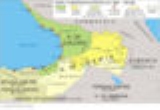
Colchis
Encyclopedia
In ancient geography
, Colchis or Kolkhis (Georgian
and Laz
: კოლხეთი, ḳolkheti or "ḳolkha"; Greek
: , Kolkhís) was an ancient Georgian
state
kingdom
and region
in Western Georgia, which played an important role in the ethnic and cultural formation of the Georgian nation
.
The Kingdom of Colchis contributed significantly to the development of medieval Georgian statehood after its unification with the eastern Georgian Kingdom of Iberia
. The term Colchians is used as the collective term for early Georgian tribes which populated the eastern coast of the Black Sea
.
In Greek mythology
, Colchis was the home of Aeëtes
and Medea
and the destination of the Argonauts
; Colchis is also thought to be the possible homeland of the Amazons
. Its geography is mostly assigned to what is now the western part of Georgia
and encompasses the present-day Georgian provinces of Samegrelo
, Imereti
, Guria
, Adjara
, Abkhazeti, Svaneti
, Racha
; the modern Turkey
’s Rize
, Trabzon
and Artvin
provinces (Lazistan
, Tao-Klarjeti
); and the modern Russia
’s Sochi
and Tuapse
districts. The Colchians were probably established on the Black Sea coast by the Middle Bronze Age
.
According to the scholar of the Caucasian studies Cyril Toumanoff
:
A second South Caucasian tribal union emerged in the 13th century BC
on the Black Sea coast under creating the Kingdom of Colchis in the western Georgia. This kingdom was a first state formation of the early Georgian tribes (including other Kartvelians such as Laz). According to most classic authors, a district which was bounded on the southwest by Pontus
, on the west by the Black Sea
as far as the river Corax (probably the present day Bzyb River
, Abkhazia
, Georgia
), on the north by the chain of the Greater Caucasus
, which lay between it and Asiatic Sarmatia
, on the east by Iberia
and Montes Moschici
(now the Lesser Caucasus
), and on the south by Armenia
. There is some little difference in authors as to the extent of the country westward: thus Strabo
makes Colchis begin at Trabzon
, while Ptolemy
, on the other hand, extends Pontus
to the Rioni River
. Pitsunda
was the last town to the north in Colchis.
The name of Colchis first appears in Aeschylus
and Pindar
. The earlier writers only speak about it under the name of Aea (Aia), the residence of the mythical king Aeëtes
: "Kolchian Aia lies at the furthest limits of sea and earth," wrote Apollonius of Rhodes
. The main river was the Phasis (now Rioni), which was according to some writers the south boundary of Colchis, but more probably flowed through the middle of that country from the Caucasus west by south to the Euxine, and the Anticites or Atticitus (now Kuban
). Arrian
mentions many others by name, but they would seem to have been little more than mountain torrents: the most important of them were Charieis, Chobus or Cobus, Singames, Tarsuras, Hippus, Astelephus, Chrysorrhoas, several of which are also noticed by Ptolemy
and Pliny
. The chief towns were Dioscurias
or Dioscuris (under the Romans
called Sebastopolis, now Sukhumi
) on the seaboard of the Euxine, Sarapana (now Shorapani
), Phasis
(now Poti
), Pityus (now Pitsunda
), Apsaros (now Gonio
), Surium
(now Vani
), Archaeopolis (now Nokalakevi
), Macheiresis, and Cyta or Cutatisium or Aia (now Kutaisi
), the traditional birthplace of Medea
. Scylax
mentions also Mala or Male, which he, in contradiction to other writers, makes the birthplace of Medea
.
, Colchis is usually defined as the area east of the Black Sea
Coast, restricted from the north by south-western slopes of the Greater Caucasus
Mountain Range, from the south by the northern slopes of the Lesser Caucasus in Georgia and Eastern Black Sea (Karadeniz) Mountains in Turkey, and from the east by Likhi Range, connecting the Greater and the Lesser Caucasus
Mountain Ranges. The central part of the region is Colchis Plain, stretching between Sokhumi and Kobuleti
; most of that lies on the elevation below 20 m a.s.l. Marginal parts of the region are mountains of the Great and the Lesser Caucasus and Likhi Range.
The climate is mild humid; near Batumi
, annual rainfall level reaches 4000 mm, which is the absolute maximum for the continental western Eurasia. The dominating natural landscapes of Colchis are temperate rainforests, yet degraded in the plain part of the region; wetlands (along the coastal parts of Colchis Plain); subalpine and alpine meadows
.
The Colchis has a high proportion of Tertiary relict plants and animals, with the closest relatives in distant parts of the world: five species of Rhododendron
s and other evergreen shrubs, wingnuts, Caucasian salamander
, Caucasian Parsley Frog, eight endemic species of lizards from the genus Darevskia
, Caucasian adder, Robert's vole, and endemic cave shrimps.
, related to the neighbouring Koban culture
, that emerged towards the Middle Bronze Age
. In at least some parts of Colchis the process of urbanization seems to have been well advanced by the end of the second millennium BC, centuries before Greek
settlement. The Colchian Late Bronze Age
(15th to 8th Century BC) saw the development of significant skill in the smelting and casting of metals that began long before this skill was mastered in Europe
. Sophisticated farming implements were made and fertile, well-watered lowlands with a mild climate promoted the growth of progressive agricultural techniques.
Colchis was inhabited by a number of related but distinct tribes whose settlements lay chiefly along the shore of the Black Sea. The chief of those were the Machelones
, Heniochi, Zydretae
, Lazi
, Chalybes
, Tabal
/Tibareni
/Tubal
, Mossynoeci
, Macrones
, Moschi
, Marres, Apsilae, Abasci, Sanigae, Coraxi, Coli, Melanchlaeni
, Geloni
and Soani (Suani)
. These tribes differed so completely in language and appearance from the surrounding nations that the ancients provided various theories to account for the phenomenon.
For example, Herodotus
states that the Colchians, with the Egyptians
and the Ethiopia
ns, were the first to practice circumcision
, a custom which he claims the Colchians themselves inherited from remnants of the army of Pharaoh
Sesostris
. He thus regarded them as Egyptians. Apollonius of Rhodes
states that the Egyptians of Colchis preserved as heirlooms a number of wooden tablets showing seas and highways with considerable accuracy. Though the 'Egyptian' theory of origin was not generally adopted by the ancients, it has been defended – but not with complete success, as Egyptians show no close physical, cultural or any genetic relationship to Colchians, and the term commonly mistranslated to mean 'black-skinned' by Herodotus translates most accurately to 'dark skinned' and was even used to describe tanned Greeks, not black Africans, as is often claimed. Claims that a black population existed in the area have never been verified, except for a few individuals imported as slaves in later eras.
Many modern theories suggest that the ancestors of the Laz
-Mingrelians
comprised the dominant ethnic and cultural presence in the region in antiquity, and hence played a significant role in the ethnogenesis of the modern Georgians
.
as the destination of the Argonauts
, the home of Medea
and the special domain of sorcery, was known to Urartians
as Qulha (aka Kolkha, or Kilkhi). Being in permanent wars with the neighbouring nations, the Colchians managed to absorb part of Diauehi
in the 750s BC, but lost several provinces (including the “royal city” of Ildemusa) to the Sarduris II of Urartu following the wars of 750-748 and 744-742 BC. Overrun by the Cimmerians
and Scythians in the 730s-720s BC, the kingdom disintegrated and came under the Achaemenid
Persian Empire towards the mid-6th century BC. The tribes living in the southern Colchis (Tibareni
, Mossynoeci
, Macrones
, Moschi
, and Marres) were incorporated in the 19th Satrap
y of the Persia, while the northern tribes submitted “voluntarily” and had to send to the Persian court 100 girls and 100 boys in every 5 years. The influence exerted on Colchis by the vast Achaemenid Empire with its thriving commerce and wide economic and commercial ties with other regions accelerated the socio-economic development of the Colchian land. Subsequently the Colchis people appear to have overthrown the Persian Authority, and to have formed an independent state. According to Ronald Suny: This western Georgian state was federated to Kartli-Iberia, and its kings ruled through skeptukhi (royal governors) who received a staff from the king.
who colonized the Colchian coast establishing here their trading posts at Phasis
, Gyenos, and Sukhumi
in the 6th-5th centuries BC. It was considered "the farthest voyage" according to an ancient Greek proverbial expression, the easternmost location in that society's known world, where the sun rose. It was situated just outside the lands conquered by Alexander the Great. Phasis
and Sukhumi
were the splendid Greek cities dominated by the mercantile oligarchies, sometimes being troubled by the Colchians from the hinterland before seemingly assimilating totally. After the fall of the Persian Empire, a significant part of Colchis locally known as Egrisi
was annexed to the recently created Kingdom of Iberia
(Kartli
) in ca. 302 BC. However, soon Colchis seceded and broke up into several small princedoms ruled by sceptuchi. They retained a degree of independence until conquered (circa 101 BC) by Mithridates VI of Pontus
.
