
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Encyclopedia
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH) refers to any of several autosomal
recessive
disease
s resulting from mutation
s of gene
s for enzyme
s mediating the biochemical steps of production of cortisol
from cholesterol
by the adrenal gland
s (steroidogenesis).
CAH is one of the possible underlying synthesis problems in Addison’s disease.
CAH is a genetic disorder in which girls are masculinized because the adrenal glands secrete large amounts of androgen during prenatal development. The extra androgen does not affect a baby boy's physical development, but in baby girls it can enlarge the clitoris so that it resembles a penis. The girls sometimes have surgery during infancy to correct their physical appearance, although this practice is highly controversial, and they can receive hormone therapy to correct the imbalance of androgen. During childhood and adolescence, girls with CAH prefer masculine activities and male playmates to a much greater extent than girls not exposed to these amounts of androgen.
Most of these conditions involve excessive or deficient production of sex steroid
s and can alter development of primary or secondary sex characteristic
s in some affected infants, children, or adults.
Due to inadequate mineralocorticoids:
Due to excess androgens:
that is required for normal endocrine function. Production begins in the second month of fetal life. Poor cortisol production is a hallmark of most forms of CAH. Inefficient cortisol production results in rising levels of ACTH
, which in turn induces overgrowth (hyperplasia) and overactivity of the steroid
-producing cells of the adrenal cortex. The defects causing adrenal hyperplasia are congenital (i.e., present at birth).
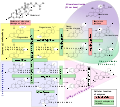 Cortisol deficiency in CAH is usually partial, and not the most serious problem for an affected person. Synthesis of cortisol shares steps with synthesis of mineralocorticoid
Cortisol deficiency in CAH is usually partial, and not the most serious problem for an affected person. Synthesis of cortisol shares steps with synthesis of mineralocorticoid
s such as aldosterone
, androgen
s such as testosterone
, and estrogen
s such as estradiol
. The resulting excessive or deficient production of these three classes of hormones produce the most important problems for people with CAH. Specific enzyme inefficiencies are associated with characteristic patterns of over- or underproduction of mineralocorticoids or sex steroid
s.
Since the 1960s most endocrinologists have referred to the forms of CAH by the traditional names in the left column, which generally correspond to the deficient enzyme activity. As exact structures and genes for the enzymes were identified in the 1980s, most of the enzymes were found to be cytochrome P450 oxidase
s and were renamed to reflect this. In some cases, more than one enzyme was found to participate in a reaction, and in other cases a single enzyme mediated in more than one reaction. There was also variation in different tissues and mammalian species.
In all its forms, congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
accounts for about 95% of diagnosed cases of CAH. Unless another specific enzyme is mentioned, "CAH" in nearly all contexts refers to 21-hydroxylase
deficiency. (The terms "salt-wasting CAH", and "simple virilizing CAH" usually refer to subtypes of this condition.) CAH due to deficiencies of enzymes other than 21-hydroxylase present many of the same management challenges as 21-hydroxylase deficiency, but some involve mineralocorticoid
excess or sex steroid
deficiency.
inefficiency produced by the specific allele
s each patient has. Some alleles result in more severe degrees of enzyme inefficiency. In general, severe degrees of inefficiency produce changes in the fetus and problems in prenatal or perinatal life. Milder degrees of inefficiency are usually associated with excessive or deficient sex hormone
effects in childhood or adolescence, while the mildest form of CAH interferes with ovulation and fertility
in adults.
All of these management issues are discussed in more detail in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
.
Dexamethasone
is used as an off-label early pre-natal treatment for the symptoms of CAH in female fetuses, but it does not treat the underlying congenital disorder. A 2007 Swedish clinical trial found that treatment may cause cognitive and behavioural defects, but the small number of test subjects means the study cannot be considered definitive. Administration of pre-natal dexamethasone has been the subject of controversy over issues of informed consent
and because treatment must predate a clinical diagnosis of CAH in the female fetus. The treatment has also raised concerns in the LGBT
community following an essay posted to the forum of the Hastings Center
, a think tank
devoted to bioethics
, which quoted published research that suggested that pre-natal treatment of female fetuses could prevent those fetuses from becoming lesbian
s after birth, may make them more likely to engage in "traditionally" female-identified behaviour and careers, and more interested in bearing and raising children. Citing a known attempt by a man using his knowledge of the fraternal birth order effect to avoid having a homosexual son by using a surrogate
, the essayists (Professor Alice Dreger of Northwestern University's Feinberg School of Medicine, Professor Ellen Feder of American University and attorney Anne Tamar-Mattis) suggest that pre-natal "dex" treatments constitute the first known attempt to use in utero
protocols to reduce the incidence of homosexuality and bisexuality
in humans. They find such tampering to be morally objectionable. Others feel this is a proven valid way of preventing homosexuality.
