
Contribution margin
Encyclopedia
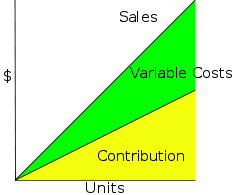
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Coon-Volume-profit , in managerial economics is a form of cost accounting. It is a simplified model, useful for elementary instruction and for short-run decisions....
, a form of management accounting
Management accounting
Management accounting or managerial accounting is concerned with the provisions and use of accounting information to managers within organizations, to provide them with the basis to make informed business decisions that will allow them to be better equipped in their management and control...
, contribution margin is the marginal profit per unit sale. It is a useful quantity in carrying out various calculations, and can be used as a measure of operating leverage
Operating leverage
The operating leverage is a measure of how revenue growth translates into growth in operating income. It is a measure of leverage, and of how risky a company's operating income is.-Definition:There are various measures of operating leverage,...
. Typically, high contribution margins are prevalent in the labour-intensive tertiary sector while low contribution margins are prevalent in the capital-intensive industrial sector.
Definition
The Unit Contribution Margin (C) is Unit Revenue (Price, P) minus Unit Variable Cost (V):
The Contribution Margin Ratio is the percentage of Contribution over Total Revenue, which can be calculated from the unit contribution over unit price or total contribution over Total Revenue:

For example, if the price is Rs10 and the unit variable cost is Rs2, then the unit contribution margin is Rs8, and the contribution margin ratio is Rs8/Rs10 = 80%.
Explanation
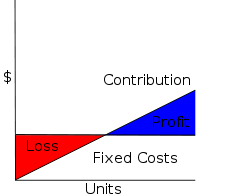
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Coon-Volume-profit , in managerial economics is a form of cost accounting. It is a simplified model, useful for elementary instruction and for short-run decisions....
(CVP): assuming the linear CVP model, the computation of Profit and Loss (Net Income
Net income
Net income is the residual income of a firm after adding total revenue and gains and subtracting all expenses and losses for the reporting period. Net income can be distributed among holders of common stock as a dividend or held by the firm as an addition to retained earnings...
) reduces as follows:

where TC = TFC + TVC is Total Cost = Total Fixed Cost + Total Variable Cost and X is Number of Units. Thus Profit is Unit Contribution times Number of Units, minus the Total Fixed Costs.
The above formula is derived as follows:
From the perspective of the matching principle
Matching principle
The matching principle is a culmination of accrual accounting and the revenue recognition principle. They both determine the accounting period, in which revenues and expenses are recognized. According to the principle, expenses are recognized when obligations are incurred The matching principle...
, one breaks down the revenue from a given sale into a part to cover the Unit Variable Cost, and a part to offset against the Total Fixed Costs. Breaking down Total Costs as:

one breaks down Total Revenue as:

Thus the Total Variable Costs
 offset, and the Net Income (Profit and Loss) is Total Contribution Margin minus Total Fixed Costs:
offset, and the Net Income (Profit and Loss) is Total Contribution Margin minus Total Fixed Costs:
Applications
Contribution arises in Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisCost-Volume-Profit Analysis
Coon-Volume-profit , in managerial economics is a form of cost accounting. It is a simplified model, useful for elementary instruction and for short-run decisions....
, where it simplifies calculation of Net Income, and especially break even analysis.
Given the contribution margin, a manager
Management
Management in all business and organizational activities is the act of getting people together to accomplish desired goals and objectives using available resources efficiently and effectively...
can easily compute breakeven
Breakeven
In economics & business, specifically cost accounting, the break-even point is the point at which cost or expenses and revenue are equal: there is no net loss or gain, and one has "broken even"...
and target income sales, and make better decisions about whether to add or subtract a product line, about how to price a product or service, and about how to structure sales commissions
Commission (remuneration)
The payment of commission as remuneration for services rendered or products sold is a common way to reward sales people. Payments often will be calculated on the basis of a percentage of the goods sold...
or bonus
Bonus
The word Bonus refers to extra pay due to good performance.Bonus may also refer to:- People :* Lawrence Bonus, a Filipino basketball player* Petrus Bonus, a physician* Bonus , a Byzantine general, active in the reign of Justin II...
es.
