economy to 54.5 miles per gallon for cars and light-duty trucks by Model Year 2025. The President was joined by Ford, GM, Chrysler, BMW, Honda, Hyundai, Jaguar/Land Rover, Kia, Mazda, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Toyota and Volvo – which together account for over 90% of all vehicles sold in the United States – as well as the United Auto Workers (UAW), and the State of California, who were integral to developing this agreement.
Volkswagen responded to July 29, 2011 agreement with the following statement:
"Volkswagen does not endorse the proposal under discussion. It places an unfairly high burden on passenger cars, while allowing special compliance flexibility for heavier light trucks. Passenger cars would be required to achieve 5% annual improvements, and light trucks 3.5% annual improvements. The largest trucks carry almost no burden for the 2017-2020 timeframe, and are granted numerous ways to mathematically meet targets in the outlying years without significant real-world gains.
The proposal encourages manufacturers and customers to shift toward larger, less efficient vehicles, defeating the goal of reduced greenhouse gas emissions."
The conservative Heartland Institute
contends that CAFE standards do not work economically to consumers' benefit, that smaller cars are more likely to be damaged in a collision, and that insurance
premiums for them are higher than for many larger cars. However, the Insurance Companies' Highway Loss Data Institute publishes data showing that larger vehicles are more expensive to insure.
CAFE advocates assert most of the gains in fuel economy over the past 30 years can be attributed to the standard itself, while opponents assert economic forces are responsible for fuel economy gains, where higher fuel prices drove customers to seek more fuel efficient vehicles. CAFE standards have come under attack by some conservative
think tanks, along with safety experts, car and truck manufacturers, some consumer and environment groups, and organized labor.
report found that the standards implemented in the 1970s and 1980s "probably resulted in an additional 1,300 to 2,600 traffic fatalities in 1993. A Harvard Center for Risk Analysis study found that CAFE standards led to "2,200 to 3,900 additional fatalities to motorists per year. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety's 2007 data show a correlation of about 250-500 fatalities per year per MPG. Proponents of higher CAFE standards argue that it is the "Footprint" model of CAFE for trucks that encourages production of larger trucks with concomitant increases in vehicle weight disparities, and point out that some small cars such as the Mini Cooper and Toyota Matrix
are four times safer than SUVs like the Chevy Blazer. They argue that the quality of the engineering design is the prime determinant of vehicular safety, not the vehicle's mass. In a 1999 article based on a 1995 IIHS report, USA Today
said that 56% of all deaths occurring in small cars were due to either single vehicle crashes or small cars impacting each other. The percentage of deaths attributed to those in small cars being hit by larger cars was one percent. In 2006, IIHS found that some of the smallest cars have good crash safety, while others do not, depending upon the engineering design. In a 2007 analysis, IIHS found that 50 percent of fatalities in small four-door vehicles were single vehicle crashes, compared to 83 percent in very large SUVs. The Mini Cooper had a fatality rate of 68 per million vehicle-years, compared to 115 for the Ford Excursion. A 2005 IIHS plot shows that in collisions between SUVs weighing 3500 lb (1,587.6 kg) and cars, the car driver is more than 4X more likely to be killed, and if the SUV weighs over 5000 lb (2,268 kg) the car driver is 9 times more likely to be killed, with 16 percent of deaths occurring in car-to-car crashes and 18 percent in car-to-truck crashes. Recent studies find about 75 percent of two-vehicle fatalities involve a truck, and about half these fatalities involve a side-impact crash. Risk to the driver of the other vehicle is almost 10 times higher when the vehicle is a one ton
pickup compared to an imported car. And a 2003 Transportation Research Board
study show greater safety disparities among vehicles of differing price, country of origin, and quality than among vehicles of different size and weight. These more recent studies tend to discount the importance of vehicle mass to traffic safety, pointing instead to the quality of engineering design as the primary factor.
It is also possible that because higher-efficiency vehicles are more expensive, auto buyers may choose to keep their older cars (some of which are less efficient) for longer before making a new purchase.
However, associated costs, such as increased deaths, may be more than offset by savings on a global scale, because increased CAFE standards reduce reliance on increasingly expensive and unreliable sources of imported petroleum and lower the probability of global climate change by reducing US emissions of carbon dioxide
.
and Big Three fame, asserted that the CAFE standard was a failure and said it was like trying to fight obesity
by requiring tailors to make only small-sized clothes.
Proponents state that automobile-purchasing decisions that may have global effects should not be left entirely up to individuals operating in a free market.
Automakers have said that small, fuel-efficient vehicles cost the auto industry billions of dollars. They cost almost as much to design and market but cannot be sold for as much as larger vehicles such as SUVs, because consumers expect small cars to be inexpensive. In 1999 USA Today reported small cars tend to depreciate
faster than larger cars, so they are worth less in value to the consumer over time. However, 2007 Edmunds depreciation data show that some small cars, primarily premium models, are among the best in holding their value.
spokesman Eron Shosteck asserted automakers produce more than 30 models rated at 30 mpg or more for the US market, and they are poor sellers. In 2004, GM retiree Charles Amann said statistically, consumers do not pick the weak-performing vehicle when given a choice of engines. However, after a spike in gas prices, a 2006 Consumer Reports
survey concluded fuel economy is the most important consideration in consumers' choice of vehicle and a 2007 Pew Charitable Trusts survey found that nine out of ten Americans favor tougher CAFE standards, including 91% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans. In 2007, the 55 mpg Toyota Prius outsold the top-selling SUV, the 17 mpg Ford Explorer. In late 2007, GM Vice Chairman Bob Lutz called hybrid gasoline-electric vehicles the "ideal solution". In 2008, GM advertised fuel economy improvements and their upcoming Chevrolet Volt
Extended Range Electric Vehicle, and developed corporate branding for their fuel economy technologies, and though GM Chairman Rick Wagoner admitted he doesn't know which fuel efficiency technologies consumers really want he said
"we are moving fast with technologies like E-85 (ethanol), all-electric, fuel cells and a wide range of hybrid offers."
In 1999, automakers asserted they couldn't lobby for the repeal of CAFE standards, because consumers would learn small cars are unsafe and not buy them, or would try to sue the manufacturers. However, NHTSA's public record shows the automakers publicly express opposition to CAFE increases.
, but legendary former Chrysler
CEO Lee Iacocca
developed the idea of marketing the minivan
as a station wagon alternative, while certifying it in the separate truck category to allow compliance with less-strict emissions standards. Eventually, this same idea led to the promotion of the SUV.
New York
, New Jersey
, Pennsylvania
, Connecticut
and California
disagreed with the NHTSA statement in the 2008-2011 Light Truck standard which claimed preemption of the state greenhouse gas
regulations, on the basis that fuel economy and carbon dioxide emissions are one and the same. The EPA claims, contrary to NHTSA, that the use of alternative fuels allows greenhouse gas
emissions to be controlled somewhat independently of fuel efficiency.
(EPA) laboratory measurements of MPG have consistently overestimated fuel economy of gasoline vehicles and underestimated diesel vehicles. John DeCicco, the automotive expert for the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF), estimated that this results in about 20% higher actual consumption than measured CAFE goals. Starting with 2008-model vehicles, the EPA has adopted a new protocol for estimating the MPG figures presented to consumers. The new protocol includes driving cycles more closely representative of today's traffic and road conditions, as well as increased air conditioner usage. This change does not affect how the EPA calculates CAFE ratings; the new protocol changes only the mileage estimates provided for consumer information.
NHTSA spends one-third of one percent of its budget on CAFE, or $0.014 per US citizen.
As noted in the 2007 United States Government Accountability Office Report to the Chairman of the U.S. Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation (page 23) "Several experts stated that this is (penalties) not enough of a monetary incentive for manufacturers to comply with CAFE."
For example, in 25 years from 1983 to 2008 Mercedes-Benz paid penalties 21 times and BMW paid penalties 20 times.
Currently CAFE penalty is $55 USD per vehicle for every 1 mpg under the standard. For the year 2006 Mercedes-Benz draw $30.3 million penalty for violating fuel economy standards. That equates to $122 per one sold vehicle (in 2006 Mercedes-Benz sales were 248,080 vehicles)
A penalty of $122 means violating CAFE by 2.22 MPG ($122 divided by $55). According to the government "fueleconomy.gov" website violating CAFE by 2.42 MPG means consuming extra 27 barrels (4.3 m³) (1134 gallons (4,292.7 l)) of mostly imported fuel in 10 years which is worth $3,490 (Based on 45% highway, 55% city driving, 15000 annual miles and a fuel price of $ 2.95 per gallon) that is 13.4% more and also it means emitting extra 14 Tons of CO2 in 10 years that is 12.7% more. These numbers are based on comparison of 2010 Mercedes ML 350 4MATIC with CAFE Unadjusted Average Fuel Economy of 21.64 MPG (this model meets 2006 CAFE requirements of 21.6 MPG) and 2010 Mercedes ML 550 4MATIC with CAFE Unadjusted Average Fuel Economy of 19.22 MPG. So consuming extra $3,490 worth of mostly imported fuel and emitting extra 14 Tons of CO2 draws a penalty of only $122 for a single luxury car buyer. $122 is only 0.3% of the price of $40,000 car (average 2010 price of a luxury car). Several experts stated that this is not enough of a monetary incentive to comply with CAFE.