Since CAH is a recessive gene, both the mother and father must be recessive carriers of CAH for a child to have CAH. Due to advances in modern medicine, those couples with the recessive CAH genes have an option to prevent CAH in their offspring through preimplantation genetic diagnosis
(PGD). In PGD, the egg is fertilized outside the women's body in a petri dish (IVF). On the 3rd day, when the embryo has developed from one cell to about 4 to 6 cells, one of those cells is removed from the embryo without harming the embryo. The embryo continues to grow until day 5 when it is either frozen or implanted into the mother. Meanwhile, the removed cell is analyzed to determine if the embryo has CAH. If the embryo is determined to have CAH, the parents may make a decision as to whether they wish to have it implanted in the mother or not.
, uterus
, tubes
, and ovaries
.
" on two occasions. The cause of death was another in a series of episodes of vomiting and diarrhea.
This account was translated by Alfred Bongiovanni from De Crecchio (Sopra un caso di apparenzi virili in una donna. Morgagni 7:154-188, 1865) in 1963 for an article in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Much of our modern understanding and treatment of CAH comes from research conducted at Johns Hopkins Medical School in Baltimore
in the middle of the 20th century. Lawson Wilkins
, "founder" of pediatric endocrinology
, worked out the apparently paradoxical pathophysiology: that hyperplasia and overproduction of adrenal androgens resulted from impaired capacity for making cortisol. He reported use of adrenal cortical extracts to treat children with CAH in 1950. Genital reconstructive surgery was also pioneered at Hopkins. After application of karyotyping
to CAH and other intersex
disorders in the 1950s, John Money
, JL Hampson, and JG Hampson persuaded both the scientific community and the public that sex assignment should not be based on any single biological criterion, and gender identity was largely learned and has no simple relationship with chromosomes or hormones. See Intersex
for a fuller history, including recent controversies over reconstructive surgery.
Hydrocortisone, fludrocortisone
, and prednisone
were available by the late 1950s. By 1980 all of the relevant steroids could be measured in blood by reference laboratories for patient care. By 1990 nearly all specific genes and enzymes had been identified.
However, the last decade has seen a number of new developments, discussed more extensively in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
:
Autosome
An autosome is a chromosome that is not a sex chromosome, or allosome; that is to say, there is an equal number of copies of the chromosome in males and females. For example, in humans, there are 22 pairs of autosomes. In addition to autosomes, there are sex chromosomes, to be specific: X and Y...
recessive
Recessive
In genetics, the term "recessive gene" refers to an allele that causes a phenotype that is only seen in a homozygous genotype and never in a heterozygous genotype. Every person has two copies of every gene on autosomal chromosomes, one from mother and one from father...
disease
Disease
A disease is an abnormal condition affecting the body of an organism. It is often construed to be a medical condition associated with specific symptoms and signs. It may be caused by external factors, such as infectious disease, or it may be caused by internal dysfunctions, such as autoimmune...
s resulting from mutation
Mutation
In molecular biology and genetics, mutations are changes in a genomic sequence: the DNA sequence of a cell's genome or the DNA or RNA sequence of a virus. They can be defined as sudden and spontaneous changes in the cell. Mutations are caused by radiation, viruses, transposons and mutagenic...
s of gene
Gene
A gene is a molecular unit of heredity of a living organism. It is a name given to some stretches of DNA and RNA that code for a type of protein or for an RNA chain that has a function in the organism. Living beings depend on genes, as they specify all proteins and functional RNA chains...
s for enzyme
Enzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
s mediating the biochemical steps of production of cortisol
Cortisol
Cortisol is a steroid hormone, more specifically a glucocorticoid, produced by the adrenal gland. It is released in response to stress and a low level of blood glucocorticoids. Its primary functions are to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis; suppress the immune system; and aid in fat,...
from cholesterol
Cholesterol
Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes...
by the adrenal gland
Adrenal gland
In mammals, the adrenal glands are endocrine glands that sit atop the kidneys; in humans, the right suprarenal gland is triangular shaped, while the left suprarenal gland is semilunar shaped...
s (steroidogenesis).
CAH is one of the possible underlying synthesis problems in Addison’s disease.
CAH is a genetic disorder in which girls are masculinized because the adrenal glands secrete large amounts of androgen during prenatal development. The extra androgen does not affect a baby boy's physical development, but in baby girls it can enlarge the clitoris so that it resembles a penis. The girls sometimes have surgery during infancy to correct their physical appearance, although this practice is highly controversial, and they can receive hormone therapy to correct the imbalance of androgen. During childhood and adolescence, girls with CAH prefer masculine activities and male playmates to a much greater extent than girls not exposed to these amounts of androgen.
Most of these conditions involve excessive or deficient production of sex steroid
Sex steroid
Sex steroids, also known as gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate androgen or estrogen receptors. Their effects are mediated by slow genomic mechanisms through nuclear receptors as well as by fast nongenomic mechanisms through membrane-associated receptors and...
s and can alter development of primary or secondary sex characteristic
Secondary sex characteristic
Secondary sex characteristics are features that distinguish the two sexes of a species, but that are not directly part of the reproductive system. They are believed to be the product of sexual selection for traits which give an individual an advantage over its rivals in courtship and aggressive...
s in some affected infants, children, or adults.