, Mithridates VI made another his son Machares
king of Colchis, who held his power but for a short period. On the defeat of Mithridates VI of Pontus
in 65 BC, Colchis was occupied by Pompey
, who captured one of the local chiefs (sceptuchus) Olthaces, and installed Aristarchus as a dynast
(65-47 BC). On the fall of Pompey, Pharnaces II
, son of Mithridates
, took advantage of Julius Caesar
being occupied in Egypt
, and reduced Colchis, Armenia
, and some part of Cappadocia
, defeating Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus, whom Caesar subsequently sent against him. His triumph was, however, short-lived. Under Polemon I
, the son and successor of Pharnaces II
, Colchis was part of the Pontus
and the Bosporan Kingdom
. After the death of Polemon (8 BC), his second wife Pythodorida of Pontus
retained possession of Colchis as well as of Pontus itself, though the kingdom of Bosporus was wrested from her power. Her son and successor Polemon II of Pontus was induced by Emperor Nero
to abdicate the throne, and both Pontus and Colchis were incorporated in the Province of Galatia
(63) and later in Cappadocia
(81).
staged a major uprising against the Romans
which ended unsuccessfully. The lowlands and coastal area were frequently raided by fierce mountain tribes, with the Soanes
and Heniochi being the most powerful of them. Paying a nominal homage to Rome
, they created their own kingdoms and enjoyed significant independence. Christianity
began to spread in the early 1st century. Traditional accounts relate the event with Saint Andrew
, Saint Simon the Zealot
, and Saint Matata. The Hellenistic
, local pagan
and Mithraic religious beliefs would however remain widespread until the 4th century. By the 130s, the kingdoms of Machelons, Heniochi, Egrisi
, Apsilia, Abasgia, and Sanigia had occupied the district from south to north. Goths
, dwelling in the Crimea
and looking for new homes, raided Colchis in 253, but were repulsed with the help of the Roman garrison of Pitsunda
. By the 3rd-4th centuries, most of the local kingdoms and principalities had been subjugated by the Lazic kings, and thereafter the country was generally referred to as Lazica (Egrisi
).
Note: During his reign, the local chiefs, sceptuchi, continued to exercise some power. One of them, Olthaces, is mentioned by the Roman sources as a captive of Pompey
in 65 BC.
, King Aeëtes
hung the Golden Fleece
until it was seized by Jason
and the Argonauts
. Colchis was also the land where the mythological Prometheus
was punished by being chained to a mountain while an eagle ate at his liver for revealing to humanity the secret of fire. Amazons
also were said to be of Scythia
n origin from Colchis. The main mythical characters from Colchis are Aeëtes
, Medea
, Absyrtus
, Chalciope
, Circe
, Eidyia
, Pasiphaë
.
Geography
Geography is the science that studies the lands, features, inhabitants, and phenomena of Earth. A literal translation would be "to describe or write about the Earth". The first person to use the word "geography" was Eratosthenes...
, Colchis or Kolkhis (Georgian
Georgian language
Georgian is the native language of the Georgians and the official language of Georgia, a country in the Caucasus.Georgian is the primary language of about 4 million people in Georgia itself, and of another 500,000 abroad...
and Laz
Laz language
The Laz language is a South Caucasian language spoken by the Laz people on the Southeast shore of the Black Sea...
: კოლხეთი, ḳolkheti or "ḳolkha"; Greek
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek is the stage of the Greek language in the periods spanning the times c. 9th–6th centuries BC, , c. 5th–4th centuries BC , and the c. 3rd century BC – 6th century AD of ancient Greece and the ancient world; being predated in the 2nd millennium BC by Mycenaean Greek...
: , Kolkhís) was an ancient Georgian
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
state
Sovereign state
A sovereign state, or simply, state, is a state with a defined territory on which it exercises internal and external sovereignty, a permanent population, a government, and the capacity to enter into relations with other sovereign states. It is also normally understood to be a state which is neither...
kingdom
Monarchy
A monarchy is a form of government in which the office of head of state is usually held until death or abdication and is often hereditary and includes a royal house. In some cases, the monarch is elected...
and region
Region
Region is most commonly found as a term used in terrestrial and astrophysics sciences also an area, notably among the different sub-disciplines of geography, studied by regional geographers. Regions consist of subregions that contain clusters of like areas that are distinctive by their uniformity...
in Western Georgia, which played an important role in the ethnic and cultural formation of the Georgian nation
Georgians
The Georgians are an ethnic group that have originated in Georgia, where they constitute a majority of the population. Large Georgian communities are also present throughout Russia, European Union, United States, and South America....
.
The Kingdom of Colchis contributed significantly to the development of medieval Georgian statehood after its unification with the eastern Georgian Kingdom of Iberia
Caucasian Iberia
Iberia , also known as Iveria , was a name given by the ancient Greeks and Romans to the ancient Georgian kingdom of Kartli , corresponding roughly to the eastern and southern parts of the present day Georgia...
. The term Colchians is used as the collective term for early Georgian tribes which populated the eastern coast of the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
.
In Greek mythology
Greek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths and legends belonging to the ancient Greeks, concerning their gods and heroes, the nature of the world, and the origins and significance of their own cult and ritual practices. They were a part of religion in ancient Greece...
, Colchis was the home of Aeëtes
Aeëtes
In Greek mythology, Aeëtes , , , was a King of Colchis , son of the sun-god Helios and the Oceanid Perseis , brother of Circe and Pasiphae, and father of Medea, Chalciope and Apsyrtus...
and Medea
Medea
Medea is a woman in Greek mythology. She was the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, niece of Circe, granddaughter of the sun god Helios, and later wife to the hero Jason, with whom she had two children, Mermeros and Pheres. In Euripides's play Medea, Jason leaves Medea when Creon, king of...
and the destination of the Argonauts
Argonauts
The Argonauts ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology who, in the years before the Trojan War, accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, the Argo, which was named after its builder, Argus. "Argonauts", therefore, literally means...
; Colchis is also thought to be the possible homeland of the Amazons
Amazons
The Amazons are a nation of all-female warriors in Greek mythology and Classical antiquity. Herodotus placed them in a region bordering Scythia in Sarmatia...
. Its geography is mostly assigned to what is now the western part of Georgia
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
and encompasses the present-day Georgian provinces of Samegrelo
Samegrelo
Samegrelo/Samargalo or Megrelia, Mingrelia is a historic province in the western part of Georgia, formerly also known as Odishi.It is inhabited by the Megrelians, an ethnic subgroup of the Georgians.-Geography and Climate:...
, Imereti
Imereti
Imereti is a province in Georgia situated along the middle and upper reaches of the Rioni river. It consists of the following Georgian administrative-territorial units:#Kutaisi #Baghdati region#Vani region#Zestafoni region...
, Guria
Guria
Guria is a region in Georgia, in the western part of the country, bordered by the eastern end of the Black Sea. The region has a population of 143,357 and Ozurgeti is a regional capital.-Geography:...
, Adjara
Adjara
Adjara , officially the Autonomous Republic of Adjara , is an autonomous republic of Georgia.Adjara is located in the southwestern corner of Georgia, bordered by Turkey to the south and the eastern end of the Black Sea...
, Abkhazeti, Svaneti
Svaneti
Svaneti is a historic province in Georgia, in the northwestern part of the country. It is inhabited by the Svans, a geographic subgroup of the Georgians.- Geography :...
, Racha
Racha
Racha is a highland area in western Georgia, located in the upper Rioni river valley and hemmed in by the Greater Caucasus mountains...
; the modern Turkey
Turkey
Turkey , known officially as the Republic of Turkey , is a Eurasian country located in Western Asia and in East Thrace in Southeastern Europe...