CAFE penalty have increased only 10% since 1983. At the same time cumulative inflation from 1983 to 2010 was 119.2%. It means that CAFE penalty in 2010 is actually 2 times less than what it was in 1983. NHTSA officials stated that, in addition to the authority the Federal Civil Penalties Inflation Adjustment Act of 1990 under EPCA, NHTSA has the authority to raise CAFE penalties to $100 per 1 mpg shortfall. NHTSA chooses not to exercise this authority.
Regulation
Regulation is administrative legislation that constitutes or constrains rights and allocates responsibilities. It can be distinguished from primary legislation on the one hand and judge-made law on the other...
s in the United States
United States
The United States of America is a federal constitutional republic comprising fifty states and a federal district...
, first enacted by the U.S. Congress in 1975, and intended to improve the average fuel economy
Fuel economy in automobiles
Fuel usage in automobiles refers to the fuel efficiency relationship between distance traveled by an automobile and the amount of fuel consumed....
of cars
Automobile
An automobile, autocar, motor car or car is a wheeled motor vehicle used for transporting passengers, which also carries its own engine or motor...
and light truck
Light truck
Light truck or light duty truck is a U.S. classification for trucks or truck-based vehicles with a payload capacity of less than 4,000 pounds...
s (truck
Truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, with the smallest being mechanically similar to an automobile...
s, van
Van
A van is a kind of vehicle used for transporting goods or groups of people.In British English usage, it can be either specially designed or based on a saloon or sedan car, the latter type often including derivatives with open backs...
s and sport utility vehicle
Sport utility vehicle
A sport utility vehicle is a generic marketing term for a vehicle similar to a station wagon, but built on a light-truck chassis. It is usually equipped with four-wheel drive for on- or off-road ability, and with some pretension or ability to be used as an off-road vehicle. Not all four-wheel...
s) sold in the US in the wake of the 1973 Arab Oil Embargo. Historically, it is the sales-weighted harmonic mean
Harmonic mean
In mathematics, the harmonic mean is one of several kinds of average. Typically, it is appropriate for situations when the average of rates is desired....
fuel economy, expressed in miles per US gallon (mpg), of a manufacturer's fleet of current model year
Model year
The model year of a product is a number used worldwide, but with a high level of prominence in North America, to describe approximately when a product was produced, and indicates the coinciding base specification of that product....
passenger cars or light trucks with a gross vehicle weight rating
Gross vehicle weight rating
A gross vehicle weight rating is the maximum allowable total weight of a road vehicle or trailer when loaded - i.e., including the weight of the vehicle itself plus passengers, and cargo....
(GVWR) of 8,500 pounds (3,856 kg) or less, manufactured for sale in the US. If the average fuel economy of a manufacturer's annual fleet of vehicle production falls below the defined standard, the manufacturer must pay a penalty
Sanctions (law)
Sanctions are penalties or other means of enforcement used to provide incentives for obedience with the law, or with rules and regulations. Criminal sanctions can take the form of serious punishment, such as corporal or capital punishment, incarceration, or severe fines...
, currently $5.50 USD per 0.1 mpg under the standard, multiplied by the manufacturer's total production for the U.S. domestic market. In addition, a Gas Guzzler Tax
Gas Guzzler Tax
The National Energy Act: Energy Tax Act of 1978 , or the Gas Guzzler Tax, imposed set tax penalties on car manufacturers who fail to meet the minimum fuel economy level of in the United States. This does not include minivans, sport utility vehicles or pick-up trucks. It is intended to discourage...
is levied on individual passenger car models (but not trucks, vans, minivans, or SUVs) that get less than 22.5 miles per US gallon.
Starting in 2011 the CAFE standards are newly expressed as mathematical functions depending on vehicle "footprint", a measure of vehicle size determined by multiplying the vehicle’s wheelbase by its average track width.
CAFE footprint requirements are set up such that a vehicle with a bigger footprint has a lower fuel economy requirement than a vehicle with a smaller footprint. For example, the 2012 Honda Fit
Honda Fit
The Honda Jazz is a five-door hatchback subcompact manufactured by the Honda Motor Company of Japan, first introduced in June 2001 and is now in its second generation. The Jazz shares Honda's Global Small Car Platform with the City/Fit Aria, Airwave/Partner, Mobilio, Mobilio Spike, Freed and Freed...
has a footprint of 40 sq ft (3.7 m²) must achieve fuel economy (as measured for CAFE) of 36 miles per US gallon, equivalent to a published fuel economy of 27 miles per US gallon, while a Ford F-150 with its footprint of 65–75 sq ft (6–7 m2) must achieve CAFE fuel economy of 22 miles per US gallon, i.e., 17 miles per US gallon published.
CAFE has separate standards for "passenger cars" and "light trucks", despite the majority of "light trucks" actually being used as passenger cars. The market share of "light trucks" grew steadily from 9.7% in 1979 to 47% in 2001 and remained in 50% numbers up to 2011.
More than 500,000 vehicles in the 1999 model year exceeded the 8500 lb (3,855.5 kg) GVWR cutoff and were thus omitted from CAFE calculations.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is an agency of the Executive Branch of the U.S. government, part of the Department of Transportation...
(NHTSA) regulates CAFE standards and the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) measures vehicle fuel efficiency. US Congress specifies that CAFE standards must be set at the "maximum feasible level" given consideration for:
- technological feasibility;
- economic practicality;
- effect of other standards on fuel economy;
- need of the nation to conserveEnergy conservationEnergy conservation refers to efforts made to reduce energy consumption. Energy conservation can be achieved through increased efficient energy use, in conjunction with decreased energy consumption and/or reduced consumption from conventional energy sources...
energy.
Historically, the EPA has encouraged consumers to buy more fuel efficient vehicles, while the NHTSA expressed concerns that smaller, more fuel efficient vehicles may lead to increased traffic fatalities.
Thus higher fuel efficiency was associated with lower traffic safety, intertwining the issues of fuel economy
Fuel economy in automobiles
Fuel usage in automobiles refers to the fuel efficiency relationship between distance traveled by an automobile and the amount of fuel consumed....
, road-traffic safety
Road-traffic safety
The term road traffic safety is about the risk of a person being killed or seriously injured while using the road network as a pedestrian, cyclist, motorist or user of on road public transport...
, air pollution
Air pollution
Air pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
, and climate change
Climate change
Climate change is a significant and lasting change in the statistical distribution of weather patterns over periods ranging from decades to millions of years. It may be a change in average weather conditions or the distribution of events around that average...
. In the mid 2000s, increasing safety of smaller cars and the poor safety record of light trucks began to reverse this association. Nevertheless, the on-road vehicle fleets in the US and Canada have the lowest overall average fuel economy among first world
First World
The concept of the First World first originated during the Cold War, where it was used to describe countries that were aligned with the United States. These countries were democratic and capitalistic. After the fall of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War, the term "First World" took on a...
nations: 25 miles per US gallon in the US, versus 45 miles per US gallon in the European Union
European Union
The European Union is an economic and political union of 27 independent member states which are located primarily in Europe. The EU traces its origins from the European Coal and Steel Community and the European Economic Community , formed by six countries in 1958...
and higher in Japan
Japan
Japan is an island nation in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean, it lies to the east of the Sea of Japan, China, North Korea, South Korea and Russia, stretching from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea and Taiwan in the south...
(2008). Furthermore, despite pervasive opinion that larger and heavier (and therefore relatively fuel-uneconomical) vehicles are safer, the US traffic fatality rate—and its trend over time—is worse than that of other first world
First World
The concept of the First World first originated during the Cold War, where it was used to describe countries that were aligned with the United States. These countries were democratic and capitalistic. After the fall of the Soviet Union and the end of the Cold War, the term "First World" took on a...
nations.
Effect on automotive fuel economy
In 2002, a committee of the National Academy of SciencesUnited States National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences is a corporation in the United States whose members serve pro bono as "advisers to the nation on science, engineering, and medicine." As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and...
wrote a report on the effects of the CAFE standard. The report's conclusions include a finding that in the absence of CAFE, and with no other fuel economy regulation substituted, motor vehicle fuel consumption would have been approximately 14 percent higher than it actually was in 2002. One cost of this increase in fuel economy is a possible increase in fatalities, estimated to be 1,300 to 2,600 increased fatalities in 1993, albeit with certain of the committee members dissenting.
