
Coker unit
Encyclopedia
A coker or coker unit is an oil refinery
processing unit that converts the residual oil from the vacuum distillation column or the atmospheric distillation column into low molecular weight hydrocarbon
gas
es, naphtha
, light and heavy gas oils, and petroleum coke
. The process thermally cracks
the long chain hydrocarbon molecules in the residual oil feed into shorter chain molecules.
This coke can either be fuel grade (high in sulphur and metals) or anode grade (low in sulphur and metals). The raw coke directly out of the coker is often referred to as green coke
. In this context, "green" means unprocessed. The further processing of green coke by calcining
in a rotary kiln
removes residual volatile hydrocarbons from the coke. The calcined petroleum coke can be further processed in an anode baking oven in order to produce anode coke of the desired shape and physical properties. The anodes are mainly used in the aluminium
and steel
industry.
, Fluid coker and Flexicoker. The one that is by far the most commonly used is the delayed coker.
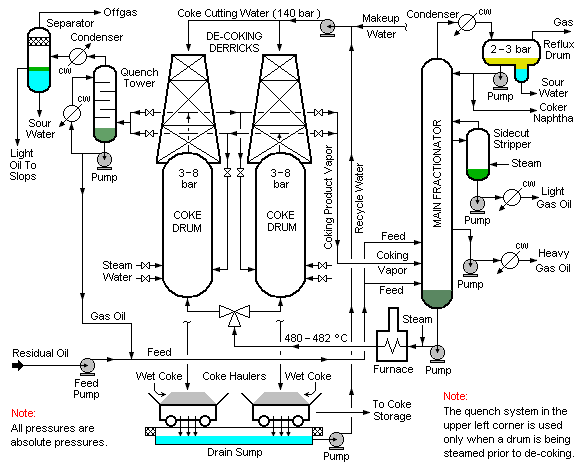
The schematic flow diagram below depicts a typical delayed coker:
Oil refinery
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where crude oil is processed and refined into more useful petroleum products, such as gasoline, diesel fuel, asphalt base, heating oil, kerosene, and liquefied petroleum gas...
processing unit that converts the residual oil from the vacuum distillation column or the atmospheric distillation column into low molecular weight hydrocarbon
Hydrocarbon
In organic chemistry, a hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon. Hydrocarbons from which one hydrogen atom has been removed are functional groups, called hydrocarbyls....
gas
Gas
Gas is one of the three classical states of matter . Near absolute zero, a substance exists as a solid. As heat is added to this substance it melts into a liquid at its melting point , boils into a gas at its boiling point, and if heated high enough would enter a plasma state in which the electrons...
es, naphtha
Naphtha
Naphtha normally refers to a number of different flammable liquid mixtures of hydrocarbons, i.e., a component of natural gas condensate or a distillation product from petroleum, coal tar or peat boiling in a certain range and containing certain hydrocarbons. It is a broad term covering among the...
, light and heavy gas oils, and petroleum coke
Petroleum coke
Petroleum coke is a carbonaceous solid derived from oil refinery coker units or other cracking processes. Other coke has traditionally been derived from coal....
. The process thermally cracks
Cracking (chemistry)
In petroleum geology and chemistry, cracking is the process whereby complex organic molecules such as kerogens or heavy hydrocarbons are broken down into simpler molecules such as light hydrocarbons, by the breaking of carbon-carbon bonds in the precursors. The rate of cracking and the end products...
the long chain hydrocarbon molecules in the residual oil feed into shorter chain molecules.
This coke can either be fuel grade (high in sulphur and metals) or anode grade (low in sulphur and metals). The raw coke directly out of the coker is often referred to as green coke
Green coke
Green coke is the primary solid carbonization product from high boiling hydrocarbon fractions obtained at temperatures below 900 K. It contains a fraction of matter that can be released as volatiles during subsequent heat treatment at temperatures up to approximately 1600 K...
. In this context, "green" means unprocessed. The further processing of green coke by calcining
Calcination
Calcination is a thermal treatment process applied to ores and other solid materials to bring about a thermal decomposition, phase transition, or removal of a volatile fraction. The calcination process normally takes place at temperatures below the melting point of the product materials...
in a rotary kiln
Rotary kiln
A Rotary kiln is a pyroprocessing device used to raise materials to a high temperature in a continuous process. Materials produced using rotary kilns include:* Cement* Lime* Refractories* Metakaolin* Titanium dioxide* Alumina* Vermiculite...
removes residual volatile hydrocarbons from the coke. The calcined petroleum coke can be further processed in an anode baking oven in order to produce anode coke of the desired shape and physical properties. The anodes are mainly used in the aluminium
Aluminium
Aluminium or aluminum is a silvery white member of the boron group of chemical elements. It has the symbol Al, and its atomic number is 13. It is not soluble in water under normal circumstances....
and steel
Steel
Steel is an alloy that consists mostly of iron and has a carbon content between 0.2% and 2.1% by weight, depending on the grade. Carbon is the most common alloying material for iron, but various other alloying elements are used, such as manganese, chromium, vanadium, and tungsten...
industry.
Types of coker units
There are three types of cokers used in oil refineries: Delayed cokerDelayed coker
A delayed coker is a type of coker whose process consists of heating a residual oil feed to its thermal cracking temperature in a furnace with multiple parallel passes. This cracks the heavy, long chain hydrocarbon molecules of the residual oil into coker gas oil and petroleum coke...
, Fluid coker and Flexicoker. The one that is by far the most commonly used is the delayed coker.
The schematic flow diagram below depicts a typical delayed coker:


