
Combinatorial chemistry
Encyclopedia
Combinatorial
chemistry
involves the rapid synthesis
or the computer simulation
of a large number of different but structurally related molecule
s or materials. It is especially common in CADD (Computer aided drug design) and can be done online with web based software, such as Molinspiration.
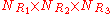 possible structures, where
possible structures, where 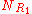 ,
, 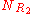 , and
, and  are the numbers of different substituents utilized.
are the numbers of different substituents utilized.
Although combinatorial chemistry has only really been taken up by industry since the 1990s, its roots can be seen as far back as the 1960s when a researcher at Rockefeller University
, Bruce Merrifield, started investigating the solid-phase synthesis
of peptide
s. Professor Pieczenik, a colleague of Nobel Laureate Merrifield, synthesized the first combinatorial library. US Patent 5,866,363. In the 1980s researcher H. Mario Geysen developed this technique further, creating arrays of different peptides on separate supports, but not a combinatorial library based on random synthesis.
In its modern form, combinatorial chemistry has probably had its biggest impact in the pharmaceutical industry. Researchers attempting to optimize the activity profile of a compound create a 'library
' of many different but related compounds. Advances in robotics
have led to an industrial approach to combinatorial synthesis, enabling companies to routinely produce over 100,000 new and unique compounds per year (see medicinal chemistry
).
In order to handle the vast number of structural possibilities, researchers often create a 'virtual library', a computational enumeration of all possible structures of a given pharmacophore
with all available reactants. Such a library can consist of thousands to millions of 'virtual' compounds. The researcher will select a subset of the 'virtual library' for actual synthesis, based upon various calculations and criteria (see ADME
, computational chemistry
, and QSAR).
has applied the techniques of combinatorial chemistry to the discovery of new materials. This work was pioneered by P.G. Schultz et al. in the mid nineties in the context of luminescent materials obtained by co-deposition of elements on a silicon substrate. His work was preceded by J. J. Hanak in 1970 but the computer and robotics tools were not available for the method to spread at the time. Work has been continued by several academic groups as well as companies with large research and development programs (Symyx Technologies
, GE
, Dow Chemical etc.). The technique has been used extensively for catalysis, coatings, electronics, and many other fields. The application of appropriate informatics tools is critical to handle, administer, and store the vast volumes of data produced. New types of Design of experiments
methods have also been developed to efficiently address the large experimental spaces that can be tackled using combinatorial methods.
, a multikinase inhibitor indicated for advanced renal cancer). The analysis of poor success rate of the approach has been suggested to connect with the rather limited chemical space
covered by products of combinatorial chemistry. When comparing the properties of compounds in combinatorial chemistry libraries to those of approved drugs and natural products, Feher and Schmidt noted that combinatorial chemistry libraries suffer particularly from the lack of chirality
, as well as structure rigidity, both of which are widely regarded as drug-like properties. Even though natural product drug discovery
has not probably been the most fashionable trend in pharmaceutical industry in recent times, a large proportion of new chemical entities still are nature-derived compounds, and thus, it has been suggested that effectiveness of combinatorial chemistry could be improved by enhancing the chemical diversity of screening libraries. As chirality and rigidity are the two most important features distinguishing approved drugs and natural products from compounds in combinatorial chemistry libraries, these are the two issues emphasized in so-called diversity oriented libraries, i.e. compound collections that aim at coverage of the chemical space, instead of just huge numbers of compounds.
(IPC), which entered into force on January 1, 2006, a special subclass has been created for patent application
s and patent
s related to invention
s in the domain of combinatorial chemistry: "C40B".
Combinatorics
Combinatorics is a branch of mathematics concerning the study of finite or countable discrete structures. Aspects of combinatorics include counting the structures of a given kind and size , deciding when certain criteria can be met, and constructing and analyzing objects meeting the criteria ,...
chemistry
Chemistry
Chemistry is the science of matter, especially its chemical reactions, but also its composition, structure and properties. Chemistry is concerned with atoms and their interactions with other atoms, and particularly with the properties of chemical bonds....
involves the rapid synthesis
Organic synthesis
Organic synthesis is a special branch of chemical synthesis and is concerned with the construction of organic compounds via organic reactions. Organic molecules can often contain a higher level of complexity compared to purely inorganic compounds, so the synthesis of organic compounds has...
or the computer simulation
Computer simulation
A computer simulation, a computer model, or a computational model is a computer program, or network of computers, that attempts to simulate an abstract model of a particular system...
of a large number of different but structurally related molecule
Molecule
A molecule is an electrically neutral group of at least two atoms held together by covalent chemical bonds. Molecules are distinguished from ions by their electrical charge...
s or materials. It is especially common in CADD (Computer aided drug design) and can be done online with web based software, such as Molinspiration.