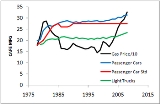
A plot of average overall vehicle fuel economy (CAFE) for new model year passenger cars, the required by law CAFE standard target fuel economy value (CAFE standard) for new model year passenger cars, and fuel prices, adjusted for inflation, shows that there has been little variation over the past 20 years. Within this period, there are three distinct periods of fuel economy change:
- from 1979-1982 the fuel economy rose as the CAFE standard rose dramatically and the price of fuel increased;
- from 1984-1986 the fuel economy rose as the CAFE standard rose and the price of fuel decreased rapidly;
- from 1986-1988 the fuel economy rose at a significantly subdued rate and eventually leveled off as the price of fuel fell and the CAFE standard was relaxed
before returning to 1986 levels in 1990. These are following by an extended period during which the passenger car CAFE standard, the observed average passenger car fuel economy, and the price of gasoline remained stable, and finally a period starting about 2003 when prices rose dramatically and fuel economy has slowly responded.
Simple economics would predict that an increase in gasoline prices would lead in the long run to an increase in the average fuel economy of the US passenger car fleet, and that a drop in gasoline prices would be associated with a reduction in the average fuel economy of the entire US fleet. There is some evidence that this happened with an increase in market share of lower fuel economy light trucks and SUVs and decline in passenger car sales, as a percentage of total fleet sales, as car buying trends changed during the 1990s, the impact of which is not reflected in this chart.
In the case of passenger cars, US average fuel economy did not fall as economic theory would predict, suggesting that CAFE standards maintained the higher fuel economy of the passenger car fleet during the long period from the end of the 1979 energy crisis
1979 energy crisis
The 1979 oil crisis in the United States occurred in the wake of the Iranian Revolution. Amid massive protests, the Shah of Iran, Mohammad Reza Pahlavi, fled his country in early 1979 and the Ayatollah Khomeini soon became the new leader of Iran. Protests severely disrupted the Iranian oil...
to the rise of gasoline prices in the early 2000s. Most recently, fuel economy has increased about one mpg from 2006 to 2007. This increase is due primarily to increased fuel efficiency of imported cars. Similarly, Simple Economics predicts that due to the US's large percentage consumption of the world's oil supply, that increasing fuel economy would drive down the gasoline prices that US consumers would otherwise have to pay—reductions
in petroleum demand in the United States helped create the collapse of OPEC
market power in 1986.
The "CAFE" and "CAFE standard" shown here only regards new model passenger car fuel economy and target fuel economy (respectively) rather than the overall US fuel economy average which tends to be dominated by used vehicles manufactured in previous years, new model light truck CAFE standards, light truck CAFE averages, or aggregate data.
Calculation
Fleet fuel economy is calculated using a harmonic meanHarmonic mean
In mathematics, the harmonic mean is one of several kinds of average. Typically, it is appropriate for situations when the average of rates is desired....
, not a simple arithmetic mean
Arithmetic mean
In mathematics and statistics, the arithmetic mean, often referred to as simply the mean or average when the context is clear, is a method to derive the central tendency of a sample space...
(average) – namely, the reciprocal of the average of the reciprocal values. For a fleet composed of four different kinds of vehicle A, B, C and D, produced in numbers nA, nB, nC and nD, with fuel economies fA, fB, fC and fD, the CAFE would be:
For example, a fleet of 4 vehicles getting 15, 13, 17, and 100 mpg has a CAFE of slightly less than 19 mpg:
While the arithmetic mean fuel economy of the fleet is just over 36 mpg:
The harmonic mean captures the fuel economy of driving each car in the fleet for the same number of miles, while the arithmetic mean captures the fuel economy of driving each car using the same amount of gas (i.e. the 13 mpg vehicle would travel 13 miles (20.9 km) with one gallon while the 100 mpg vehicle would travel 100 miles).
For the purposes of CAFE, a manufacturer's car output is divided into a domestic fleet (vehicles with more than 75 percent U.S., Canadian
Canada
Canada is a North American country consisting of ten provinces and three territories. Located in the northern part of the continent, it extends from the Atlantic Ocean in the east to the Pacific Ocean in the west, and northward into the Arctic Ocean...
or post-NAFTA
North American Free Trade Agreement
The North American Free Trade Agreement or NAFTA is an agreement signed by the governments of Canada, Mexico, and the United States, creating a trilateral trade bloc in North America. The agreement came into force on January 1, 1994. It superseded the Canada – United States Free Trade Agreement...
Mexican
Mexico
The United Mexican States , commonly known as Mexico , is a federal constitutional republic in North America. It is bordered on the north by the United States; on the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; on the southeast by Guatemala, Belize, and the Caribbean Sea; and on the east by the Gulf of...
content) and a foreign fleet (everything else). Each of these fleets must separately meet the requirements. The two-fleet requirement was developed by the United Automobile Workers (UAW) as a means to ensure job creation in the US. The UAW successfully lobbied
Lobbying
Lobbying is the act of attempting to influence decisions made by officials in the government, most often legislators or members of regulatory agencies. Lobbying is done by various people or groups, from private-sector individuals or corporations, fellow legislators or government officials, or...
Congress to write this provision into the enabling legislation – and continues to advocate this position. The two fleet rule for light trucks was removed in 1996.
For the fuel economy calculation for alternative fuel
Alternative fuel
Alternative fuels, known as non-conventional or advanced fuels, are any materials or substances that can be used as fuels, other than conventional fuels...
vehicles, a gallon of alternative fuel is deemed to contain 15% fuel (which is approximately the amount of gasoline in a gallon of E85)
as an incentive to develop alternative fuel vehicles. The mileage for dual-fuel vehicles, such as E85 capable models, is computed as the average of its alternative fuel rating—divided by 0.15 (equal to multiplying by 6.666) -- and its gasoline rating. Thus an E85-capable vehicle that gets 15 mpg on E-85 and 25 mpg on gasoline might logically be rated at 20 mpg. But in fact the average, for CAFE purposes, despite perhaps only one percent of the fuel used in E85-capable vehicles is actually E85, is computed as 100 mpg for E-85 and the standard 25 mpg for gasoline, or 62.5 mpg. However, the total increase in a manufacturer's average fuel economy rating due to dual-fueled vehicles cannot exceed 1.2mpg. Section 32906 reduces the increase due to dual-fueled vehicles to 0 through 2020.
Manufacturers are also allowed to earn CAFE "credits" in any year they exceed CAFE requirements, which they may use to offset deficiencies in other years. CAFE credits can be applied to the three years before or after the year in which they are earned. The reason for this flexibility is so manufacturers are penalized only for persistent failure to meet the requirements, not for transient non-compliance due to market conditions.
Historical standards
Fuel economy regulations were first introduced in 1978, only for passenger vehicles. The next year, a second category was defined for light trucks. These were distinguished from heavy duty vehicles by a gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) of 6000 pounds or less. The GVWR threshold was raised to 8500 pounds in 1980 and has remained at that level through 2007. Thus certain large trucks and SUV's are exempt, such as the HummerHummer
Hummer was a brand of trucks and SUVs, first marketed in 1992 when AM General began selling a civilian version of the M998 Humvee. In 1998, General Motors purchased the brand name and marketed three vehicles: the original Hummer H1, based on the Humvee; and the H2 and H3 models that were...
and the Ford Excursion
Ford Excursion
The Ford Excursion is a full-size sport utility vehicle that was produced by the Ford Motor Company between model years 2000 and 2005 . Based on the Super Duty pickup truck platform, it served as Ford's largest SUV in its lineup during the tenure of its production and mainly competed against the...
. From 1979-1991, separate standards were established for two wheel drive (2WD) and four wheel drive (4WD) light trucks, but for most of this period, car makers were allowed to choose between these separate standards or a combined standard to be applied to the entire fleet of light trucks they sold that model year. In 1980 and 1981, respectively, a manufacturer whose light truck fleet was powered exclusively by basic engines which were not also used in passenger cars could meet standards of 14 mpg and 14.5 mpg.
