
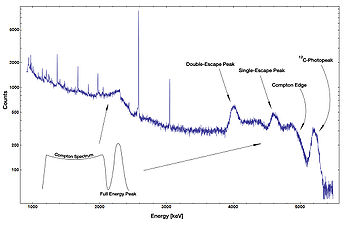
Compton edge
Encyclopedia
In spectrophotometry
, the Compton edge is a feature of the spectrograph that results from the Compton scattering
in the scintillator
or detector
. When a gamma-ray scatters off the scintillator but escapes, only a fraction of its energy is registered by the detector. This leads to a spectrum of gamma-rays in the data that is not really there. The highest energy that occurs from this process is the Compton edge.
 In a Compton scattering
In a Compton scattering
process, an incident photon collides with an electron in a material. The amount of energy exchanged varies with angle, and is given by the formula:

or
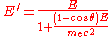
The amount of energy transferred to the material varies with the angle of deflection. As approaches zero, none of the energy is transferred. The maximum amount of energy is transferred when
approaches zero, none of the energy is transferred. The maximum amount of energy is transferred when  approaches 180 degrees.
approaches 180 degrees.
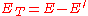

It is impossible for the photon to transfer any more energy via this process, hence there is a sharp cutoff at this energy giving rise to the name Compton edge.
Spectrophotometry
In chemistry, spectrophotometry is the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength...
, the Compton edge is a feature of the spectrograph that results from the Compton scattering
Compton scattering
In physics, Compton scattering is a type of scattering that X-rays and gamma rays undergo in matter. The inelastic scattering of photons in matter results in a decrease in energy of an X-ray or gamma ray photon, called the Compton effect...
in the scintillator
Scintillator
A scintillator is a special material, which exhibits scintillation—the property of luminescence when excited by ionizing radiation. Luminescent materials, when struck by an incoming particle, absorb its energy and scintillate, i.e., reemit the absorbed energy in the form of light...
or detector
Particle detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify high-energy particles, such as those produced by nuclear decay, cosmic radiation, or reactions in a...
. When a gamma-ray scatters off the scintillator but escapes, only a fraction of its energy is registered by the detector. This leads to a spectrum of gamma-rays in the data that is not really there. The highest energy that occurs from this process is the Compton edge.
Background

Compton scattering
In physics, Compton scattering is a type of scattering that X-rays and gamma rays undergo in matter. The inelastic scattering of photons in matter results in a decrease in energy of an X-ray or gamma ray photon, called the Compton effect...
process, an incident photon collides with an electron in a material. The amount of energy exchanged varies with angle, and is given by the formula:

or
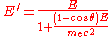
- E is the energy of the incident photon.
- E' is the energy of the outgoing photon, which escapes the material.
-
 is the mass of the electron.
is the mass of the electron. - c is the speed of light.
-
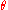 is the angle of deflection for the photon.
is the angle of deflection for the photon.
The amount of energy transferred to the material varies with the angle of deflection. As
 approaches zero, none of the energy is transferred. The maximum amount of energy is transferred when
approaches zero, none of the energy is transferred. The maximum amount of energy is transferred when 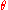 approaches 180 degrees.
approaches 180 degrees.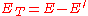

It is impossible for the photon to transfer any more energy via this process, hence there is a sharp cutoff at this energy giving rise to the name Compton edge.

