
Compressibility factor
Encyclopedia
The compressibility factor (Z), also known as the compression factor, is a useful thermodynamic property for modifying the ideal gas law
to account for the real gas
behavior. In general, deviation from ideal behavior becomes more significant the closer a gas is to a phase change, the lower the temperature or the larger the pressure. Compressibility factor values are usually obtained by calculation from equations of state (EOS), such as the virial equation which take compound specific empirical constants as input. For a gas that is a mixture of two or more pure gases (air or natural gas, for example), a gas composition
is required before compressibility can be calculated.
Alternatively, the compressibility factor for specific gases can be read from generalized compressibility charts that plot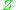 as a function of pressure at constant temperature.
as a function of pressure at constant temperature.
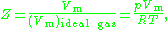
where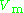 is the molar volume
is the molar volume
,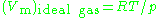 is the molar volume of the corresponding ideal gas,
is the molar volume of the corresponding ideal gas, 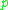 is the pressure
is the pressure
,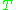 is the temperature
is the temperature
, and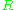 is the gas constant
is the gas constant
. For engineering applications, it is frequently expressed as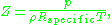
where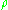 is the density
is the density
of the gas and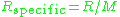 is the specific gas constant
is the specific gas constant
,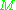 being the molar mass
being the molar mass
.
For an ideal gas
the compressibility factor is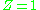 per definition. In many real world applications requirements for accuracy demand that deviations from ideal gas behaviour, i.e., real gas
per definition. In many real world applications requirements for accuracy demand that deviations from ideal gas behaviour, i.e., real gas
behaviour, is taken into account. The value of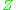 generally increases with pressure and decreases with temperature. At high pressures molecules are colliding more often. This allows repulsive forces between molecules to have a noticeable effect, making the molar volume of the real gas (
generally increases with pressure and decreases with temperature. At high pressures molecules are colliding more often. This allows repulsive forces between molecules to have a noticeable effect, making the molar volume of the real gas (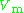 ) greater than the molar volume of the corresponding ideal gas (
) greater than the molar volume of the corresponding ideal gas (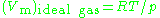 ), which causes
), which causes 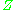 to exceed one. When pressures are lower, the molecules are freer to move. In this case attractive forces dominate, making
to exceed one. When pressures are lower, the molecules are freer to move. In this case attractive forces dominate, making 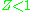 . The closer the gas is to its critical point
. The closer the gas is to its critical point
or its boiling point, the more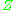 deviates from the ideal case.
deviates from the ideal case.
 The unique relationship between the compressibility factor and the reduced temperature,
The unique relationship between the compressibility factor and the reduced temperature, 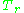 , and the reduced pressure,
, and the reduced pressure, 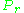 , was first recognized by Johannes Diderik van der Waals
, was first recognized by Johannes Diderik van der Waals
in 1873 and is known as the two-parameter principle of corresponding states. The principle of corresponding states expresses the generalization that the properties of a gas which are dependent on intermolecular forces are related to the critical properties of the gas in a universal way. That provides a most important basis for developing correlations of molecular properties.
As for the compressibility of gases, the principle of corresponding states indicates that any pure gas at the same reduced temperature,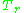 , and reduced pressure,
, and reduced pressure, 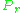 , should have the same compressibility factor.
, should have the same compressibility factor.
The reduced temperature and pressure are defined by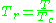 and
and 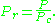
Here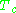 and
and 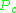 are known as the critical temperature and critical pressure of a gas. They are characteristics of each specific gas with
are known as the critical temperature and critical pressure of a gas. They are characteristics of each specific gas with 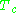 being the temperature above which it is not possible to liquify a given gas and
being the temperature above which it is not possible to liquify a given gas and 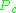 is the minimum pressure required to liquify a given gas at its critical temperature. Together they define the critical point of a fluid above which distinct liquid and gas phases of a given fluid do not exist.
is the minimum pressure required to liquify a given gas at its critical temperature. Together they define the critical point of a fluid above which distinct liquid and gas phases of a given fluid do not exist.