| Model Year | Passenger Cars | Light Trucks | ||
| 2WD | 4WD | Combined | ||
| 1978 | 18.0 | |||
| 1979 | 19.0 | 17.2 | 15.8 | 17.2 |
| 1980 | 20.0 | 16.0 | 14.0 | |
| 1981 | 22.0 | 16.7 | 15.0 | |
| 1982 | 24.0 | 18.0 | 16.0 | 17.5 |
| 1983 | 26.0 | 19.5 | 17.5 | 19.0 |
| 1984 | 27.0 | 20.3 | 18.5 | 20.0 |
| 1985 | 27.5 | 19.7 | 18.9 | 19.5 |
| 1986 | 26.0 | 20.5 | 19.5 | 20.0 |
| 1987 | 26.0 | 21.0 | 19.5 | 20.5 |
| 1988 | 26.0 | 21.0 | 19.5 | 20.5 |
| 1989 | 26.5 | 21.5 | 19.0 | 20.5 |
| 1990 | 27.5 | 20.5 | 19.0 | 20.0 |
| 1991 | 27.5 | 20.7 | 19.1 | 20.2 |
| 1992 | 27.5 | 20.2 | ||
| 1993 | 27.5 | 20.4 | ||
| 1994 | 27.5 | 20.5 | ||
| 1995 | 27.5 | 20.6 | ||
| 1996 | 27.5 | 20.7 | ||
| 1997 | 27.5 | 20.7 | ||
| 1998 | 27.5 | 20.7 | ||
| 1999 | 27.5 | 20.7 | ||
| 2000 | 27.5 | 20.7 | ||
| 2001 | 27.5 | 20.7 | ||
| 2002 | 27.5 | 20.7 | ||
| 2003 | 27.5 | 20.7 | ||
| 2004 | 27.5 | 20.7 | ||
| 2005 | 27.5 | 21.0 | ||
| 2006 | 27.5 | 21.6 | ||
| 2007 | 27.5 | 22.2 | ||
| 2008 | 27.5 | 22.5 | ||
| 2009 | 27.5 | 23.1 | ||
| 2010 | 27.5 | 23.5 | ||
| 2011 | 30.2 | 24.1 |
Since 1980, the traditional Japanese manufacturers have increased their combined fleet average fuel economy by 1.6 miles per gallon according to the March 30, 2009 Summary of Fuel Economy Performance published annually by NHTSA. During this time, they also increased their sales in the US by 221%. The traditional European manufacturers actually decreased their fleet average fuel economy by 2 miles per gallon while increasing their sales volume by 91%. The traditional US manufacturers, Chrysler, Ford and General Motors, increased their fleet average fuel economy by 4.1 miles per gallon since 1980 according to the latest government figures. During this time the sales of US manufacturers decreased by 29%.
Current standards
Cars and light trucks are considered separately for CAFE and are held to different standards. As of early 2004, the average for cars must exceed 27.5 mpg, and the light truck average must exceed 20.7 mpg. Trucks under 8500 pounds must average 22.5 mpg in 2008, 23.1 mpg in 2009, and 23.5 mpg in 2010. After this, new rules set varying targets based on truck size "footprint."In late 2007, CAFE standards received their first overhaul in more than 30 years. On December 19, President Bush signed into law the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 is an Act of Congress concerning the energy policy of the United States...
, which requires in part that automakers boost fleetwide gas mileage to 35 mpg by the year 2020. This requirement applies to all passenger automobiles, including "light trucks." Politicians had faced increased public pressure to raise CAFE standards; a July 2007 poll conducted in 30 congressional districts in seven states revealed 84-90% in favor of legislating mandatory increases.
Overall fuel economy for both cars and light trucks in the U.S. market reached its highest level in 1987, when manufacturers managed 26.2 mpg (8.98 L/100 km). The average in 2004 was 24.6 mpg. In that time, vehicles increased in size from an average of 3,220 pounds to 4,066 pounds (1,461 kg to 1,844 kg), in part due to an increase in truck ownership during that time from 28% to 53%.
A number of manufacturers choose to pay CAFE penalties rather than attempt to comply with the regulations. As of model year
Model year
The model year of a product is a number used worldwide, but with a high level of prominence in North America, to describe approximately when a product was produced, and indicates the coinciding base specification of that product....
2006, BMW
BMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
, DaimlerChrysler
DaimlerChrysler
Daimler AG is a German car corporation. By unit sales, it is the thirteenth-largest car manufacturer and second-largest truck manufacturer in the world. In addition to automobiles, Daimler manufactures buses and provides financial services through its Daimler Financial Services arm...
, Volkswagen
Volkswagen
Volkswagen is a German automobile manufacturer and is the original and biggest-selling marque of the Volkswagen Group, which now also owns the Audi, Bentley, Bugatti, Lamborghini, SEAT, and Škoda marques and the truck manufacturer Scania.Volkswagen means "people's car" in German, where it is...
, Ferrari
Ferrari
Ferrari S.p.A. is an Italian sports car manufacturer based in Maranello, Italy. Founded by Enzo Ferrari in 1929, as Scuderia Ferrari, the company sponsored drivers and manufactured race cars before moving into production of street-legal vehicles as Ferrari S.p.A. in 1947...
, Porsche
Porsche
Porsche Automobil Holding SE, usually shortened to Porsche SE a Societas Europaea or European Public Company, is a German based holding company with investments in the automotive industry....
and Maserati
Maserati
Maserati is an Italian luxury car manufacturer established on December 1, 1914, in Bologna. The company's headquarters is now in Modena, and its emblem is a trident. It has been owned by the Italian car giant Fiat S.p.A. since 1993...
failed to meet CAFE requirements.
For the 2008 model year, Mercedes-Benz had the lowest fleet average while Lotus had the highest.
The effect of Energy Independence and Security Act on CAFE standards
On December 19, 2007, President George W. BushGeorge W. Bush
George Walker Bush is an American politician who served as the 43rd President of the United States, from 2001 to 2009. Before that, he was the 46th Governor of Texas, having served from 1995 to 2000....
signed the Energy Independence and Security Act. This Act aims at improving vehicle fuel economy. The Act set a goal for the national fuel economy standard of 35 miles per gallon (mpg) by 2020. This would increase the fuel economy standards by 40 percent and save the United States billions of gallons of fuel. This standard is the first standard that has been set above the Corporate Average Fuel Economy standards (CAFE) since it was created in 1975.
CAFE standards since 1975 have increased very slowly till date. In 1978, the CAFE standard for passenger cars was 18.0mpg. At the time of the signing of the Energy Independence and Security Act (EISA) in 2007, the standard for passenger cars was 27.5mpg which was the same as the standard that was set in 1990. This has been the peak standard for passenger cars. This peak standard was first set in 1985 and then it was lowered to 26mpg in 1986 and got back to the peak again in 1990. The combined standard for light trucks experienced a much more gradual increase from 17.5mpg in 1982 to 22.2mpg in 2007. The light truck Average Fuel Economy Standards for model years (MY) 2005 to 2007 were 21.0mpg for MY2005, 21.6mpg for MY2006 and 22.2mpg for MY2007.
In 2006, the rule making for light trucks for model years 2008 - 2011 included a reform to the structure for CAFE standards for light truck and gave manufacturers the option for model years 2008-2010 to comply with the reformed standard or to comply with the unreformed standard. The reformed standard was based on the vehicle foot print. The unreformed standard for 2008 was set to be 22.5mpg.
To achieve the target of 35mpg authorized under EISA for the combined fleet of passenger cars and light truck for MY2020, NHTSA is required to continue raising the CAFE standards.In determining a new CAFE standard, NHTSA must assess the environmental impacts of each new standard and the effect of this standard on employment. With the EISA, NHTSA needed to take new analysis including taking a fresh look at the potential impacts under the National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) and assessing whether or not the impacts are significant within the meaning of NEPA.
NHTSA has to issue its new standards eighteen months before the model year for fleet. According to NHTSA report, in order to achieve this industry wide combined fleet of at least 35mpg, NHTSA must set new standards well in advance of the model year so as to provide the automobile manufacturers with lead time enough to make extensive necessary changes in their automobiles. The EISA also called for a reform where the standards set by the Transportation Department would be are “attribute based” so as to ensure that the safety of vehicles is not compromised for higher standards.
New CAFE credit trading provisions
CAFE changes enacted by the 110th Congress (The Energy Independence and Security Act P.L. 110-140, H.R. 6), instructed NHTSA to establish a credit trading and transferring scheme to allow manufacturers to transfer credits between categories, as well as sell them to other manufacturers or non-manufacturers. In addition, the period over which credits could be carried forward was extended from three years to five. Traded or transferred credits may not be used to meet the minimum standard in the domestic passenger car fleet, however they may be used to meet the `attribute standard'. This latter allowance has drawn criticism from the UAW which fears it will lead manufacturers to increase the importation of small cars to offset shortfalls in the domestic market.These new flexibilities were implemented by regulation on March 23, 2009 in the Final Rule for 2011 Model Year Passenger Cars and Light Trucks.
Calculations using official CAFE data, and the newly proposed credit trading flexibility contained in the September 28, 2009 Notice of Proposed Rulemaking show that ninety-eight percent of the benefit derived from just the cross fleet credit trading provision flows to Toyota. According to these calculations 75% of the benefit from the two new CAFE credit trading provisions, cross fleet trading and 5-year carry-forward, falls to foreign manufacturers. Toyota can use the provision to avoid or reduce compliance on average by 0.69 mpg per year through 2020,
- Hyundai (1.01 mpg),
- Nissan (0.65),
- Honda (0.83 mpg),
- Mitsubishi (0.13 mpg),
- Subaru (0.08),
- Chrysler (0.14 mpg),
- GM (0.09 mpg), and
- Ford (0.18 mpg) also benefit.
