
Charge radius
Encyclopedia
The rms charge radius is a measure of the size of an atomic nucleus
, particularly of a proton
or a deuteron. It can be measured by the scattering of electron
s by the nucleus and also inferred from the effects of finite nuclear size on electron energy levels as measured in atomic spectra.
, in that neither atoms nor their nuclei have definite boundaries. However, the nucleus can be modelled as a sphere of positive charge for the interpretation of electron scattering experiments: because there is no definite boundary to the nucleus, the electrons "see" a range of cross-sections, for which a mean can be taken. The qualification of "rms" (for "root mean square") arises because it is the nuclear cross-section, proportional to the square of the radius, which is determining for electron scattering.
For deuterons and higher nuclei, it is conventional to distinguish between the scattering charge radius, rd (obtained from scattering data), and the bound-state charge radius, Rd, which includes the Darwin–Foldy term to account for the behaviour of the anomalous magnetic moment in an electromagnetic field and which is appropriate for treating spectroscopic data. The two radii are related by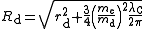
where me and md are the masses of the electron and the deuteron respectively while λC is the Compton wavelength
of the electron. For the proton, the two radii are the same.
in 1909, under the direction of Ernest Rutherford
at the Physical Laboratories of the University of Manchester
, UK. The famous experiment involved the scattering of α-particles by gold
foil, with some of the particles being scattered through angles of more than 90°, that is coming back to the same side of the foil as the α-source. Rutherford was able to put an upper limit on the radius of the gold nucleus of 34 femtometres.
Later studies found an empirical relation between the charge radius and the mass number
, A, for heavier nuclei (A > 20):
where r0 is an empirical constant of 1.2–1.5 fm. This gives a charge radius for the gold nucleus (A = 197) of about 7.5 fm.
s by nuclei. There is most interest in knowing the charge radii of proton
s and deuterons, as these can be compared with the spectrum of atomic hydrogen
/deuterium
: the finite size of the nucleus causes a shift in the electronic energy levels which shows up as a change in the frequency of the spectral lines. Such comparisons are a test of quantum electrodynamics
(QED). Since 2002, the proton and deuteron charge radii have been independently refined parameters in the CODATA set of recommended values for physical constants, that is both scattering data and spectroscopic data are used to determine the recommended values.
The 2010 CODATA recommended values are:
Recent work on the spectrum of muonic hydrogen (an exotic atom
consisting of a proton and a negative muon
) indicates a significantly lower value for the proton charge radius, 0.84184(67) fm: the reason for this discrepancy is not clear.
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the very dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford's interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford. The...
, particularly of a proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
or a deuteron. It can be measured by the scattering of electron
Electron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s by the nucleus and also inferred from the effects of finite nuclear size on electron energy levels as measured in atomic spectra.
Definition
The problem of defining a radius for the atomic nucleus is similar to the problem of atomic radiusAtomic radius
The atomic radius of a chemical element is a measure of the size of its atoms, usually the mean or typical distance from the nucleus to the boundary of the surrounding cloud of electrons...
, in that neither atoms nor their nuclei have definite boundaries. However, the nucleus can be modelled as a sphere of positive charge for the interpretation of electron scattering experiments: because there is no definite boundary to the nucleus, the electrons "see" a range of cross-sections, for which a mean can be taken. The qualification of "rms" (for "root mean square") arises because it is the nuclear cross-section, proportional to the square of the radius, which is determining for electron scattering.
For deuterons and higher nuclei, it is conventional to distinguish between the scattering charge radius, rd (obtained from scattering data), and the bound-state charge radius, Rd, which includes the Darwin–Foldy term to account for the behaviour of the anomalous magnetic moment in an electromagnetic field and which is appropriate for treating spectroscopic data. The two radii are related by
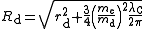
where me and md are the masses of the electron and the deuteron respectively while λC is the Compton wavelength
Compton wavelength
The Compton wavelength is a quantum mechanical property of a particle. It was introduced by Arthur Compton in his explanation of the scattering of photons by electrons...
of the electron. For the proton, the two radii are the same.