’s Rize
Rize
Rize is the capital of Rize Province, in northeast Turkey, on the Black Sea coast.-Etymology:The name comes from Greek or Ριζαίον , meaning "mountain slopes". In modern times, its name in Greek was usually Ριζούντα . Its Latin forms are Rhizus and Rhizaeum...
, Trabzon
Trabzon
Trabzon is a city on the Black Sea coast of north-eastern Turkey and the capital of Trabzon Province. Trabzon, located on the historical Silk Road, became a melting pot of religions, languages and culture for centuries and a trade gateway to Iran in the southeast and the Caucasus to the northeast...
and Artvin
Artvin
-History:See Artvin Province for the history of the region.-Places of interest:* Artvin or Livana castle, built in 937There are a number of Ottoman Empire houses and public buildings including:* Salih Bey mosque, built in 1792...
provinces (Lazistan
Lazistan
Lazistan was the Ottoman administrative name for the sanjak comprising the Laz or Lazuri-speaking population on the southeastern shore of the Black Sea. However, its boundaries did not coincide with the Laz-speaking area...
, Tao-Klarjeti
Tao-Klarjeti
Tao-Klarjeti is the term conventionally used in modern history writing to describe the historic south-western Georgian principalities, now forming part of north-eastern Turkey and divided among the provinces of Erzurum, Artvin, Ardahan and Kars...
); and the modern Russia
Russia
Russia or , officially known as both Russia and the Russian Federation , is a country in northern Eurasia. It is a federal semi-presidential republic, comprising 83 federal subjects...
’s Sochi
Sochi
Sochi is a city in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, situated just north of Russia's border with the de facto independent republic of Abkhazia, on the Black Sea coast. Greater Sochi sprawls for along the shores of the Black Sea near the Caucasus Mountains...
and Tuapse
Tuapse
Tuapse is a town in Krasnodar Krai, Russia, situated on the northeast shore of the Black Sea, south of Gelendzhik and north of Sochi. It serves as the administrative center of Tuapsinsky District, although administratively it is separate from it...
districts. The Colchians were probably established on the Black Sea coast by the Middle Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
.
Geography and toponyms
The kingdom of Colchis, which existed from the sixth to the first centuries BC is regarded as the first early Georgian state and the term Colchians was used as the collective term for early Georgian tribes which populated the eastern coast of the Black Sea.According to the scholar of the Caucasian studies Cyril Toumanoff
Cyril Toumanoff
Cyril Leo Heraclius, Prince Toumanoff was an United States-based historian and genealogist who mostly specialized in the history and genealogies of medieval Georgia, Armenia, the Byzantine Empire, and Iran...
:
A second South Caucasian tribal union emerged in the 13th century BC
13th century BC
The 13th century BC was the period from 1300 to 1201 BC.-Events:*1300 BC: Cemetery H culture comes to an end.*1292 BC: End of the Eighteenth dynasty of Egypt, start of the Nineteenth Dynasty....
on the Black Sea coast under creating the Kingdom of Colchis in the western Georgia. This kingdom was a first state formation of the early Georgian tribes (including other Kartvelians such as Laz). According to most classic authors, a district which was bounded on the southwest by Pontus
Pontus
Pontus or Pontos is a historical Greek designation for a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in modern-day northeastern Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region in antiquity by the Greeks who colonized the area, and derived from the Greek name of the Black Sea: Πόντος...
, on the west by the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
as far as the river Corax (probably the present day Bzyb River
Bzyb River
Soviet President Nikita Khrushchev once proposed a major dam and hydroelectric power generation facility on the Bzyb River, since his favourite resort was located near the mouth of the river at Pitsunda. However, this proposal was ruled out by his experts who opined that a dam built on the Bzyb...
, Abkhazia
Abkhazia
Abkhazia is a disputed political entity on the eastern coast of the Black Sea and the south-western flank of the Caucasus.Abkhazia considers itself an independent state, called the Republic of Abkhazia or Apsny...
, Georgia
Georgia (country)
Georgia is a sovereign state in the Caucasus region of Eurasia. Located at the crossroads of Western Asia and Eastern Europe, it is bounded to the west by the Black Sea, to the north by Russia, to the southwest by Turkey, to the south by Armenia, and to the southeast by Azerbaijan. The capital of...
), on the north by the chain of the Greater Caucasus
Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains is a mountain system in Eurasia between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea in the Caucasus region .The Caucasus Mountains includes:* the Greater Caucasus Mountain Range and* the Lesser Caucasus Mountains....
, which lay between it and Asiatic Sarmatia
Sarmatians
The Iron Age Sarmatians were an Iranian people in Classical Antiquity, flourishing from about the 5th century BC to the 4th century AD....
, on the east by Iberia
Caucasian Iberia
Iberia , also known as Iveria , was a name given by the ancient Greeks and Romans to the ancient Georgian kingdom of Kartli , corresponding roughly to the eastern and southern parts of the present day Georgia...
and Montes Moschici
Moschia
Moschia is a mountainous region of Georgia between Iberia, Armenia, and Colchis. The Moschian Mountains were the connecting chain between the Caucasus and Anti Taurus Mountains...
(now the Lesser Caucasus
Caucasus Mountains
The Caucasus Mountains is a mountain system in Eurasia between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea in the Caucasus region .The Caucasus Mountains includes:* the Greater Caucasus Mountain Range and* the Lesser Caucasus Mountains....
), and on the south by Armenia
Armenia
Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
. There is some little difference in authors as to the extent of the country westward: thus Strabo
Strabo
Strabo, also written Strabon was a Greek historian, geographer and philosopher.-Life:Strabo was born to an affluent family from Amaseia in Pontus , a city which he said was situated the approximate equivalent of 75 km from the Black Sea...
makes Colchis begin at Trabzon
Trabzon
Trabzon is a city on the Black Sea coast of north-eastern Turkey and the capital of Trabzon Province. Trabzon, located on the historical Silk Road, became a melting pot of religions, languages and culture for centuries and a trade gateway to Iran in the southeast and the Caucasus to the northeast...
, while Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
, on the other hand, extends Pontus
Pontus
Pontus or Pontos is a historical Greek designation for a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in modern-day northeastern Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region in antiquity by the Greeks who colonized the area, and derived from the Greek name of the Black Sea: Πόντος...
to the Rioni River
Rioni River
The Rioni or Rion River is the main river of western Georgia. It originates in the Caucasus Mountains, in the region of Racha and flows west to the Black Sea, entering it north of the city of Poti...
. Pitsunda
Pitsunda
Pitsunda is a resort town in Gagra district of Abkhazia.The town was founded by the Greeks in the 5th century BC as a trade colony Pityus or Pitiunt. Excavations guided by Andria Apakidze unearthed remains of three 4th-century churches and a bath with superb mosaic floors...
was the last town to the north in Colchis.
The name of Colchis first appears in Aeschylus
Aeschylus
Aeschylus was the first of the three ancient Greek tragedians whose work has survived, the others being Sophocles and Euripides, and is often described as the father of tragedy. His name derives from the Greek word aiskhos , meaning "shame"...
and Pindar
Pindar
Pindar , was an Ancient Greek lyric poet. Of the canonical nine lyric poets of ancient Greece, his work is the best preserved. Quintilian described him as "by far the greatest of the nine lyric poets, in virtue of his inspired magnificence, the beauty of his thoughts and figures, the rich...
. The earlier writers only speak about it under the name of Aea (Aia), the residence of the mythical king Aeëtes
Aeëtes
In Greek mythology, Aeëtes , , , was a King of Colchis , son of the sun-god Helios and the Oceanid Perseis , brother of Circe and Pasiphae, and father of Medea, Chalciope and Apsyrtus...
: "Kolchian Aia lies at the furthest limits of sea and earth," wrote Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius Rhodius, also known as Apollonius of Rhodes , early 3rd century BCE – after 246 BCE, was a poet, and a librarian at the Library of Alexandria...
. The main river was the Phasis (now Rioni), which was according to some writers the south boundary of Colchis, but more probably flowed through the middle of that country from the Caucasus west by south to the Euxine, and the Anticites or Atticitus (now Kuban
Kuban
Kuban is a geographic region of Southern Russia surrounding the Kuban River, on the Black Sea between the Don Steppe, Volga Delta and the Caucasus...