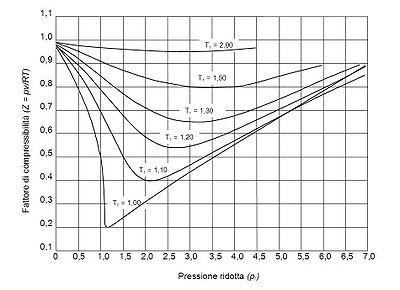
The pressure-volume-temperature (PVT) data for real gases varies from one pure gas to another. However, when the compressibility factors of various single-component gases are graphed versus pressure along with temperature isotherms many of the graphs exhibit similar isotherm shapes.
In order to obtain a generalized graph that can be used for many different gases, the reduced pressure and temperature,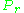 and
and 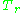 , are used to normalize the compressibility factor data. Figure 2 is an example of a generalized compressibility factor graph derived from hundreds of experimental PVT data points of 10 pure gases, namely methane, ethane, ethylene, propane, n-butane, i-pentane, n-hexane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and steam.
, are used to normalize the compressibility factor data. Figure 2 is an example of a generalized compressibility factor graph derived from hundreds of experimental PVT data points of 10 pure gases, namely methane, ethane, ethylene, propane, n-butane, i-pentane, n-hexane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and steam.
There are more detailed generalized compressibility factor graphs based on as many as 25 or more different pure gases, such as the Nelson-Obert graphs. Such graphs are said to have an accuracy within 1-2 percent for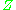 values greater than 0.6 and within 4-6 percent for
values greater than 0.6 and within 4-6 percent for 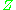 values of 0.3-0.6.
values of 0.3-0.6.
The generalized compressibility factor graphs may be considerably in error for strongly polar gases which are gases for which the centers of positive and negative charge do not coincide. In such cases the estimate for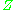 may be in error by as much as 15-20 percent.
may be in error by as much as 15-20 percent.
The quantum gases hydrogen, helium, and neon do not conform to the corresponding-states behavior and the reduced pressure and temperature for those three gases should be redefined in the following manner to improve the accuracy of predicting their compressibility factors when using the generalized graphs:
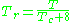 and
and 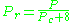
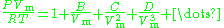
Where the coefficients in the numerator are known as virial coefficients and are functions of temperature.
The virial coefficients account for interactions between successively larger groups of molecules. For example,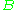 accounts for interactions between pairs,
accounts for interactions between pairs, 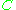 for interactions between three gas molecules, and so on. Because interactions between large numbers of molecules are rare, the virial equation is usually truncated after the third term.
for interactions between three gas molecules, and so on. Because interactions between large numbers of molecules are rare, the virial equation is usually truncated after the third term.
The Real gas
article features more theoretical methods to compute compressibility factors
becomes important. As a rule of thumb, the ideal gas law is reasonably accurate up to a pressure of about 2 atm
, and even higher for small non-associating molecules. For example methyl chloride, a highly polar molecule
and therefore with significant intermolecular forces, the experimental value for the compressibility factor is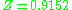 at a pressure of 10 atm and temperature of 100 °C. For air (small non-polar molecules) at approximately the same conditions, the compressibility factor is only
at a pressure of 10 atm and temperature of 100 °C. For air (small non-polar molecules) at approximately the same conditions, the compressibility factor is only 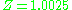 (see table below for 10 bars
(see table below for 10 bars
, 400 K).
and 20 percent oxygen
. Both molecules are small and non-polar (and therefore non-associating). We can therefore expect that the behaviour of air within broad temperature and pressure ranges can be approximated as an ideal gas with reasonable accuracy. Experimental values for the compressibility factor confirm this.
generated with :de:Wikipedia:Helferlein/VBA-Macro for EXCEL tableconversion V1.7<\hiddentext>>
Source: (table 3-162). values are calculated from values of pressure, volume (or density), and temperature in Vassernan, Kazavchinskii, and Rabinovich, "Thermophysical Properties of Air and Air Components;' Moscow, Nauka, 1966, and NBS-NSF Trans. TT 70-50095, 1971: and Vassernan and Rabinovich, "Thermophysical Properties of Liquid Air and Its Component, "Moscow, 1968, and NBS-NSF Trans. 69-55092, 1970.