The estimated value of the CAFE exemption gained by Toyota is $2.5 billion; Honda’s benefit is worth $0.8 billion, and Nissan’s benefit is valued at $0.9 billion in reduced CAFE compliance costs. Foreign companies gained $5.5 billion in benefits compared with the $1.8 billion that went to the Detroit Three.
Future

Pickup truck
A pickup truck is a light motor vehicle with an open-top rear cargo area .-Definition:...
s and cargo
Cargo
Cargo is goods or produce transported, generally for commercial gain, by ship, aircraft, train, van or truck. In modern times, containers are used in most intermodal long-haul cargo transport.-Marine:...
van
Van
A van is a kind of vehicle used for transporting goods or groups of people.In British English usage, it can be either specially designed or based on a saloon or sedan car, the latter type often including derivatives with open backs...
s over 8500 pounds gross vehicle weight rating (GVWR) would have remained exempt.
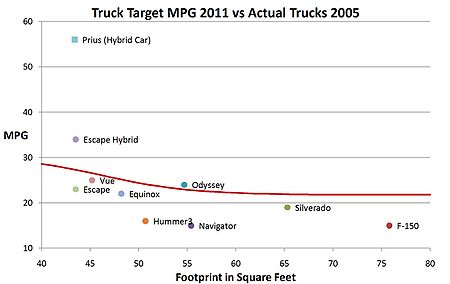
Under the new final light truck CAFE standard 2008-2011, fuel economy standards would have been restructured so that they are based on a measure of vehicle size called "footprint," the product of multiplying a vehicle's wheelbase by its track width. A target level of fuel economy would have been established for each increment in footprint using a continuous mathematical formula. Smaller footprint light trucks had higher fuel economy targets and larger trucks lower targets. Manufacturers who made more large trucks would have been allowed to meet a lower overall CAFE target, manufacturers who make more small trucks would have needed to meet a higher standard. Unlike previous CAFE standards there was no requirement for a manufacturer or the industry as a whole to meet any particular overall actual MPG target, since that will depend on the mix of sizes of trucks manufactured and ultimately purchased by consumers. Some critics pointed out that this might have had the unintended consequence
Unintended consequence
In the social sciences, unintended consequences are outcomes that are not the outcomes intended by a purposeful action. The concept has long existed but was named and popularised in the 20th century by American sociologist Robert K. Merton...
of pushing manufacturers to make ever-larger vehicles to avoid strict economy standards. However, the equation used to calculate the fuel economy target had a built in mechanism that provides an incentive to reduce vehicle size to about 52 square feet (the approximate midpoint of the current light truck fleet.)
The Ninth Circuit Court of Appeals found these new Light Truck rules to be arbitrary and capricious; contrary to the Energy Policy and Conservation Act; incorrectly set a value of zero dollars to the global warming damage caused by truck emissions; failed to set a "backstop" to prevent trucks from emitting more CO2 than in previous years; failed to set standards for vehicles in the 8,500 to 10000 lb (4,535.9 kg) range; that the environmental impact assessment was inadequate, and that the rules may have had significant negative impact on the environment. The court directed NHTSA to prepare a new standard as quickly as possible and to fully evaluate that new standard's impact on the environment.
In addition to the new light truck rules of 2006 and the Ninth Court decision, in December 2007 Congress passed the Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 is an Act of Congress concerning the energy policy of the United States...
which will affect CAFE standards of both cars and trucks and additionally work trucks and medium and heavy duty on-highway vehicles. This standard requires ratable increases in fuel efficiency during the model years 2011 to 2020 reaching 35 mpg in 2020 for the total fleet of passenger and non-passenger automobiles. In the years 2021 to 2030 the standards requires MPG to be the "maximum feasible" fuel economy. The law allows NHTSA to issue additional requirements for cars and trucks based on the "footprint" model or other mathematical standard. Additionally each manufacturer must meet a minimum standard of the higher of either 27.5 mpg for passenger automobiles or 92% of the projected average for all manufacturers. National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is an agency of the Executive Branch of the U.S. government, part of the Department of Transportation...
(NHTSA) is directed based on National Academy of Sciences
United States National Academy of Sciences
The National Academy of Sciences is a corporation in the United States whose members serve pro bono as "advisers to the nation on science, engineering, and medicine." As a national academy, new members of the organization are elected annually by current members, based on their distinguished and...
studies to set medium and heavy-duty truck MPG standards to the "maximum feasible". Additionally the law phases out the mpg credit previously granted to E85
E85
E85 is an abbreviation for an ethanol fuel blend of up to 85% denatured ethanol fuel and gasoline or other hydrocarbon by volume. E85 is commonly used by flex-fuel vehicles in the US, Canada, and Europe. Some of the benefits of E85 over conventional gasoline powered vehicles include the potential...
flexible-fuel vehicle
Flexible-fuel vehicle
A flexible-fuel vehicle or dual-fuel vehicle is an alternative fuel vehicle with an internal combustion engine designed to run on more than one fuel, usually gasoline blended with either ethanol or methanol fuel, and both fuels are stored in the same common tank...
manufacturers and adds in one for biodiesel
Biodiesel
Biodiesel refers to a vegetable oil- or animal fat-based diesel fuel consisting of long-chain alkyl esters. Biodiesel is typically made by chemically reacting lipids with an alcohol....
, and it adds a requirement that NHTSA publish replacement tire fuel efficiency ratings. The bill also adds support for initial state and local infrastructure for plug-in electric vehicles. How the Ninth Court decision will be reconciled to this new law remains undecided, but if the court issue is resolved and the new law goes into effect and if actual achieved combined corporate CAFE remains at 26.7 mpg until then, then average fleet-wide new vehicle mpg would increase by 0.8 mpg a year starting in 2011.
On April 22, 2008 NHTSA responded to this Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007
The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 is an Act of Congress concerning the energy policy of the United States...
with proposed new fuel economy standards for cars and trucks effective model year 2011. It is not clear how the 9th Circuit Court of Appeals case will interact with these new rules. The new rules also introduce the "footprint" model for cars as well as trucks, where if a manufacturer makes more large cars and trucks they will be allowed to meet a lower standard for fuel economy. This means that an overall fuel efficiency for a particular manufacturer nor the fleet as a whole cannot be predicted with certainly since it will depend on the actual product mix manufactured. However, if the product mix is as NHTSA predicts, car fuel economy would increase from a current standard of 27.5 mpgU.S. (11.7 km/L) to 31 mpgU.S. (13.2 km/L) in 2011. The new regulations are designed to be "optimized" with respect to a certain set of assumptions which include: gas prices in 2016 will be $2.25 a U.S. gallon (59.4¢/L), all new car purchasers will pay 7% interest rates on their vehicles purchases, and only care about fuel costs for the first 5 years of a vehicle's life, and that the value of global warming is $7 per ton CO2. This corresponds to a global warming
Global warming
Global warming refers to the rising average temperature of Earth's atmosphere and oceans and its projected continuation. In the last 100 years, Earth's average surface temperature increased by about with about two thirds of the increase occurring over just the last three decades...
value of $4.31 savings a year per car under the new regulations. Further, the new regulations assume that no advanced hybrids
Hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
(Toyota Prius
Toyota Prius
The Toyota Prius is a full hybrid electric mid-size hatchback, formerly a compact sedan developed and manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation...
), plug-in hybrids and extended range electric vehicles (Chevrolet Volt
Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by General Motors. The Volt has been on sale in the U.S. market since mid-December 2010, and is the most fuel-efficient compact car sold in the United States, as rated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency...
), electric car
Electric car
An electric car is an automobile which is propelled by electric motor, using electrical energy stored in batteries or another energy storage device. Electric cars were popular in the late-19th century and early 20th century, until advances in internal combustion engine technology and mass...
s (Th!nk City
Th!nk City
The Th!nk City is a small two-seater or 2+2-seater highway capable electric car produced by Think Global and production partner Valmet Automotive, with a top speed of and an all-electric range of on a full charge....
), nor alternative fuel vehicles (Honda Civic GX
Honda Civic GX
The Honda Civic GX is a passenger car factory-built to run on compressed natural gas . The GX is based on the Honda Civic and is available for fleet sales in all 50 states in the US...
) will be used to achieve these fuel economies. The new rules also propose again that California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
(and the other States following California's lead) be stripped of their historic right to set their own more stringent automotive air pollution standards.
