Coal power in the United States
Encyclopedia
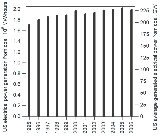
In 2009, there were 1436 coal-powered units at the electrical utilities across the US, with the total nominal capacity of 338.732 GW
(compared to 1024 units at nominal 278 GW in 2000).
The actual average generated power from coal in 2006 was 227.1 GWh (1.991 trillion kilowatt-hours per year), the highest in the world and still slightly ahead of China (1.95 trillion kilowatt-hours per year) at that time. Back in 2000, the US average production of electricity from coal was 224.3 GWh (1.966 trillion kilowatt-hours per year). In 2006, the U.S. consumed 1026636000 short ton or 92.3% of coal for electricity generation.
Recent trends, comparisons, and forecasts
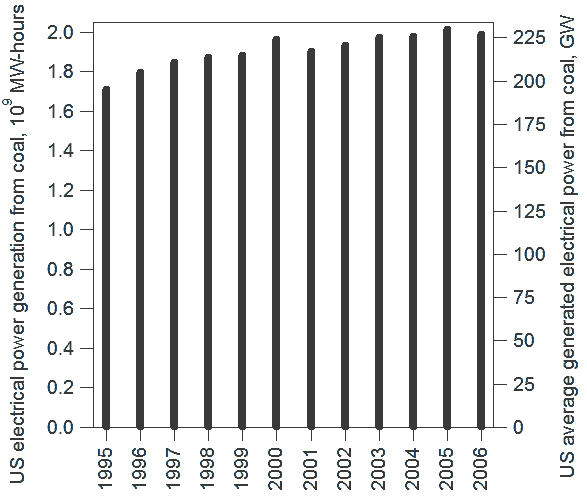
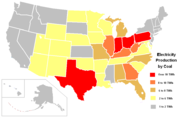
Average share of electricity generated from coal in the US has dropped from 52.8% in 1997 to 45.0% in 2009.
The coal plants are mostly base-load plants
Base load power plant
Baseload is the minimum amount of power that a utility or distribution company must make available to its customers, or the amount of power required to meet minimum demands based on reasonable expectations of customer requirements...
and account for about 32% of the peak electricity production in the summer, when the electricity demand is the highest and the auxiliary (mostly non-coal) plants are added to the grid.
As of 7/7/11, utility companies will shut down and retire aging coal-fired power plants following the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) announcement of the Cross-State Air Pollution Rule (CSAP).
Canceled and slowed proposals
- On October 19, 2007, the Kansas Department of Health and Environment was the first government agency to reject a permit for a new coal-fired plant on the basis of carbon dioxide emissions which had been planned by the Sunflower Electric Power Corporation.
- Southwestern Power Group's Bowie Power Station proposed an IGCC plant that was scrapped in favor of a natural gasNatural gasNatural gas is a naturally occurring gas mixture consisting primarily of methane, typically with 0–20% higher hydrocarbons . It is found associated with other hydrocarbon fuel, in coal beds, as methane clathrates, and is an important fuel source and a major feedstock for fertilizers.Most natural...
plant. Regulatory uncertainty was cited as one of the reasons. - A Florida Power & Light's Glades Power Plant proposed plant of 1,960 MW was rejected by the Florida Public Service Commission. Uncertainty over possible future carbon taxCarbon taxA carbon tax is an environmental tax levied on the carbon content of fuels. It is a form of carbon pricing. Carbon is present in every hydrocarbon fuel and is released as carbon dioxide when they are burnt. In contrast, non-combustion energy sources—wind, sunlight, hydropower, and nuclear—do not...
es was cited as one of the reasons. - An air permit for a plant in KentuckyKentuckyThe Commonwealth of Kentucky is a state located in the East Central United States of America. As classified by the United States Census Bureau, Kentucky is a Southern state, more specifically in the East South Central region. Kentucky is one of four U.S. states constituted as a commonwealth...
was rejected in August 2007 in a circuit court on the basis that the air pollution control analysis was inadequate. - Cancellation of 8 (out of promised 11) proposed coal plants of former TXU Corporation in TexasTexasTexas is the second largest U.S. state by both area and population, and the largest state by area in the contiguous United States.The name, based on the Caddo word "Tejas" meaning "friends" or "allies", was applied by the Spanish to the Caddo themselves and to the region of their settlement in...
by the current owners, Kohlberg Kravis Roberts & Co.Kohlberg Kravis Roberts & Co.KKR & Co. L.P. is an American-based global private equity firm, specializing in leveraged buyouts, based in New York. The firm sponsors and manages private equity investment funds. Since its inception, the firm has completed over $400 billion of private equity transactions and was a pioneer in...
and TPG, was finalized on October 15, 2007.
Safety
Coal power has historically been known for being a dangerous working environment. The Mine Safety and Health AdministrationMine Safety and Health Administration
The Mine Safety and Health Administration is an agency of the United States Department of Labor which administers the provisions of the Federal Mine Safety and Health Act of 1977 to enforce compliance with mandatory safety and health standards as a means to eliminate fatal accidents, to reduce...
of the United States Department of Labor
United States Department of Labor
The United States Department of Labor is a Cabinet department of the United States government responsible for occupational safety, wage and hour standards, unemployment insurance benefits, re-employment services, and some economic statistics. Many U.S. states also have such departments. The...
reports deaths by state and year for the period of 1996 to 2009; total deaths for that time frame were 437. In the US there were 47 deaths in 2006, 34 in 2007, and 30 deaths in 2008.
Accident types include:
- Power haulage - 47%
- Electrical - 13%
- Machinery - 9%
- Falling material - 7%
- Ignition/explosions - 7%
- Slips/falls - 4%
- Explosives - 4%
- Other - 9%
Reference: http://www.cdc.gov/niosh/mining/pubs/pdfs/icat.pdf
Environmental impacts
In the United States, three coal-fired power plants reported the largest toxic air releases in 2001 :- CP&L Roxboro Steam Electric Plant in Semora, North CarolinaSemora, North CarolinaSemora is an unincorporated community in Caswell County, North Carolina. It lies just northwest of Hyco Lake and has some presence in Person County. Semora is home to one of the oldest churches in North Carolina: ....
. The four-unit, 2,462 megawatt facility is one of the largest power plants in the United States. - Reliant EnergyReliant EnergyRRI Energy, Inc. , based in Houston, Texas, United States, was an energy company that provided electricity to wholesale customers in the United States. The company was one of the largest independent power producers in the nation with more than 14,000 megawatts of power generation capacity across...
's Keystone Power PlantKeystone Power PlantThe Keystone Generating Station is a 1,711 MW baseload coal-fired power plant located on roughly at , in Plumcreek Township, southeastern Armstrong County, Pennsylvania near Crooked Creek, just west of Shelocta, Pennsylvania....
in Shelocta, PennsylvaniaShelocta, PennsylvaniaShelocta is a borough in Indiana County, Pennsylvania, United States. The population was 127 at the 2000 census. The Keystone Generating Station is located to the west of the borough, in Plumcreek Township, Armstrong County, Pennsylvania.-Geography:...
. - Georgia PowerGeorgia PowerGeorgia Power is an electric utility headquartered in Atlanta, Georgia, United States. It is the largest of the four electric utilities that are owned and operated by Southern Company....
Bowen Steam Electric Generating Plant in Cartersville, GeorgiaCartersville, GeorgiaCartersville is a town in Bartow County, in the U.S. state of Georgia. As of the 2010 census, the city had a population of 19,7314. The city is the county seat of Bartow County.-Geography:Cartersville was named for Colonel Farish Carter....
.
The Environmental Protection Agency classified the 44 sites as potential hazards to communities, which means the waste sites could cause death and significant property damage if an event such as a storm, a terrorist attack or a structural failure caused a spill. They estimate that about 300 dry landfills and wet storage ponds are used around the country to store ash from coal-fired power plants. The storage facilities hold the noncombustible ingredients of coal and the ash trapped by equipment designed to reduce air pollution.