values are calculated from values of pressure, volume (or density), and temperature in Vassernan, Kazavchinskii, and Rabinovich, "Thermophysical Properties of Air and Air Components;' Moscow, Nauka, 1966, and NBS-NSF Trans. TT 70-50095, 1971: and Vassernan and Rabinovich, "Thermophysical Properties of Liquid Air and Its Component, "Moscow, 1968, and NBS-NSF Trans. 69-55092, 1970.
Ideal gas law
The ideal gas law is the equation of state of a hypothetical ideal gas. It is a good approximation to the behavior of many gases under many conditions, although it has several limitations. It was first stated by Émile Clapeyron in 1834 as a combination of Boyle's law and Charles's law...
to account for the real gas
Real gas
Real gases – as opposed to a perfect or ideal gas – exhibit properties that cannot be explained entirely using the ideal gas law. To understand the behaviour of real gases, the following must be taken into account:* compressibility effects;...
behavior. In general, deviation from ideal behavior becomes more significant the closer a gas is to a phase change, the lower the temperature or the larger the pressure. Compressibility factor values are usually obtained by calculation from equations of state (EOS), such as the virial equation which take compound specific empirical constants as input. For a gas that is a mixture of two or more pure gases (air or natural gas, for example), a gas composition
Gas composition
Gas composition: any gas can be characterised by listing the pure substances it contains, and stating for each substance its proportion of the gas mixture's molecule count.To give a familiar example, air has a composition of:...
is required before compressibility can be calculated.
Alternatively, the compressibility factor for specific gases can be read from generalized compressibility charts that plot
 as a function of pressure at constant temperature.
as a function of pressure at constant temperature.Definition and physical significance
The compressibility factor is defined as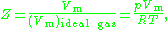
where
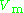 is the molar volume
is the molar volumeMolar volume
The molar volume, symbol Vm, is the volume occupied by one mole of a substance at a given temperature and pressure. It is equal to the molar mass divided by the mass density...
,
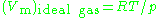 is the molar volume of the corresponding ideal gas,
is the molar volume of the corresponding ideal gas, 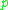 is the pressure
is the pressurePressure
Pressure is the force per unit area applied in a direction perpendicular to the surface of an object. Gauge pressure is the pressure relative to the local atmospheric or ambient pressure.- Definition :...
,
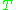 is the temperature
is the temperatureTemperature
Temperature is a physical property of matter that quantitatively expresses the common notions of hot and cold. Objects of low temperature are cold, while various degrees of higher temperatures are referred to as warm or hot...
, and
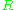 is the gas constant
is the gas constantGas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
. For engineering applications, it is frequently expressed as
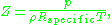
where
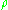 is the density
is the densityDensity
The mass density or density of a material is defined as its mass per unit volume. The symbol most often used for density is ρ . In some cases , density is also defined as its weight per unit volume; although, this quantity is more properly called specific weight...
of the gas and
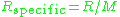 is the specific gas constant
is the specific gas constantGas constant
The gas constant is a physical constant which is featured in many fundamental equations in the physical sciences, such as the ideal gas law and the Nernst equation. It is equivalent to the Boltzmann constant, but expressed in units of energy The gas constant (also known as the molar, universal,...
,
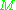 being the molar mass
being the molar massMolar mass
Molar mass, symbol M, is a physical property of a given substance , namely its mass per amount of substance. The base SI unit for mass is the kilogram and that for amount of substance is the mole. Thus, the derived unit for molar mass is kg/mol...
.