Introduction
Synthesis of molecules in a combinatorial fashion can quickly lead to large numbers of molecules. For example, a molecule with three points of diversity (R1, R2, and R3) can generate possible structures, where
possible structures, where  ,
,  , and
, and  are the numbers of different substituents utilized.
are the numbers of different substituents utilized.Although combinatorial chemistry has only really been taken up by industry since the 1990s, its roots can be seen as far back as the 1960s when a researcher at Rockefeller University
Rockefeller University
The Rockefeller University is a private university offering postgraduate and postdoctoral education. It has a strong concentration in the biological sciences. It is also known for producing numerous Nobel laureates...
, Bruce Merrifield, started investigating the solid-phase synthesis
Solid-phase synthesis
In chemistry, solid-phase synthesis is a method in which molecules are bound on a bead and synthesized step-by-step in a reactant solution; compared with normal synthesis in a liquid state, it is easier to remove excess reactant or byproduct from the product. In this method, building blocks are...
of peptide
Peptide
Peptides are short polymers of amino acid monomers linked by peptide bonds. They are distinguished from proteins on the basis of size, typically containing less than 50 monomer units. The shortest peptides are dipeptides, consisting of two amino acids joined by a single peptide bond...
s. Professor Pieczenik, a colleague of Nobel Laureate Merrifield, synthesized the first combinatorial library. US Patent 5,866,363. In the 1980s researcher H. Mario Geysen developed this technique further, creating arrays of different peptides on separate supports, but not a combinatorial library based on random synthesis.
In its modern form, combinatorial chemistry has probably had its biggest impact in the pharmaceutical industry. Researchers attempting to optimize the activity profile of a compound create a 'library
Chemical library
A chemical library or compound library is a collection of stored chemicals usually used ultimately in high-throughput screening or industrial manufacture. The chemical library can consist in simple terms of a series of stored chemicals...
' of many different but related compounds. Advances in robotics
Robotics
Robotics is the branch of technology that deals with the design, construction, operation, structural disposition, manufacture and application of robots...
have led to an industrial approach to combinatorial synthesis, enabling companies to routinely produce over 100,000 new and unique compounds per year (see medicinal chemistry
Medicinal chemistry
Medicinal chemistry and pharmaceutical chemistry are disciplines at the intersection of chemistry, especially synthetic organic chemistry, and pharmacology and various other biological specialties, where it is involved with design, chemical synthesis and development for market of pharmaceutical...
).
In order to handle the vast number of structural possibilities, researchers often create a 'virtual library', a computational enumeration of all possible structures of a given pharmacophore
Pharmacophore
thumb|right|300px|An example of a pharmacophore model.A pharmacophore is an abstract description of molecular features which are necessary for molecular recognition of a ligand by a biological macromolecule....
with all available reactants. Such a library can consist of thousands to millions of 'virtual' compounds. The researcher will select a subset of the 'virtual library' for actual synthesis, based upon various calculations and criteria (see ADME
ADME
ADME is an acronym in pharmacokinetics and pharmacology for absorption, distribution, metabolism, and excretion, and describes the disposition of a pharmaceutical compound within an organism...
, computational chemistry
Computational chemistry
Computational chemistry is a branch of chemistry that uses principles of computer science to assist in solving chemical problems. It uses the results of theoretical chemistry, incorporated into efficient computer programs, to calculate the structures and properties of molecules and solids...
, and QSAR).
Materials Science
Materials scienceMaterials science
Materials science is an interdisciplinary field applying the properties of matter to various areas of science and engineering. This scientific field investigates the relationship between the structure of materials at atomic or molecular scales and their macroscopic properties. It incorporates...
has applied the techniques of combinatorial chemistry to the discovery of new materials. This work was pioneered by P.G. Schultz et al. in the mid nineties in the context of luminescent materials obtained by co-deposition of elements on a silicon substrate. His work was preceded by J. J. Hanak in 1970 but the computer and robotics tools were not available for the method to spread at the time. Work has been continued by several academic groups as well as companies with large research and development programs (Symyx Technologies
Symyx Technologies
Symyx Technologies is a pioneer in the area of combinatorial chemistry applied to heterogeneous catalysis and homogeneous catalysis, polymer formulations, electronic and magnetic materials....
, GE
General Electric
General Electric Company , or GE, is an American multinational conglomerate corporation incorporated in Schenectady, New York and headquartered in Fairfield, Connecticut, United States...
, Dow Chemical etc.). The technique has been used extensively for catalysis, coatings, electronics, and many other fields. The application of appropriate informatics tools is critical to handle, administer, and store the vast volumes of data produced. New types of Design of experiments
Design of experiments
In general usage, design of experiments or experimental design is the design of any information-gathering exercises where variation is present, whether under the full control of the experimenter or not. However, in statistics, these terms are usually used for controlled experiments...
methods have also been developed to efficiently address the large experimental spaces that can be tackled using combinatorial methods.