). Arrian
Arrian
Lucius Flavius Arrianus 'Xenophon , known in English as Arrian , and Arrian of Nicomedia, was a Roman historian, public servant, a military commander and a philosopher of the 2nd-century Roman period...
mentions many others by name, but they would seem to have been little more than mountain torrents: the most important of them were Charieis, Chobus or Cobus, Singames, Tarsuras, Hippus, Astelephus, Chrysorrhoas, several of which are also noticed by Ptolemy
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy , was a Roman citizen of Egypt who wrote in Greek. He was a mathematician, astronomer, geographer, astrologer, and poet of a single epigram in the Greek Anthology. He lived in Egypt under Roman rule, and is believed to have been born in the town of Ptolemais Hermiou in the...
and Pliny
Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus , better known as Pliny the Elder, was a Roman author, naturalist, and natural philosopher, as well as naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and personal friend of the emperor Vespasian...
. The chief towns were Dioscurias
Sukhumi
Sukhumi is the capital of Abkhazia, a disputed region on the Black Sea coast. The city suffered heavily during the Georgian-Abkhaz conflict in the early 1990s.-Naming:...
or Dioscuris (under the Romans
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
called Sebastopolis, now Sukhumi
Sukhumi
Sukhumi is the capital of Abkhazia, a disputed region on the Black Sea coast. The city suffered heavily during the Georgian-Abkhaz conflict in the early 1990s.-Naming:...
) on the seaboard of the Euxine, Sarapana (now Shorapani
Shorapani
Shorapani is a small Georgian town, situated in the Zestaponi District, part of the region of Imereti. Founded in the 3rd century BC, it served as a residence of the eristavi of Argveti in the Antiquity and the early Middle Ages.Near the town are the ruins of a fortress, mentioned as Sarapana by...
), Phasis
Phasis (town)
Phasis was an ancient and early medieval city on the eastern Black Sea coast, founded in the 7th/6th century BC as a colony of the Milesian Greeks at the mouth of the eponymous river in Colchis, near the modern-day port city of Poti, Georgia.-Etymology:...
(now Poti
Poti
Poti is a port city in Georgia, located on the eastern Black Sea coast in the region of Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti in the west of the country. Built near the site of the ancient Greek colony of Phasis, the city has become a major port city and industrial center since the early 20th century. It is also...
), Pityus (now Pitsunda
Pitsunda
Pitsunda is a resort town in Gagra district of Abkhazia.The town was founded by the Greeks in the 5th century BC as a trade colony Pityus or Pitiunt. Excavations guided by Andria Apakidze unearthed remains of three 4th-century churches and a bath with superb mosaic floors...
), Apsaros (now Gonio
Gonio
Gonio fortress , is a Roman fortification in Adjara, on the Black sea, 15 km south of Batumi, at the mouth of the Chorokhi river. The village sits 4 km north of the Turkish border....
), Surium
Vani
Vani is a town in Imereti region of western Georgia, at the Sulori river , 41 km southwest from the regional capital Kutaisi...
(now Vani
Vani
Vani is a town in Imereti region of western Georgia, at the Sulori river , 41 km southwest from the regional capital Kutaisi...
), Archaeopolis (now Nokalakevi
Nokalakevi
Nokalakevi, also known as Archaeopolis, is a village and archaeological site in the Senaki municipality, Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti region, Georgia.- History :...
), Macheiresis, and Cyta or Cutatisium or Aia (now Kutaisi
Kutaisi
Kutaisi is Georgia's second largest city and the capital of the western region of Imereti. It is 221 km to the west of Tbilisi.-Geography:...
), the traditional birthplace of Medea
Medea
Medea is a woman in Greek mythology. She was the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, niece of Circe, granddaughter of the sun god Helios, and later wife to the hero Jason, with whom she had two children, Mermeros and Pheres. In Euripides's play Medea, Jason leaves Medea when Creon, king of...
. Scylax
Scylax of Caryanda
Scylax of Caryanda was a renowned Carian explorer and writer of the 6th and 5th centuries BCE.-Exploration and literary works:In about 515 BCE, Scylax was sent by King Darius I of Persia to follow the course of the Indus River and discover where it led. Scylax and his companions set out from city...
mentions also Mala or Male, which he, in contradiction to other writers, makes the birthplace of Medea
Medea
Medea is a woman in Greek mythology. She was the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, niece of Circe, granddaughter of the sun god Helios, and later wife to the hero Jason, with whom she had two children, Mermeros and Pheres. In Euripides's play Medea, Jason leaves Medea when Creon, king of...
.
Physical-geographic characteristics
In physical geographyPhysical geography
Physical geography is one of the two major subfields of geography. Physical geography is that branch of natural science which deals with the study of processes and patterns in the natural environment like the atmosphere, biosphere and geosphere, as opposed to the cultural or built environment, the...
, Colchis is usually defined as the area east of the Black Sea
Black Sea
The Black Sea is bounded by Europe, Anatolia and the Caucasus and is ultimately connected to the Atlantic Ocean via the Mediterranean and the Aegean seas and various straits. The Bosphorus strait connects it to the Sea of Marmara, and the strait of the Dardanelles connects that sea to the Aegean...
Coast, restricted from the north by south-western slopes of the Greater Caucasus
Greater Caucasus
Greater Caucasus , sometimes translated as "Caucasus Major", "Big Caucasus" or "Large Caucasus") is the major mountain range of the Caucasus Mountains....
Mountain Range, from the south by the northern slopes of the Lesser Caucasus in Georgia and Eastern Black Sea (Karadeniz) Mountains in Turkey, and from the east by Likhi Range, connecting the Greater and the Lesser Caucasus
Lesser Caucasus
Lesser Caucasus is one of the two main mountain ranges of Caucasus mountains, of length about 600 km....
Mountain Ranges. The central part of the region is Colchis Plain, stretching between Sokhumi and Kobuleti
Kobuleti
Kobuleti is a town in Georgia's southwestern region of Ajaria. It is situated on the eastern coast of the Black Sea. Kobuleti is a sea resort, visited annually by Georgians and many former Soviet Union residents. From the 17th century into the 19th, Kobuleti was a fiefdom of the Tavdgiridze...
; most of that lies on the elevation below 20 m a.s.l. Marginal parts of the region are mountains of the Great and the Lesser Caucasus and Likhi Range.
The climate is mild humid; near Batumi
Batumi
Batumi is a seaside city on the Black Sea coast and capital of Adjara, an autonomous republic in southwest Georgia. Sometimes considered Georgia's second capital, with a population of 121,806 , Batumi serves as an important port and a commercial center. It is situated in a subtropical zone, rich in...
, annual rainfall level reaches 4000 mm, which is the absolute maximum for the continental western Eurasia. The dominating natural landscapes of Colchis are temperate rainforests, yet degraded in the plain part of the region; wetlands (along the coastal parts of Colchis Plain); subalpine and alpine meadows
Alpine Meadows
The term Alpine Meadows may refer to:* Alpine Meadows, California, an unincorporated community in California* Alpine Meadows Lodge, outside Golden, British Columbia* Alpine Meadows Ranch, designed by Frank Lloyd Wright in Darby, Montana...
.
The Colchis has a high proportion of Tertiary relict plants and animals, with the closest relatives in distant parts of the world: five species of Rhododendron
Rhododendron
Rhododendron is a genus of over 1 000 species of woody plants in the heath family, most with showy flowers...
s and other evergreen shrubs, wingnuts, Caucasian salamander
Caucasian Salamander
The Caucasian Salamander is a species of salamander in the Salamandridae family.It is found in Georgia and Turkey.Its natural habitats are temperate forests and rivers....
, Caucasian Parsley Frog, eight endemic species of lizards from the genus Darevskia
Darevskia
Darevskia is a genus of wall lizards of the family Lacertidae.-Species:*Darevskia alpina*Darevskia armeniaca*Darevskia bendimahiensis*Darevskia brauneri*Darevskia caucasica*Darevskia clarkorum*Darevskia daghestanica...
, Caucasian adder, Robert's vole, and endemic cave shrimps.
Earliest times
The eastern Black Sea region in antiquity was home to the well-developed bronze culture known as the Colchian cultureColchian culture
Colchian culture is a late Bronze Age and Iron Age culture of the western Caucasus, mostly in western Georgia. It was partially succeeded by the Koban culture in northern and central Caucasus....
, related to the neighbouring Koban culture
Koban culture
The Koban culture is a late Bronze Age and Iron Age culture of the northern and central Caucasus. It is preceded by the Colchian culture of the western Caucasus and the Kharachoi culture further east....