For an ideal gas
Ideal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of a set of randomly-moving, non-interacting point particles. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.At normal conditions such as...
the compressibility factor is
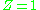 per definition. In many real world applications requirements for accuracy demand that deviations from ideal gas behaviour, i.e., real gas
per definition. In many real world applications requirements for accuracy demand that deviations from ideal gas behaviour, i.e., real gasReal gas
Real gases – as opposed to a perfect or ideal gas – exhibit properties that cannot be explained entirely using the ideal gas law. To understand the behaviour of real gases, the following must be taken into account:* compressibility effects;...
behaviour, is taken into account. The value of
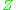 generally increases with pressure and decreases with temperature. At high pressures molecules are colliding more often. This allows repulsive forces between molecules to have a noticeable effect, making the molar volume of the real gas (
generally increases with pressure and decreases with temperature. At high pressures molecules are colliding more often. This allows repulsive forces between molecules to have a noticeable effect, making the molar volume of the real gas (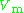 ) greater than the molar volume of the corresponding ideal gas (
) greater than the molar volume of the corresponding ideal gas (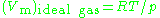 ), which causes
), which causes 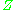 to exceed one. When pressures are lower, the molecules are freer to move. In this case attractive forces dominate, making
to exceed one. When pressures are lower, the molecules are freer to move. In this case attractive forces dominate, making 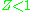 . The closer the gas is to its critical point
. The closer the gas is to its critical pointCritical point (thermodynamics)
In physical chemistry, thermodynamics, chemistry and condensed matter physics, a critical point, also called a critical state, specifies the conditions at which a phase boundary ceases to exist...
or its boiling point, the more
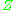 deviates from the ideal case.
deviates from the ideal case.Generalized compressibility factor graphs for pure gases

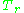 , and the reduced pressure,
, and the reduced pressure, 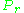 , was first recognized by Johannes Diderik van der Waals
, was first recognized by Johannes Diderik van der WaalsJohannes Diderik van der Waals
Johannes Diderik van der Waals was a Dutch theoretical physicist and thermodynamicist famous for his work on an equation of state for gases and liquids....
in 1873 and is known as the two-parameter principle of corresponding states. The principle of corresponding states expresses the generalization that the properties of a gas which are dependent on intermolecular forces are related to the critical properties of the gas in a universal way. That provides a most important basis for developing correlations of molecular properties.
As for the compressibility of gases, the principle of corresponding states indicates that any pure gas at the same reduced temperature,
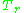 , and reduced pressure,
, and reduced pressure, 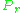 , should have the same compressibility factor.
, should have the same compressibility factor.The reduced temperature and pressure are defined by
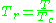 and
and 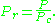
Here
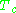 and
and 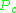 are known as the critical temperature and critical pressure of a gas. They are characteristics of each specific gas with
are known as the critical temperature and critical pressure of a gas. They are characteristics of each specific gas with 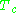 being the temperature above which it is not possible to liquify a given gas and
being the temperature above which it is not possible to liquify a given gas and 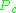 is the minimum pressure required to liquify a given gas at its critical temperature. Together they define the critical point of a fluid above which distinct liquid and gas phases of a given fluid do not exist.
is the minimum pressure required to liquify a given gas at its critical temperature. Together they define the critical point of a fluid above which distinct liquid and gas phases of a given fluid do not exist.The pressure-volume-temperature (PVT) data for real gases varies from one pure gas to another. However, when the compressibility factors of various single-component gases are graphed versus pressure along with temperature isotherms many of the graphs exhibit similar isotherm shapes.
In order to obtain a generalized graph that can be used for many different gases, the reduced pressure and temperature,
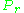 and
and 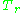 , are used to normalize the compressibility factor data. Figure 2 is an example of a generalized compressibility factor graph derived from hundreds of experimental PVT data points of 10 pure gases, namely methane, ethane, ethylene, propane, n-butane, i-pentane, n-hexane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and steam.