Associated conditions
The symptoms of CAH vary depending upon the form of CAH and the gender of the patient. Symptoms can include:Due to inadequate mineralocorticoids:
- vomitingVomitingVomiting is the forceful expulsion of the contents of one's stomach through the mouth and sometimes the nose...
due to salt-wastingNatriuresisNatriuresis is the process of excretion of sodium in the urine via action of the kidneys. Natriuresis is promoted by Brain and Atrial natriuretic peptides, and it is inhibited by chemicals such as aldosterone...
leading to dehydrationDehydrationIn physiology and medicine, dehydration is defined as the excessive loss of body fluid. It is literally the removal of water from an object; however, in physiological terms, it entails a deficiency of fluid within an organism...
and death
Due to excess androgens:
- ambiguous genitalia, in some females, such that it can be initially difficult to determine sex
- early pubic hairPubarchePubarche refers to the first appearance of pubic hair in a child. Pubarche is one of the physical changes of puberty but should not be equated with it since it may occur independently of complete puberty...
and rapid growth in childhood - precocious pubertyPrecocious pubertyAs a medical term, precocious puberty describes puberty occurring at an unusually early age. In most of these children, the process is normal in every respect except the unusually early age, and simply represents a variation of normal development. In a minority of children, the early development is...
or failure of pubertyPubertyPuberty is the process of physical changes by which a child's body matures into an adult body capable of reproduction, as initiated by hormonal signals from the brain to the gonads; the ovaries in a girl, the testes in a boy...
to occur (sexual infantilism: absent or delayed pubertyDelayed pubertyPuberty is described as delayed puberty with exceptions when an organism has passed the usual age of onset of puberty with no physical or hormonal signs that it is beginning. Puberty may be delayed for several years and still occur normally, in which case it is considered constitutional delay, a...
) - excessive facial hairHirsutismHirsutism or frazonism is the excessive hairiness on women in those parts of the body where terminal hair does not normally occur or is minimal - for example, a beard or chest hair. It refers to a male pattern of body hair and it is therefore primarily of cosmetic and psychological concern...
, virilizationVirilizationIn biology and medicine, virilization refers to the biological development of sex differences, changes that make a male body different from a female body. Most of the changes of virilization are produced by androgens...
, and/or menstrual irregularityMenstrual cycleThe menstrual cycle is the scientific term for the physiological changes that can occur in fertile women for the purpose of sexual reproduction. This article focuses on the human menstrual cycle....
in adolescence - infertilityInfertilityInfertility primarily refers to the biological inability of a person to contribute to conception. Infertility may also refer to the state of a woman who is unable to carry a pregnancy to full term...
due to anovulationAnovulationAn anovulatory cycle is a menstrual cycle during which the ovaries do not release an oocyte. Therefore, ovulation does not take place. However, a woman who does not ovulate at each menstrual cycle is not necessarily going through menopause... - enlarged clitorisClitorisThe clitoris is a sexual organ that is present only in female mammals. In humans, the visible button-like portion is located near the anterior junction of the labia minora, above the opening of the urethra and vagina. Unlike the penis, which is homologous to the clitoris, the clitoris does not...
and shallow vaginaVaginaThe vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
Classification
Cortisol is an adrenal steroid hormoneSteroid hormone
A steroid hormone is a steroid that acts as a hormone. Steroid hormones can be grouped into five groups by the receptors to which they bind: glucocorticoids, mineralocorticoids, androgens, estrogens, and progestogens...
that is required for normal endocrine function. Production begins in the second month of fetal life. Poor cortisol production is a hallmark of most forms of CAH. Inefficient cortisol production results in rising levels of ACTH
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone , also known as 'corticotropin', 'Adrenocorticotrophic hormone', is a polypeptide tropic hormone produced and secreted by the anterior pituitary gland. It is an important component of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and is often produced in response to biological...
, which in turn induces overgrowth (hyperplasia) and overactivity of the steroid
Steroid
A steroid is a type of organic compound that contains a characteristic arrangement of four cycloalkane rings that are joined to each other. Examples of steroids include the dietary fat cholesterol, the sex hormones estradiol and testosterone, and the anti-inflammatory drug dexamethasone.The core...
-producing cells of the adrenal cortex. The defects causing adrenal hyperplasia are congenital (i.e., present at birth).

Mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones characterised by their similarity to aldosterone and their influence on salt and water balances.-Physiology:...
s such as aldosterone
Aldosterone
Aldosterone is a hormone that increases the reabsorption of sodium ions and water and the release of potassium in the collecting ducts and distal convoluted tubule of the kidneys' functional unit, the nephron. This increases blood volume and, therefore, increases blood pressure. Drugs that...
