
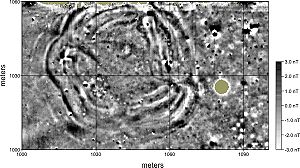
Circular ditches
Encyclopedia

Germany
Germany , officially the Federal Republic of Germany , is a federal parliamentary republic in Europe. The country consists of 16 states while the capital and largest city is Berlin. Germany covers an area of 357,021 km2 and has a largely temperate seasonal climate...
, Austria
Austria
Austria , officially the Republic of Austria , is a landlocked country of roughly 8.4 million people in Central Europe. It is bordered by the Czech Republic and Germany to the north, Slovakia and Hungary to the east, Slovenia and Italy to the south, and Switzerland and Liechtenstein to the...
, Slovakia
Slovakia
The Slovak Republic is a landlocked state in Central Europe. It has a population of over five million and an area of about . Slovakia is bordered by the Czech Republic and Austria to the west, Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east and Hungary to the south...
, and the Czech Republic
Czech Republic
The Czech Republic is a landlocked country in Central Europe. The country is bordered by Poland to the northeast, Slovakia to the east, Austria to the south, and Germany to the west and northwest....
. Their diameters range from ca. 20 to ca. 130 m, and they date to the 5th millennium BC. Tools, bones, and some artefacts were found in their context. The largest of these arrangements to date was found in Leipzig
Leipzig
Leipzig Leipzig has always been a trade city, situated during the time of the Holy Roman Empire at the intersection of the Via Regia and Via Imperii, two important trade routes. At one time, Leipzig was one of the major European centres of learning and culture in fields such as music and publishing...
in the 1990s. Another large find was at the nearby village of Aythra, outside of Leipzig
Leipzig
Leipzig Leipzig has always been a trade city, situated during the time of the Holy Roman Empire at the intersection of the Via Regia and Via Imperii, two important trade routes. At one time, Leipzig was one of the major European centres of learning and culture in fields such as music and publishing...
. From finds in the context of these ditches, and associated settlements of longhouses, it was established that they were in use for about 200 years, until roughly 4600 BC.
Background
The people that built these structures are associated with the Linear Ceramic culture. They appear to have lived in communal long housesNeolithic long house
The Neolithic long house was a long, narrow timber dwelling built by the first farmers in Europe beginning at least as early as the period 5000 to 6000 BC. This type of architecture represents the largest free-standing structure in the world in its era...
and subsisted by farming
Animal husbandry
Animal husbandry is the agricultural practice of breeding and raising livestock.- History :Animal husbandry has been practiced for thousands of years, since the first domestication of animals....
cattle
Cattle
Cattle are the most common type of large domesticated ungulates. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae, are the most widespread species of the genus Bos, and are most commonly classified collectively as Bos primigenius...
, goat
Goat
The domestic goat is a subspecies of goat domesticated from the wild goat of southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the Bovidae family and is closely related to the sheep as both are in the goat-antelope subfamily Caprinae. There are over three hundred distinct breeds of...
s, pig
Pig
A pig is any of the animals in the genus Sus, within the Suidae family of even-toed ungulates. Pigs include the domestic pig, its ancestor the wild boar, and several other wild relatives...
s, and sheep. The structures were built in a stretch of Central European land some 760 km (472.2 mi) across, over a period of one or two hundred years. They are believed to have migrated into this region during the 6th millennium BC from the plain of the Danube
Danube
The Danube is a river in the Central Europe and the Europe's second longest river after the Volga. It is classified as an international waterway....
in what is now Hungary
Hungary
Hungary , officially the Republic of Hungary , is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is situated in the Carpathian Basin and is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine and Romania to the east, Serbia and Croatia to the south, Slovenia to the southwest and Austria to the west. The...
and Serbia
Serbia
Serbia , officially the Republic of Serbia , is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central and Southeast Europe, covering the southern part of the Carpathian basin and the central part of the Balkans...
. They made tools of wood
Wood
Wood is a hard, fibrous tissue found in many trees. It has been used for hundreds of thousands of years for both fuel and as a construction material. It is an organic material, a natural composite of cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of lignin which resists compression...
, stone
Rock (geology)
In geology, rock or stone is a naturally occurring solid aggregate of minerals and/or mineraloids.The Earth's outer solid layer, the lithosphere, is made of rock. In general rocks are of three types, namely, igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic...
, and bone
Bone
Bones are rigid organs that constitute part of the endoskeleton of vertebrates. They support, and protect the various organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells and store minerals. Bone tissue is a type of dense connective tissue...
, and artwork of ceramic
Ceramic
A ceramic is an inorganic, nonmetallic solid prepared by the action of heat and subsequent cooling. Ceramic materials may have a crystalline or partly crystalline structure, or may be amorphous...
and pottery
Pottery
Pottery is the material from which the potteryware is made, of which major types include earthenware, stoneware and porcelain. The place where such wares are made is also called a pottery . Pottery also refers to the art or craft of the potter or the manufacture of pottery...
.
Function
An article in the British newspaper The IndependentThe Independent
The Independent is a British national morning newspaper published in London by Independent Print Limited, owned by Alexander Lebedev since 2010. It is nicknamed the Indy, while the Sunday edition, The Independent on Sunday, is the Sindy. Launched in 1986, it is one of the youngest UK national daily...
of June 11, 2005 identified these structures as "monumental temples", although there has been no scientific assessment of their purpose.
Pre-Columbian America
Wichita (tribe)
The Wichita people are indigenous inhabitants of North America, who traditionally spoke the Wichita language, a Caddoan language. They have lived in Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas...
tribe. These structures, called "council circles", occur near the center of these sites, and previous archaeological excavations have suggested they consist of a central patio surrounded by four semisubterranean structures. The function of the council circles is unclear. Waldo Wedel has suggested they may be ceremonial structures, possibly associated with solstice observations. Recent analysis suggests that many non-local artifacts occur exclusively or primarily within council circles, implying the structures were occupied by political and/or ritual leaders of the Great Bend aspect peoples. Other archaeologists leave open the possibility that the council circle earthen works served a defensive role.

