
Climateprediction.net
Encyclopedia
Climateprediction.net, or CPDN, is a distributed computing
project to investigate and reduce uncertainties in climate modelling
. It aims to do this by running hundreds of thousands of different models (a large climate ensemble
) using the donated idle time of ordinary personal computers, thereby leading to a better understanding of how models are affected by small changes in the many parameters
known to influence the global climate.
The project relies on the volunteer computing
model using the BOINC framework where voluntary participants agree to run some processes of the project at the client-side
in their personal computers after receiving tasks from the server-side
for treatment.
CPDN, which is run primarily by Oxford University in England
, has harnessed more computing power and generated more data than any other climate modelling project. It has produced over 100 million model years of data so far. , there are more than 32,000 active participants from 147 countries with a total BOINC credit
of more than 14 billion, reporting about 90 teraflops
(90 trillion operations per second) of processing power.
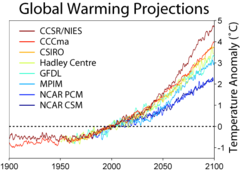 The aim of the Climateprediction.net project is to investigate the uncertainties in various parameterizations that have to be made in state-of-the-art climate models. The model is run thousands of times with slight perturbations to various physics parameters (a 'large ensemble
The aim of the Climateprediction.net project is to investigate the uncertainties in various parameterizations that have to be made in state-of-the-art climate models. The model is run thousands of times with slight perturbations to various physics parameters (a 'large ensemble
') and the project examines how the model output changes. These parameters are not known exactly, and the variations are within what is subjectively considered to be a plausible range. This will allow the project to improve understanding of how sensitive the models are to small changes and also to things like changes in carbon dioxide
and sulphur cycle
. In the past, estimates of climate change have had to be made using one or, at best, a very small ensemble (tens rather than thousands) of model runs. By using participants' computers, the project will be able to improve understanding of, and confidence in, climate change predictions more than would ever be possible using the supercomputers currently available to scientists.
The Climateprediction.net experiment should help to "improve methods to quantify uncertainties of climate projections and scenarios, including long-term ensemble simulations using complex models", identified by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
(IPCC) in 2001 as a high priority. Hopefully, the experiment will give decision makers a better scientific basis for addressing one of the biggest potential global problems of the 21st century.
As shown in the graph above, the various models have a fairly wide distribution of results over time. For each curve, on the far right, there is a bar showing the final temperature range for the corresponding model version. As you can see and would expect, the further into the future the model is extended, the wider the variances between them. Roughly half of the variation depends on the future climate forcing scenario rather than uncertainties in the model. Any reduction in those variations whether from better scenarios or improvements in the models are wanted. Climateprediction.net is working on model uncertainties not the scenarios.
The crux of the problem is that scientists can run models and see that x% of the models warm y degrees in response to z climate forcings, but how do we know x% is a good representation of the probability of that happening in the real world? The answer is that scientists are uncertain about this and want to improve the level of confidence that can be achieved. Some models will be good and some poor at producing past climate when given past climate forcings and initial conditions (a hindcast
). It does make sense to trust the models that do well at recreating the past more than those that do poorly. Therefore models that do poorly will be downweighted.
 The different models that Climateprediction.net has and will distribute are detailed below in chronological order. Therefore, anyone who has joined recently is likely to be running the Transient Coupled Model
The different models that Climateprediction.net has and will distribute are detailed below in chronological order. Therefore, anyone who has joined recently is likely to be running the Transient Coupled Model
.
first thought about the need for large Climate ensemble
s in 1997, but was only introduced to the success of SETI@home
in 1999. The first funding proposal in April 1999 was rejected as utterly unrealistic.
Following a presentation at the World Climate Conference
in Hamburg
in September 1999 and a commentary in Nature
entitled Do it yourself climate prediction in October 1999, thousands signed up to this supposedly imminently available program. The Dot-com bubble
bursting did not help and the project realised they would have to do most of the programming themselves rather than outsourcing.
It was launched September 12, 2003 and on September 13, 2003 the project exceeded the capacity of the Earth Simulator
to become the world's largest climate modelling facility.
The 2003 launch only offered a Windows
"classic" client. On 26 August 2004 a BOINC client was launched which supported Windows, Linux
and Mac OS X
clients. "Classic" will continue to be available for a number of years in support of the Open University
course. BOINC has stopped distributing classic models in favour of sulfur cycle models. A more user friendly BOINC client and website called GridRepublic, which supports climateprediction and other BOINC projects, was released in beta in 2006.