On January 26, 2009, President Barack Obama directed the Department of Transportation to review relevant legal, technological, and scientific considerations associated with establishing more stringent fuel economy standards, and to finalize the 2011 model year standard by the end of March. This single-model year standard was issued March 27, 2009 and is about one mpg lower than the fuel economy standards previously recommended under the Bush Administration. "These standards are important steps in the nation's quest to achieve energy independence and bring more fuel efficient vehicles to American families," said Secretary LaHood. The new standards will raise the industry-wide combined average to 27.3 miles per US gallon (11.6 km/L) (a 2 miles per US gallon increase over the 2010 model year average), as estimated by the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). It will save about 887000000 U.S.gal of fuel and reduce carbon dioxide emissions by 8.3 million metric tons. This 2011 single-year standard will use an attribute-based system, which sets fuel economy standards for individual vehicle models, based on the "footprint" model. Secretary LaHood also noted that work on the multi-year fuel economy plan for model years after 2011 is already well underway. The review will include an evaluation of fuel saving technologies, market conditions and future product plans from the manufacturers. The effort will be coordinated with interested stakeholders and other federal agencies, including the Environmental Protection Agency. The news rules were immediately challenged in court again by the Center for Biological Diversity as not addressing the inadequacies found by the previous court rulings. The interaction between these future rules, the collapse of the auto industry in the United States, the listing by EPA on March 20, 2009 of CO2 as a global warming pollution dangerous to human welfare, and the willingness indicated by environmental groups to apply once again to the courts for a ruling that these standards are inadequate, again left the future of fuel economy standards in the United States in doubt.
On May 19, 2009 President Barack Obama
Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II is the 44th and current President of the United States. He is the first African American to hold the office. Obama previously served as a United States Senator from Illinois, from January 2005 until he resigned following his victory in the 2008 presidential election.Born in...
proposed a new national fuel economy program which adopts uniform federal standards to regulate both fuel economy and greenhouse gas emissions while preserving the legal authorities of DOT, EPA and California. The program covers model year 2012 to model year 2016 and ultimately requires an average fuel economy standard of 35.5 mpgus in 2016 (of 39 miles per gallon for cars and 30 mpg for trucks), a jump from the current average for all vehicles of 25 miles per gallon. Obama said, "The status quo
Status quo
Statu quo, a commonly used form of the original Latin "statu quo" – literally "the state in which" – is a Latin term meaning the current or existing state of affairs. To maintain the status quo is to keep the things the way they presently are...
is no longer acceptable." The result is a projected reduction in oil consumption of approximately 1.8 Goilbbl over the life of the program and a projected total reduction in greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions of approximately 900 million metric tons. Ten car companies and the UAW embraced the national program because it provides certainty and predictability to 2016 and includes flexibilities that will significantly reduce the cost of compliance. Stated goals for the program included: saving consumers money over the long term in increased fuel efficiency, preserving consumer choice—the new rules do not dictate the size of cars, trucks and SUVs that manufacturers can produce; rather it requires that all sizes of vehicles become more energy efficient, reduced air pollution in the form of greenhouse gas emissions and other conventional pollutants, one national policy for all automakers, instead of three standards (a DOT standard, an EPA standard and a California standard that would apply to 13 other states), and industry desires: clarity, predictability and certainty concerning the rules while giving them flexibility on how to meet the expected outcomes and the lead time they need to innovate. The new policy will result in yearly 5% increases in efficiency from 2012 through 2016, 1.8 Goilbbl of oil saved cumulatively over the lifetime of the program and significant reductions in greenhouse gas emissions equivalent to taking 177 million of today's cars off the road.
There are a large number of technologies that manufacturers can apply to improve fuel efficiency short of implementing hybrid
Hybrid electric vehicle
A hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
or plug-in hybrid technologies. Applied aggressively, at a cost of several thousand dollars per vehicle, the Union of Concerned Scientists
Union of Concerned Scientists
The Union of Concerned Scientists is a nonprofit science advocacy group based in the United States. The UCS membership includes many private citizens in addition to professional scientists. James J...
estimates that these technologies can almost double MPG.
Some technologies, such as four valves per cylinder, are already widely applied in cars, but not trucks. Manufacturers dispute how effective these technologies are, their retail price, and how willing customers are to pay for these improvements. Payback
Payback
Payback may refer to:*Payback period, the period of time required for the return on an investment*Revenge*Operation Payback, an ongoing hacker operation*Payback , a 1999 film, starring Mel Gibson; remake of the 1967 film Point Blank...
on these improvements is highly dependent on fuel prices.
On July 29, 2011 President Obama announced a historic agreement with thirteen major automakers to pursue the next phase in the Administration’s national vehicle program, increasing fuel economy to 54.5 miles per gallon for cars and light-duty trucks by Model Year 2025. The President was joined by Ford, GM, Chrysler, BMW, Honda, Hyundai, Jaguar/Land Rover, Kia, Mazda, Mitsubishi, Nissan, Toyota and Volvo – which together account for over 90% of all vehicles sold in the United States – as well as the United Auto Workers (UAW), and the State of California, who were integral to developing this agreement.
| Model Year | Passenger Cars | Light Trucks | ||||||
| "footprint": 41 sq ft (3.8 m²) or smaller (e.g. 2011 Honda Fit) | "footprint": 55 sq ft (5.1 m²) or bigger (e.g. Mercedes-Benz S-Class) | "footprint": 41 sq ft (3.8 m²) or smaller (e.g. Nissan Juke) | "footprint": 75 sq ft (7 m²) or bigger (e.g. Ford F-150) | |||||
| CAFE | EPA Window Sticker | CAFE | EPA Window Sticker | CAFE | EPA Window Sticker | CAFE | EPA Window Sticker | |
| 2012 | 36 | 27 | 28 | 21 | 30 | 23 | 22 | 17 |
| 2013 | 37 | 28 | 28.5 | 22 | 31 | 24 | 22.5 | 17 |
| 2014 | 38 | 28 | 29 | 22 | 32 | 24 | 23 | 18 |
| 2015 | 39 | 29 | 30 | 23 | 33 | 25 | 23.5 | 18 |
| 2016 | 41 | 31 | 31 | 24 | 34 | 26 | 24.5 | 19 |
| 2017 | 44 | 33 | 33 | 25 | 36 | 27 | 25 | 19 |
| 2018 | 45 | 34 | 34 | 26 | 37 | 28 | 25 | 19 |
| 2019 | 47 | 35 | 35 | 26 | 38 | 28 | 25 | 19 |
| 2020 | 49 | 36 | 36 | 27 | 39 | 29 | 25 | 19 |
| 2021 | 51 | 37 | 38 | 28 | 42 | 31 | 25 | 19 |
| 2022 | 53 | 38 | 40 | 30 | 44 | 33 | 26 | 20 |
| 2023 | 56 | 40 | 42 | 31 | 46 | 34 | 27 | 21 |
| 2024 | 58 | 41 | 44 | 33 | 48 | 36 | 28.5 | 22 |
| 2025 | 61 | 43 | 46 | 34 | 50 | 37 | 30 | 23 |
Volkswagen responded to July 29, 2011 agreement with the following statement:
"Volkswagen does not endorse the proposal under discussion. It places an unfairly high burden on passenger cars, while allowing special compliance flexibility for heavier light trucks. Passenger cars would be required to achieve 5% annual improvements, and light trucks 3.5% annual improvements. The largest trucks carry almost no burden for the 2017-2020 timeframe, and are granted numerous ways to mathematically meet targets in the outlying years without significant real-world gains.
The proposal encourages manufacturers and customers to shift toward larger, less efficient vehicles, defeating the goal of reduced greenhouse gas emissions."
Active debate
CAFE does not directly offer incentives for customers to choose fuel efficient vehicles, nor does it directly affect fuel prices. Rather, it attempts to accomplish these goals indirectly by making it more expensive for automakers to build inefficient vehicles by introducing penalties.The conservative Heartland Institute
Heartland Institute
The Heartland Institute is a libertarian, American public policy think tank based in Chicago, Illinois which advocates free market policies. The Institute is designated as a 501 non-profit by the Internal Revenue Service and advised by a 15 member board of directors, which meets quarterly. As of...
contends that CAFE standards do not work economically to consumers' benefit, that smaller cars are more likely to be damaged in a collision, and that insurance
Insurance
In law and economics, insurance is a form of risk management primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent, uncertain loss. Insurance is defined as the equitable transfer of the risk of a loss, from one entity to another, in exchange for payment. An insurer is a company selling the...
premiums for them are higher than for many larger cars. However, the Insurance Companies' Highway Loss Data Institute publishes data showing that larger vehicles are more expensive to insure.
CAFE advocates assert most of the gains in fuel economy over the past 30 years can be attributed to the standard itself, while opponents assert economic forces are responsible for fuel economy gains, where higher fuel prices drove customers to seek more fuel efficient vehicles. CAFE standards have come under attack by some conservative
Conservatism
Conservatism is a political and social philosophy that promotes the maintenance of traditional institutions and supports, at the most, minimal and gradual change in society. Some conservatives seek to preserve things as they are, emphasizing stability and continuity, while others oppose modernism...
think tanks, along with safety experts, car and truck manufacturers, some consumer and environment groups, and organized labor.