, androgen
Androgen
Androgen, also called androgenic hormone or testoid, is the generic term for any natural or synthetic compound, usually a steroid hormone, that stimulates or controls the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors...
s such as testosterone
Testosterone
Testosterone is a steroid hormone from the androgen group and is found in mammals, reptiles, birds, and other vertebrates. In mammals, testosterone is primarily secreted in the testes of males and the ovaries of females, although small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands...
, and estrogen
Estrogen
Estrogens , oestrogens , or œstrogens, are a group of compounds named for their importance in the estrous cycle of humans and other animals. They are the primary female sex hormones. Natural estrogens are steroid hormones, while some synthetic ones are non-steroidal...
s such as estradiol
Estradiol
Estradiol is a sex hormone. Estradiol is abbreviated E2 as it has 2 hydroxyl groups in its molecular structure. Estrone has 1 and estriol has 3 . Estradiol is about 10 times as potent as estrone and about 80 times as potent as estriol in its estrogenic effect...
. The resulting excessive or deficient production of these three classes of hormones produce the most important problems for people with CAH. Specific enzyme inefficiencies are associated with characteristic patterns of over- or underproduction of mineralocorticoids or sex steroid
Sex steroid
Sex steroids, also known as gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate androgen or estrogen receptors. Their effects are mediated by slow genomic mechanisms through nuclear receptors as well as by fast nongenomic mechanisms through membrane-associated receptors and...
s.
| Common medical term | % | OMIM | Enzyme(s) | Locus Locus (genetics) In the fields of genetics and genetic computation, a locus is the specific location of a gene or DNA sequence on a chromosome. A variant of the DNA sequence at a given locus is called an allele. The ordered list of loci known for a particular genome is called a genetic map... |
Substrate(s) | Product(s) | Mineralocorticoid Mineralocorticoid Mineralocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones characterised by their similarity to aldosterone and their influence on salt and water balances.-Physiology:... s |
Androgen Androgen Androgen, also called androgenic hormone or testoid, is the generic term for any natural or synthetic compound, usually a steroid hormone, that stimulates or controls the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors... s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 21-hydroxylase CAH Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency , in all its forms, accounts for over 95% of diagnosed cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and "CAH" in most contexts refers to 21-hydroxylase deficiency... |
90-95% | P450c21 | 6p21.3 | 17OH-progesterone 17-Hydroxyprogesterone 17-Hydroxyprogesterone is a C-21 steroid hormone produced during the synthesis of glucocorticoids and sex steroids.As a hormone, 17OHP also interacts with the progesterone receptor.-Production:... → progesterone Progesterone Progesterone also known as P4 is a C-21 steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryogenesis of humans and other species... → |
11-deoxycortisol DOC 11-Deoxycorticosterone 11-Deoxycorticosterone is a steroid hormone produced by the adrenal gland that possesses mineralocorticoid activity and acts as a precursor to aldosterone. As its names indicate, it can be understood as 21-hydroxy- variant of progesterone or a 11-deoxy- variant of corticosterone... |
↓ | ↑ | |
| 11β-hydroxylase CAH | 5% | P450c11β | 8q21-22 | 11-deoxycortisol→ DOC→ |
cortisol Cortisol Cortisol is a steroid hormone, more specifically a glucocorticoid, produced by the adrenal gland. It is released in response to stress and a low level of blood glucocorticoids. Its primary functions are to increase blood sugar through gluconeogenesis; suppress the immune system; and aid in fat,... corticosterone Corticosterone Corticosterone is a 21-carbon steroid hormone of the corticosteroid type produced in the cortex of the adrenal glands.-Roles:In many species, including amphibians, reptiles, rodents and birds, corticosterone is a main glucocorticoid, involved in regulation of fuel, immune reactions, and stress... |
↑ | ↑ | |
| 3β-HSD CAH Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency 3β-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase II deficient congenital adrenal hyperplasia is an uncommon form of CAH resulting from a mutation in the gene for one of the key enzymes in cortisol synthesis by the adrenal gland, 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type II... |
very rare | 3βHSD II | 1p13 | pregnenolone Pregnenolone Pregnenolone is a steroid hormone involved in the steroidogenesis of progesterone, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. As such it is a prohormone. Pregnenolone sulfate is a GABAA antagonist and increases neurogenesis in the hippocampus.-Chemistry:Like other steroids,... → 17OH-pregnenolone→ DHEA→ |
progesterone Progesterone Progesterone also known as P4 is a C-21 steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryogenesis of humans and other species... 17OH-progesterone androstenedione Androstenedione Androstenedione is a 19-carbon steroid hormone produced in the adrenal glands and the gonads as an intermediate step in the biochemical pathway that produces the androgen testosterone and the estrogens estrone and estradiol.-Synthesis:Androstenedione is the common precursor of male and female sex... |
↓ | ↓ | |
| 17α-hydroxylase CAH Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17α-hydroxylase deficiency is an uncommon form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia resulting from a defect in the gene for the enzyme CYP17A1. It produces decreased synthesis of both cortisol and sex steroids, with resulting increase in mineralocorticoid production... |