, that emerged towards the Middle Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
. In at least some parts of Colchis the process of urbanization seems to have been well advanced by the end of the second millennium BC, centuries before Greek
Ancient Greece
Ancient Greece is a civilization belonging to a period of Greek history that lasted from the Archaic period of the 8th to 6th centuries BC to the end of antiquity. Immediately following this period was the beginning of the Early Middle Ages and the Byzantine era. Included in Ancient Greece is the...
settlement. The Colchian Late Bronze Age
Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a period characterized by the use of copper and its alloy bronze as the chief hard materials in the manufacture of some implements and weapons. Chronologically, it stands between the Stone Age and Iron Age...
(15th to 8th Century BC) saw the development of significant skill in the smelting and casting of metals that began long before this skill was mastered in Europe
Europe
Europe is, by convention, one of the world's seven continents. Comprising the westernmost peninsula of Eurasia, Europe is generally 'divided' from Asia to its east by the watershed divides of the Ural and Caucasus Mountains, the Ural River, the Caspian and Black Seas, and the waterways connecting...
. Sophisticated farming implements were made and fertile, well-watered lowlands with a mild climate promoted the growth of progressive agricultural techniques.
Colchis was inhabited by a number of related but distinct tribes whose settlements lay chiefly along the shore of the Black Sea. The chief of those were the Machelones
Machelones
The Machelones were a Colchian tribe located to the far south of the Phasis . There are several references to them in Classical sources...
, Heniochi, Zydretae
Zydretae
The Zydretae were an ancient people of Colchis recorded by the Classical accounts as dwelling on the coast of the Pontus Euxinus , on the southern side of the Apsarus river , and between the Machelonoi and the Lazi tribes...
, Lazi
Egrisi
Lazica or Egrisi in Georgian |Georgia]], named after the Laz tribe, which at some time dominated the local ruling élite.The kingdom flourished between the 6th century BC and the 7th century AD. It covered part of the territory of the former kingdom Colchis and subjugated the territory of modern...
, Chalybes
Chalybes
The Chalybes or Chaldoi were a tribe of proto-Georgians. Classical Antiquity credited with the invention of ferrous metallurgy....
, Tabal
Tabal
Tabal was a Luwian speaking Neo-Hittite kingdom of South Central Anatolia. According to archaeologist Kurt Bittel, the kingdom of Tabal first appeared after the collapse of the Hittite Empire....
/Tibareni
Tibareni
The Tibareni were a people referred to in Herodotus, Xenophon, Strabo and other classical authors. In classical times, they and other related tribes, the Chalybes and the Mossynoeci, were considered the founders of metallurgy...
/Tubal
Tubal
Tubal, תובל or תבל , in Genesis 10 , was the name of a son of Japheth, son of Noah.Many authors, following the Jewish historian Flavius Josephus , related the name to Iber- Caucasian Iberia...
, Mossynoeci
Mossynoeci
Mossynoeci is a name that the Greeks of the Euxine Sea applied to the peoples of Pontus, the northern Anatolian coast west of Trebizond.-Herodotus:...
, Macrones
Macrones
The Macrones were an ancient Colchian tribe in the east of Pontus, about the Moschici Mountains .The Macrones are first mentioned by Herodotus , who relates that they, along with Moschi, Tabal, Mossynoeci, and Mares, formed the nineteenth satrapy within the Achaemenid Persian Empire and fought...
, Moschi
Meskheti
Meskheti is in a mountainous area of Moschia and is a former province in southwestern Georgia. The ancient Georgian tribes of Meskhi and Mosiniks were the indigenous population of this region. A majority of the modern Georgian population of Meskheti are descendants of these ancient tribes...
, Marres, Apsilae, Abasci, Sanigae, Coraxi, Coli, Melanchlaeni
Melanchlaeni
Melanchlaeni may refer to two ancient tribes. One is a tribe mentioned by Herodotus that lived north of Scythia. They have been identified by some with various Finnic tribes .The other tribe is mentioned by Pliny the Elder....
, Geloni
Gelonians
The Gelonians , also known as Helonians , are mentioned as a nation in northwestern Scythia by Herodotus. Herodotus states that they were originally Hellenes who settled among the Budinoi, and that they are bilingual in Greek and the Scythian language.Their capital was called Gelonos or Helonos,...
and Soani (Suani)
Svaneti
Svaneti is a historic province in Georgia, in the northwestern part of the country. It is inhabited by the Svans, a geographic subgroup of the Georgians.- Geography :...
. These tribes differed so completely in language and appearance from the surrounding nations that the ancients provided various theories to account for the phenomenon.
For example, Herodotus
Herodotus
Herodotus was an ancient Greek historian who was born in Halicarnassus, Caria and lived in the 5th century BC . He has been called the "Father of History", and was the first historian known to collect his materials systematically, test their accuracy to a certain extent and arrange them in a...
states that the Colchians, with the Egyptians
Egyptians
Egyptians are nation an ethnic group made up of Mediterranean North Africans, the indigenous people of Egypt.Egyptian identity is closely tied to geography. The population of Egypt is concentrated in the lower Nile Valley, the small strip of cultivable land stretching from the First Cataract to...
and the Ethiopia
Ethiopia
Ethiopia , officially known as the Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia, is a country located in the Horn of Africa. It is the second-most populous nation in Africa, with over 82 million inhabitants, and the tenth-largest by area, occupying 1,100,000 km2...
ns, were the first to practice circumcision
Circumcision
Male circumcision is the surgical removal of some or all of the foreskin from the penis. The word "circumcision" comes from Latin and ....
, a custom which he claims the Colchians themselves inherited from remnants of the army of Pharaoh
Pharaoh
Pharaoh is a title used in many modern discussions of the ancient Egyptian rulers of all periods. The title originates in the term "pr-aa" which means "great house" and describes the royal palace...
Sesostris
Sesostris
Sesostris was the name of a legendary king of ancient Egypt who led a military expedition into parts of Europe, as related by Herodotus.-Account of Herodotus:...
. He thus regarded them as Egyptians. Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius of Rhodes
Apollonius Rhodius, also known as Apollonius of Rhodes , early 3rd century BCE – after 246 BCE, was a poet, and a librarian at the Library of Alexandria...
states that the Egyptians of Colchis preserved as heirlooms a number of wooden tablets showing seas and highways with considerable accuracy. Though the 'Egyptian' theory of origin was not generally adopted by the ancients, it has been defended – but not with complete success, as Egyptians show no close physical, cultural or any genetic relationship to Colchians, and the term commonly mistranslated to mean 'black-skinned' by Herodotus translates most accurately to 'dark skinned' and was even used to describe tanned Greeks, not black Africans, as is often claimed. Claims that a black population existed in the area have never been verified, except for a few individuals imported as slaves in later eras.
Many modern theories suggest that the ancestors of the Laz
Laz people
The Laz are an ethnic group native to the Black Sea coastal regions of Turkey and Georgia...
-Mingrelians
Samegrelo
Samegrelo/Samargalo or Megrelia, Mingrelia is a historic province in the western part of Georgia, formerly also known as Odishi.It is inhabited by the Megrelians, an ethnic subgroup of the Georgians.-Geography and Climate:...
comprised the dominant ethnic and cultural presence in the region in antiquity, and hence played a significant role in the ethnogenesis of the modern Georgians
Georgians
The Georgians are an ethnic group that have originated in Georgia, where they constitute a majority of the population. Large Georgian communities are also present throughout Russia, European Union, United States, and South America....
.
Qulha (Kolkha)
In the 13th century BC, the Kingdom of Colchis was formed as a result of the increasing consolidation of the tribes inhabiting the region. This power, celebrated in Greek mythologyGreek mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths and legends belonging to the ancient Greeks, concerning their gods and heroes, the nature of the world, and the origins and significance of their own cult and ritual practices. They were a part of religion in ancient Greece...
as the destination of the Argonauts
Argonauts
The Argonauts ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology who, in the years before the Trojan War, accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, the Argo, which was named after its builder, Argus. "Argonauts", therefore, literally means...