A thermohaline circulation
slowdown experiment was launched in May 2004 under the classic framework to coincide with the film The Day After Tomorrow
. This program can still be run but is no longer downloadable. The scientific analysis has been written up in Nick Faull's thesis. A paper about the thesis is still to be completed. There is no further planned research with this model.
A sulfur cycle model was launched in August 2005. They took longer to complete than the original models as a result of having five phases instead of three. Each timestep was also more complicated.
By November 2005, the number of completed results totalled 45,914 classic models, 3,455 thermohaline models, 85,685 BOINC models and 352 sulfur cycle models. This represented over 6 million model years processed.
In February 2006, the project moved on to more realistic climate models. A BBC Climate Change Experiment was launched, attracting around 23,000 participants on the first day. The transient climate simulation
introduced realistic oceans. This allowed the experiment to investigate changes in the climate response as the climate forcings are changed, rather than an equilibrium response to a significant change like doubling the carbon dioxide
level. Therefore, the experiment has now moved on to doing a hindcast of 1920 to 2000 as well as a forecast of 2000 to 2080. This model takes much longer.
The BBC
gave the project publicity with over 120,000 participating computers in the first three weeks.
In March 2006, a high resolution model was released as another project, the Seasonal Attribution Project
.
In April 2006, the coupled models were found to have a data input problem. The work was useful for a different purpose than advertised. New models had to be handed out.
in January 2005 and show that with only slight changes to the parameters within plausible ranges, the models can show climate sensitivities ranging from less than 2 °C to more than 11 °C (see and explanation). The higher climate sensitivities have been challenged as implausible. For example by Gavin Schmidt (a climate modeler with the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York).
is defined as the equilibrium response of global mean temperature to doubling levels of carbon dioxide. Current levels of carbon dioxide are around 380 ppm and growing at a rate of 1.8 ppm per year compared with preindustrial levels of 280 ppm.
Climate sensitivities of greater than 5 °C are widely accepted as being catastrophic. The possibility of such high sensitivities being plausible given observations had been reported prior to the Climateprediction.net experiment but "this is the first time GCMs
have produced such behaviour".
Even the models with very high climate sensitivity were found to be "as realistic as other state-of-the-art climate models". The test of realism was done with a root mean square error test. This does not check on realism of seasonal changes and it is possible that more diagnostic measures may place stronger constraints on what is realistic. Improved realism tests are being developed.
It is important to the experiment and the goal of obtaining a probability distribution function
(pdf) of climate outcomes to get a very wide range of behaviours even if only to rule out some behaviours as unrealistic. Unless a very large number of data points are used to create the pdf, the pdf is not reliable. Therefore, models with climate sensitivities as high as 11 °C are included even though they are inaccurate. More worrying is the lack of models with climate sensitivity of less than 2 °C. The sulfur cycle experiment is likely to extend the range downwards.
When an internally consistent representation of the origins of model-data discrepancy is used to calculate the probability density function of climate sensitivity, the 5th and 95th percentiles are 2.2 K and 6.8 K respectively. These results are sensitive, particularly the upper bound, to the representation of the origins of model data discrepancy.
short course and teaching material available for schools to teach subjects relating to climate and climate modelling. There is also teaching material available for use in Key Stage 3/4 Science, A level Physics (Advanced Physics), Key Stage 3/4 Mathematics, Key Stage 3/4 Geography, 21st Century Science, Science for Public Understanding, Use of Mathematics, Primary.
model but with only a "slab" ocean rather than a full dynamic ocean. This is faster (and requires less memory) than the full model, but lacks dynamical feedbacks from the ocean, which are incorporated into the full coupled-ocean-atmosphere models used to make projections of climate change out to 2100.
Each downloaded model comes with a slight variation in the various model parameters
.
There is an initial "calibration phase" of 15 model years in which the model calculates the "flux correction"; extra ocean-atmosphere fluxes that are needed to keep the model ocean in balance (the model ocean does not include currents; these fluxes to some extent replace the heat that would be transported by the missing currents).
Then there is a "control phase" of 15 years in which the ocean temperatures are allowed to vary. The flux correction ought to keep the model stable, but feedback
s developed in some of the runs. There is a quality control check, based on the annual mean temperatures, and models which fail this check are discarded.
Then there is a "double CO2 phase" in which the CO2 content is instantaneously doubled and the model run for a further 15 years, which in some cases is not quite sufficient model time to settle down to a new (warmer) equilibrium. In this phase some models which produced physically unrealistic results were again discarded.
The quality control checks in the control and 2*CO2 phases were quite weak: they suffice to exclude obviously unphysical models but do not include (for example) a test of the simulation of the seasonal cycle; hence some of the models passed may still be unrealistic. Further quality control measures are being developed.