very rare | P450c17 P450c17 CYP17A1 also known as cytochrome P450 17A1, or steroid 17-alpha-monooxygenase, or 17α-hydroxylase/17,20 lyase/17,20 desmolase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that acts upon pregnenolone and progesterone to add a hydroxyl group at carbon 17 of the steroid D ring , or acts upon 17-hydroxyprogesterone... |
10q24.3 | pregnenolone Pregnenolone Pregnenolone is a steroid hormone involved in the steroidogenesis of progesterone, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. As such it is a prohormone. Pregnenolone sulfate is a GABAA antagonist and increases neurogenesis in the hippocampus.-Chemistry:Like other steroids,... → progesterone Progesterone Progesterone also known as P4 is a C-21 steroid hormone involved in the female menstrual cycle, pregnancy and embryogenesis of humans and other species... → 17OH-pregnenolone→ |
17OH-pregnenolone 17OH-progesterone DHEA |
↑ | ↓ | |
| lipoid CAH Lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia Lipoid congenital adrenal hyperplasia is an endocrine disorder that is an uncommon and potentially lethal form of congenital adrenal hyperplasia... (20,22-desmolase) |
very rare | StAR Star A star is a massive, luminous sphere of plasma held together by gravity. At the end of its lifetime, a star can also contain a proportion of degenerate matter. The nearest star to Earth is the Sun, which is the source of most of the energy on Earth... P450scc |
8p11.2 15q23-q24 |
transport of cholesterol Cholesterol Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes... cholesterol Cholesterol Cholesterol is a complex isoprenoid. Specifically, it is a waxy steroid of fat that is produced in the liver or intestines. It is used to produce hormones and cell membranes and is transported in the blood plasma of all mammals. It is an essential structural component of mammalian cell membranes... → |
into mitochondria pregnenolone Pregnenolone Pregnenolone is a steroid hormone involved in the steroidogenesis of progesterone, mineralocorticoids, glucocorticoids, androgens, and estrogens. As such it is a prohormone. Pregnenolone sulfate is a GABAA antagonist and increases neurogenesis in the hippocampus.-Chemistry:Like other steroids,... |
↓ | ↓ |
Since the 1960s most endocrinologists have referred to the forms of CAH by the traditional names in the left column, which generally correspond to the deficient enzyme activity. As exact structures and genes for the enzymes were identified in the 1980s, most of the enzymes were found to be cytochrome P450 oxidase
Cytochrome P450 oxidase
The cytochrome P450 superfamily is a large and diverse group of enzymes. The function of most CYP enzymes is to catalyze the oxidation of organic substances. The substrates of CYP enzymes include metabolic intermediates such as lipids and steroidal hormones, as well as xenobiotic substances...
s and were renamed to reflect this. In some cases, more than one enzyme was found to participate in a reaction, and in other cases a single enzyme mediated in more than one reaction. There was also variation in different tissues and mammalian species.
In all its forms, congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency , in all its forms, accounts for over 95% of diagnosed cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and "CAH" in most contexts refers to 21-hydroxylase deficiency...
accounts for about 95% of diagnosed cases of CAH. Unless another specific enzyme is mentioned, "CAH" in nearly all contexts refers to 21-hydroxylase
21-Hydroxylase
Steroid 21-hydroxylase is a cytochrome P450 enzyme that is involved with the biosynthesis of the steroid hormones aldosterone and cortisol.In humans, 21-Hydroxylase is encoded by the gene CYP21A2.-Names and classification:...
deficiency. (The terms "salt-wasting CAH", and "simple virilizing CAH" usually refer to subtypes of this condition.) CAH due to deficiencies of enzymes other than 21-hydroxylase present many of the same management challenges as 21-hydroxylase deficiency, but some involve mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoid
Mineralocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones characterised by their similarity to aldosterone and their influence on salt and water balances.-Physiology:...
excess or sex steroid
Sex steroid
Sex steroids, also known as gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate androgen or estrogen receptors. Their effects are mediated by slow genomic mechanisms through nuclear receptors as well as by fast nongenomic mechanisms through membrane-associated receptors and...
deficiency.
Penetrance
Further variability is introduced by the degree of enzymeEnzyme
Enzymes are proteins that catalyze chemical reactions. In enzymatic reactions, the molecules at the beginning of the process, called substrates, are converted into different molecules, called products. Almost all chemical reactions in a biological cell need enzymes in order to occur at rates...
inefficiency produced by the specific allele
Allele
An allele is one of two or more forms of a gene or a genetic locus . "Allel" is an abbreviation of allelomorph. Sometimes, different alleles can result in different observable phenotypic traits, such as different pigmentation...
s each patient has. Some alleles result in more severe degrees of enzyme inefficiency. In general, severe degrees of inefficiency produce changes in the fetus and problems in prenatal or perinatal life. Milder degrees of inefficiency are usually associated with excessive or deficient sex hormone
Sex steroid
Sex steroids, also known as gonadal steroids, are steroid hormones that interact with vertebrate androgen or estrogen receptors. Their effects are mediated by slow genomic mechanisms through nuclear receptors as well as by fast nongenomic mechanisms through membrane-associated receptors and...
effects in childhood or adolescence, while the mildest form of CAH interferes with ovulation and fertility
Fertility
Fertility is the natural capability of producing offsprings. As a measure, "fertility rate" is the number of children born per couple, person or population. Fertility differs from fecundity, which is defined as the potential for reproduction...
in adults.