, the home of Medea
Medea
Medea is a woman in Greek mythology. She was the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, niece of Circe, granddaughter of the sun god Helios, and later wife to the hero Jason, with whom she had two children, Mermeros and Pheres. In Euripides's play Medea, Jason leaves Medea when Creon, king of...
and the special domain of sorcery, was known to Urartians
Urartu
Urartu , corresponding to Ararat or Kingdom of Van was an Iron Age kingdom centered around Lake Van in the Armenian Highland....
as Qulha (aka Kolkha, or Kilkhi). Being in permanent wars with the neighbouring nations, the Colchians managed to absorb part of Diauehi
Diauehi
Diauehi was an ancient people in northeastern Anatolia, mentioned in the Urartian inscriptions. It is usually identified with Daiaeni of the Yonjalu inscription of the Assyrian king Tiglath-Pileser I’s third year...
in the 750s BC, but lost several provinces (including the “royal city” of Ildemusa) to the Sarduris II of Urartu following the wars of 750-748 and 744-742 BC. Overrun by the Cimmerians
Cimmerians
The Cimmerians or Kimmerians were ancient equestrian nomads of Indo-European origin.According to the Greek historian Herodotus, of the 5th century BC, the Cimmerians inhabited the region north of the Caucasus and the Black Sea during the 8th and 7th centuries BC, in what is now Ukraine and Russia...
and Scythians in the 730s-720s BC, the kingdom disintegrated and came under the Achaemenid
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire , sometimes known as First Persian Empire and/or Persian Empire, was founded in the 6th century BCE by Cyrus the Great who overthrew the Median confederation...
Persian Empire towards the mid-6th century BC. The tribes living in the southern Colchis (Tibareni
Tabal
Tabal was a Luwian speaking Neo-Hittite kingdom of South Central Anatolia. According to archaeologist Kurt Bittel, the kingdom of Tabal first appeared after the collapse of the Hittite Empire....
, Mossynoeci
Mossynoeci
Mossynoeci is a name that the Greeks of the Euxine Sea applied to the peoples of Pontus, the northern Anatolian coast west of Trebizond.-Herodotus:...
, Macrones
Macrones
The Macrones were an ancient Colchian tribe in the east of Pontus, about the Moschici Mountains .The Macrones are first mentioned by Herodotus , who relates that they, along with Moschi, Tabal, Mossynoeci, and Mares, formed the nineteenth satrapy within the Achaemenid Persian Empire and fought...
, Moschi
Meskheti
Meskheti is in a mountainous area of Moschia and is a former province in southwestern Georgia. The ancient Georgian tribes of Meskhi and Mosiniks were the indigenous population of this region. A majority of the modern Georgian population of Meskheti are descendants of these ancient tribes...
, and Marres) were incorporated in the 19th Satrap
Satrap
Satrap was the name given to the governors of the provinces of the ancient Median and Achaemenid Empires and in several of their successors, such as the Sassanid Empire and the Hellenistic empires....
y of the Persia, while the northern tribes submitted “voluntarily” and had to send to the Persian court 100 girls and 100 boys in every 5 years. The influence exerted on Colchis by the vast Achaemenid Empire with its thriving commerce and wide economic and commercial ties with other regions accelerated the socio-economic development of the Colchian land. Subsequently the Colchis people appear to have overthrown the Persian Authority, and to have formed an independent state. According to Ronald Suny: This western Georgian state was federated to Kartli-Iberia, and its kings ruled through skeptukhi (royal governors) who received a staff from the king.
Greek colonization
The advanced economy and favorable geographic and natural conditions of the area attracted the Milesian GreeksMiletus
Miletus was an ancient Greek city on the western coast of Anatolia , near the mouth of the Maeander River in ancient Caria...
who colonized the Colchian coast establishing here their trading posts at Phasis
Poti
Poti is a port city in Georgia, located on the eastern Black Sea coast in the region of Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti in the west of the country. Built near the site of the ancient Greek colony of Phasis, the city has become a major port city and industrial center since the early 20th century. It is also...
, Gyenos, and Sukhumi
Sukhumi
Sukhumi is the capital of Abkhazia, a disputed region on the Black Sea coast. The city suffered heavily during the Georgian-Abkhaz conflict in the early 1990s.-Naming:...
in the 6th-5th centuries BC. It was considered "the farthest voyage" according to an ancient Greek proverbial expression, the easternmost location in that society's known world, where the sun rose. It was situated just outside the lands conquered by Alexander the Great. Phasis
Poti
Poti is a port city in Georgia, located on the eastern Black Sea coast in the region of Samegrelo-Zemo Svaneti in the west of the country. Built near the site of the ancient Greek colony of Phasis, the city has become a major port city and industrial center since the early 20th century. It is also...
and Sukhumi
Sukhumi
Sukhumi is the capital of Abkhazia, a disputed region on the Black Sea coast. The city suffered heavily during the Georgian-Abkhaz conflict in the early 1990s.-Naming:...
were the splendid Greek cities dominated by the mercantile oligarchies, sometimes being troubled by the Colchians from the hinterland before seemingly assimilating totally. After the fall of the Persian Empire, a significant part of Colchis locally known as Egrisi
Egrisi
Lazica or Egrisi in Georgian |Georgia]], named after the Laz tribe, which at some time dominated the local ruling élite.The kingdom flourished between the 6th century BC and the 7th century AD. It covered part of the territory of the former kingdom Colchis and subjugated the territory of modern...
was annexed to the recently created Kingdom of Iberia
Caucasian Iberia
Iberia , also known as Iveria , was a name given by the ancient Greeks and Romans to the ancient Georgian kingdom of Kartli , corresponding roughly to the eastern and southern parts of the present day Georgia...
(Kartli
Kartli
Kartli is a historical region in central-to-eastern Georgia traversed by the river Mtkvari , on which Georgia's capital, Tbilisi, is situated. Known to the Classical authors as Iberia, Kartli played a crucial role in ethnic and political consolidation of the Georgians in the Middle Ages...
) in ca. 302 BC. However, soon Colchis seceded and broke up into several small princedoms ruled by sceptuchi. They retained a degree of independence until conquered (circa 101 BC) by Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates VI or Mithradates VI Mithradates , from Old Persian Mithradatha, "gift of Mithra"; 134 BC – 63 BC, also known as Mithradates the Great and Eupator Dionysius, was king of Pontus and Armenia Minor in northern Anatolia from about 120 BC to 63 BC...
.
Under Pontus
Mithradates VI quelled an uprising in the region in 83 BC and gave Colchis to his son Mithridates, who was soon executed being suspected in having plotted against his father. During the Third Mithridatic WarThird Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War was the last and longest of three Mithridatic Wars fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and his allies and the Roman Republic...
, Mithridates VI made another his son Machares
Machares
Machares was a Pontian prince and son of King Mithridates VI of Pontus and Queen Laodice. He was made by his father ruler of the Bosporan Kingdom after Mithridates, for the second time, reduced that country, after the short war with the Roman Murena, in 80 BC....
king of Colchis, who held his power but for a short period. On the defeat of Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates VI or Mithradates VI Mithradates , from Old Persian Mithradatha, "gift of Mithra"; 134 BC – 63 BC, also known as Mithradates the Great and Eupator Dionysius, was king of Pontus and Armenia Minor in northern Anatolia from about 120 BC to 63 BC...
in 65 BC, Colchis was occupied by Pompey
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, also known as Pompey or Pompey the Great , was a military and political leader of the late Roman Republic...
, who captured one of the local chiefs (sceptuchus) Olthaces, and installed Aristarchus as a dynast
Dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers considered members of the same family. Historians traditionally consider many sovereign states' history within a framework of successive dynasties, e.g., China, Ancient Egypt and the Persian Empire...
(65-47 BC). On the fall of Pompey, Pharnaces II
Pharnaces II of Pontus
Pharnaces II of Pontus, also known as Pharnaces II was a prince, then King of Pontus and the Bosporan until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek Macedonian ancestry. Pharnaces II was the youngest son and child born to King Mithridates VI of Pontus from his first wife, his sister Queen...
, son of Mithridates
Mithridates VI of Pontus
Mithridates VI or Mithradates VI Mithradates , from Old Persian Mithradatha, "gift of Mithra"; 134 BC – 63 BC, also known as Mithradates the Great and Eupator Dionysius, was king of Pontus and Armenia Minor in northern Anatolia from about 120 BC to 63 BC...
, took advantage of Julius Caesar
Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar was a Roman general and statesman and a distinguished writer of Latin prose. He played a critical role in the gradual transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire....
being occupied in Egypt
Ancient Egypt
Ancient Egypt was an ancient civilization of Northeastern Africa, concentrated along the lower reaches of the Nile River in what is now the modern country of Egypt. Egyptian civilization coalesced around 3150 BC with the political unification of Upper and Lower Egypt under the first pharaoh...