The temperature in the doubled CO2 phase is exponentially extrapolated to work out the equilibrium temperature. Difference in temperature between this and the control phase then gives a measure of the climate sensitivity
of that particular version of the model.
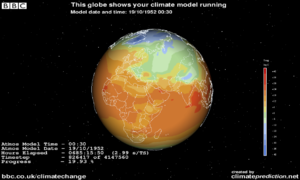
s to visually indicate the activity of the application, but they do not usually show its results as they are being calculated. By contrast, climateprediction.net not only uses a built-in visualisation to show the climate of the world being modelled, but it is interactive which allows different aspects of climate (temperature, rainfall, etc.) to be displayed. In addition, there are other, more advanced visualisation programs that allow the user to see more of what the model is doing (usually by analysing previously generated results) and to compare different runs and models.
Unfortunately as of December 2008 there is no visualisation tool that works with the newer CPDN models. Neither CPView nor Advanced Visualisation were updated so far to display data gathered from those models. So users can only visualize the data through the screensaver.
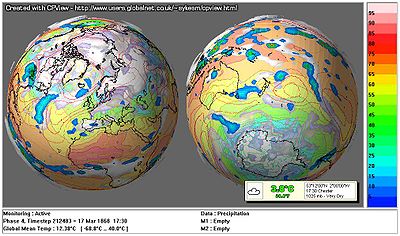 The real-time desktop visualisation for the model launched in 2003 was developed, by NAG, enabling users to track the progress of their simulation as the cloud cover and temperature changes over the surface of the globe. Other, more advanced visualisation programs in use include CPView and IDL Advanced Visualisation. They have similar functionality. CPView was written by Martin Sykes, a participant in the experiment. The IDL Advanced Visualisation was written by Andy Heaps of the University of Reading
The real-time desktop visualisation for the model launched in 2003 was developed, by NAG, enabling users to track the progress of their simulation as the cloud cover and temperature changes over the surface of the globe. Other, more advanced visualisation programs in use include CPView and IDL Advanced Visualisation. They have similar functionality. CPView was written by Martin Sykes, a participant in the experiment. The IDL Advanced Visualisation was written by Andy Heaps of the University of Reading
(UK
), and modified to work with the BOINC version by Tesella Support Services plc.
Only CPView allows you to look at unusual diagnostics, rather than the usual Temperature, Pressure, Rainfall, Snow, and Clouds. Up to 5 sets of data can be displayed on a map. It also has a wider range of functions like Max, Min, further memory functions, and other features.
The Advanced Visualisation has functions for graphs of local areas and over 1 day, 2 days, and 7 days, as well as the more usual graphs of season and annual averages (which both packages do). There are also Latitude - Height plots and Time - Height plots.
The download size is much smaller for CPView and CPView works with Windows 98
.
Running the visualisation/screensaver may slow down the processing and is not recommended to be used.
Distributed computing
Distributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. A distributed system consists of multiple autonomous computers that communicate through a computer network. The computers interact with each other in order to achieve a common goal...
project to investigate and reduce uncertainties in climate modelling
Global climate model
A General Circulation Model is a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean and based on the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources . These equations are the basis for complex computer programs commonly...
. It aims to do this by running hundreds of thousands of different models (a large climate ensemble
Climate ensemble
In physics, a statistical ensemble is a large set of copies of a system, considered all at once; each copy of the system representing a different possible detailed realisation of the system, consistent with the system's observed macroscopic properties....
) using the donated idle time of ordinary personal computers, thereby leading to a better understanding of how models are affected by small changes in the many parameters
Parametrization (climate)
Parameterization in a weather or climate model within numerical weather prediction refers to the method of replacing processes that are too small-scale or complex to be physically represented in the model by a simplified process. This can be contrasted with other processes—e.g., large-scale flow of...
known to influence the global climate.
The project relies on the volunteer computing
Volunteer computing
Volunteer computing is a type of distributed computing in which computer owners donate their computing resources to one or more "projects".-History:...
model using the BOINC framework where voluntary participants agree to run some processes of the project at the client-side
Client-side
Client-side refers to operations that are performed by the client in a client–server relationship in a computer network.Typically, a client is a computer application, such as a web browser, that runs on a user's local computer or workstation and connects to a server as necessary...
in their personal computers after receiving tasks from the server-side
Server-side
Server-side refers to operations that are performed by the server in a client–server relationship in computer networking.Typically, a server is a software program, such as a web server, that runs on a remote server, reachable from a user's local computer or workstation...
for treatment.
CPDN, which is run primarily by Oxford University in England
England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Scotland to the north and Wales to the west; the Irish Sea is to the north west, the Celtic Sea to the south west, with the North Sea to the east and the English Channel to the south separating it from continental...