Diversity-oriented libraries
Even though combinatorial chemistry has been an essential part of early drug discovery for more than two decades, so far only one de novo combinatorial chemistry-synthesized chemical has been approved for clinical use by FDA (sorafenibSorafenib
Sorafenib , is a drug approved for the treatment of primary kidney cancer and advanced primary liver cancer ....
, a multikinase inhibitor indicated for advanced renal cancer). The analysis of poor success rate of the approach has been suggested to connect with the rather limited chemical space
Chemical space
Chemical space is the space spanned by all possible molecules and chemical compounds – that is, all stoichiometric combinations of electrons and atomic nuclei, in all possible topology isomers. Chemical reactions allow us to move in chemical space...
covered by products of combinatorial chemistry. When comparing the properties of compounds in combinatorial chemistry libraries to those of approved drugs and natural products, Feher and Schmidt noted that combinatorial chemistry libraries suffer particularly from the lack of chirality
Chirality (chemistry)
A chiral molecule is a type of molecule that lacks an internal plane of symmetry and thus has a non-superimposable mirror image. The feature that is most often the cause of chirality in molecules is the presence of an asymmetric carbon atom....
, as well as structure rigidity, both of which are widely regarded as drug-like properties. Even though natural product drug discovery
Drug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which drugs are discovered or designed.In the past most drugs have been discovered either by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous discovery...
has not probably been the most fashionable trend in pharmaceutical industry in recent times, a large proportion of new chemical entities still are nature-derived compounds, and thus, it has been suggested that effectiveness of combinatorial chemistry could be improved by enhancing the chemical diversity of screening libraries. As chirality and rigidity are the two most important features distinguishing approved drugs and natural products from compounds in combinatorial chemistry libraries, these are the two issues emphasized in so-called diversity oriented libraries, i.e. compound collections that aim at coverage of the chemical space, instead of just huge numbers of compounds.
Patent classification subclass
In the 8th edition of the International Patent ClassificationInternational Patent Classification
The International Patent Classification is a hierarchical patent classification system created under the Strasbourg Agreement and updated on a regular basis by a Committee of Experts, consisting of representatives of the Contracting States of that Agreement with observers from other...
(IPC), which entered into force on January 1, 2006, a special subclass has been created for patent application
Patent application
A patent application is a request pending at a patent office for the grant of a patent for the invention described and claimed by that application. An application consists of a description of the invention , together with official forms and correspondence relating to the application...
s and patent
Patent
A patent is a form of intellectual property. It consists of a set of exclusive rights granted by a sovereign state to an inventor or their assignee for a limited period of time in exchange for the public disclosure of an invention....
s related to invention
Invention
An invention is a novel composition, device, or process. An invention may be derived from a pre-existing model or idea, or it could be independently conceived, in which case it may be a radical breakthrough. In addition, there is cultural invention, which is an innovative set of useful social...
s in the domain of combinatorial chemistry: "C40B".
See also
- Dynamic combinatorial chemistryDynamic combinatorial chemistryDynamic combinatorial chemistry is defined as combinatorial chemistry under thermodynamic control.-Introduction:In a dynamic combinatorial library, all constituents are in equilibrium. The interconversion of library members into one another is through a reversible process that can involve covalent...
- CheminformaticsCheminformaticsCheminformatics is the use of computer and informational techniques, applied to a range of problems in the field of chemistry. These in silico techniques are used in pharmaceutical companies in the process of drug discovery...
- Drug discoveryDrug discoveryIn the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which drugs are discovered or designed.In the past most drugs have been discovered either by identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous discovery...
- High-throughput screeningHigh-throughput screeningHigh-throughput screening is a method for scientific experimentation especially used in drug discovery and relevant to the fields of biology and chemistry. Using robotics, data processing and control software, liquid handling devices, and sensitive detectors, High-Throughput Screening allows a...
- Mathematical chemistryMathematical chemistryMathematical chemistry is the area of research engaged in novel applications of mathematics to chemistry; it concerns itself principally with the mathematical modeling of chemical phenomena...
- Combinatorial biologyCombinatorial biologyIn biotechnology, combinatorial biology is the creation of a large number of compounds through technologies such as phage display. Similar to combinatorial chemistry, compounds are produced by biosynthesis rather than organic chemistry. This process was developed independently by Richard A....
- Molecular modeling
External links
- IUPAC's "Glossary of Terms Used in Combinatorial Chemistry"
- ACS Combinatorial Science (formerly Journal of Combinatorial Chemistry)
- Combinatorial Chemistry Review
- Molecular Diversity
- Combinatorial Chemistry and High Throughput Screening
- Combinatorial Chemistry: an Online Journal
- SmiLib - A free open-source software for combinatorial library enumeration
- GLARE - A free open-source software for combinatorial library design