Contribution margin analysis is a measure of operating leverage
Operating leverage
The operating leverage is a measure of how revenue growth translates into growth in operating income. It is a measure of leverage, and of how risky a company's operating income is.-Definition:There are various measures of operating leverage,...
: it measures how growth in sales translates to growth in profits.
The contribution margin is computed by using a contribution income statement: a management accounting version of the income statement that has been reformatted to group together a business's fixed and variable costs.
Contribution is different than Gross Margin
Gross margin
Gross margin is the difference between revenue and cost before accounting for certain other costs...
in that a contribution calculation seeks to separate out variable costs (included in the contribution calculation) from fixed costs (not included in the contribution calculation) on the basis of economic analysis of the nature of the expense whereas gross margin is determined using accounting standards. Calculating the contribution margin is an excellent tool for managers to help determine whether to keep or drop certain aspects of the business. For example, a production line with positive contribution margin should be kept even it causes negative total profit, when the contribution margin offsets part of the fixed cost. However, it should be dropped if contribution margin is negative because the company would suffer from every unit it produces.
The contribution margin analysis is also applicable when the tax authority performs tax investigation, by identifying target interviewee who has unusual high contribution margin ratio then other companies in the same industry.
Contribution margin is also one of the factors to judge whether a company has monopoly power in competition law
Competition law
Competition law, known in the United States as antitrust law, is law that promotes or maintains market competition by regulating anti-competitive conduct by companies....
, such as use of the Lerner Index test.
Examples
Here's an example of a contribution format income statement:| Sales | $ 462,452 |
| Less Variable Costs Variable cost Variable costs are expenses that change in proportion to the activity of a business. Variable cost is the sum of marginal costs over all units produced. It can also be considered normal costs. Fixed costs and variable costs make up the two components of total cost. Direct Costs, however,... : |
|
| Cost of goods sold Cost of goods sold refers to the inventory costs of those goods a business has sold during a particular period. Costs are associated with particular goods using one of several formulas, including specific identification, first-in first-out , or average cost... Sales Commissions Commission (remuneration) The payment of commission as remuneration for services rendered or products sold is a common way to reward sales people. Payments often will be calculated on the basis of a percentage of the goods sold... Delivery Charges |
$ 230,934 $ 58,852 $ 13,984 |
| Total Variable Costs | $ 303,770 |
| Contribution Margin (34%) | $ 158,682 |
| Less Fixed Costs Fixed cost In economics, fixed costs are business expenses that are not dependent on the level of goods or services produced by the business. They tend to be time-related, such as salaries or rents being paid per month, and are often referred to as overhead costs... : |
|
| Advertising Advertising is a form of communication used to persuade an audience to take some action with respect to products, ideas, or services. Most commonly, the desired result is to drive consumer behavior with respect to a commercial offering, although political and ideological advertising is also common... Depreciation Depreciation Depreciation refers to two very different but related concepts:# the decrease in value of assets , and# the allocation of the cost of assets to periods in which the assets are used .... Insurance Insurance In law and economics, insurance is a form of risk management primarily used to hedge against the risk of a contingent, uncertain loss. Insurance is defined as the equitable transfer of the risk of a loss, from one entity to another, in exchange for payment. An insurer is a company selling the... Payroll Payroll In a company, payroll is the sum of all financial records of salaries for an employee, wages, bonuses and deductions. In accounting, payroll refers to the amount paid to employees for services they provided during a certain period of time. Payroll plays a major role in a company for several reasons... Taxes Rent Utilities Wages |
$ 1,850 $ 13,250 $ 5,400 $ 8,200 $ 9,600 $ 17,801 $ 40,000 |
| Total Fixed Costs | $ 96,101 |
| Net Operating Income | $ 62,581 |
The Beta Company's contribution margin for the year was 34 percent. This means that, for every dollar of sales, after the costs that were directly related to the sales were subtracted, 34 cents remained to contribute toward paying for the indirect costs and for profit.