, has harnessed more computing power and generated more data than any other climate modelling project. It has produced over 100 million model years of data so far. , there are more than 32,000 active participants from 147 countries with a total BOINC credit
BOINC Credit System
Within the BOINC platform for volunteer computing, the BOINC Credit System helps volunteers keep track of how much CPU time they have donated to various distributed computing projects. The credit system is designed to avoid cheating by validating results before granting credit on projects...
of more than 14 billion, reporting about 90 teraflops
FLOPS
In computing, FLOPS is a measure of a computer's performance, especially in fields of scientific calculations that make heavy use of floating-point calculations, similar to the older, simpler, instructions per second...
(90 trillion operations per second) of processing power.
Aims

Climate ensemble
In physics, a statistical ensemble is a large set of copies of a system, considered all at once; each copy of the system representing a different possible detailed realisation of the system, consistent with the system's observed macroscopic properties....
') and the project examines how the model output changes. These parameters are not known exactly, and the variations are within what is subjectively considered to be a plausible range. This will allow the project to improve understanding of how sensitive the models are to small changes and also to things like changes in carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
and sulphur cycle
Sulfur cycle
The sulfur cycle are the collection of processes by which sulfur moves to and from minerals and living systems. Such biogeochemical cycles are important in geology because they affect many minerals...
. In the past, estimates of climate change have had to be made using one or, at best, a very small ensemble (tens rather than thousands) of model runs. By using participants' computers, the project will be able to improve understanding of, and confidence in, climate change predictions more than would ever be possible using the supercomputers currently available to scientists.
The Climateprediction.net experiment should help to "improve methods to quantify uncertainties of climate projections and scenarios, including long-term ensemble simulations using complex models", identified by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change
The Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change is a scientific intergovernmental body which provides comprehensive assessments of current scientific, technical and socio-economic information worldwide about the risk of climate change caused by human activity, its potential environmental and...
(IPCC) in 2001 as a high priority. Hopefully, the experiment will give decision makers a better scientific basis for addressing one of the biggest potential global problems of the 21st century.
As shown in the graph above, the various models have a fairly wide distribution of results over time. For each curve, on the far right, there is a bar showing the final temperature range for the corresponding model version. As you can see and would expect, the further into the future the model is extended, the wider the variances between them. Roughly half of the variation depends on the future climate forcing scenario rather than uncertainties in the model. Any reduction in those variations whether from better scenarios or improvements in the models are wanted. Climateprediction.net is working on model uncertainties not the scenarios.
The crux of the problem is that scientists can run models and see that x% of the models warm y degrees in response to z climate forcings, but how do we know x% is a good representation of the probability of that happening in the real world? The answer is that scientists are uncertain about this and want to improve the level of confidence that can be achieved. Some models will be good and some poor at producing past climate when given past climate forcings and initial conditions (a hindcast
Hindcast
A hindcast is a way of testing a mathematical model. Known or closely estimated inputs for past events are entered into the model to see how well the output matches the known results. Hindcasting is also known as backtesting....
). It does make sense to trust the models that do well at recreating the past more than those that do poorly. Therefore models that do poorly will be downweighted.
The experiments

Transient climate simulation
A transient climate simulation is a mode of running a global climate model in which a period of time is simulated with continuously-varying concentrations of greenhouse gases so that the climate of the model represents a realistic mode of possible change in the real world.- Related models :This...
.
- Classic Slab Model - The original experiment not under BOINC. See #The original model for further details. This model remains in use solely for the OU short course.
- BOINC Slab Model - The same as the classic Slab Model, but released under BOINC.
- ThermoHaline CirculationThermohaline circulationThe term thermohaline circulation refers to a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes....
Model (THC) - An investigation of how the climate might change in the event of a decrease in the strength of the ThermoHaline Circulation. This experiment has now been closed to new participants as they have sufficient results. It was a four phase modelFour phase modelMaturity of Organizations and Business Excellence - The Four-Phase ModelThe Four-Phase Model is a model for managers and management consultants developed by Prof.dr.ing. Teun W. Hardjono to analyze the present organization and to determine what the organizational control points and interventions...
totaling 60 model years. The first three phases were identical to the above Slab Models. The fourth phase imposed the effects of a 50% slowdown in the Thermohaline circulation by imposing SSTSea surface temperatureSea surface temperature is the water temperature close to the oceans surface. The exact meaning of surface varies according to the measurement method used, but it is between and below the sea surface. Air masses in the Earth's atmosphere are highly modified by sea surface temperatures within a...