Effect on traffic safety
Historically, NHTSA has expressed concerns that automotive manufacturers will increase mileage by reducing vehicle weight, which might lead to weight disparities in the vehicle population and increased danger for occupants of lighter vehicles. However, vehicle safety ratings are now made available to consumers by NHTSA and by the Insurance Institute for Highway Safety. A National Research CouncilUnited States National Research Council
The National Research Council of the USA is the working arm of the United States National Academies, carrying out most of the studies done in their names.The National Academies include:* National Academy of Sciences...
report found that the standards implemented in the 1970s and 1980s "probably resulted in an additional 1,300 to 2,600 traffic fatalities in 1993. A Harvard Center for Risk Analysis study found that CAFE standards led to "2,200 to 3,900 additional fatalities to motorists per year. The Insurance Institute for Highway Safety's 2007 data show a correlation of about 250-500 fatalities per year per MPG. Proponents of higher CAFE standards argue that it is the "Footprint" model of CAFE for trucks that encourages production of larger trucks with concomitant increases in vehicle weight disparities, and point out that some small cars such as the Mini Cooper and Toyota Matrix
Toyota Matrix
The Toyota Matrix, sometimes officially referred to as the Toyota Corolla Matrix, is a compact hatchback manufactured by the Toyota Motor Corporation in Canada, to be sold in the United States, Canada, and Mexico...
are four times safer than SUVs like the Chevy Blazer. They argue that the quality of the engineering design is the prime determinant of vehicular safety, not the vehicle's mass. In a 1999 article based on a 1995 IIHS report, USA Today
USA Today
USA Today is a national American daily newspaper published by the Gannett Company. It was founded by Al Neuharth. The newspaper vies with The Wall Street Journal for the position of having the widest circulation of any newspaper in the United States, something it previously held since 2003...
said that 56% of all deaths occurring in small cars were due to either single vehicle crashes or small cars impacting each other. The percentage of deaths attributed to those in small cars being hit by larger cars was one percent. In 2006, IIHS found that some of the smallest cars have good crash safety, while others do not, depending upon the engineering design. In a 2007 analysis, IIHS found that 50 percent of fatalities in small four-door vehicles were single vehicle crashes, compared to 83 percent in very large SUVs. The Mini Cooper had a fatality rate of 68 per million vehicle-years, compared to 115 for the Ford Excursion. A 2005 IIHS plot shows that in collisions between SUVs weighing 3500 lb (1,587.6 kg) and cars, the car driver is more than 4X more likely to be killed, and if the SUV weighs over 5000 lb (2,268 kg) the car driver is 9 times more likely to be killed, with 16 percent of deaths occurring in car-to-car crashes and 18 percent in car-to-truck crashes. Recent studies find about 75 percent of two-vehicle fatalities involve a truck, and about half these fatalities involve a side-impact crash. Risk to the driver of the other vehicle is almost 10 times higher when the vehicle is a one ton
Ton
The ton is a unit of measure. It has a long history and has acquired a number of meanings and uses over the years. It is used principally as a unit of weight, and as a unit of volume. It can also be used as a measure of energy, for truck classification, or as a colloquial term.It is derived from...
pickup compared to an imported car. And a 2003 Transportation Research Board
Transportation Research Board
The Transportation Research Board is a division of the National Research Council, which serves as an independent adviser to the President, the Congress and federal agencies on scientific and technical questions of national importance...
study show greater safety disparities among vehicles of differing price, country of origin, and quality than among vehicles of different size and weight. These more recent studies tend to discount the importance of vehicle mass to traffic safety, pointing instead to the quality of engineering design as the primary factor.
Increased oil and automobile usage
As fuel efficiency rises, people drive their cars more, which can mitigate some of the gains in carbon dioxide emissions from the higher standards. According to the National Academies Report (Page 19) a 10% improvement in fuel efficiency leads to an average increase in travel distance of 1-2%. This phenomenon is referred to as the "rebound effect". The report stated (page 20) that the fuel efficiency improvements of light-duty vehicles have reduced the overall U.S. emissions of CO2 by 7%.It is also possible that because higher-efficiency vehicles are more expensive, auto buyers may choose to keep their older cars (some of which are less efficient) for longer before making a new purchase.
However, associated costs, such as increased deaths, may be more than offset by savings on a global scale, because increased CAFE standards reduce reliance on increasingly expensive and unreliable sources of imported petroleum and lower the probability of global climate change by reducing US emissions of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
.
Economic arguments
In the May 6, 2007 edition of Autoline Detroit, Bob Lutz, an automobile designer/executive of BMWBMW
Bayerische Motoren Werke AG is a German automobile, motorcycle and engine manufacturing company founded in 1916. It also owns and produces the Mini marque, and is the parent company of Rolls-Royce Motor Cars. BMW produces motorcycles under BMW Motorrad and Husqvarna brands...
and Big Three fame, asserted that the CAFE standard was a failure and said it was like trying to fight obesity
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition in which excess body fat has accumulated to the extent that it may have an adverse effect on health, leading to reduced life expectancy and/or increased health problems...
by requiring tailors to make only small-sized clothes.
Proponents state that automobile-purchasing decisions that may have global effects should not be left entirely up to individuals operating in a free market.
Automakers have said that small, fuel-efficient vehicles cost the auto industry billions of dollars. They cost almost as much to design and market but cannot be sold for as much as larger vehicles such as SUVs, because consumers expect small cars to be inexpensive. In 1999 USA Today reported small cars tend to depreciate
Depreciation
Depreciation refers to two very different but related concepts:# the decrease in value of assets , and# the allocation of the cost of assets to periods in which the assets are used ....
faster than larger cars, so they are worth less in value to the consumer over time. However, 2007 Edmunds depreciation data show that some small cars, primarily premium models, are among the best in holding their value.
Automaker viewpoints & consumer preferences
Historically, automakers and some conservative groups have believed consumers do not prioritize fuel economy. In 2003, Alliance of Automobile ManufacturersAlliance of Automobile Manufacturers
The Alliance of Automobile Manufacturers is a trade group of automobile manufacturers that operate in the United States. Their mission is to "represent the common interests of its members and provide a forum to enable them to advance public policies that meet consumer and societal needs for clean,...
spokesman Eron Shosteck asserted automakers produce more than 30 models rated at 30 mpg or more for the US market, and they are poor sellers. In 2004, GM retiree Charles Amann said statistically, consumers do not pick the weak-performing vehicle when given a choice of engines. However, after a spike in gas prices, a 2006 Consumer Reports
Consumer Reports
Consumer Reports is an American magazine published monthly by Consumers Union since 1936. It publishes reviews and comparisons of consumer products and services based on reporting and results from its in-house testing laboratory. It also publishes cleaning and general buying guides...
survey concluded fuel economy is the most important consideration in consumers' choice of vehicle and a 2007 Pew Charitable Trusts survey found that nine out of ten Americans favor tougher CAFE standards, including 91% of Democrats and 85% of Republicans. In 2007, the 55 mpg Toyota Prius outsold the top-selling SUV, the 17 mpg Ford Explorer. In late 2007, GM Vice Chairman Bob Lutz called hybrid gasoline-electric vehicles the "ideal solution". In 2008, GM advertised fuel economy improvements and their upcoming Chevrolet Volt
Chevrolet Volt
The Chevrolet Volt is a plug-in hybrid electric vehicle manufactured by General Motors. The Volt has been on sale in the U.S. market since mid-December 2010, and is the most fuel-efficient compact car sold in the United States, as rated by the United States Environmental Protection Agency...
Extended Range Electric Vehicle, and developed corporate branding for their fuel economy technologies, and though GM Chairman Rick Wagoner admitted he doesn't know which fuel efficiency technologies consumers really want he said
"we are moving fast with technologies like E-85 (ethanol), all-electric, fuel cells and a wide range of hybrid offers."
In 1999, automakers asserted they couldn't lobby for the repeal of CAFE standards, because consumers would learn small cars are unsafe and not buy them, or would try to sue the manufacturers. However, NHTSA's public record shows the automakers publicly express opposition to CAFE increases.
SUVs and minivans created due to original mandate
The definitions for cars and trucks are not the same for fuel economy and emission standards. For example, a Chrysler PT Cruiser is defined as a car for emissions purposes and a truck for fuel economy purposes. Under the current light truck fuel economy rules, the PT Cruiser will have a higher fuel economy target (28.05 mpg beginning in 2011) than it would if it were classified as a passenger car. CAFE standards signaled the end of the traditional long station wagonStation wagon
A station wagon is a body style variant of a sedan/saloon with its roof extended rearward over a shared passenger/cargo volume with access at the back via a third or fifth door , instead of a trunk lid...
, but legendary former Chrysler
Chrysler
Chrysler Group LLC is a multinational automaker headquartered in Auburn Hills, Michigan, USA. Chrysler was first organized as the Chrysler Corporation in 1925....
