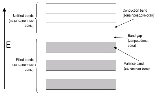
Conduction band
Encyclopedia
In the solid-state physics
field of semiconductor
s and insulators, the conduction band is the range of electron
energies, higher than that of the valence band
, sufficient to free an electron from binding with its individual atom
and allow it to move freely within the atomic lattice of the material. Electrons within the conduction band are mobile charge carrier
s in solids, responsible for conduction of electric current
s in metals and other good electrical conductors.
Solid-state physics
Solid-state physics is the study of rigid matter, or solids, through methods such as quantum mechanics, crystallography, electromagnetism, and metallurgy. It is the largest branch of condensed matter physics. Solid-state physics studies how the large-scale properties of solid materials result from...
field of semiconductor
Semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
s and insulators, the conduction band is the range of electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
energies, higher than that of the valence band
Valence band
In solids, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in which electrons are normally present at absolute zero temperature....
, sufficient to free an electron from binding with its individual atom
Atom
The atom is a basic unit of matter that consists of a dense central nucleus surrounded by a cloud of negatively charged electrons. The atomic nucleus contains a mix of positively charged protons and electrically neutral neutrons...
and allow it to move freely within the atomic lattice of the material. Electrons within the conduction band are mobile charge carrier
Charge carrier
In physics, a charge carrier is a free particle carrying an electric charge, especially the particles that carry electric currents in electrical conductors. Examples are electrons and ions...
s in solids, responsible for conduction of electric current
Electric current
Electric current is a flow of electric charge through a medium.This charge is typically carried by moving electrons in a conductor such as wire...
s in metals and other good electrical conductors.
See also
- Band TheoryElectronic band structureIn solid-state physics, the electronic band structure of a solid describes those ranges of energy an electron is "forbidden" or "allowed" to have. Band structure derives from the diffraction of the quantum mechanical electron waves in a periodic crystal lattice with a specific crystal system and...
- Electrical conduction for more information about conduction in solids, and another description of band structure.
- Fermi seaFermi liquidFermi liquid theory is a theoretical model of interacting fermions that describes the normal state of most metals at sufficiently low temperatures. The interaction between the particles of the many-body system does not need to be small...
- SemiconductorSemiconductorA semiconductor is a material with electrical conductivity due to electron flow intermediate in magnitude between that of a conductor and an insulator. This means a conductivity roughly in the range of 103 to 10−8 siemens per centimeter...
for a full explanation of the band structure of materials. - Valence bandValence bandIn solids, the valence band is the highest range of electron energies in which electrons are normally present at absolute zero temperature....