, are used to normalize the compressibility factor data. Figure 2 is an example of a generalized compressibility factor graph derived from hundreds of experimental PVT data points of 10 pure gases, namely methane, ethane, ethylene, propane, n-butane, i-pentane, n-hexane, nitrogen, carbon dioxide and steam.There are more detailed generalized compressibility factor graphs based on as many as 25 or more different pure gases, such as the Nelson-Obert graphs. Such graphs are said to have an accuracy within 1-2 percent for
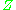 values greater than 0.6 and within 4-6 percent for
values greater than 0.6 and within 4-6 percent for 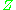 values of 0.3-0.6.
values of 0.3-0.6.The generalized compressibility factor graphs may be considerably in error for strongly polar gases which are gases for which the centers of positive and negative charge do not coincide. In such cases the estimate for
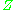 may be in error by as much as 15-20 percent.
may be in error by as much as 15-20 percent.The quantum gases hydrogen, helium, and neon do not conform to the corresponding-states behavior and the reduced pressure and temperature for those three gases should be redefined in the following manner to improve the accuracy of predicting their compressibility factors when using the generalized graphs:
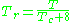 and
and 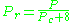
Theoretical models
The virial equation is especially useful to describe the causes of non-ideality at a molecular level (very few gases are mono-atomic) as it is derived directly from statistical mechanics: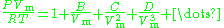
Where the coefficients in the numerator are known as virial coefficients and are functions of temperature.
The virial coefficients account for interactions between successively larger groups of molecules. For example,
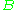 accounts for interactions between pairs,
accounts for interactions between pairs, 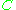 for interactions between three gas molecules, and so on. Because interactions between large numbers of molecules are rare, the virial equation is usually truncated after the third term.
for interactions between three gas molecules, and so on. Because interactions between large numbers of molecules are rare, the virial equation is usually truncated after the third term.The Real gas
Real gas
Real gases – as opposed to a perfect or ideal gas – exhibit properties that cannot be explained entirely using the ideal gas law. To understand the behaviour of real gases, the following must be taken into account:* compressibility effects;...
article features more theoretical methods to compute compressibility factors
Experimental values
It is extremely difficult to generalize at what pressures or temperatures the deviation from the ideal gasIdeal gas
An ideal gas is a theoretical gas composed of a set of randomly-moving, non-interacting point particles. The ideal gas concept is useful because it obeys the ideal gas law, a simplified equation of state, and is amenable to analysis under statistical mechanics.At normal conditions such as...
becomes important. As a rule of thumb, the ideal gas law is reasonably accurate up to a pressure of about 2 atm
Atmosphere (unit)
The standard atmosphere is an international reference pressure defined as 101325 Pa and formerly used as unit of pressure. For practical purposes it has been replaced by the bar which is 105 Pa...
, and even higher for small non-associating molecules. For example methyl chloride, a highly polar molecule
Chemical polarity
In chemistry, polarity refers to a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole or multipole moment. Polar molecules interact through dipole–dipole intermolecular forces and hydrogen bonds. Molecular polarity is dependent on the difference in...
and therefore with significant intermolecular forces, the experimental value for the compressibility factor is
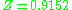 at a pressure of 10 atm and temperature of 100 °C. For air (small non-polar molecules) at approximately the same conditions, the compressibility factor is only
at a pressure of 10 atm and temperature of 100 °C. For air (small non-polar molecules) at approximately the same conditions, the compressibility factor is only 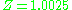 (see table below for 10 bars
(see table below for 10 barsBar (unit)
The bar is a unit of pressure equal to 100 kilopascals, and roughly equal to the atmospheric pressure on Earth at sea level. Other units derived from the bar are the megabar , kilobar , decibar , centibar , and millibar...
, 400 K).
Compressibility of air
Normal air comprises in crude numbers 80 percent nitrogenNitrogen
Nitrogen is a chemical element that has the symbol N, atomic number of 7 and atomic mass 14.00674 u. Elemental nitrogen is a colorless, odorless, tasteless, and mostly inert diatomic gas at standard conditions, constituting 78.08% by volume of Earth's atmosphere...
and 20 percent oxygen
Oxygen
Oxygen is the element with atomic number 8 and represented by the symbol O. Its name derives from the Greek roots ὀξύς and -γενής , because at the time of naming, it was mistakenly thought that all acids required oxygen in their composition...