, and reduced Colchis, Armenia
Armenia
Armenia , officially the Republic of Armenia , is a landlocked mountainous country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia...
, and some part of Cappadocia
Cappadocia
Cappadocia is a historical region in Central Anatolia, largely in Nevşehir Province.In the time of Herodotus, the Cappadocians were reported as occupying the whole region from Mount Taurus to the vicinity of the Euxine...
, defeating Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus, whom Caesar subsequently sent against him. His triumph was, however, short-lived. Under Polemon I
Polemon I of Pontus
Polemon Pythodoros, also known as Polemon I or Polemon I of Pontus was the Roman Client King of Cilicia, Pontus, Colchis and the Bosporan Kingdom....
, the son and successor of Pharnaces II
Pharnaces II of Pontus
Pharnaces II of Pontus, also known as Pharnaces II was a prince, then King of Pontus and the Bosporan until his death. He was a monarch of Persian and Greek Macedonian ancestry. Pharnaces II was the youngest son and child born to King Mithridates VI of Pontus from his first wife, his sister Queen...
, Colchis was part of the Pontus
Pontus
Pontus or Pontos is a historical Greek designation for a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in modern-day northeastern Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region in antiquity by the Greeks who colonized the area, and derived from the Greek name of the Black Sea: Πόντος...
and the Bosporan Kingdom
Bosporan Kingdom
The Bosporan Kingdom or the Kingdom of the Cimmerian Bosporus was an ancient state, located in eastern Crimea and the Taman Peninsula on the shores of the Cimmerian Bosporus...
. After the death of Polemon (8 BC), his second wife Pythodorida of Pontus
Pythodorida of Pontus
Pythodorida or Pythodoris of Pontus was a Roman Client Queen of Pontus, Bosporan, Cilicia and Cappadocia.-Origins & Early Life:Pythodorida is also known as Pythodoris I and Pantos Pythodorida. According to an honorific inscription dedicated to her in Athens Greece in the late 1st century BC, her...
retained possession of Colchis as well as of Pontus itself, though the kingdom of Bosporus was wrested from her power. Her son and successor Polemon II of Pontus was induced by Emperor Nero
Nero
Nero , was Roman Emperor from 54 to 68, and the last in the Julio-Claudian dynasty. Nero was adopted by his great-uncle Claudius to become his heir and successor, and succeeded to the throne in 54 following Claudius' death....
to abdicate the throne, and both Pontus and Colchis were incorporated in the Province of Galatia
Galatia
Ancient Galatia was an area in the highlands of central Anatolia in modern Turkey. Galatia was named for the immigrant Gauls from Thrace , who settled here and became its ruling caste in the 3rd century BC, following the Gallic invasion of the Balkans in 279 BC. It has been called the "Gallia" of...
(63) and later in Cappadocia
Cappadocia
Cappadocia is a historical region in Central Anatolia, largely in Nevşehir Province.In the time of Herodotus, the Cappadocians were reported as occupying the whole region from Mount Taurus to the vicinity of the Euxine...
(81).
Under Roman rule
Despite the fact that all major fortresses along the seacoast were occupied by the Romans, their rule was relatively loose. In 69, the people of Pontus and Colchis under AnicetusAnicetus (Pontus)
Anicetus was the leader of an unsuccessful anti-Roman uprising in Polemonia in 69. Formerly a freedman of King Polemon II of Pontus, Anicetus commanded the royal fleet until Pontus was converted into a Roman province under Emperor Nero in 63...
staged a major uprising against the Romans
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire was the post-Republican period of the ancient Roman civilization, characterised by an autocratic form of government and large territorial holdings in Europe and around the Mediterranean....
which ended unsuccessfully. The lowlands and coastal area were frequently raided by fierce mountain tribes, with the Soanes
Svaneti
Svaneti is a historic province in Georgia, in the northwestern part of the country. It is inhabited by the Svans, a geographic subgroup of the Georgians.- Geography :...
and Heniochi being the most powerful of them. Paying a nominal homage to Rome
Rome
Rome is the capital of Italy and the country's largest and most populated city and comune, with over 2.7 million residents in . The city is located in the central-western portion of the Italian Peninsula, on the Tiber River within the Lazio region of Italy.Rome's history spans two and a half...
, they created their own kingdoms and enjoyed significant independence. Christianity
Christianity
Christianity is a monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus as presented in canonical gospels and other New Testament writings...
began to spread in the early 1st century. Traditional accounts relate the event with Saint Andrew
Saint Andrew
Saint Andrew , called in the Orthodox tradition Prōtoklētos, or the First-called, is a Christian Apostle and the brother of Saint Peter. The name "Andrew" , like other Greek names, appears to have been common among the Jews from the 3rd or 2nd century BC. No Hebrew or Aramaic name is recorded for him...
, Saint Simon the Zealot
Simon the Zealot
The apostle called Simon Zelotes, Simon the Zealot, in Luke 6:15 and Acts 1:13; and Simon Kananaios or Simon Cananeus , was one of the most obscure among the apostles of Jesus. Little is recorded of him aside from his name...
, and Saint Matata. The Hellenistic
Hellenistic civilization
Hellenistic civilization represents the zenith of Greek influence in the ancient world from 323 BCE to about 146 BCE...
, local pagan
Paganism
Paganism is a blanket term, typically used to refer to non-Abrahamic, indigenous polytheistic religious traditions....
and Mithraic religious beliefs would however remain widespread until the 4th century. By the 130s, the kingdoms of Machelons, Heniochi, Egrisi
Egrisi
Lazica or Egrisi in Georgian |Georgia]], named after the Laz tribe, which at some time dominated the local ruling élite.The kingdom flourished between the 6th century BC and the 7th century AD. It covered part of the territory of the former kingdom Colchis and subjugated the territory of modern...
, Apsilia, Abasgia, and Sanigia had occupied the district from south to north. Goths
Goths
The Goths were an East Germanic tribe of Scandinavian origin whose two branches, the Visigoths and the Ostrogoths, played an important role in the fall of the Roman Empire and the emergence of Medieval Europe....
, dwelling in the Crimea
Crimea
Crimea , or the Autonomous Republic of Crimea , is a sub-national unit, an autonomous republic, of Ukraine. It is located on the northern coast of the Black Sea, occupying a peninsula of the same name...
and looking for new homes, raided Colchis in 253, but were repulsed with the help of the Roman garrison of Pitsunda
Pitsunda
Pitsunda is a resort town in Gagra district of Abkhazia.The town was founded by the Greeks in the 5th century BC as a trade colony Pityus or Pitiunt. Excavations guided by Andria Apakidze unearthed remains of three 4th-century churches and a bath with superb mosaic floors...
. By the 3rd-4th centuries, most of the local kingdoms and principalities had been subjugated by the Lazic kings, and thereafter the country was generally referred to as Lazica (Egrisi
Egrisi
Lazica or Egrisi in Georgian |Georgia]], named after the Laz tribe, which at some time dominated the local ruling élite.The kingdom flourished between the 6th century BC and the 7th century AD. It covered part of the territory of the former kingdom Colchis and subjugated the territory of modern...
).
Rulers
Little is known of the rulers of Colchis;- Kuji, a presiding prince (eristavi) of EgrisiEgrisiLazica or Egrisi in Georgian |Georgia]], named after the Laz tribe, which at some time dominated the local ruling élite.The kingdom flourished between the 6th century BC and the 7th century AD. It covered part of the territory of the former kingdom Colchis and subjugated the territory of modern...
under the authority of Pharnavaz I of IberiaPharnavaz I of IberiaPharnavaz I was the first king of Kartli, an ancient Georgian kingdom known as Iberia to the Classical sources, who is credited by the medieval Georgian written tradition with founding the kingship of Kartli and the Parnavaziani dynasty...
(ca 302-237 BC) (according to the medieval Georgian annals).
- Akes (Basileus Aku) (end of the 4th century BC), king of Colchis; his name is found on a coin issued by him.
- Saulaces, "king" in the 2nd century BC (according to some ancient sources).
- Mithridates (fl.FloruitFloruit , abbreviated fl. , is a Latin verb meaning "flourished", denoting the period of time during which something was active...