changes in the north Atlantic derived from other runs. - Sulfur Cycle Model - An investigation of the effect of sulfate aerosols on the climate. The experiment will model sulfurSulfurSulfur or sulphur is the chemical element with atomic number 16. In the periodic table it is represented by the symbol S. It is an abundant, multivalent non-metal. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with chemical formula S8. Elemental sulfur is a bright yellow...
in a number of compound forms including dimethyl sulfideDimethyl sulfideDimethyl sulfide or methylthiomethane is an organosulfur compound with the formula 2S. Dimethyl sulfide is a water-insoluble flammable liquid that boils at and has a characteristic disagreeable odor. It is a component of the smell produced from cooking of certain vegetables, notably maize,...
and sulfate aerosols. This experiment started in August 2005 and was a pre-requirement for the HindcastHindcastA hindcast is a way of testing a mathematical model. Known or closely estimated inputs for past events are entered into the model to see how well the output matches the known results. Hindcasting is also known as backtesting....
. It is a 5 phase model totalling 75 model years. Timesteps are around 70% longer, making the model around 2.8 times longer than the initial slab model. While a few models are still tricking, model have not been issued since 2006. - Coupled Spin-Up Model - Inclusion of oceanic influences into the basic model in a more dynamic and realistic way than the initial Slab Model. This was a pre-requirement for the HindcastHindcastA hindcast is a way of testing a mathematical model. Known or closely estimated inputs for past events are entered into the model to see how well the output matches the known results. Hindcasting is also known as backtesting....
. This has been completed and, as planned, was not publicly released. The fastest 200 - 500 computers were invited to join because it is a 200 year model and results were needed by February 2006 for the Transient coupled model launch. - Transient coupled model - This comprises an 80 year HindcastHindcastA hindcast is a way of testing a mathematical model. Known or closely estimated inputs for past events are entered into the model to see how well the output matches the known results. Hindcasting is also known as backtesting....
and an 80 year ForecastWeather forecastingWeather forecasting is the application of science and technology to predict the state of the atmosphere for a given location. Human beings have attempted to predict the weather informally for millennia, and formally since the nineteenth century...
. The HindcastHindcastA hindcast is a way of testing a mathematical model. Known or closely estimated inputs for past events are entered into the model to see how well the output matches the known results. Hindcasting is also known as backtesting....
is to test how well the models perform at recreating the climate of 1920 to 2000. It was launched February 2006 under BBC Climate Change ExperimentBBC Climate Change ExperimentThe BBC Climate Change Experiment was a BOINC project led by Oxford University with several partners including the UK Met Office, the BBC, the Open University and Reading University...
branding and later also released from the CPDN site. - Seasonal Attribution ProjectSeasonal Attribution ProjectThe Seasonal Attribution Project is a Climateprediction.net sub-project, with support from the WWF. It runs a high resolution model in order to try to determine the extent to which extreme weather events are attributable to human-induced global warming....
- This is a high resolution model for a single model year to look at extreme precipitation events. This experiment is much shorter due to its single model year, but there are 13.5 times as many cells and timesteps are only 10 minutes instead of 30 minutes. This extra resolution means it requires at least 1.5 GigabyteGigabyteThe gigabyte is a multiple of the unit byte for digital information storage. The prefix giga means 109 in the International System of Units , therefore 1 gigabyte is...
s of RAMRam-Animals:*Ram, an uncastrated male sheep*Ram cichlid, a species of freshwater fish endemic to Colombia and Venezuela-Military:*Battering ram*Ramming, a military tactic in which one vehicle runs into another...
. It uses the HadAM3-N144 climate model.
History
Myles AllenMyles Allen
Myles R. Allen is head of the Climate Dynamics group at the University of Oxford's Atmospheric, Oceanic and Planetary Physics Department. He is the Principal Investigator of the distributed computing project Climateprediction.net , and was principally responsible for starting this project.He has...
first thought about the need for large Climate ensemble
Climate ensemble
In physics, a statistical ensemble is a large set of copies of a system, considered all at once; each copy of the system representing a different possible detailed realisation of the system, consistent with the system's observed macroscopic properties....
s in 1997, but was only introduced to the success of SETI@home
SETI@home
SETI@home is an Internet-based public volunteer computing project employing the BOINC software platform, hosted by the Space Sciences Laboratory, at the University of California, Berkeley, in the United States. SETI is an acronym for the Search for Extra-Terrestrial Intelligence...
in 1999. The first funding proposal in April 1999 was rejected as utterly unrealistic.