. Both molecules are small and non-polar (and therefore non-associating). We can therefore expect that the behaviour of air within broad temperature and pressure ranges can be approximated as an ideal gas with reasonable accuracy. Experimental values for the compressibility factor confirm this.
| Pressure, bar (absolute) | ||||||||||||||
| Temp, K | 1 | 5 | 10 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 150 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 400 | 500 |
| 75 | 0.0052 | 0.0260 | 0.0519 | 0.1036 | 0.2063 | 0.3082 | 0.4094 | 0.5099 | 0.7581 | 1.0125 | | | | |
||||||||||||||
| 80 | | 0.0250 | 0.0499 | 0.0995 | 0.1981 | 0.2958 | 0.3927 | 0.4887 | 0.7258 | 0.9588 | 1.1931 | 1.4139 | | |
||||||||||||||
| 90 | 0.9764 | 0.0236 | 0.0453 | 0.0940 | 0.1866 | 0.2781 | 0.3686 | 0.4681 | 0.6779 | 0.8929 | 1.1098 | 1.3110 | 1.7161 | 2.1105 |
||||||||||||||
| 100 | 0.9797 | 0.8872 | 0.0453 | 0.0900 | 0.1782 | 0.2635 | 0.3498 | 0.4337 | 0.6386 | 0.8377 | 1.0395 | 1.2227 | 1.5937 | 1.9536 |
||||||||||||||
| 120 | 0.9880 | 0.9373 | 0.8860 | 0.6730 | 0.1778 | 0.2557 | 0.3371 | 0.4132 | 0.5964 | 0.7720 | 0.9530 | 1.1076 | 1.5091 | 1.7366 |
||||||||||||||
| 140 | 0.9927 | 0.9614 | 0.9205 | 0.8297 | 0.5856 | 0.3313 | 0.3737 | 0.4340 | 0.5909 | 0.7699 | 0.9114 | 1.0393 | 1.3202 | 1.5903 |
||||||||||||||
| 160 | 0.9951 | 0.9748 | 0.9489 | 0.8954 | 0.7803 | 0.6603 | 0.5696 | 0.5489 | 0.6340 | 0.7564 | 0.8840 | 1.0105 | 1.2585 | 1.4970 |
||||||||||||||
| 180 | 0.9967 | 0.9832 | 0.9660 | 0.9314 | 0.8625 | 0.7977 | 0.7432 | 0.7084 | 0.7180 | 0.7986 | 0.9000 | 1.0068 | 1.2232 | 1.4361 |
||||||||||||||
| 200 | 0.9978 | 0.9886 | 0.9767 | 0.9539 | 0.9100 | 0.8701 | 0.8374 | 0.8142 | 0.8061 | 0.8549 | 0.9311 | 1.0185 | 1.2054 | 1.3944 |
||||||||||||||
| 250 | 0.9992 | 0.9957 | 0.9911 | 0.9822 | 0.9671 | 0.9549 | 0.9463 | 0.9411 | 0.9450 | 0.9713 | 1.0152 | 1.0702 | 1.1990 | 1.3392 |
||||||||||||||
| 300 | 0.9999 | 0.9987 | 0.9974 | 0.9950 | 0.9917 | 0.9901 | 0.9903 | 0.9930 | 1.0074 | 1.0326 | 1.0669 | 1.1089 | 1.2073 | 1.3163 |
||||||||||||||
| 350 | 1.0000 | 1.0002 | 1.0004 | 1.0014 | 1.0038 | 1.0075 | 1.0121 | 1.0183 | 1.0377 | 1.0635 | 1.0947 | 1.1303 | 1.2116 | 1.3015 |
||||||||||||||
| 400 | 1.0002 | 1.0012 | 1.0025 | 1.0046 | 1.0100 | 1.0159 | 1.0229 | 1.0312 | 1.0533 | 1.0795 | 1.1087 | 1.1411 | 1.2117 | 1.2890 |
||||||||||||||
| 450 | 1.0003 | 1.0016 | 1.0034 | 1.0063 | 1.0133 | 1.0210 | 1.0287 | 1.0374 | 1.0614 | 1.0913 | 1.1183 | 1.1463 | 1.2090 | 1.2778 |
||||||||||||||
| 500 | 1.0003 | 1.0020 | 1.0034 | 1.0074 | 1.0151 | 1.0234 | 1.0323 | 1.0410 | 1.0650 | 1.0913 | 1.1183 | 1.1463 | 1.2051 | 1.2667 |
||||||||||||||
| 600 | 1.0004 | 1.0022 | 1.0039 | 1.0081 | 1.0164 | 1.0253 | 1.0340 | 1.0434 | 1.0678 | 1.0920 | 1.1172 | 1.1427 | 1.1947 | 1.2475 |
||||||||||||||
