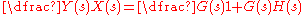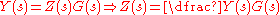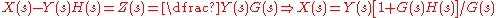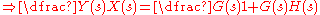
Closed-loop transfer function
Encyclopedia
A closed-loop transfer function in control theory
is a mathematical expression (algorithm
) describing the net result of the effects of a closed (feedback
) loop on the input signal to the circuits enclosed by the loop.
is measured at the output
. The output signal waveform
can be calculated from the closed-loop transfer function and the input signal waveform.
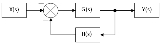
An example of a closed-loop transfer function is shown below:
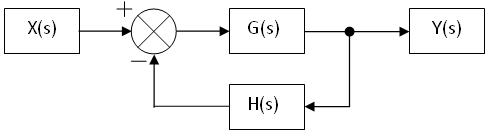
The summing node and the G(s) and H(s) blocks can all be combined into one block, which would have the following transfer function:
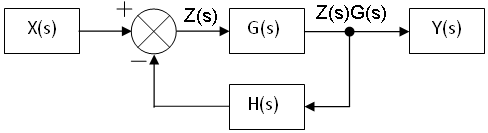
Using this figure we can write
Control theory
Control theory is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering and mathematics that deals with the behavior of dynamical systems. The desired output of a system is called the reference...
is a mathematical expression (algorithm
Algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm is an effective method expressed as a finite list of well-defined instructions for calculating a function. Algorithms are used for calculation, data processing, and automated reasoning...
) describing the net result of the effects of a closed (feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
) loop on the input signal to the circuits enclosed by the loop.
Overview
The closed-loop transfer functionTransfer function
A transfer function is a mathematical representation, in terms of spatial or temporal frequency, of the relation between the input and output of a linear time-invariant system. With optical imaging devices, for example, it is the Fourier transform of the point spread function i.e...
is measured at the output
Output
Output is the term denoting either an exit or changes which exit a system and which activate/modify a process. It is an abstract concept, used in the modeling, system design and system exploitation.-In control theory:...
. The output signal waveform
Waveform
Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation.In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form. In these cases, the term 'waveform' refers to the shape of a graph...
can be calculated from the closed-loop transfer function and the input signal waveform.
An example of a closed-loop transfer function is shown below:

The summing node and the G(s) and H(s) blocks can all be combined into one block, which would have the following transfer function:
Derivation
Let's define an intermediate signal Z shown as follows:
Using this figure we can write