CEO Lee Iacocca
Lee Iacocca
Lido Anthony "Lee" Iacocca is an American businessman known for engineering the Mustang, the unsuccessful Ford Pinto, being fired from Ford Motor Company, and his revival of the Chrysler Corporation in the 1980s...
developed the idea of marketing the minivan
Minivan
Minivan is a type of van designed for personal use. Minivans are typically either two-box or one box designs for maximum interior volume – and are taller than a sedan, hatchback, or a station wagon....
as a station wagon alternative, while certifying it in the separate truck category to allow compliance with less-strict emissions standards. Eventually, this same idea led to the promotion of the SUV.
New York
New York
New York is a state in the Northeastern region of the United States. It is the nation's third most populous state. New York is bordered by New Jersey and Pennsylvania to the south, and by Connecticut, Massachusetts and Vermont to the east...
, New Jersey
New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Northeastern and Middle Atlantic regions of the United States. , its population was 8,791,894. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York, on the southeast and south by the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Pennsylvania and on the southwest by Delaware...
, Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania
The Commonwealth of Pennsylvania is a U.S. state that is located in the Northeastern and Mid-Atlantic regions of the United States. The state borders Delaware and Maryland to the south, West Virginia to the southwest, Ohio to the west, New York and Ontario, Canada, to the north, and New Jersey to...
, Connecticut
Connecticut
Connecticut is a state in the New England region of the northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, and the state of New York to the west and the south .Connecticut is named for the Connecticut River, the major U.S. river that approximately...
and California
California
California is a state located on the West Coast of the United States. It is by far the most populous U.S. state, and the third-largest by land area...
disagreed with the NHTSA statement in the 2008-2011 Light Truck standard which claimed preemption of the state greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
regulations, on the basis that fuel economy and carbon dioxide emissions are one and the same. The EPA claims, contrary to NHTSA, that the use of alternative fuels allows greenhouse gas
Greenhouse gas
A greenhouse gas is a gas in an atmosphere that absorbs and emits radiation within the thermal infrared range. This process is the fundamental cause of the greenhouse effect. The primary greenhouse gases in the Earth's atmosphere are water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, and ozone...
emissions to be controlled somewhat independently of fuel efficiency.
Calculations of MPG overestimated
The United States Environmental Protection AgencyUnited States Environmental Protection Agency
The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
(EPA) laboratory measurements of MPG have consistently overestimated fuel economy of gasoline vehicles and underestimated diesel vehicles. John DeCicco, the automotive expert for the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF), estimated that this results in about 20% higher actual consumption than measured CAFE goals. Starting with 2008-model vehicles, the EPA has adopted a new protocol for estimating the MPG figures presented to consumers. The new protocol includes driving cycles more closely representative of today's traffic and road conditions, as well as increased air conditioner usage. This change does not affect how the EPA calculates CAFE ratings; the new protocol changes only the mileage estimates provided for consumer information.
NHTSA spends one-third of one percent of its budget on CAFE, or $0.014 per US citizen.
Low Penalty
Some critics argue that CAFE fines do not seem to be having much impact in the fuel economy drive.As noted in the 2007 United States Government Accountability Office Report to the Chairman of the U.S. Senate Committee on Commerce, Science, and Transportation (page 23) "Several experts stated that this is (penalties) not enough of a monetary incentive for manufacturers to comply with CAFE."
For example, in 25 years from 1983 to 2008 Mercedes-Benz paid penalties 21 times and BMW paid penalties 20 times.
Currently CAFE penalty is $55 USD per vehicle for every 1 mpg under the standard. For the year 2006 Mercedes-Benz draw $30.3 million penalty for violating fuel economy standards. That equates to $122 per one sold vehicle (in 2006 Mercedes-Benz sales were 248,080 vehicles)
A penalty of $122 means violating CAFE by 2.22 MPG ($122 divided by $55). According to the government "fueleconomy.gov" website violating CAFE by 2.42 MPG means consuming extra 27 barrels (4.3 m³) (1134 gallons (4,292.7 l)) of mostly imported fuel in 10 years which is worth $3,490 (Based on 45% highway, 55% city driving, 15000 annual miles and a fuel price of $ 2.95 per gallon) that is 13.4% more and also it means emitting extra 14 Tons of CO2 in 10 years that is 12.7% more. These numbers are based on comparison of 2010 Mercedes ML 350 4MATIC with CAFE Unadjusted Average Fuel Economy of 21.64 MPG (this model meets 2006 CAFE requirements of 21.6 MPG) and 2010 Mercedes ML 550 4MATIC with CAFE Unadjusted Average Fuel Economy of 19.22 MPG. So consuming extra $3,490 worth of mostly imported fuel and emitting extra 14 Tons of CO2 draws a penalty of only $122 for a single luxury car buyer. $122 is only 0.3% of the price of $40,000 car (average 2010 price of a luxury car). Several experts stated that this is not enough of a monetary incentive to comply with CAFE.
CAFE penalty have increased only 10% since 1983. At the same time cumulative inflation from 1983 to 2010 was 119.2%. It means that CAFE penalty in 2010 is actually 2 times less than what it was in 1983. NHTSA officials stated that, in addition to the authority the Federal Civil Penalties Inflation Adjustment Act of 1990 under EPCA, NHTSA has the authority to raise CAFE penalties to $100 per 1 mpg shortfall. NHTSA chooses not to exercise this authority.
Other arguments in favor
Other conservative groups support higher gas mileage on the basis of national security, or on the basis of stewardship of the Earth.See also
- Air pollutionAir pollutionAir pollution is the introduction of chemicals, particulate matter, or biological materials that cause harm or discomfort to humans or other living organisms, or cause damage to the natural environment or built environment, into the atmosphere....
- Battery electric vehicleBattery electric vehicleA battery electric vehicle, or BEV, is a type of electric vehicle that uses chemical energy stored in rechargeable battery packs. BEVs use electric motors and motor controllers instead of, or in addition to, internal combustion engines for propulsion.A battery-only electric vehicle or...
- California Air Resources BoardCalifornia Air Resources BoardThe California Air Resources Board, also known as CARB or ARB, is the "clean air agency" in the government of California. Established in 1967 in the Mulford-Carrell Act, combining the Bureau of Air Sanitation and the Motor Vehicle Pollution Control Board, CARB is a department within the...
- Carbon taxCarbon taxA carbon tax is an environmental tax levied on the carbon content of fuels. It is a form of carbon pricing. Carbon is present in every hydrocarbon fuel and is released as carbon dioxide when they are burnt. In contrast, non-combustion energy sources—wind, sunlight, hydropower, and nuclear—do not...
- Emission standardEmission standardEmission standards are requirements that set specific limits to the amount of pollutants that can be released into the environment. Many emissions standards focus on regulating pollutants released by automobiles and other powered vehicles but they can also regulate emissions from industry, power...
- Energy Independence and Security Act
- Range-extended vehicle
- Fuel efficiencyFuel efficiencyFuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the efficiency of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier fuel into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device, which in turn may vary per application, and this spectrum of variance is...
- Fuel economy in automobilesFuel economy in automobilesFuel usage in automobiles refers to the fuel efficiency relationship between distance traveled by an automobile and the amount of fuel consumed....
- Hybrid electric vehicleHybrid electric vehicleA hybrid electric vehicle is a type of hybrid vehicle and electric vehicle which combines a conventional internal combustion engine propulsion system with an electric propulsion system. The presence of the electric powertrain is intended to achieve either better fuel economy than a conventional...
- Light truckLight truckLight truck or light duty truck is a U.S. classification for trucks or truck-based vehicles with a payload capacity of less than 4,000 pounds...
- Miles per gallon
- Miles per gallon gasoline equivalentMiles per gallon gasoline equivalentMiles per gallon gasoline equivalent is a measure of the average distance traveled per unit of energy consumed. MPGe is used by the U.S...
- National Highway Traffic Safety AdministrationNational Highway Traffic Safety AdministrationThe National Highway Traffic Safety Administration is an agency of the Executive Branch of the U.S. government, part of the Department of Transportation...
- Plug-in hybrid
- Road-traffic safetyRoad-traffic safetyThe term road traffic safety is about the risk of a person being killed or seriously injured while using the road network as a pedestrian, cyclist, motorist or user of on road public transport...
- United States Environmental Protection AgencyUnited States Environmental Protection AgencyThe U.S. Environmental Protection Agency is an agency of the federal government of the United States charged with protecting human health and the environment, by writing and enforcing regulations based on laws passed by Congress...
External links
- 49 U.S.C. Chapter 329 - Automobile Fuel Economy (2009) CAFE legislation on U.S. House of Representatives Downloadable U.S. Code (.txt)
- NHTSA: CAFE Overview
- NHTSA: Corporate Average Fuel Economy
- Light Truck Rule criticism.
- Is Bigger Safer? It Ain't Necessarily So
- Federal Proposal Would Unlink Fuel Economy Requirements From Their Safety Consequences
- Effectiveness and Impact of Corporate Average Fuel Economy (CAFE) Standards, National Academy of Sciences
- Obama's CAFE Fuel Economy Standards to Create Fleet of Tiny, Expensive Vehicles