| 800 | 1.0004 | 1.0020 | 1.0038 | 1.0077 | 1.0157 | 1.0240 | 1.0321 | 1.0408 | 1.0621 | 1.0844 | 1.1061 | 1.1283 | 1.1720 | 1.2150 |
||||||||||||||
| 1000 | 1.0004 | 1.0018 | 1.0037 | 1.0068 | 1.0142 | 1.0215 | 1.0290 | 1.0365 | 1.0556 | 1.0744 | 1.0948 | 1.1131 | 1.1515 | 1.1889 |
||||||||||||||
Source: (table 3-162).
 values are calculated from values of pressure, volume (or density), and temperature in Vassernan, Kazavchinskii, and Rabinovich, "Thermophysical Properties of Air and Air Components;' Moscow, Nauka, 1966, and NBS-NSF Trans. TT 70-50095, 1971: and Vassernan and Rabinovich, "Thermophysical Properties of Liquid Air and Its Component, "Moscow, 1968, and NBS-NSF Trans. 69-55092, 1970.
values are calculated from values of pressure, volume (or density), and temperature in Vassernan, Kazavchinskii, and Rabinovich, "Thermophysical Properties of Air and Air Components;' Moscow, Nauka, 1966, and NBS-NSF Trans. TT 70-50095, 1971: and Vassernan and Rabinovich, "Thermophysical Properties of Liquid Air and Its Component, "Moscow, 1968, and NBS-NSF Trans. 69-55092, 1970.Compressibility of ammonia gas
Ammonia is small but highly polar molecule with significant interactions. Values can be obtained from Perry 4th ed (awaits future library visit)See also
- Real gasReal gasReal gases – as opposed to a perfect or ideal gas – exhibit properties that cannot be explained entirely using the ideal gas law. To understand the behaviour of real gases, the following must be taken into account:* compressibility effects;...
- Theorem of corresponding statesTheorem of corresponding statesAccording to van der Waals, the theorem of corresponding states indicates that all fluids, when compared at the same reduced temperature and reduced pressure, have approximately the same compressibility factor and all deviate from ideal gas behavior to about the same degree.Material constants that...
- Principle of corresponding states
- Van der Waals equationVan der Waals equationThe van der Waals equation is an equation of state for a fluid composed of particles that have a non-zero volume and a pairwise attractive inter-particle force It was derived by Johannes Diderik van der Waals in 1873, who received the Nobel prize in 1910 for "his work on the equation of state for...
- FugacityFugacityIn chemical thermodynamics, the fugacity of a real gas is an effective pressure which replaces the true mechanical pressure in accurate chemical equilibrium calculations. It is equal to the pressure of an ideal gas which has the same chemical potential as the real gas. For example, nitrogen gas ...
External links
- Compressibility factor (gases) A Citizendium article.
- Real Gases includes a discussion of compressibility factors.
- EnggCyclopedia's compressibility factor calculator based critical properties
- EnggCyclopedia's compressibility factor calculator for natural gas