65 BC), under the authority of PontusPontusPontus or Pontos is a historical Greek designation for a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in modern-day northeastern Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region in antiquity by the Greeks who colonized the area, and derived from the Greek name of the Black Sea: Πόντος...
.
- Machares (fl. 65 BC), under the authority of PontusPontusPontus or Pontos is a historical Greek designation for a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in modern-day northeastern Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region in antiquity by the Greeks who colonized the area, and derived from the Greek name of the Black Sea: Πόντος...
.
Note: During his reign, the local chiefs, sceptuchi, continued to exercise some power. One of them, Olthaces, is mentioned by the Roman sources as a captive of Pompey
Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus, also known as Pompey or Pompey the Great , was a military and political leader of the late Roman Republic...
in 65 BC.
- Aristarchus (65-47 BC), a dynasty under the authority of PompeyPompeyGnaeus Pompeius Magnus, also known as Pompey or Pompey the Great , was a military and political leader of the late Roman Republic...
.
Colchis in mythology
According to the Greek mythology, Colchis was a fabulously wealthy land situated on the mysterious periphery of the heroic world. Here in the sacred grove of the war god AresAres
Ares is the Greek god of war. He is one of the Twelve Olympians, and the son of Zeus and Hera. In Greek literature, he often represents the physical or violent aspect of war, in contrast to the armored Athena, whose functions as a goddess of intelligence include military strategy and...
, King Aeëtes
Aeëtes
In Greek mythology, Aeëtes , , , was a King of Colchis , son of the sun-god Helios and the Oceanid Perseis , brother of Circe and Pasiphae, and father of Medea, Chalciope and Apsyrtus...
hung the Golden Fleece
Golden Fleece
In Greek mythology, the Golden Fleece is the fleece of the gold-haired winged ram, which can be procured in Colchis. It figures in the tale of Jason and his band of Argonauts, who set out on a quest by order of King Pelias for the fleece in order to place Jason rightfully on the throne of Iolcus...
until it was seized by Jason
Jason
Jason was a late ancient Greek mythological hero from the late 10th Century BC, famous as the leader of the Argonauts and their quest for the Golden Fleece. He was the son of Aeson, the rightful king of Iolcus...
and the Argonauts
Argonauts
The Argonauts ) were a band of heroes in Greek mythology who, in the years before the Trojan War, accompanied Jason to Colchis in his quest to find the Golden Fleece. Their name comes from their ship, the Argo, which was named after its builder, Argus. "Argonauts", therefore, literally means...
. Colchis was also the land where the mythological Prometheus
Prometheus
In Greek mythology, Prometheus is a Titan, the son of Iapetus and Themis, and brother to Atlas, Epimetheus and Menoetius. He was a champion of mankind, known for his wily intelligence, who stole fire from Zeus and gave it to mortals...
was punished by being chained to a mountain while an eagle ate at his liver for revealing to humanity the secret of fire. Amazons
Amazons
The Amazons are a nation of all-female warriors in Greek mythology and Classical antiquity. Herodotus placed them in a region bordering Scythia in Sarmatia...
also were said to be of Scythia
Scythia
In antiquity, Scythian or Scyths were terms used by the Greeks to refer to certain Iranian groups of horse-riding nomadic pastoralists who dwelt on the Pontic-Caspian steppe...
n origin from Colchis. The main mythical characters from Colchis are Aeëtes
Aeëtes
In Greek mythology, Aeëtes , , , was a King of Colchis , son of the sun-god Helios and the Oceanid Perseis , brother of Circe and Pasiphae, and father of Medea, Chalciope and Apsyrtus...
, Medea
Medea
Medea is a woman in Greek mythology. She was the daughter of King Aeëtes of Colchis, niece of Circe, granddaughter of the sun god Helios, and later wife to the hero Jason, with whom she had two children, Mermeros and Pheres. In Euripides's play Medea, Jason leaves Medea when Creon, king of...
, Absyrtus
Absyrtus
Absyrtus, or Apsyrtus , was in Greek mythology the son of Aeëtes and a brother of Medea and Chalciope. His mother is variously given: Hyginus calls her Ipsia, Hesiod and Apollodorus call her Eidyia, Apollonius calls her Asterodeia, and others Neaera or Eurylyte.When Medea fled with Jason, she took...
, Chalciope
Chalciope
Chalciope , in Greek mythology, is a name that may refer to several characters.* Chalciope, daughter of King Aeetes of Colchis, sister of Medea and wife of Phrixus, by whom she had four sons: Argus, Phrontis, Melas and Cytisorus...
, Circe
Circe
In Greek mythology, Circe is a minor goddess of magic , described in Homer's Odyssey as "The loveliest of all immortals", living on the island of Aeaea, famous for her part in the adventures of Odysseus.By most accounts, Circe was the daughter of Helios, the god of the sun, and Perse, an Oceanid...
, Eidyia
Eidyia
In Greek mythology, Eidyia was a daughter of Oceanus and Tethys, and queen to Aeetes, king of Colchis. Mother of Medea, Chalciope and Apsyrtus, she was also the youngest of the Oceanides. Some sources called her the goddess of knowledge....
, Pasiphaë
Pasiphaë
In Greek mythology, Pasiphaë , "wide-shining" was the daughter of Helios, the Sun, by the eldest of the Oceanids, Perse; Like her doublet Europa, her origins were in the East, in her case at Colchis, the palace of the Sun; she was given in marriage to King Minos of Crete. With Minos, she was the...
.
See also
- EgrisiEgrisiLazica or Egrisi in Georgian |Georgia]], named after the Laz tribe, which at some time dominated the local ruling élite.The kingdom flourished between the 6th century BC and the 7th century AD. It covered part of the territory of the former kingdom Colchis and subjugated the territory of modern...
(as a successor stateSuccession of statesSuccession of states is a theory and practice in international relations regarding the recognition and acceptance of a newly created sovereign state by other states, based on a perceived historical relationship the new state has with a prior state...
of Colchis) - History of GeorgiaHistory of Georgia (country)The nation of Georgia was first unified as a kingdom under the Bagrationi dynasty in the 9th to 10th century, arising from a number of predecessor states of ancient Colchis and Iberia...
- PontusPontusPontus or Pontos is a historical Greek designation for a region on the southern coast of the Black Sea, located in modern-day northeastern Turkey. The name was applied to the coastal region in antiquity by the Greeks who colonized the area, and derived from the Greek name of the Black Sea: Πόντος...
- Roman GeorgiaRoman GeorgiaRoman Georgia was the area of Georgia under Roman control. Between the 1st century BC and the 7th century AD Rome controlled directly or indirectly the kingdoms of Colchis and Iberia in the Caucasus region .-History:Rome's conquests reached the Caucasus area at the end of the 2nd century BC, when...
Further reading
- Braund, David. 1994. Georgia in Antiquity: A History of Colchis and Transcaucasian Iberia 550 BC-AD 562. Clarendon Press, Oxford. ISBN 0-19-814473-3
- Gocha R. Tsetskhladze. Pichvnari and Its Environs, 6th c BC-4th c AD. Annales Littéraires de l'Université de Franche-Comté, 659, Editeurs: M. Clavel-Lévêque, E. Geny, P. Lévêque. Paris: Presses Universitaires Franc-Comtoises, 1999. ISBN 2-913322-42-5
- Otar Lordkipanidze. Phasis: The River and City of Colchis. Geographica Historica 15, Franz Steiner 2000. ISBN 3-515-07271-3
- Alexander MelamidAlexander MelamidAlexander Melamid is a Russian painter and performance artist who emigrated to New York City from the Soviet Union in 1977 with Vitaly Komar. He was born in Moscow and attended the Stroganov Art Institute, where he collaborated with Komar in the Russian SOTS ART movement...
. Colchis today. (northeastern Turkey): An article from: The Geographical Review. American Geographical Society, 1993. ISBN B000925IWE - Akaki Urushadze. The Country of the Enchantress Media, Tbilisi, 1984 (in Russian and English)
External links
- Golden graves, archeological evidences
- Kolkhoba: Laz language
- Colchis
- History of Laz-Mingrelians
- Colchis
- Colchis
- LoveToKnow Article on Colchis
- Colchis in Dictionary of Greek and Roman Geography (1854) (ed. William Smith, LLD)
- Kingdom of Colchis (Egrisi)
- Colchian coins
- Strabo on Colchis
- Herodotus on Colchis
- Pliny on Colchis
- "Colchis Gives Birth to a Nation," From the Cradle of Wine