Following a presentation at the World Climate Conference
World Climate Conference
The world climate conferences are a series of international meetings, organized by the World Meteorological Organization , about global climate issues. The first two conferences largely focused on climate change in addition to climate research and forecasting...
in Hamburg
Hamburg
-History:The first historic name for the city was, according to Claudius Ptolemy's reports, Treva.But the city takes its modern name, Hamburg, from the first permanent building on the site, a castle whose construction was ordered by the Emperor Charlemagne in AD 808...
in September 1999 and a commentary in Nature
Nature (journal)
Nature, first published on 4 November 1869, is ranked the world's most cited interdisciplinary scientific journal by the Science Edition of the 2010 Journal Citation Reports...
entitled Do it yourself climate prediction in October 1999, thousands signed up to this supposedly imminently available program. The Dot-com bubble
Dot-com bubble
The dot-com bubble was a speculative bubble covering roughly 1995–2000 during which stock markets in industrialized nations saw their equity value rise rapidly from growth in the more...
bursting did not help and the project realised they would have to do most of the programming themselves rather than outsourcing.
It was launched September 12, 2003 and on September 13, 2003 the project exceeded the capacity of the Earth Simulator
Earth Simulator
The Earth Simulator , developed by the Japanese government's initiative "Earth Simulator Project", was a highly parallel vector supercomputer system for running global climate models to evaluate the effects of global warming and problems in solid earth geophysics...
to become the world's largest climate modelling facility.
The 2003 launch only offered a Windows
Microsoft Windows
Microsoft Windows is a series of operating systems produced by Microsoft.Microsoft introduced an operating environment named Windows on November 20, 1985 as an add-on to MS-DOS in response to the growing interest in graphical user interfaces . Microsoft Windows came to dominate the world's personal...
"classic" client. On 26 August 2004 a BOINC client was launched which supported Windows, Linux
Linux
Linux is a Unix-like computer operating system assembled under the model of free and open source software development and distribution. The defining component of any Linux system is the Linux kernel, an operating system kernel first released October 5, 1991 by Linus Torvalds...
and Mac OS X
Mac OS X
Mac OS X is a series of Unix-based operating systems and graphical user interfaces developed, marketed, and sold by Apple Inc. Since 2002, has been included with all new Macintosh computer systems...
clients. "Classic" will continue to be available for a number of years in support of the Open University
Open University
The Open University is a distance learning and research university founded by Royal Charter in the United Kingdom...
course. BOINC has stopped distributing classic models in favour of sulfur cycle models. A more user friendly BOINC client and website called GridRepublic, which supports climateprediction and other BOINC projects, was released in beta in 2006.
A thermohaline circulation
Thermohaline circulation
The term thermohaline circulation refers to a part of the large-scale ocean circulation that is driven by global density gradients created by surface heat and freshwater fluxes....
slowdown experiment was launched in May 2004 under the classic framework to coincide with the film The Day After Tomorrow
The Day After Tomorrow
The Day After Tomorrow is a 2004 American science-fiction disaster film that depicts the catastrophic effects of global warming in a series of extreme weather events that usher in global cooling which leads to a new ice age. The film did well at the box office, grossing $542,771,772 internationally...
. This program can still be run but is no longer downloadable. The scientific analysis has been written up in Nick Faull's thesis. A paper about the thesis is still to be completed. There is no further planned research with this model.
A sulfur cycle model was launched in August 2005. They took longer to complete than the original models as a result of having five phases instead of three. Each timestep was also more complicated.
By November 2005, the number of completed results totalled 45,914 classic models, 3,455 thermohaline models, 85,685 BOINC models and 352 sulfur cycle models. This represented over 6 million model years processed.
In February 2006, the project moved on to more realistic climate models. A BBC Climate Change Experiment was launched, attracting around 23,000 participants on the first day. The transient climate simulation
Transient climate simulation
A transient climate simulation is a mode of running a global climate model in which a period of time is simulated with continuously-varying concentrations of greenhouse gases so that the climate of the model represents a realistic mode of possible change in the real world.- Related models :This...
introduced realistic oceans. This allowed the experiment to investigate changes in the climate response as the climate forcings are changed, rather than an equilibrium response to a significant change like doubling the carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide is a naturally occurring chemical compound composed of two oxygen atoms covalently bonded to a single carbon atom...
level. Therefore, the experiment has now moved on to doing a hindcast of 1920 to 2000 as well as a forecast of 2000 to 2080. This model takes much longer.
The BBC
BBC
The British Broadcasting Corporation is a British public service broadcaster. Its headquarters is at Broadcasting House in the City of Westminster, London. It is the largest broadcaster in the world, with about 23,000 staff...
gave the project publicity with over 120,000 participating computers in the first three weeks.