Treatment
Treatment of all forms of CAH may include any of:- supplying enough glucocorticoidGlucocorticoidGlucocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones that bind to the glucocorticoid receptor , which is present in almost every vertebrate animal cell...
to reduce hyperplasia and overproduction of androgenAndrogenAndrogen, also called androgenic hormone or testoid, is the generic term for any natural or synthetic compound, usually a steroid hormone, that stimulates or controls the development and maintenance of male characteristics in vertebrates by binding to androgen receptors...
s or mineralocorticoidMineralocorticoidMineralocorticoids are a class of steroid hormones characterised by their similarity to aldosterone and their influence on salt and water balances.-Physiology:...
s - providing replacement mineralocorticoid and extra salt if the person is deficient
- providing replacement testosteroneTestosteroneTestosterone is a steroid hormone from the androgen group and is found in mammals, reptiles, birds, and other vertebrates. In mammals, testosterone is primarily secreted in the testes of males and the ovaries of females, although small amounts are also secreted by the adrenal glands...
or estrogenEstrogenEstrogens , oestrogens , or œstrogens, are a group of compounds named for their importance in the estrous cycle of humans and other animals. They are the primary female sex hormones. Natural estrogens are steroid hormones, while some synthetic ones are non-steroidal...
at puberty if the person is deficient - additional treatments to optimize growth by delaying puberty or delaying bone maturation
All of these management issues are discussed in more detail in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency , in all its forms, accounts for over 95% of diagnosed cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and "CAH" in most contexts refers to 21-hydroxylase deficiency...
.
Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone
Dexamethasone is a potent synthetic member of the glucocorticoid class of steroid drugs. It acts as an anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressant...
is used as an off-label early pre-natal treatment for the symptoms of CAH in female fetuses, but it does not treat the underlying congenital disorder. A 2007 Swedish clinical trial found that treatment may cause cognitive and behavioural defects, but the small number of test subjects means the study cannot be considered definitive. Administration of pre-natal dexamethasone has been the subject of controversy over issues of informed consent
Informed consent
Informed consent is a phrase often used in law to indicate that the consent a person gives meets certain minimum standards. As a literal matter, in the absence of fraud, it is redundant. An informed consent can be said to have been given based upon a clear appreciation and understanding of the...
and because treatment must predate a clinical diagnosis of CAH in the female fetus. The treatment has also raised concerns in the LGBT
LGBT
LGBT is an initialism that collectively refers to "lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender" people. In use since the 1990s, the term "LGBT" is an adaptation of the initialism "LGB", which itself started replacing the phrase "gay community" beginning in the mid-to-late 1980s, which many within the...
community following an essay posted to the forum of the Hastings Center
Hastings Center
The Hastings Center, founded in 1969, is an independent, non-partisan, non-profit bioethics research institute based in the United States. It is dedicated to the examination of essential questions in health care, biotechnology, and the environment...
, a think tank
Think tank
A think tank is an organization that conducts research and engages in advocacy in areas such as social policy, political strategy, economics, military, and technology issues. Most think tanks are non-profit organizations, which some countries such as the United States and Canada provide with tax...
devoted to bioethics
Bioethics
Bioethics is the study of controversial ethics brought about by advances in biology and medicine. Bioethicists are concerned with the ethical questions that arise in the relationships among life sciences, biotechnology, medicine, politics, law, and philosophy....
, which quoted published research that suggested that pre-natal treatment of female fetuses could prevent those fetuses from becoming lesbian
Lesbian
Lesbian is a term most widely used in the English language to describe sexual and romantic desire between females. The word may be used as a noun, to refer to women who identify themselves or who are characterized by others as having the primary attribute of female homosexuality, or as an...
s after birth, may make them more likely to engage in "traditionally" female-identified behaviour and careers, and more interested in bearing and raising children. Citing a known attempt by a man using his knowledge of the fraternal birth order effect to avoid having a homosexual son by using a surrogate
Surrogacy
Surrogacy is an arrangement in which a woman carries and delivers a child for another couple or person. This woman may be the child's genetic mother , or she may carry the pregnancy to delivery after having an embryo, to which she has no genetic relationship whatsoever, transferred to her uterus...