Contribution format income statements can be drawn up with data from more than one year's income statements, when a person is interested in tracking contribution margins over time. Perhaps even more usefully, they can be drawn up for each product line or service. Here's an example, showing a breakdown of Beta's three main product lines:
| Line A | Line B | Line C | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | $120,400 | $202,050 | $140,002 |
| Less Variable Costs: | |||
| Cost of Goods Sold | $70,030 | $100,900 | $60,004 |
| Sales Commissions | $18,802 | $40,050 | $0 |
| Delivery Charges | $ 900 | $ 8,084 | $ 5,000 |
| Total Variable Costs | $ 89,732 | $ 149,034 | $ 65,004 |
| Contribution Margin | $ 30,668 | $ 53,016 | $ 74,998 |
| percentage | 25% | 26% | 54% |
Although this shows only the top half of the contribution format income statement
Income statement
Income statement is a company's financial statement that indicates how the revenue Income statement (also referred to as profit and loss statement (P&L), statement of financial performance, earnings statement, operating statement or statement of operations) is a company's financial statement that...
, it's immediately apparent that Product Line C is Beta's most profitable one, even though Beta gets more sales revenue from Line B(which is also an example of what is called Partial Contribution Margin - an income statement that references only variable costs). It appears that Beta would do well by emphasizing Line C in its product mix. Moreover, the statement indicates that perhaps prices for line A and line B products are too low. This is information that can't be gleaned from the regular income statements that an accountant
Accountant
An accountant is a practitioner of accountancy or accounting , which is the measurement, disclosure or provision of assurance about financial information that helps managers, investors, tax authorities and others make decisions about allocating resources.The Big Four auditors are the largest...
routinely draws up each period.
Contribution Margin as a measure of efficiency in the operating room
The following discussion focuses on Contribution Margin (mean) per operating room hour in the operating room and how it relates to operating room efficiency.FIGURE: Metric Measure for OR efficiencyMacario A. Are Your Hospital Operating Rooms "Efficient"? Anesthesiology 2006; 105:237-40.
| Metric Measures | 0 | 1 | 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Excess Staffing Costs | >10% | 5-10% | <5% |
| Start-time tardiness (mean tardiness for elective cases/day) | >60 min | 45-60 min | <45 min |
| Case cancellation rate | >10% | 5-10% | <5% |
| Post Anesthesia Care Unit (PACU) admission delays (% workdays with at least one delay in PACU admission) | >20% | 10-20% | <10% |
| Contribution Margin Contribution margin In cost-volume-profit analysis, a form of management accounting, contribution margin is the marginal profit per unit sale. It is a useful quantity in carrying out various calculations, and can be used as a measure of operating leverage... (mean) per operating room hour |
<$1,000/hr | $1–2,000/hr | >$2,000/hr |
| Operating Room Turnover Time (mean setup and cleanup turnover times for all cases) | >40 min | 25-40 min | <25 min |
| Prediction Bias (bias in case duration estimates per 8 hours of operating room time) | >15 min | 5-15 min | <5 min |
| Prolonged turnovers (%turnovers > 60 min) | >25% | 10-25% | <10% |
A surgical suite can schedule itself efficiently but fail to have a positive contribtution margin if many surgeons are slow, use too many instruments or expensive implants, etc. These are all measured by the contribution margin per OR hr. The contribution margin per hour of OR time is the hospital revenue generated by a surgical case, less all the hospitalization variable labor and supply costs. Variable costs, such as implants, vary directly with the volume of cases performed.
This is because fee-for-service hospitals have a positive contribution margin for almost all elective cases mostly due to a large percentage of OR costs being fixed. For USA hospitals not on a fixed annual budget, contribution margin per OR hour averages one to two thousand USD per OR hour.