In March 2006, a high resolution model was released as another project, the Seasonal Attribution Project
Seasonal Attribution Project
The Seasonal Attribution Project is a Climateprediction.net sub-project, with support from the WWF. It runs a high resolution model in order to try to determine the extent to which extreme weather events are attributable to human-induced global warming....
.
In April 2006, the coupled models were found to have a data input problem. The work was useful for a different purpose than advertised. New models had to be handed out.
Results to date
The first results of the experiment were published in NatureNature (journal)
Nature, first published on 4 November 1869, is ranked the world's most cited interdisciplinary scientific journal by the Science Edition of the 2010 Journal Citation Reports...
in January 2005 and show that with only slight changes to the parameters within plausible ranges, the models can show climate sensitivities ranging from less than 2 °C to more than 11 °C (see and explanation). The higher climate sensitivities have been challenged as implausible. For example by Gavin Schmidt (a climate modeler with the NASA Goddard Institute for Space Studies in New York).
Explanation
Climate sensitivityClimate sensitivity
Climate sensitivity is a measure of how responsive the temperature of the climate system is to a change in the radiative forcing. It is usually expressed as the temperature change associated with a doubling of the concentration of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere.The equilibrium climate...
is defined as the equilibrium response of global mean temperature to doubling levels of carbon dioxide. Current levels of carbon dioxide are around 380 ppm and growing at a rate of 1.8 ppm per year compared with preindustrial levels of 280 ppm.
Climate sensitivities of greater than 5 °C are widely accepted as being catastrophic. The possibility of such high sensitivities being plausible given observations had been reported prior to the Climateprediction.net experiment but "this is the first time GCMs
Climate model
Climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the climate system to projections of future climate...
have produced such behaviour".
Even the models with very high climate sensitivity were found to be "as realistic as other state-of-the-art climate models". The test of realism was done with a root mean square error test. This does not check on realism of seasonal changes and it is possible that more diagnostic measures may place stronger constraints on what is realistic. Improved realism tests are being developed.
It is important to the experiment and the goal of obtaining a probability distribution function
Probability distribution function
Depending upon which text is consulted, a probability distribution function is any of:* a probability distribution function,* a cumulative distribution function,* a probability mass function, or* a probability density function....
(pdf) of climate outcomes to get a very wide range of behaviours even if only to rule out some behaviours as unrealistic. Unless a very large number of data points are used to create the pdf, the pdf is not reliable. Therefore, models with climate sensitivities as high as 11 °C are included even though they are inaccurate. More worrying is the lack of models with climate sensitivity of less than 2 °C. The sulfur cycle experiment is likely to extend the range downwards.
Piani et al. (2005)
Published in Geophysical Review Letters, this paper concludes:When an internally consistent representation of the origins of model-data discrepancy is used to calculate the probability density function of climate sensitivity, the 5th and 95th percentiles are 2.2 K and 6.8 K respectively. These results are sensitive, particularly the upper bound, to the representation of the origins of model data discrepancy.
Use in education
There is an Open UniversityOpen University
The Open University is a distance learning and research university founded by Royal Charter in the United Kingdom...
short course and teaching material available for schools to teach subjects relating to climate and climate modelling. There is also teaching material available for use in Key Stage 3/4 Science, A level Physics (Advanced Physics), Key Stage 3/4 Mathematics, Key Stage 3/4 Geography, 21st Century Science, Science for Public Understanding, Use of Mathematics, Primary.
The original model
The original experiment is run with HadSM3, which is the atmosphere from the HadCM3HadCM3
HadCM3 is a coupled atmosphere-ocean general circulation model developed at the Hadley Centre in the United Kingdom...
model but with only a "slab" ocean rather than a full dynamic ocean. This is faster (and requires less memory) than the full model, but lacks dynamical feedbacks from the ocean, which are incorporated into the full coupled-ocean-atmosphere models used to make projections of climate change out to 2100.
Each downloaded model comes with a slight variation in the various model parameters
Parametrization (climate)
Parameterization in a weather or climate model within numerical weather prediction refers to the method of replacing processes that are too small-scale or complex to be physically represented in the model by a simplified process. This can be contrasted with other processes—e.g., large-scale flow of...
.
There is an initial "calibration phase" of 15 model years in which the model calculates the "flux correction"; extra ocean-atmosphere fluxes that are needed to keep the model ocean in balance (the model ocean does not include currents; these fluxes to some extent replace the heat that would be transported by the missing currents).
Then there is a "control phase" of 15 years in which the ocean temperatures are allowed to vary. The flux correction ought to keep the model stable, but feedback
Feedback
Feedback describes the situation when output from an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or occurrences of the same Feedback describes the situation when output from (or information about the result of) an event or phenomenon in the past will influence an occurrence or...
s developed in some of the runs. There is a quality control check, based on the annual mean temperatures, and models which fail this check are discarded.