, the essayists (Professor Alice Dreger of Northwestern University's Feinberg School of Medicine, Professor Ellen Feder of American University and attorney Anne Tamar-Mattis) suggest that pre-natal "dex" treatments constitute the first known attempt to use in utero
In utero
In utero is a Latin term literally meaning "in the womb". In biology, the phrase describes the state of an embryo or fetus. In legal contexts, the phrase is used to refer to unborn children. Under common law, unborn children are still considered to exist for property transfer purposes.-See also:*...
protocols to reduce the incidence of homosexuality and bisexuality
Bisexuality
Bisexuality is sexual behavior or an orientation involving physical or romantic attraction to both males and females, especially with regard to men and women. It is one of the three main classifications of sexual orientation, along with a heterosexual and a homosexual orientation, all a part of the...
in humans. They find such tampering to be morally objectionable. Others feel this is a proven valid way of preventing homosexuality.
Since CAH is a recessive gene, both the mother and father must be recessive carriers of CAH for a child to have CAH. Due to advances in modern medicine, those couples with the recessive CAH genes have an option to prevent CAH in their offspring through preimplantation genetic diagnosis
Preimplantation genetic diagnosis
In medicine and genetics pre-implantation genetic diagnosis refers to procedures that are performed on embryos prior to implantation, sometimes even on oocytes prior to fertilization. PGD is considered another way to prenatal diagnosis...
(PGD). In PGD, the egg is fertilized outside the women's body in a petri dish (IVF). On the 3rd day, when the embryo has developed from one cell to about 4 to 6 cells, one of those cells is removed from the embryo without harming the embryo. The embryo continues to grow until day 5 when it is either frozen or implanted into the mother. Meanwhile, the removed cell is analyzed to determine if the embryo has CAH. If the embryo is determined to have CAH, the parents may make a decision as to whether they wish to have it implanted in the mother or not.
Screening for CAH in neonates
Currently, in the United States and over 40 other countries, every child born is screened for CAH at birth. This test will detect elevated levels of 17-hydroxy-progesterone (17-OHP). Detecting high levels of 17-OHP enables early detection of CAH. Newborns detected early enough can be placed on medication and live a relatively normal life.Before 20th century
An Italian anatomist, Luigi De Crecchio provided the earliest known description of a case of probable CAH.I propose in this narrative that it is sometimes extremely difficult and even impossible to determine sex during life. In one of the anatomicalDe Crecchio then described the internal organs, which included a normal vaginaAnatomyAnatomy is a branch of biology and medicine that is the consideration of the structure of living things. It is a general term that includes human anatomy, animal anatomy , and plant anatomy...
theaters of the hospital..., there arrived toward the end of January a cadaver which in life was the body of a certain Joseph Marzo... The general physiognomy was decidedly male in all respects. There were no feminine curves to the body. There was a heavy beard. There was some delicacy of structure with muscles that were not very well developed... The distribution of pubic hairPubic hairPubic hair is hair in the frontal genital area, the crotch, and sometimes at the top of the inside of the legs; these areas form the pubic region....
was typical of the male. Perhaps the lower extremities were somewhat delicate, resembling the female, and were covered with hair... The penisPenisThe penis is a biological feature of male animals including both vertebrates and invertebrates...
was curved posteriorly and measured 6 cm, or with stretching, 10 cm. The coronaGlans penisThe glans penis is the sensitive bulbous structure at the distal end of the penis. The glans penis is anatomically homologous to the clitoral glans of the female...
was 3 cm long and 8 cm in circumference. There was an ample prepuceForeskinIn male human anatomy, the foreskin is a generally retractable double-layered fold of skin and mucous membrane that covers the glans penis and protects the urinary meatus when the penis is not erect...
. There was a first grade hypospadiasHypospadiasHypospadias is a birth defect of the urethra in the male that involves an abnormally placed urinary meatus...
... There were two folds of skin coming from the top of the penis and encircling it on either side. These were somewhat loose and resembled labia majoraLabia majoraThe labia majora are two prominent longitudinal cutaneous folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum and form the lateral boundaries of the pudendal cleft, which contains the labia minora, interlabial sulci, clitoral hood, clitoral glans, frenulum clitoridis, the...
.
Vagina
The vagina is a fibromuscular tubular tract leading from the uterus to the exterior of the body in female placental mammals and marsupials, or to the cloaca in female birds, monotremes, and some reptiles. Female insects and other invertebrates also have a vagina, which is the terminal part of the...
, uterus
Uterus
The uterus or womb is a major female hormone-responsive reproductive sex organ of most mammals including humans. One end, the cervix, opens into the vagina, while the other is connected to one or both fallopian tubes, depending on the species...
, tubes
Fallopian tube
The Fallopian tubes, also known as oviducts, uterine tubes, and salpinges are two very fine tubes lined with ciliated epithelia, leading from the ovaries of female mammals into the uterus, via the utero-tubal junction...
, and ovaries
Ovary
The ovary is an ovum-producing reproductive organ, often found in pairs as part of the vertebrate female reproductive system. Ovaries in anatomically female individuals are analogous to testes in anatomically male individuals, in that they are both gonads and endocrine glands.-Human anatomy:Ovaries...
.