History
The first estimate of a nuclear charge radius was made by Hans Geiger and Ernest MarsdenErnest Marsden
Sir Ernest Marsden was an English-New Zealand physicist. He was born in East Lancashire, living in Rishton and educated at Queen Elizabeth's Grammar School, Blackburn, where an inter-house trophy rewarding academic excellence bears his name.He met Ernest Rutherford at the University of Manchester...
in 1909, under the direction of Ernest Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford
Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson OM, FRS was a New Zealand-born British chemist and physicist who became known as the father of nuclear physics...
at the Physical Laboratories of the University of Manchester
University of Manchester
The University of Manchester is a public research university located in Manchester, United Kingdom. It is a "red brick" university and a member of the Russell Group of research-intensive British universities and the N8 Group...
, UK. The famous experiment involved the scattering of α-particles by gold
Gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au and an atomic number of 79. Gold is a dense, soft, shiny, malleable and ductile metal. Pure gold has a bright yellow color and luster traditionally considered attractive, which it maintains without oxidizing in air or water. Chemically, gold is a...
foil, with some of the particles being scattered through angles of more than 90°, that is coming back to the same side of the foil as the α-source. Rutherford was able to put an upper limit on the radius of the gold nucleus of 34 femtometres.
Later studies found an empirical relation between the charge radius and the mass number
Mass number
The mass number , also called atomic mass number or nucleon number, is the total number of protons and neutrons in an atomic nucleus. Because protons and neutrons both are baryons, the mass number A is identical with the baryon number B as of the nucleus as of the whole atom or ion...
, A, for heavier nuclei (A > 20):
- R ≈ r0A⅓
where r0 is an empirical constant of 1.2–1.5 fm. This gives a charge radius for the gold nucleus (A = 197) of about 7.5 fm.
Modern measurements
Modern direct measurements are based on the scattering of electronElectron
The electron is a subatomic particle with a negative elementary electric charge. It has no known components or substructure; in other words, it is generally thought to be an elementary particle. An electron has a mass that is approximately 1/1836 that of the proton...
s by nuclei. There is most interest in knowing the charge radii of proton
Proton
The proton is a subatomic particle with the symbol or and a positive electric charge of 1 elementary charge. One or more protons are present in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons. The number of protons in each atom is its atomic number....
s and deuterons, as these can be compared with the spectrum of atomic hydrogen
Hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with atomic number 1. It is represented by the symbol H. With an average atomic weight of , hydrogen is the lightest and most abundant chemical element, constituting roughly 75% of the Universe's chemical elemental mass. Stars in the main sequence are mainly...
/deuterium
Deuterium
Deuterium, also called heavy hydrogen, is one of two stable isotopes of hydrogen. It has a natural abundance in Earth's oceans of about one atom in of hydrogen . Deuterium accounts for approximately 0.0156% of all naturally occurring hydrogen in Earth's oceans, while the most common isotope ...
: the finite size of the nucleus causes a shift in the electronic energy levels which shows up as a change in the frequency of the spectral lines. Such comparisons are a test of quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics
Quantum electrodynamics is the relativistic quantum field theory of electrodynamics. In essence, it describes how light and matter interact and is the first theory where full agreement between quantum mechanics and special relativity is achieved...
(QED). Since 2002, the proton and deuteron charge radii have been independently refined parameters in the CODATA set of recommended values for physical constants, that is both scattering data and spectroscopic data are used to determine the recommended values.
The 2010 CODATA recommended values are:
- proton: Rp = 0.8775(51)*10-15 m
- deuteron: Rd = 2.1424(21)*10-15 m
Recent work on the spectrum of muonic hydrogen (an exotic atom
Exotic atom
An exotic atom is an otherwise normal atom in which one or more sub-atomic particles have been replaced by other particles of the same charge. For example, electrons may be replaced by other negatively charged particles such as muons or pions...
consisting of a proton and a negative muon
Muon
The muon |mu]] used to represent it) is an elementary particle similar to the electron, with a unitary negative electric charge and a spin of ½. Together with the electron, the tau, and the three neutrinos, it is classified as a lepton...
) indicates a significantly lower value for the proton charge radius, 0.84184(67) fm: the reason for this discrepancy is not clear.