Then there is a "double CO2 phase" in which the CO2 content is instantaneously doubled and the model run for a further 15 years, which in some cases is not quite sufficient model time to settle down to a new (warmer) equilibrium. In this phase some models which produced physically unrealistic results were again discarded.
The quality control checks in the control and 2*CO2 phases were quite weak: they suffice to exclude obviously unphysical models but do not include (for example) a test of the simulation of the seasonal cycle; hence some of the models passed may still be unrealistic. Further quality control measures are being developed.
The temperature in the doubled CO2 phase is exponentially extrapolated to work out the equilibrium temperature. Difference in temperature between this and the control phase then gives a measure of the climate sensitivity
Climate sensitivity
Climate sensitivity is a measure of how responsive the temperature of the climate system is to a change in the radiative forcing. It is usually expressed as the temperature change associated with a doubling of the concentration of carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere.The equilibrium climate...
of that particular version of the model.
Visualisations
Most distributed computing projects have screensaverScreensaver
A screensaver is a type of computer program initially designed to prevent phosphor burn-in on CRT and plasma computer monitors by blanking the screen or filling it with moving images or patterns when the computer is not in use...
s to visually indicate the activity of the application, but they do not usually show its results as they are being calculated. By contrast, climateprediction.net not only uses a built-in visualisation to show the climate of the world being modelled, but it is interactive which allows different aspects of climate (temperature, rainfall, etc.) to be displayed. In addition, there are other, more advanced visualisation programs that allow the user to see more of what the model is doing (usually by analysing previously generated results) and to compare different runs and models.
Unfortunately as of December 2008 there is no visualisation tool that works with the newer CPDN models. Neither CPView nor Advanced Visualisation were updated so far to display data gathered from those models. So users can only visualize the data through the screensaver.

University of Reading
The University of Reading is a university in the English town of Reading, Berkshire. The University was established in 1892 as University College, Reading and received its Royal Charter in 1926. It is based on several campuses in, and around, the town of Reading.The University has a long tradition...
(UK
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern IrelandIn the United Kingdom and Dependencies, other languages have been officially recognised as legitimate autochthonous languages under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages...
), and modified to work with the BOINC version by Tesella Support Services plc.
Only CPView allows you to look at unusual diagnostics, rather than the usual Temperature, Pressure, Rainfall, Snow, and Clouds. Up to 5 sets of data can be displayed on a map. It also has a wider range of functions like Max, Min, further memory functions, and other features.
The Advanced Visualisation has functions for graphs of local areas and over 1 day, 2 days, and 7 days, as well as the more usual graphs of season and annual averages (which both packages do). There are also Latitude - Height plots and Time - Height plots.
The download size is much smaller for CPView and CPView works with Windows 98
Windows 98
Windows 98 is a graphical operating system by Microsoft. It is the second major release in the Windows 9x line of operating systems. It was released to manufacturing on 15 May 1998 and to retail on 25 June 1998. Windows 98 is the successor to Windows 95. Like its predecessor, it is a hybrid...
.
Running the visualisation/screensaver may slow down the processing and is not recommended to be used.
See also
- List of distributed computing projects
- Climate modelClimate modelClimate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the atmosphere, oceans, land surface, and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the climate system to projections of future climate...
- Global climate modelGlobal climate modelA General Circulation Model is a mathematical model of the general circulation of a planetary atmosphere or ocean and based on the Navier–Stokes equations on a rotating sphere with thermodynamic terms for various energy sources . These equations are the basis for complex computer programs commonly...
- Distributed computingDistributed computingDistributed computing is a field of computer science that studies distributed systems. A distributed system consists of multiple autonomous computers that communicate through a computer network. The computers interact with each other in order to achieve a common goal...
- BOINC
- Climate ensembleClimate ensembleIn physics, a statistical ensemble is a large set of copies of a system, considered all at once; each copy of the system representing a different possible detailed realisation of the system, consistent with the system's observed macroscopic properties....
- Sensitivity analysisSensitivity analysisSensitivity analysis is the study of how the variation in the output of a statistical model can be attributed to different variations in the inputs of the model. Put another way, it is a technique for systematically changing variables in a model to determine the effects of such changes.In any...
and Uncertainty analysisUncertainty analysisCalibrated parameter does not necessarily represents reality, as reality is much more complex. Any any prediction has its own complexities of reality that cannot be represented uniquely in the calibrated model; tehrefore, there is a potential error. Such error must be accounted for when making...