It was of the greatest importance to determine the habits, tendencies, passions, and general character of this individual... I was determined to get as complete a story as possible, determined to get at the base of the facts and to avoid undue exaggeration which was rampant in the conversation of many of the people present at the time of the dissection.He interviewed many people and satisfied himself that Joseph Marzo "conducted himself within the sexual area exclusively as a male, "even to the point of contracting the "French disease
Syphilis
Syphilis is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the spirochete bacterium Treponema pallidum subspecies pallidum. The primary route of transmission is through sexual contact; however, it may also be transmitted from mother to fetus during pregnancy or at birth, resulting in congenital syphilis...
" on two occasions. The cause of death was another in a series of episodes of vomiting and diarrhea.
This account was translated by Alfred Bongiovanni from De Crecchio (Sopra un caso di apparenzi virili in una donna. Morgagni 7:154-188, 1865) in 1963 for an article in the New England Journal of Medicine.
20th and 21st century
The association of excessive sex steroid effects with diseases of the adrenal cortex have been recognized for over a century. The term adrenogenital syndrome was applied to both sex-steroid producing tumors and severe forms of CAH for much of the 20th century, before some of the forms of CAH were understood. Congenital adrenal hyperplasia, which also dates to the first half of the century, has become the preferred term to reduce ambiguity and to emphasize the underlying pathophysiology of the disorders.Much of our modern understanding and treatment of CAH comes from research conducted at Johns Hopkins Medical School in Baltimore
Baltimore
Baltimore is the largest independent city in the United States and the largest city and cultural center of the US state of Maryland. The city is located in central Maryland along the tidal portion of the Patapsco River, an arm of the Chesapeake Bay. Baltimore is sometimes referred to as Baltimore...
in the middle of the 20th century. Lawson Wilkins
Lawson Wilkins
-References:...
, "founder" of pediatric endocrinology
Pediatric endocrinology
Pediatric endocrinology is a medical subspecialty dealing with variations of physical growth and sexual development in childhood, as well as diabetes and other disorders of the endocrine glands....
, worked out the apparently paradoxical pathophysiology: that hyperplasia and overproduction of adrenal androgens resulted from impaired capacity for making cortisol. He reported use of adrenal cortical extracts to treat children with CAH in 1950. Genital reconstructive surgery was also pioneered at Hopkins. After application of karyotyping
Karyotype
A karyotype is the number and appearance of chromosomes in the nucleus of an eukaryotic cell. The term is also used for the complete set of chromosomes in a species, or an individual organism.p28...
to CAH and other intersex
Intersex
Intersex, in humans and other animals, is the presence of intermediate or atypical combinations of physical features that usually distinguish female from male...
disorders in the 1950s, John Money
John Money
John William Money was a psychologist, sexologist and author, specializing in research into sexual identity and biology of gender...
, JL Hampson, and JG Hampson persuaded both the scientific community and the public that sex assignment should not be based on any single biological criterion, and gender identity was largely learned and has no simple relationship with chromosomes or hormones. See Intersex
Intersex
Intersex, in humans and other animals, is the presence of intermediate or atypical combinations of physical features that usually distinguish female from male...
for a fuller history, including recent controversies over reconstructive surgery.
Hydrocortisone, fludrocortisone
Fludrocortisone
Fludrocortisone is a synthetic corticosteroid with moderate glucocorticoid potency and much greater mineralocorticoid potency. The brand name in the U.S. and Canada is Florinef.-Uses:...
, and prednisone
Prednisone
Prednisone is a synthetic corticosteroid drug that is particularly effective as an immunosuppressant drug. It is used to treat certain inflammatory diseases and some types of cancer, but has significant adverse effects...
were available by the late 1950s. By 1980 all of the relevant steroids could be measured in blood by reference laboratories for patient care. By 1990 nearly all specific genes and enzymes had been identified.
However, the last decade has seen a number of new developments, discussed more extensively in congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency , in all its forms, accounts for over 95% of diagnosed cases of congenital adrenal hyperplasia, and "CAH" in most contexts refers to 21-hydroxylase deficiency...
:
- debate over the value of genital reconstructive surgeryGenital reconstructive surgeryGenital reconstructive surgery refers to surgery performed on the genitalia of infants, children, or adults for the purpose of correcting birth defects or other anatomic abnormalities, or for the purpose of transforming normal genitalia of one sex into genitalia resembling the other...
and changing standards - debate over sex assignmentSex assignmentSex assignment refers to the assigning of the biological sex at the birth of a baby. In the majority of births, a relative, midwife, or physician inspects the genitalia when the baby is delivered, sees ordinary male or female genitalia, and declares, "it's a girl" or "it's a boy" without the...
of severely virilized XX infants - new treatments to improve height outcomes
- newborn screeningNewborn screeningNewborn screening is the process by which infants are screened shortly after birth for a list of disorders that are treatable, but difficult or impossible to detect clinically. Screening programs are often run by state or national governing bodies with the goal of screening all infants born in the...
programs to detect CAH at birth - increasing attempts to treat CAH before birth