Sulfur dioxide emissions
86 coal powered plants have a capacity of 107.1 GW, or 9.9% of total U.S. electric capacity, they emitted 5,389,592 tons of SO2 in 2006 – which represents 28.6% of U.S. SO2 emissions from all sources.Carbon footprint: CO2 emissions
Emissions from electricity generationElectricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric energy from other forms of energy.The fundamental principles of electricity generation were discovered during the 1820s and early 1830s by the British scientist Michael Faraday...
account for the largest share of U.S. greenhouse gases, 38.9% of U.S. production of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
in 2006 (with transportation emissions close behind, at 31%). Although coal power only accounted for 49% of the U.S. electricity production in 2006, it was responsible for 83% of CO2 emissions caused by electricity generation that year, or 1,970 Tg
Teragram
Teragram may refer to:* 1012 grams, equivalent to a megatonne. See Orders of magnitude * Teragram Corporation...
of CO2 emissions. Further 130 Tg of CO2 were released by other industrial coal-burning applications.
Mercury pollution
U.S. coal-fired electricity-generating power plants owned by utilitiesElectric utility
An electric utility is a company that engages in the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity for sale generally in a regulated market. The electrical utility industry is a major provider of energy in most countries. It is indispensable to factories, commercial establishments,...
emitted an estimated 48 tons of mercury
Mercury (element)
Mercury is a chemical element with the symbol Hg and atomic number 80. It is also known as quicksilver or hydrargyrum...
in 1999, the largest source of man-made mercury pollution in the U.S. In 1995-96, this accounted for 32.6% of all mercury emitted into the air by human activity in the U.S. In addition, 13.1% was emitted by coal-fired industrial and mixed-use commercial boilers, and 0.3% by coal-fired residential boilers, bringing the total U.S. mercury pollution due to coal combustion to 46% of the U.S. man-made mercury sources. In contrast, China's coal-fired power plants emitted an estimated 200 ± 90 tons of mercury in 1999, which was about 38% of Chinese human-generated mercury emissions (45% being emitted from non-ferrous metals smelting). Mercury in emissions from power plants can be reduced by the use of activated carbon.
Advocates
In 2007 an advertising campaign was launched to improve public opinion on coal power titled America's Power. This was done by the American Coalition for Clean Coal Electricity (then known as Americans for Balanced Energy Choices), a pro-coal organization started in 2000.Opposition
In the face of increasing electricity demand through the 2000s, the US has seen a "Growing Trend Against Coal-Fired Power Plants". In 2006 through 2007 there was first a bullish market attitude towards coal with the expectation of a new wave of plants, but political barriers and pollution concerns escalated exponentially, which is likely to damage plans for new generation and put pressure on older plants. In 2007, 59 proposed coal plants were cancelled, abandoned, or placed on hold by sponsors as a result of financing obstacles, regulatory decisions, judicial rulings, and new global warming legislation.The Stop Coal campaign has called for a moratorium on the construction of any new coal plants and for the phase out of all existing plants, citing concern for global warming. Others have called for a carbon tax
Carbon tax
A carbon tax is an environmental tax levied on the carbon content of fuels. It is a form of carbon pricing. Carbon is present in every hydrocarbon fuel and is released as carbon dioxide when they are burnt. In contrast, non-combustion energy sources—wind, sunlight, hydropower, and nuclear—do not...
and a requirement of carbon sequestration
Carbon capture and storage
Carbon capture and storage , alternatively referred to as carbon capture and sequestration, is a technology to prevent large quantities of from being released into the atmosphere from the use of fossil fuel in power generation and other industries. It is often regarded as a means of mitigating...
for all coal power plants.
The creation in January 2009 of a Presidential task force (to look at ways to alter the energy direction of the United States energy providers) favors the trend away from coal-fired power plants.
See also
- Coal mining in the United StatesCoal mining in the United StatesCoal mining in the United States is a major industry, and reached an all-time high of 1.06 Gt in 2008, being mined in 25 states. The US was a net exporter of coal in 2008, with the surplus of exports over imports equalling 4% of the total mined.- Coal mining areas :Twenty-six states produce coal...
- Coal power in ChinaCoal power in ChinaThe People's Republic of China is the largest consumer of coal in the world, and is about to become the largest user of coal-derived electricity, generating 1.95 trillion kilowatt-hours per year, or 68.7% of its electricity from coal as of 2006...
- Mountaintop removal mining
- SuperfundSuperfundSuperfund is the common name for the Comprehensive Environmental Response, Compensation, and Liability Act of 1980 , a United States federal law designed to clean up sites contaminated with hazardous substances...

